前列腺癌是威胁人类健康和生命的全球性公共卫生问题,对男性泌尿生殖系统造成巨大危害[1]。2019年美国癌症研究协会和美国国家癌症研究所的统计数据显示,前列腺癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,是全世界男性第二常见的恶性肿瘤[2],其死亡人数占男性生殖器官肿瘤性疾病死亡人数的90%以上[3]。我国前列腺癌的发病率低于欧美国家(60.3/10万vs 80.7/10万)[4-5],但随着人口老龄化的加剧及饮食结构和生活环境的变化,我国前列腺癌的发病率呈逐年上升趋势[6]。
Gleason分级是前列腺癌进展和生存的最有力预测指标之一,是判断前列腺癌治疗方式的决定因素[7]。Gleason评分系统通过分析腺体分化的程度对前列腺进行组织学识别,然后依据主要肿瘤组织评分及次要肿瘤组织评分判断肿瘤的异质性。Gleason评分3+4分和4+3分的患者有不同的生物学特性,Gleason评分4+3分的前列腺癌患者病死率是Gleason评分3+4分患者的3倍[8]。
影像组学是将传统的影像图像转换为可挖掘的数据信息并进行高通量定量分析的一种研究方法[9],其突破了基于形态学及半定量分析的传统影像医学模式,融合了数字影像信息、统计学、机器学习等方法,从而充分深入挖掘和分析隐含在图像中的额外信息以最高效地利用影像学检查结果[10]。MRI影像组学特征可以在组织病理学和基因组学水平体现前列腺癌的侵袭性[11]。2015年发布的前列腺影像报告和数据系统(prostate imaging reporting and data system,PI-RADS)2.0更好地规范了前列腺MRI的检查和解释[12];2019年PI-RADS 2.1提出双参数磁共振成像(biparametric magnetic resonance imaging,bpMRI)概念[仅包括T2加权像(T2-weighted imaging,T2WI)和弥散加权成像(diffusion-weighted imaging,DWI)],以简化前列腺MRI序列[13]。bpMRI的诊断准确性及效能与包括T2WI、DWI和动态增强(dynamic contrast enhancement,DCE)的多参数磁共振成像(multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging,mpMRI)相当,阅片者间的一致性良好,无须使用造影剂,图像的采集及解读时间较mpMRI显著缩短[14]。MRI影像组学分析方法能够提高PI-RADS 2.0的诊断能力,添加组学特征后能显著改善PI-RADS 2.0对前列腺肿瘤的诊断效能[15]。bpMRI影像组学纹理分析可用于诊断前列腺癌,不仅能为鉴别诊断低危与中高危前列腺癌提供可靠的量化信息,而且有助于前列腺癌病理分级[16]。本研究旨在探讨利用bpMRI影像组学机器学习模型对低风险(Gleason评分≤3+4分)与高风险(Gleason评分≥4+3分)前列腺癌进行病理风险分层。
1 资料和方法 1.1 临床资料回顾性分析2015年4月至2017年7月于海军军医大学(第二军医大学)长海医院接受治疗、术后病理证实为前列腺癌的128例患者的病例资料。纳入标准:(1)术前接受MRI检查,且检查时间与手术时间间隔<7 d;(2)术前PI-RADS 2.1评分≥3分;(3)在MRI检查之前未进行前列腺穿刺活检和手术、放射或内分泌治疗。排除标准:(1)术后病理诊断为前列腺间叶肿瘤或其他瘤样病变;(2)患者放置导尿管后;(3)MRI图像存在伪影,或病灶过小影响病灶分割。本研究通过海军军医大学(第二军医大学)长海医院伦理委员会审批。
纳入的128例患者年龄为37~90岁,平均(68.88±8.01)岁。血清前列腺特异抗原(prostate-specific antigen,PSA)为0.70~234.00 ng/mL,平均(29.19±21.4)ng/mL。前列腺病灶体积为0.20~90.30 cm3,中位数为2.15 cm3;病灶位于外周带61例,移行带56例,弥漫分布11例;PI-RADS评分3分3例,4分57例,5分68例。
1.2 检查设备与扫描参数采用3 T超导型磁共振系统(MAGNETOM Skyra,德国Siemens Healthcare公司),使用标准18通道相控阵体部线圈及32通道集成脊柱线圈采集信号。患者检查前排空肠道及膀胱,禁食4~6 h。前列腺行水平面、冠状面、矢状面二维T2WI快速自旋回波扫描,水平面T2WI扫描参数:重复时间/回波时间(repetition time/echo time,TR/TE)5 460 ms/104 ms,视野180 mm×180 mm,矩阵384×384,层厚4 mm,层数24,层间距0 mm,回波链长度18,采集时间为3 min 49 s。水平面DWI扫描参数:TR/TE 5 100 ms/ 89 ms,224 mm×280 mm,矩阵120×150,层厚4 mm,层数20,层间距0 mm,b值为0、1 500 s/mm2,采集时间为7 min 59 s。水平面DWI扫描定位时尽可能保证与T2WI序列的层面一致。
1.3 前列腺病理结果和风险分层所有患者均行根治性前列腺切除术,并获得前列腺大体标本。病理标本均经H-E染色及免疫组织化学染色分析,由1名具有20年工作经验的泌尿病理科医师观察组织切片,确定病灶的位置和边界,选取具有最高Gleason评分的癌灶进行分析,依照国际泌尿外科病理学会(International Society of Urological Pathology,ISUP)2014年共识会议制定的前列腺癌分级指南[17]进行评分。待分层病例中病灶Gleason评分3+3分36例、3+4分24例、4+3分18例、4+4分23例、4+5分15例、5+4分7例、5+5分5例,分层后低风险组(Gleason评分≤3+4分)60例、高风险组(Gleason评分≥4+3分)68例。
1.4 前列腺癌影像组学分析 1.4.1 MRI图像预处理提取前列腺bpMRI序列[包括水平面T2WI和表观弥散系数(apparent diffusion coefficient,ADC)]图像影像组学特征。将每例患者的T2WI和ADC图像(DICOM格式)导入A.K. 3.0.1软件(美国GE Healthcare公司)。在病灶分割前对图像进行标准化预处理以提高纹理识别率,采用µ±3σ方法对图像进行灰度归一化,剔除超过3σ的灰度信号,并采用64级灰度进行灰度量化,最后使用1 mm×1 mm×1 mm的体素大小进行等视重采样[18-19]。
1.4.2 MRI病灶分割对所有病灶采用相同的勾画标准,以保证预处理后的T2WI和ADC图像中感兴趣区一致,并由同一名有10年前列腺MRI诊断经验的影像科医师进行视觉验证。结合PI-RADS 2.1评分诊断标准[13],将MRI上显示的病变位置和范围与相应病理描述严格匹配。外周带病变勾画以ADC图像为主,DWI和T2WI为辅;移行带病变勾画以T2WI为主,DWI和ADC为辅。选择Gleason评分最高且直径最大的病灶层面手工勾画感兴趣区获得二维数据。病变分割的观察者内和观察者间的可重复性是基于特征提取的重复性。随机选择30例患者,将临床数据盲化,由A、B 2名放射科诊断医师提取其影像组学特征,评价特征提取的观察者内和观察者间的可重复性。放射科医师A和B在前列腺MRI诊断方面分别有10年和4年的临床经验,在影像组学特征提取方面也都具有3年的经验。
1.4.3 影像组学特征提取与选择使用A.K. 3.0.1软件进行特征提取和选择。计算机提取的特征类型包括基于梯度的直方图特征、形态特征、灰度共生矩阵(gray-level co-occurrence matrix,GLCM)、灰度游程矩阵(gray-level run-length matrix,GLRLM)、灰度大小区域矩阵(gray-level size zone matrix,GLSZM)和Haralick特征。虽然提取了大量特征,但并非所有特征都有助于预测前列腺癌的病理风险分层,因此我们使用2种特征选择方法确定最佳的区分特征子集。首先进行最大相关及最小冗余算法以消除冗余和不相关的特征,随后进行最小绝对收缩和选择算子(least absolute shrinkage and selection operator,LASSO)分析,选择优化后的特征子集构建最终的影像组学模型。
1.4.4 模型构建采用单因素和多因素logistic回归分析,找出与前列腺癌病理风险分层有明显相关性的特征,建立临床模型。随机将70%的患者分配到训练集(90例),30%的患者分配到验证集(38例),使用所选择的关键特征训练logistic回归模型,对具有不同病理风险的前列腺癌进行分类,建立影像组学模型。计算影像组学评分(Radscore)的公式是通过对选定的特征进行logistic回归分析而产生的,这些特征有各自的加权系数。基于影像组学模型和临床显著特征,建立综合考虑影像组学特征和临床危险因素权重的临床-影像组学联合模型。
1.5 统计学处理采用单因素logistic回归筛选临床危险因素,然后将P<0.05的临床特征引入多因素logistic回归建立临床模型。Logistic回归采用似然比检验,以Akaike信息准则作为停止准则,逐步向后选择相关特征。采用方差膨胀因子(variance inflation factor,VIF)评价共线性度,排除VIF>10的特征。依据ROC曲线的AUC及95% CI量化每个模型的性能,使用deLong检验确定临床模型、影像组学模型和临床-影像组学联合模型之间AUC值的差异是否有统计学意义。构建临床-影像组学联合模型的诺模图,使用上述临床指标及临床特征以辅助对前列腺癌的风险分层,通过量化验证集中不同阈值概率下的临床净收益确定基于影像组学的诺模图的临床效能[20],并绘制临床模型、影像组学模型和临床-影像组学联合模型的决策曲线。使用R 4.0.3软件进行上述分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以x±s表示,不符合正态分布的计量资料以中位数(范围)表示;计数资料和等级资料以例数表示。检验水准(α)为0.05。
2 结果 2.1 临床模型在临床因素方面,单因素和多因素logistic回归分析结果显示,PI-RADS评分和PSA对预测前列腺癌风险分层差异有统计学意义(P均<0.05),年龄、病灶体积、病灶位置差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。根据PI-RADS评分和PSA建立logistic回归分类器构建临床模型,其评分=0.608×PI-RADS评分+0.021×PSA(ng/mL)-3.011,预测效能见表 1。
|
|
表 1 3种模型对前列腺癌的风险分层预测效能 Tab 1 Predictive efficacy of 3 models in risk stratification of prostate cancer |
2.2 影像组学模型
采用组内相关系数(intraclass correlation coefficient,ICC)评价特征提取的观察者内和观察者间的一致性,ICC>0.75表示一致性好。随机选择30例患者的影像资料,基于放射科医师A首次及间隔2周后再次提取的T2WI和ADC图像特征的观察者内ICC分别为0.84~0.95和0.81~0.92,基于放射科医师A(首次)和B的T2WI和ADC图像特征提取的观察者间ICC分别为0.77~0.92和0.76~0.91。由放射科医师A完成其余98例患者图像的处理。利用放射科医师A提取的特征建立影像组学模型,其中90例患者的数据用于机器学习(训练集),38例患者的数据用于验证(验证集)。共提取396个组学特征,包括6类:42个直方图特征、9个形态特征、144个GLCM特征、180个GLRLM特征、11个GLSZM特征和10个Haralick特征,使用LASSO logistic回归分类器进行特征选择,将396个组学特征约简为10个具有非零系数的潜在预测因子,见图 1。
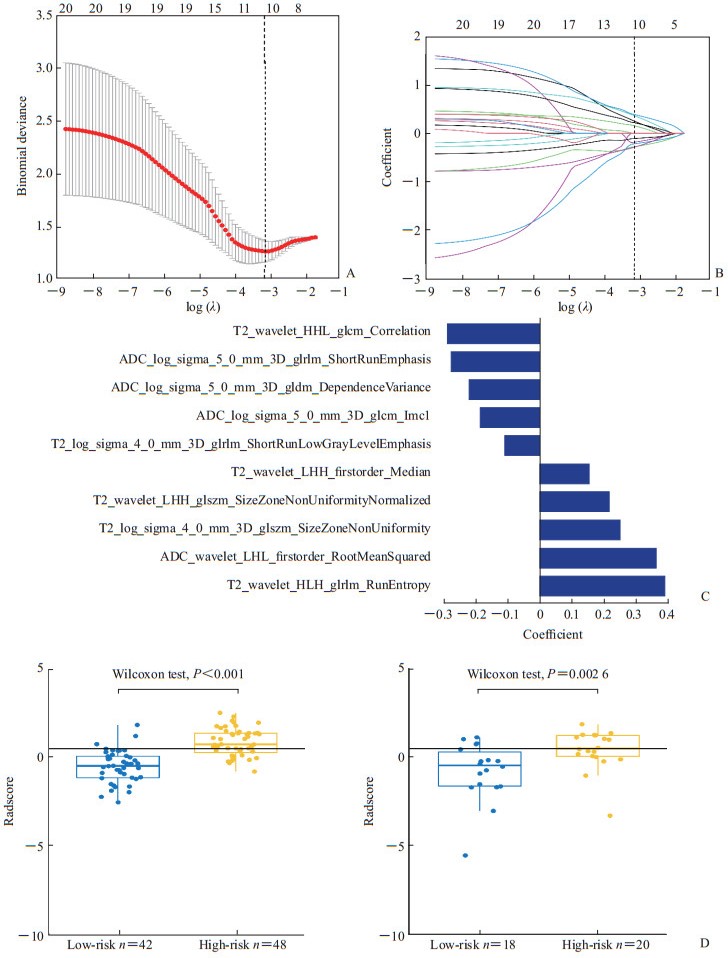
|
图 1 前列腺癌MRI影像组学特征提取 Fig 1 MRI radiomics feature extraction of prostate cancer A: Curve of binomial deviation of MRI radiomics model varying with parameter λ; B: Curve of radiomics characteristic coefficient of MRI radiomics model varying with parameter λ; C: Radiomics features screened by MRI radiomics model; D: Comparison of radiomics score (Radscore) between low-risk (Gleason score≤3+4) and high-risk (Gleason score≥4+3) prostate cancer patients of MRI radiomics model training set (left) and validation set (right). The vertical dotted lines in Fig 1A and 1B represent the optimal value of the super parameter λ. In this case, the model and data show the best fit. The numbers above Fig 1A and 1B represent the number of features. As shown in the figure, when the best λ value is obtained, the nearest feature number is 10. The logarithmic function in Fig 1A, 1B and 1C is natural logarithm. The horizontal lines in Fig 1D represent the cut-off value of Radscore (0.43). MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging. |
相对重要的特征被合并至影像组学评分中,其表示加权特征的总和如下:Radscore=0.250×T2_log_sigma_4_0_mm_3D_glszm_SizeZoneNonUniformity-0.279×ADC_log_sigma_5_0_mm_3D_glrlm_ShortRunEmphasis+0.389×T2_wavelet_HLH_glrlm_RunEntropy-0.187×ADC_log_sigma_5_0_mm_3D_glcm_Imc1-0.220×ADC_log_sigma_5_0_mm_3D_gldm_DependenceVariance-0.289×T2_wavelet_HHL_glcm_Correlation-0.110×T2_log_sigma_4_0_mm_3D_glrlm_ShortRunLowGrayLevelEmphasis+0.154×T2_wavelet_LHH_firstorder_Median+0.363×ADC_wavelet_LHL_firstorder_RootMeanSquared+0.217×T2_wavelet_LHH_glszm_SizeZoneNon-UniformityNormalized+0.154。bpMRI影像组学模型对前列腺癌病理风险分层的预测效能见表 1。
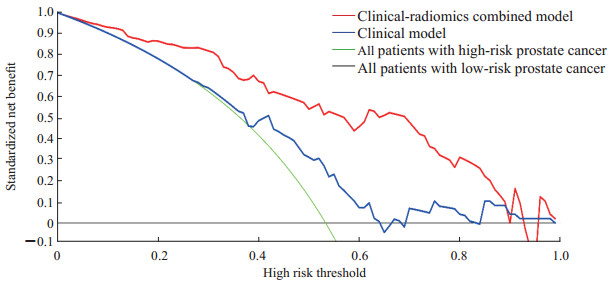
2.3 临床-影像组学联合模型结合PI-RADS评分、PSA和影像组学评分建立临床-影像组学联合模型,其评分=0.190×PI-RADS评分+0.002×PSA(ng/mL)+1.939×Radscore-0.995,对前列腺癌风险分层的诺模图如图 2所示。临床-影像组学联合模型显示出对前列腺癌病理风险分层有良好的预测能力(表 1)。临床-影像组学联合模型的诊断效能与影像组学模型相当,并且优于临床模型(表 1、图 3)。临床-影像组学联合模型预测前列腺癌风险分层的校准曲线见图 4,结果提示预测结果与病理结果一致性良好。决策曲线(图 5)表明,使用临床-影像组学联合模型预测前列腺癌的风险分层比使用临床模型有更高的临床净收益。
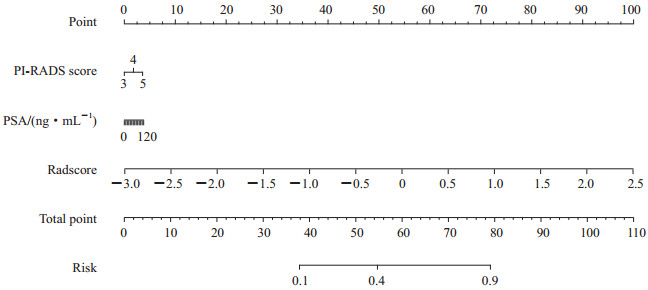
|
图 2 临床-影像组学联合模型对前列腺癌风险分层的诺模图 Fig 2 Nomograph of risk stratification of prostate cancer by clinical-radiomics combined model PI-RADS: Prostate imaging reporting and data system; PSA: Prostate-specific antigen; Radscore: Radiomics score. |
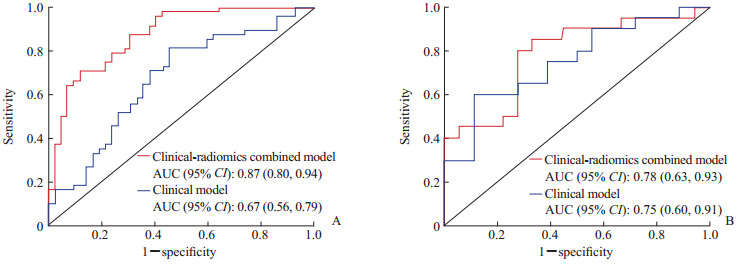
|
图 3 临床-影像组学联合模型和临床模型ROC曲线对比 Fig 3 Comparison of ROC curves between clinical-radiomics combined model and clinical model A: Training set; B: Validation set. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; AUC: Area under curve; CI: Confidence interval. |
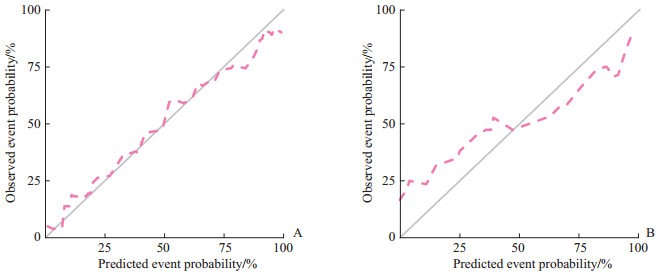
|
图 4 临床-影像组学联合模型预测前列腺癌风险分层与病理结果一致性的校准曲线 Fig 4 Calibration curves of clinical-radiomics combined model for predicting the consistency of risk stratification and pathological results of prostate cancer A: Training set; B: Validation set. |
|
图 5 临床-影像组学联合模型和临床模型决策曲线 Fig 5 Clinical-radiomics combined model and clinical model decision curves |
3 讨论
MRI技术结合靶向穿刺活检用于临床显著性前列腺癌的检出越来越普遍,但常规前列腺mpMRI采集时间长、成本高,且检查单位和阅片者之间存在差异性,限制了其应用的普及。bpMRI足以发现大多数临床上有意义的前列腺癌,检测临床显著性前列腺癌的能力不逊于mpMRI,其图像采集及解读时间短,也不会产生造影剂管理的成本和潜在风险[14, 21-23]。PI-RADS 2.1的出现将使bpMRI在前列腺癌检测中的应用愈加广泛。
随着人工智能技术的蓬勃发展,以纹理分析技术、影像组学、深度学习为代表的人工智能影像分析技术对图像特征信息的分析和阐释更为深入、精准,这些图像的特征信息和病理分级具有明显相关性。影像组学作为一个先进的图像量化工具,为前列腺癌的精准个体化治疗提供了新的研究方向[24-25]。研究表明,从不同的MRI扫描序列(T2WI、DWI、DCE和ADC)中提取的影像组学特征可以作为前列腺癌诊断及侵袭性、分期、治疗反应预测的可行性生物标志物[26-29]。前列腺影像组学研究也揭示MRI影像特征与前列腺癌区域的Gleason评分、生化复发[29]和基因表达[30]之间有很好的相关性。Gleason评分可以反映前列腺癌的侵袭性,并且是疾病进展和死亡率的重要预测因子。研究表明Gleason评分为7分的肿瘤具有异质性,与Gleason评分为3+4分前列腺癌患者相比,Gleason评分为4+3分者生化复发率更高[31]。因此本研究根据Gleason评分将前列腺癌患者分为高风险组(Gleason评分≥4+3分)与低风险组(Gleason评分≤3+4分)具有重要的临床意义。
本研究建立了基于前列腺bpMRI的影像组学模型和临床-影像组学联合模型,两者对前列腺癌的病理风险均具有一定的预测效能,将临床信息添加到联合影像组学模型中时没有发现预测效能明显改善,原因可能是所选择的临床信息在多变量分析中的效能不显著或样本量较小。多名学者利用MRI纹理分析对前列腺癌Gleason评分进行了研究。Wibmer等[32]研究了MRI的Haralick纹理在区分Gleason评分≤7分与>7分中的作用,并揭示了ADC图像对Gleason评分的有效性。Vignati等[29]和Chaddad等[33]强调了影像组学特征在预测前列腺癌Gleason评分中的价值。Turkbey等[34]和Donati等[35]证明ADC图像在预测前列腺癌侵袭性方面是有用的。Chaddad等[36]利用影像组学特征分析预测Gleason评分,结果表明影像组学特征可以作为非侵入性生物标志物用于预测前列腺癌的Gleason评分。Gong等[37]通过对全前列腺的影像组学特征提取,证明T2WI-DWI影像组学模型可预测Gleason评分>7分的前列腺癌。
本研究进一步支持了影像组学特征在预测高级别前列腺癌中的作用,采用LASSO logistic回归模型进行最终的影像组学特征筛选和建模,共纳入6个T2WI相关特征和4个ADC相关特征,其中T2WI的Correlation、RunEntropy和ADC图像的ShortRunEmphasis、RootMeanSquared特征在前列腺癌病理分层影像组学评分中所占权重较高。研究表明前列腺癌的Correlation低于前列腺的非癌组织,对前列腺癌的鉴别有一定价值[38],本研究中低级别和高级别的前列腺癌有显著差异,进一步表明Correlation具有评价前列腺癌侵袭性的潜在价值。T2WI的RunEntropy反映高级别的前列腺癌成分较低级别前列腺癌复杂,灰度分布程度更为混乱,研究表明RunEntropy与小细胞肺癌[39]、软组织肉瘤[40]的组织病理学分级亦有明显相关性。ShortRunEmphasis在越粗糙的图像上值越大,ADC图像的ShortRunEmphasis反映了低级别的前列腺癌图像纹理更加细腻均匀,该特征也曾用于影像组学鉴别不同病理类型的原发性肝癌[41]。RootMeanSquared亦是描述图像纹理均匀程度的指标,高级别的前列腺癌图像纹理较为粗糙。既往相关研究证明,临床因素与前列腺癌分级之间存在一定相关性[42-43],PI-RADS评分可用于预测前列腺癌的侵袭性,前列腺癌患者的血清PSA水平高于正常值并不是由于PSA产生和分泌增加,而是由于前列腺结构破坏导致PSA入血增多所致[44],PI-RADS评分越高发生高级别肿瘤的可能性越大,侵袭性强的前列腺癌患者血清中的PSA水平通常较高。本研究中血清PSA、PI-RADS评分显示出一定的前列腺癌风险预测能力,但与bpMRI影像组学模型和临床-影像组学联合模型相比,临床模型在训练集和验证集中的准确性都较低,表明目前用于前列腺癌风险分层的临床因素预测价值有限;前列腺病灶体积及年龄与Gleason分级之间没有明显相关性,可能是病例数量有限及病例纳入受限的缘故。
本研究存在如下局限性:(1)属于单中心研究,采用的扫描设备和序列相同,可一定程度避免数据产生较大差异性,但对结果的推广不利,需要多中心、大样本的研究验证;(2)我们勾画的是二维病灶,未能完全反映前列腺的整体影像组学特征信息;(3)在勾画病变感兴趣区时,ADC图像分辨率较低且MRI图像与病理切片难以完全匹配,这对感兴趣区勾画的准确性带来一定影响。
本研究建立了bpMRI影像组学与临床因素联合的模型预测前列腺癌的风险分层,可用于评估前列腺癌的侵袭性,该模型具有一定的诊断效能和临床净收益。将影像组学特征和临床因素结合到诺模图中可为医师提供一种定量和直观的方法,有助于其更有信心地评估前列腺癌的临床风险。虽然本研究建立的影像组学模型能够定量评估前列腺癌的风险、相对客观,而且有些研究已经评估了影像组学特征的可重复性,但对MRI影像组学特征的稳定性知之甚少,需要开展多中心、大样本的研究。MRI影像组学准确性的评估和优化将是我们今后研究的重点。
| [1] |
WONG M C, GOGGINS W B, WANG H H, FUNG F D, LEUNG C, WONG S Y, et al. Global incidence and mortality for prostate cancer: analysis of temporal patterns and trends in 36 countries[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 70: 862-874. DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.043 |
| [2] |
CULP M B, SOERJOMATARAM I, EFSTATHIOU J A, BRAY F, JEMAL A. Recent global patterns in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates[J]. Eur Urol, 2020, 77: 38-52. DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.005 |
| [3] |
SIEGEL R L, MILLER K D, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70: 7-30. DOI:10.3322/caac.21590 |
| [4] |
CHEN W, ZHENG R, BAADE P D, ZHANG S, ZENG H, BRAY F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2016, 66: 115-132. DOI:10.3322/caac.21338 |
| [5] |
FENG R M, ZONG Y N, CAO S M, XU R H. Current cancer situation in China: good or bad news from the 2018 global cancer statistics?[J/OL]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2019, 39: 22. DOI: 10.1186/s40880-019-0368-6.
|
| [6] |
CHEN L, ZHANG Y H, WANG S, ZHANG Y, HUANG T, CAI Y D. Prediction and analysis of essential genes using the enrichments of gene ontology and KEGG pathways[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2017, 12: e0184129. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184129.
|
| [7] |
HAN M, PARTIN A W, POUND C R, EPSTEIN J I, WALSH P C. Long-term biochemical disease-free and cancer-specific survival following anatomic radical retropubic prostatectomy. The 15-year Johns Hopkins experience[J]. Urol Clin North Am, 2001, 28: 555-565. DOI:10.1016/S0094-0143(05)70163-4 |
| [8] |
STARK J R, PERNER S, STAMPFER M J, SINNOTT J A, FINN S, EISENSTEIN A S, et al. Gleason score and lethal prostate cancer: does 3+4=4+3?[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2009, 27: 3459-3464. DOI:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.4669 |
| [9] |
RIZZO S, BOTTA F, RAIMONDI S, ORIGGI D, FANCIULLO C, MORGANTI A G, et al. Radiomics: the facts and the challenges of image analysis[J/OL]. Eur Radiol Exp, 2018, 2: 36. DOI: 10.1186/s41747-018-0068-z.
|
| [10] |
史张, 刘崎. 影像组学技术方法的研究及挑战[J]. 放射学实践, 2018, 33: 633-636. |
| [11] |
HECTORS S J, CHERNY M, YADAV K K, BEKSAÇ A T, THULASIDASS H, LEWIS S, et al. Radiomics features measured with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging predict prostate cancer aggressiveness[J]. J Urol, 2019, 202: 498-505. DOI:10.1097/JU.0000000000000272 |
| [12] |
WEINREB J C, BARENTSZ J O, CHOYKE P L, CORNUD F, HAIDER M A, MACURA K J, et al. PI-RADS prostate imaging-reporting and data system: 2015, version 2[J]. Eur Urol, 2016, 69: 16-40. DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2015.08.052 |
| [13] |
TURKBEY B, ROSENKRANTZ A B, HAIDER M A, PADHANI A R, VILLEIRS G, MACURA K J, et al. Prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2.1:2019 update of prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2[J]. Eur Urol, 2019, 76: 340-351. DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2019.02.033 |
| [14] |
KUHL C K, BRUHN R, KRÄMER N, NEBELUNG S, HEIDENREICH A, SCHRADING S. Abbreviated biparametric prostate MR imaging in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen[J]. Radiology, 2017, 285: 493-505. DOI:10.1148/radiol.2017170129 |
| [15] |
WANG J, WU C J, BAO M L, ZHANG J, WANG X N, ZHANG Y D. Machine learning-based analysis of MR radiomics can help to improve the diagnostic performance of PI-RADS v2 in clinically relevant prostate cancer[J]. Eur Radiol, 2017, 27: 4082-4090. DOI:10.1007/s00330-017-4800-5 |
| [16] |
张沥, 张鑫, 王睿, 宦怡, 李陇超. MRI纹理分析对前列腺癌及Gleason分级的诊断价值[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志, 2019, 42: 264-268. |
| [17] |
EGEVAD L, DELAHUNT B, SRIGLEY J R, SAMARATUNGA H. International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading of prostate cancer-An ISUP consensus on contemporary grading[J]. APMIS, 2016, 124: 433-435. DOI:10.1111/apm.12533 |
| [18] |
GIBBS P, TURNBULL L W. Textural analysis of contrast-enhanced MR images of the breast[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2003, 50: 92-98. DOI:10.1002/mrm.10496 |
| [19] |
COLLEWET G, STRZELECKI M, MARIETTE F. Influence of MRI acquisition protocols and image intensity normalization methods on texture classification[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2004, 22: 81-91. DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2003.09.001 |
| [20] |
VICKERS A J, CRONIN A M, ELKIN E B, GONEN M. Extensions to decision curve analysis, a novel method for evaluating diagnostic tests, prediction models and molecular markers[J/OL]. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, 2008, 8: 53. DOI: 10.1186/1472-6947-8-53.
|
| [21] |
KHAWAJA A Z, CASSIDY D B, AL SHAKARCHI J, MCGROGAN D G, INSTON N G, JONES R G. Revisiting the risks of MRI with gadolinium based contrast agents-review of literature and guidelines[J]. Insights Imaging, 2015, 6: 553-558. DOI:10.1007/s13244-015-0420-2 |
| [22] |
MCDONALD R J, MCDONALD J S, KALLMES D F, JENTOFT M E, MURRAY D L, THIELEN K R, et al. Intracranial gadolinium deposition after contrast-enhanced MR imaging[J]. Radiology, 2015, 275: 772-782. DOI:10.1148/radiol.15150025 |
| [23] |
MCDONALD R J, MCDONALD J S, KALLMES D F, JENTOFT M E, PAOLINI M A, MURRAY D L, et al. Gadolinium deposition in human brain tissues after contrast-enhanced MR imaging in adult patients without intracranial abnormalities[J]. Radiology, 2017, 285: 546-554. DOI:10.1148/radiol.2017161595 |
| [24] |
ABDOLLAHI H, MOSTAFAEI S, CHERAGHI S, SHIRI I, RABI MAHDAVI S, KAZEMNEJAD A. Cochlea CT radiomics predicts chemoradiotherapy induced sensorineural hearing loss in head and neck cancer patients: a machine learning and multi-variable modelling study[J]. Phys Med, 2018, 45: 192-197. DOI:10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.10.008 |
| [25] |
宋涛, 陆建平, 张倩雯. 人工智能医学影像技术在胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤分级中的应用[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2020, 41: 433-438. SONG T, LU J P, ZHANG Q W. Application of artificial intelligence medical imaging technology in grading of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms[J]. Acad J Sec Mil Med Univ, 2020, 41: 433-438. |
| [26] |
STOYANOVA R, TAKHAR M, TSCHUDI Y, FORD J C, SOLÓRZANO G, ERHO N, et al. Prostate cancer radiomics and the promise of radiogenomics[J]. Transl Cancer Res, 2016, 5: 432-447. DOI:10.21037/tcr.2016.06.20 |
| [27] |
NIU X K, CHEN Z F, CHEN L, LI J, PENG T, LI X. Clinical application of biparametric MRI texture analysis for detection and evaluation of high-grade prostate cancer in zone-specific regions[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2018, 210: 549-556. DOI:10.2214/AJR.17.18494 |
| [28] |
BATES A, MILES K. Prostate-specific membrane antigen PET/MRI validation of MR textural analysis for detection of transition zone prostate cancer[J]. Eur Radiol, 2017, 27: 5290-5298. DOI:10.1007/s00330-017-4877-x |
| [29] |
VIGNATI A, MAZZETTI S, GIANNINI V, RUSSO F, BOLLITO E, PORPIGLIA F, et al. Texture features on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: new potential biomarkers for prostate cancer aggressiveness[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2015, 60: 2685-2701. DOI:10.1088/0031-9155/60/7/2685 |
| [30] |
STOYANOVA R, POLLACK A, TAKHAR M, LYNNE C, PARRA N, LAM L L, et al. Association of multiparametric MRI quantitative imaging features with prostate cancer gene expression in MRI-targeted prostate biopsies[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7: 53362-53376. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.10523 |
| [31] |
LAU W K, BLUTE M L, BOSTWICK D G, WEAVER A L, SEBO T J, ZINCKE H. Prognostic factors for survival of patients with pathological Gleason score 7 prostate cancer: differences in outcome between primary Gleason grades 3 and 4[J]. J Urol, 2001, 166: 1692-1697. DOI:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)65655-8 |
| [32] |
WIBMER A, HRICAK H, GONDO T, MATSUMOTO K, VEERARAGHAVAN H, FEHR D, et al. Haralick texture analysis of prostate MRI: utility for differentiating non-cancerous prostate from prostate cancer and differentiating prostate cancers with different Gleason scores[J]. Eur Radiol, 2015, 25: 2840-2850. DOI:10.1007/s00330-015-3701-8 |
| [33] |
CHADDAD A, KUCHARCZYK M J, NIAZI T. Multimodal radiomic features for the predicting Gleason score of prostate cancer[J/OL]. Cancers (Basel), 2018, 10: 249. DOI: 10.3390/cancers10080249.
|
| [34] |
TURKBEY B, SHAH V P, PANG Y X, BERNARDO M, XU S, KRUECKER J, et al. Is apparent diffusion coefficient associated with clinical risk scores for prostate cancers that are visible on 3-T MR images?[J]. Radiology, 2011, 258: 488-495. DOI:10.1148/radiol.10100667 |
| [35] |
DONATI O F, MAZAHERI Y, AFAQ A, VARGAS H A, ZHENG J T, MOSKOWITZ C S, et al. Prostate cancer aggressiveness: assessment with whole-lesion histogram analysis of the apparent diffusion coefficient[J]. Radiology, 2014, 271: 143-152. DOI:10.1148/radiol.13130973 |
| [36] |
CHADDAD A, NIAZI T, PROBST S, BLADOU F, ANIDJAR M, BAHORIC B. Predicting Gleason score of prostate cancer patients using radiomic analysis[J/OL]. Front Oncol, 2018, 8: 630. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00630.
|
| [37] |
GONG L X, XU M, FANG M J, ZOU J, YANG S D, YU X Y, et al. Noninvasive prediction of high-grade prostate cancer via biparametric MRI radiomics[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2020, 52: 1102-1109. DOI:10.1002/jmri.27132 |
| [38] |
ROMEO V, RICCIARDI C, CUOCOLO R, STANZIONE A, VERDE F, SARNO L, et al. Machine learning analysis of MRI-derived texture features to predict placenta accreta spectrum in patients with placenta previa[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 64: 71-76. DOI:10.1016/j.mri.2019.05.017 |
| [39] |
SHIRI I, MALEKI H, HAJIANFAR G, ABDOLLAHI H, ASHRAFINIA S, HATT M, et al. Next-generation radiogenomics sequencing for prediction of EGFR and KRAS mutation status in NSCLC patients using multimodal imaging and machine learning algorithms[J]. Mol Imaging Biol, 2020, 22: 1132-1148. DOI:10.1007/s11307-020-01487-8 |
| [40] |
ZHANG Y, ZHU Y F, SHI X M, TAO J, CUI J J, DAI Y, et al. Soft tissue sarcomas: preoperative predictive histopathological grading based on radiomics of MRI[J]. Acad Radiol, 2019, 26: 1262-1268. DOI:10.1016/j.acra.2018.09.025 |
| [41] |
张加辉, 陈峰, 薛星, 张思影, 尧林鹏, 王小丽, 等. 基于支持向量机的MRI影像组学方法鉴别不同病理分型原发性肝癌的价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2018, 52: 333-337. |
| [42] |
ISARIYAWONGSE B K, SUN L, BAÑEZ L L, ROBERTSON C, POLASCIK T J, MALONEY K, et al. Significant discrepancies between diagnostic and pathologic Gleason sums in prostate cancer: the predictive role of age and prostate-specific antigen[J]. Urology, 2008, 72: 882-886. DOI:10.1016/j.urology.2008.02.021 |
| [43] |
LOPES VENDRAMI C, MCCARTHY R J, CHATTERJEE A, CASALINO D, SCHAEFFER E M, CATALONA W J, et al. The utility of prostate specific antigen density, prostate health index, and prostate health index density in predicting positive prostate biopsy outcome is dependent on the prostate biopsy methods[J]. Urology, 2019, 129: 153-159. DOI:10.1016/j.urology.2019.03.018 |
| [44] |
GÜNDOĞDU E, EMEKLI E, KEBAPÇI M. Evaluation of relationships between the final Gleason score, PI-RADS v2 score, ADC value, PSA level, and tumor diameter in patients that underwent radical prostatectomy due to prostate cancer[J]. Radiol Med, 2020, 125: 827-837. DOI:10.1007/s11547-020-01183-1 |
 2021, Vol. 42
2021, Vol. 42


