2. 海军军医大学(第二军医大学)长海医院虹口院区口腔种植与颌面外科, 上海 200081
2. Department of Oral Implant and Maxillofacial Surgery, Hongkou Branch of Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University(Second Military Medical University), Shanghai 200081, China
牙周炎、肿瘤、创伤等均可导致牙槽骨缺损,而牙槽骨缺损可直接或间接引起牙齿缺失[1-2],因此如何促进牙槽骨的修复是口腔医学领域研究的重点。修复牙槽骨缺损的疗法包括自体和异体骨移植、膜引导骨再生技术[3]、牙周组织工程[4]等,近年来基于复合支架材料、种子细胞和细胞生长因子的牙周组织工程逐渐成为理想的牙槽骨再生疗法[4-5]。
牙周膜干细胞(periodontal ligament stem cell,PDLSC)是来源于牙周膜组织中的一类成体干细胞,具有自我增殖和多向分化潜能,在一定条件下可以向牙周膜主要细胞分化,进而形成牙周膜和牙槽骨,最后形成新的牙周附着结构修复牙周缺损,是治疗牙周炎、恢复牙周组织的关键细胞[5-6]。骨形态发生蛋白(bone morphogenetic protein,BMP)作为调控细胞生长和成骨分化的重要生长因子,具有趋化和诱导干细胞成骨分化的能力,其中BMP9作为BMP家族重要成员具有较强的诱导成骨活性,并且其促进骨组织形成的过程和生理性的骨形成类似[7-8]。已有研究证实BMP9诱导PDLSC成骨分化具有一定的效果[9],但成骨效率未达到临床预期,尚未应用于临床,因此如何充分发挥干细胞和成骨活性因子的成骨潜力是近期研究的热点。
生物物理性刺激作为一种经济、安全、可有效促进骨组织发生和增强骨密度的物理辅助疗法,近年来得到了广泛的重视[10]。在医学领域运用脉冲电磁场(pulsed electromagnetic field,PEMF)治疗骨相关疾病已有40多年的历史,其能够缩短骨折愈合时间、增加骨密度、改善骨的力学特性[11]。大量体外实验表明适宜磁场参数的PEMF能够促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,但是研究发现PEMF作为单一的物理刺激在治疗骨折愈合时效果一般,仅可作为传统方案的辅助疗法[12-13]。有实验表明,PEMF与其他成骨诱导因子(如BMP2、磷酸钙盐、β-甘油磷酸)联合作用时可明显提高细胞增殖活性及成骨标志分子的表达及矿化结节的生成[14]。然而,目前PEMF用于治疗牙周病、促进牙槽骨修复和牙周组织工程方面的研究较少。本项研究选择已经证实具有较好促进成骨效果的15 Hz低频PEMF[10, 15-16],探究不同磁场强度PEMF对BMP9诱导PDLSC成骨分化的影响,期望为促进牙槽骨组织的再生修复提供一种无创的辅助治疗手段。
1 材料和方法 1.1 主要试剂FBS购自美国Gibco公司;DMEM培养基、PBS、青霉素/链霉素(双抗)、蛋白裂解液、胰蛋白酶购自美国Corning公司;CD146分选磁珠套装购自德国Miltenyi Biotec公司;兔抗人STRO-1抗体、兔抗人CD146抗体、鼠抗人角蛋白抗体、鼠抗人波形蛋白抗体购自英国Abcam公司;TRIzol、Prime Script RT Master Mix、SYBR Green Ⅱ-PCR Kit等PCR相关试剂购自日本TaKaRa Bio公司;基因引物序列由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成(表 1);碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)活性检测试剂盒、山羊抗鼠二抗、骨桥蛋白(osteopontin,OPN)一抗、骨钙蛋白(osteoclain,OCN)一抗、蛋白质印迹检测相关试剂均购自上海碧云天生物技术有限公司。
|
|
表 1 基因引物序列 Tab 1 Sequences of gene primers |
1.2 改良组织块贴壁法获取牙周膜细胞
本研究方案经海军军医大学(第二军医大学)长海医院医学伦理委员会审批。在患者及其监护人签署知情同意书后,收集因正畸治疗需要拔除的健康前磨牙(患者年龄为12~14岁),4 ℃保存并运输至实验室。用刀片刮取牙根中1/3牙周膜组织,用含体积分数1%双抗的生理盐水反复清洗,收集并转移牙周膜组织碎片至60 mm培养皿中,将经消毒的盖玻片置于组织块上,小心移入培养皿,放入5% CO2饱和湿度的细胞培养箱中孵育,待组织块呈现半干涸状态时,加入完全培养基(含10% FBS的DMEM培养基)孵育,根据细胞生长情况每3~5 d换液1次,当细胞汇合至70%~80%时传代。
1.3 免疫磁珠法分选PDLSC取第3代牙周膜细胞清洗后,以1 500 r/min (离心半径20 cm)离心5 min后弃上清获得细胞沉淀。按照说明书要求,在避光条件下,每107个细胞加20 μL CD146免疫磁珠、20 μL分选用封闭液和60 μL缓冲液,充分吹打均匀后4 ℃避光孵育20 min,清洗细胞后加入3 mL缓冲液重悬细胞。将分选柱安装在磁力分选架的磁力槽中,加入孵育好的细胞悬液,于分选柱下方收集未结合CD146磁珠的细胞悬液。将分选柱从磁力架上取下置于15 mL离心管上并远离磁场,于分选柱上方加入5 mL缓冲液并快速推动分选柱配套的活塞,使结合CD146磁珠的细胞悬液流出,收集细胞悬液,清洗细胞后用新鲜培养基重悬细胞并移至培养皿。
1.4 流式细胞术鉴定经细胞表面标志取第3代经分选后细胞,胰酶消化并收集、计数、清洗后调整细胞密度为1×107/mL;在避光条件下用封闭液(含2% FBS的PBS)封闭30 min,离心获得细胞沉淀。添加别藻蓝蛋白(allophycocyanin,APC)标记的CD146流式抗体和异硫氰酸荧光素(fluoresceine isothiocyanate,FITC)标记的STRO-1流式抗体,避光孵育20 min,清洗细胞获得悬液。将细胞悬液上机检测。
1.5 免疫荧光染色鉴定细胞的组织来源取第3代经分选后细胞,转移至6孔板,让细胞爬至玻片上生长。待细胞融合至60%左右,使用4%多聚甲醛溶液固定30 min,加入破膜工作液室温孵育10 min,封闭后分别加入鼠抗人角蛋白一抗和鼠抗人波形蛋白一抗,湿盒内4 ℃孵育过夜。加入山羊抗鼠二抗室温避光孵育50 min,以DAPI复染细胞核,避光室温孵育10 min,封片后在荧光显微镜下观察并拍照。
1.6 BMP9对PDLSC成骨分化作用效果研究取第3代经分选后细胞,分为不感染任何病毒组(空白组)、感染含GFP基因片段的重组过表达腺病毒(Ad-GFP)组(Ad-GFP组)、含GFP基因片段和BMP9基因片段的重组过表达腺病毒(Ad-GFP-BMP9)组(Ad-GFP-BMP9组)。空白组不做任何干预,Ad-GFP组和Ad-GFP-BMP9组分别感染Ad-GFP和Ad-GFP-BMP9病毒(2种腺病毒为本研究团队2015年合成),感染3 d后换骨诱导培养液培养。
1.7 低频PEMF干预BMP9诱导PDLSC成骨分化实验取第3代经分选后细胞成功感染Ad-GFP-BMP9后,分为空白对照组、0.6 mT组、1.2 mT组、1.8 mT组、2.4 mT组、3.0 mT组,更换成骨诱导培养液并分别以0、0.6、1.2、1.8、2.4、3.0 mT PEMF进行干预。本实验所用低频PEMF干预装置由空军军医大学生物医学工程系提供技术支持(专利号:ZL02224739.4)[17],整套装置包括低频PEMF发生器(集成电脑控制系统、数模转化系统、信号放大装置、磁场传感器和温度传感器)、80匝赫姆霍兹线圈、示波器、CO2培养箱、连接线路等,产生脉冲频率15 Hz、脉冲宽度0.2 ms、脉冲间隔0.02 ms、脉冲群宽度5 ms、脉冲群间隔60 ms、磁场强度为0~3.0 mT的均匀磁场。实验时,将线圈、线材严格消毒并置于细胞培养箱中,调节低频PEMF发生器参数控制赫姆霍兹线圈产生电磁场,均匀辐照位于线圈中的培养皿,通过磁场和温度传感器实时监测磁场强度及温度的变化,确保实验的可控性。
1.8 ALP活性检测分别于实验第4、7、10天收集细胞,将0.2% Triton X-100加入细胞培养孔中,适当匀浆后稀释,上酶标仪检测,按说明书要求操作,在450 nm处检测光密度,计算ALP活性。
1.9 qRT-PCR检测基因表达分别于实验第4、7、10、14天收集细胞,用0.2% Triton X-100裂解细胞,提取总RNA,逆转录为cDNA,通过qRT-PCR检测成骨标志物基因ALP、OPN、Runt相关转录因子2(runt-related transcription factor 2,Runx2)表达。
1.10 蛋白质印迹法检测蛋白表达分别于实验第4、7、10、14天收集细胞,用RIPA裂解细胞,采用BCA法测定蛋白浓度,电泳槽梳孔中加入蛋白样品电泳。转膜封闭后加入一抗和内参抗体,4 ℃过夜,清洗膜,加入二抗孵育1 h后清洗,然后扫膜,使用ImageJ软件分析灰度值,计算目的蛋白的相对表达量。
1.11 统计学处理采用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计学分析,采用GraphPad Prism 8软件绘图。计量资料以x±s表示,组间比较用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用Tukey’s检验。检验水准(α)为0.05。
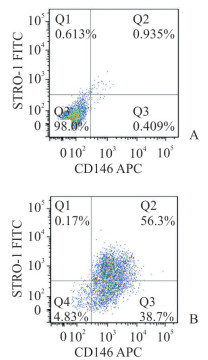
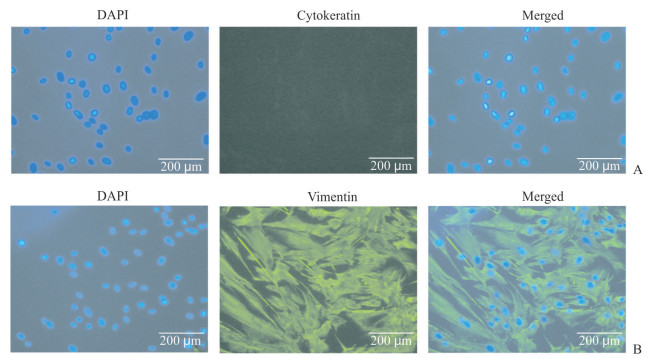
2 结果 2.1 PDLSC鉴定结果经免疫磁珠分选法获得的细胞CD146和STRO-1双标阳性率约为56.3%(图 1)。利用免疫荧光染色技术判断细胞来源,结果显示角蛋白阴性表达,波形蛋白阳性表达,证明所分选的细胞为中胚层来源的间充质细胞,且无外胚层来源的细胞污染(图 2)。
|
图 1 流式细胞术检测经分选细胞中的CD146与STRO-1阳性细胞 Fig 1 CD146+ and STRO-1+ cells detected by flow cytometry A: Control; B: The double standard positive rates of CD146 and STRO-1 in cells obtained by immunomagnetic beads were 56.3%. APC: Allophycocyanin; FITC: Fluoresceine isothiocyanate |
|
图 2 免疫荧光染色检测细胞来源 Fig 2 Cell origin detected by immunofluorescence staining Immunofluorescence staining showed that the isolated PDLSCs were cytokeratin-negative (A) and vimentin-positive (B). DAPI: 4', 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; PDLSC: Periodontal ligament stem cell |
2.2 Ad-GFP-BMP9感染PDLSC后BMP9蛋白过表达
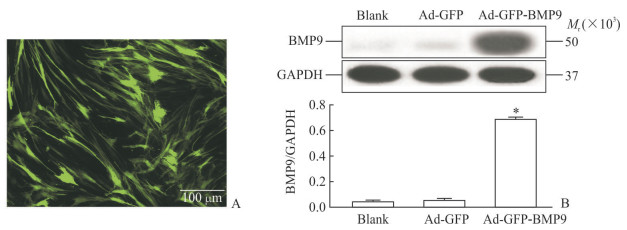
Ad-GFP-BMP9感染PDLSC第3天即可在荧光显微镜下观察到明显绿色荧光(图 3A),蛋白质印迹检测结果显示Ad-GFP-BMP9组BMP9蛋白表达高于空白组和Ad-GFP组(P<0.05,图 3B)。
|
图 3 Ad-GFP-BMP9感染PDLSC后BMP9蛋白过表达情况 Fig 3 Overexpression of BMP9 in PDLSC after Ad-GFP-BMP9 transfection A: Observation of fluorescence area showed GFP expression in the PDLSCs 3 days after transfected with Ad-GFP-BMP9. B: Western blotting showed that the Ad-GFP-BMP9 transfected PDLSCs had stable and high expression of BMP9 at day 3. Ad: Adenovirus; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; PDLSC: Periodontal ligament stem cell; BMP9: Bone morphogenetic protein 9. *P < 0.05 vs blank group and Ad-GFP group. n=4, x±s |
2.3 PEMF干预下BMP9诱导PDLSC成骨分化过程中细胞形态学变化
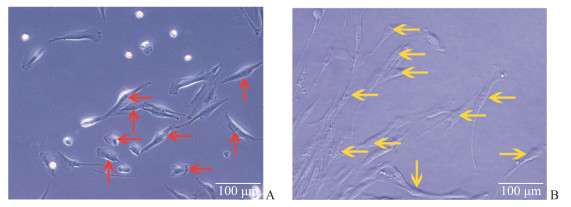
经过免疫磁珠分选后获取的PDLSC呈圆形、椭圆形、星形或不规则形,细胞小且胞质内细胞器也较少,细胞核呈卵圆形且占细胞内体积分数较大(图 4A)。感染Ad-GFP-BMP9的PDLSC经2.4 mT的PEMF刺激作用7 d后,细胞体积稍增大,呈梭形、不规则形、多角形、鳞形,细胞核缩小且占细胞内体积分数较小(图 4B)。
|
图 4 PEMF干预下BMP9诱导PDLSC成骨分化过程中细胞形态学变化 Fig 4 Morphological changes of PDLSC during osteogenic differentiation induced by BMP9 after PEMF stimulation A: PDLSCs were round, fusiform, and small (arrows). The cells had less cytoplasm and a large nucleus. B: After PEMF stimulation for 7 days, Ad-GFP-BMP9 transfected PDLSCs (arrows) showed spindle-shaped, irregular, polygonal, and squamous shapes. The nucleus shrank and occupied a small volume fraction in the cell. PEMF: Pulsed electromagnetic field; BMP9: Bone morphogenetic protein 9; PDLSC: Periodontal ligament stem cell |
2.4 BMP9对PDLSC ALP活性及成骨相关基因和蛋白表达的影响
实验第4、7、10天,Ad-GFP-BMP9组ALP活性和ALP基因表达均高于空白组和Ad-GFP组(P<0.05,图 5A、5B);实验第4、7天,Ad-GFP-BMP9组Runx2基因表达高于空白组和Ad-GFP组(P<0.05,图 5C);实验第10、14天,Ad-GFP-BMP9组OPN基因表达高于空白组和Ad-GFP组(P<0.05,图 5D);实验第14天,Ad-GFP-BMP9组OCN、OPN蛋白相对表达均高于空白组和Ad-GFP组(图 5E、5F)。
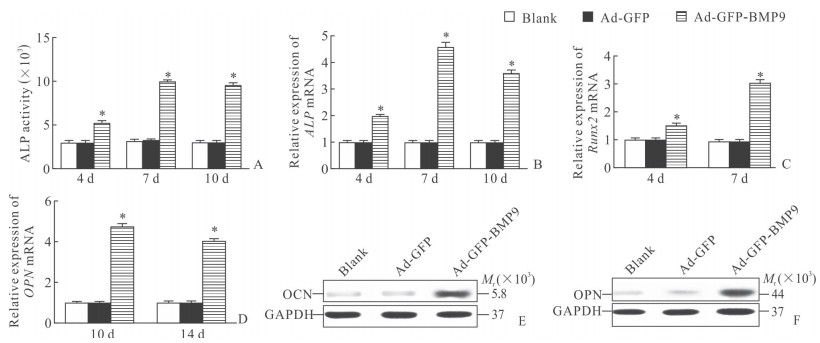
|
图 5 BMP9对PDLSC中ALP活性及成骨相关基因和蛋白表达的影响 Fig 5 Effects of BMP9 on ALP activity and the expression of osteogenic genes and proteins in PDLSCs A: The ALP activity was measured via a quantitative kit on days 4, 7, and 10 in the early osteogenic phase of PDLSCs; B: qRT-PCR analysis of ALP gene expression on days 4, 7, and 10. C, D: qRT-PCR analysis of Runx2 (C) and OPN (D) mRNA expression on days 4, 7, 10, and 14, respectively. E, F: Western blotting suggested that BMP9 significantly enhanced OCN (E) and OPN(F) proteins expression on day 14. BMP9: Bone morphogenetic protein 9; PDLSC: Periodontal ligament stem cell; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; qRT-PCR: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; Runx2: Runt-related transcription factor 2; OCN: Osteoclain; OPN: Osteopontin; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. *P < 0.05 vs control group and Ad-GEP group. n=4, x±s |
2.5 PEMF干预对BMP9诱导PDLSC成骨分化的影响
由图 6A可见,感染Ad-GFP-BMP9的PDLSC经15 Hz的PEMF刺激作用第4天时,1.8 mT组、2.4 mT组、3.0 mT组ALP活性均高于空白对照组(P<0.05);第7、10天时,1.2 mT组、1.8 mT组、2.4 mT组、3.0 mT组ALP活性均高于空白对照组(P<0.05),并且2.4 mT组最高(P<0.05)。由图 6B可见,感染Ad-GFP-BMP9的PDLSC经15 Hz的PEMF刺激作用第4、7、10天,1.2 mT组、1.8 mT组、2.4 mT组、3.0 mT组ALP基因表达高于空白对照组(P<0.05),并且2.4 mT组最高(P<0.05)。第4、7天Runx2基因检测和第10、14天OPN基因检测结果与ALP基因趋势相似(图 6C、6D)。由图 6E、6F可见,PEMF干预第14天,1.2 mT组、1.8 mT组、2.4 mT组、3.0 mT组OCN和OPN蛋白表达均高于空白对照组,并且2.4 mT组最高。
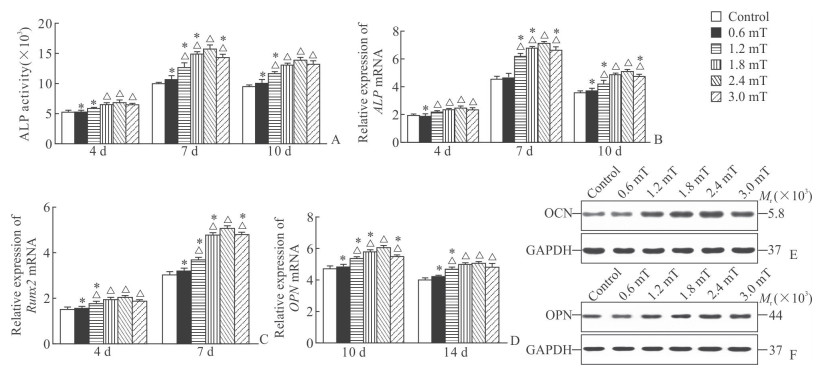
|
图 6 PEMF干预下BMP9诱导PDLSC成骨分化过程中ALP活性及成骨基因和蛋白的表达情况 Fig 6 ALP activity and the osteogenesis-related gene and protein expression during osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs induced by BMP9 after PEMF stimulation A: ALP activity in PDLSCs co-infected with Ad-GFP-BMP9 or exposed to PEMF stimulation of different intensities (0.6, 1.2, 1.8, 2.4, 3.0 mT) was measured via a quantitative kit on days 4, 7, and 10. B-D: Expression of ALP (B), Runx2 (C) and OPN (D) genes in PDLSCs co-infected with Ad-GFP-BMP9 or exposed to PEMF stimulation of different intensities are detected by qRT-PCR on days 4, 7, 10, and 14, respectively. E, F: Expression of OCN (E) and OPN (F) proteins in PDLSCs co-infected with Ad-GFP-BMP9 or exposed to PEMF stimulation of different intensities detected by Western blotting on day 14. PEMF: Pulsed electromagnetic field; BMP9: Bone morphogenetic protein 9; PDLSC: Periodontal ligament stem cells; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; Runx2: Runt-related transcription factor 2; OPN: Osteopontin; qRT-PCR: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; OCN: Osteoclain; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. *P < 0.05 vs 2.4 mT group; △P < 0.05 vs control group. n=4, x±s |
3 讨论
骨的形成和发育在体内是一系列漫长且复杂的生理过程,因客观条件和现有技术的限制,目前还难以对实验研究中骨生长发育进行实时、全面的评测[18]。通过建立体外成骨模型消除体内的内源性干扰因素的影响,并检测骨形成发展过程中各种成骨标志物的表达量间接分析骨生长和发育,是目前实验研究普遍采用的手段[16, 19-20]。研究发现Runx2在成骨早期数量增多、活性增强,该转录因子可以上调多种成骨基因的表达,在细胞成骨分化、骨发育方面起重要作用[22]。成骨早期ALP同样起重要作用,ALP可以水解有机磷酸酶,导致PO43-水平局部升高,从而对钙化抑制剂产生破坏,启动钙化过程[22]。成骨中期,OPN、OCN等非胶原性糖蛋白表达增多,这些糖蛋白将沿着Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的长轴与Ca2+、P3+结合到胶原分子侧链的胶原氨基酸残基上形成羟磷灰石结晶,最后通过骨改建形成具有生理功能的骨组织[23-24]。本研究通过建立体外PDLSC成骨模型并进行PEMF干预,在成骨早期检测Runx2和ALP基因表达,在成骨分化的中期检测OPN和OCN基因和蛋白表达量,间接判断PEMF是否可以增强BMP9诱导的PDLSC成骨分化效果。
PDLSC是Seo等[6]发现并命名的一种来源于牙周膜组织的多能干细胞,可以向成纤维细胞、成骨细胞、成牙骨质细胞和破骨细胞等牙周膜主要细胞分化,在修复牙周组织缺损方面发挥重要作用[25]。在成骨效率方面,学者们比较了PDLSC、骨髓间充质干细胞和牙髓干细胞等牙周组织工程的主要种子细胞后,认为PDLSC的增殖和成骨分化能力均强于其他种子细胞[4-5, 26-27],因此本研究选取PDLSC作为修复牙槽缺损的种子细胞。BMP是一类多功能生长因子,属于TGF-β超家族,成骨调控是其主要功能[28],迄今为止至少有43种人类BMP被发现,其中BMP9作为BMP家族重要成员,具有较强的趋化和诱导干细胞成骨分化的能力[7, 29],而且其促进骨组织形成的过程和生理性的骨形成类似[7-8],因此常被应用于组织工程的成骨调控。
电磁场自20世纪70年代起便作为一种相对安全的物理辅助疗法应用于医学领域,尤其在治疗骨质疏松症、骨不连、促进骨折愈合等方面取得一定的疗效[30-31]。PEMF作为一种物理刺激,其主要参数包括脉冲时间、频率和磁场强度,多项研究表明PEMF作用于细胞存在一个非线性的“窗口效应”,即只有在适宜参数条件下PEMF才能发挥作用[32-33]。研究发现脉冲电磁场的各项参数中,频率对生物体的影响最大[34],最有效的电磁场频率范围应接近机体正常功能活动频率[30-32],其中频率为7.5~50 Hz的PEMF对细胞具有促进增殖和成骨作用[10, 14, 35-37]。此外磁场强度也是PEMF另一个重要作用参数,Simmons等[38]认为骨髓间充质干细胞在12 Hz、1.1 mT的PEMF干预下细胞增殖活性提高,而且细胞符合成骨细胞的形态特征和生物学特性。Kang等[39]研究证实30 Hz、1 mT的PEMF具有诱导脂肪干细胞的成骨分化作用。Wang等[14]研究认为15 Hz、2.4 mT的PEMF对大鼠的骨质疏松有抑制作用。Zhai等[36]发现15.38 Hz、2.0 mT的PEMF对MC3T3-E1细胞具有明显的成骨促进作用。另有研究表明磁场作用时间对成骨效果也具有重要影响。Song等[40]研究发现用1 mT、15 Hz的正弦电磁场作用于大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,每天持续辐照1、4、8 h,发现成骨相关基因的表达随作用时间的增加而增强。Yu等[41]研究发现将大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞与大鼠成骨细胞共培养,并暴露于1 mT、50 Hz的正弦电磁场下,每天作用2~8 h,结果显示每天作用8 h时细胞成骨向分化明显增加。Ceccarelli等[42]对成骨向分化的人骨髓间充质干细胞加载2 mT、75 Hz的脉冲电磁场,每天加载5 min、10 min、30 min、1 h、4 h、8 h,证实成骨效果具有时间依赖性。由于细胞类型及细胞所处分化状态的不同,导致PEMF发挥作用的波形、磁场强度、磁场频率、干预时间等作用参数也不完全相同,因此对于不同细胞种类需要筛选适宜的磁场参数,才能使得PEMF充分发挥作用[30]。
尽管大量学者探索出不同细胞种类的适宜磁场参数,以较大限度刺激干细胞成骨效能,但依然难以达临床预期,在治疗骨折愈合或骨修复时效果一般,仅仅作为传统方案的辅助疗法[12-13]。另有研究发现PEMF与其他生物活性因子共同作用时具有增效作用,并且两者相联合后仍然存在“窗口效应”[10, 12-13]。Selvamurugan等[12]研究发现PEMF联合BMP2可以更好地增强大鼠原代成骨细胞的成骨能力。Okada等[43]研究发现PEMF加BMP2上调椎间盘细胞基质合成的作用超过单独使用BMP2或PEMF的作用。Wang等[10]研究发现PEMF联合BMP可以更好地促进干细胞成骨分化。本研究在BMP9诱导PDLSC的体外成骨时进行15 Hz、不同磁场强度的PEMF,每12 h辐照1 h,结果显示在1.2、1.8、2.4、3.0 mT的PEMF刺激下,成骨标志物Runx2、ALP、OPN、OCN在不同时间点均较单独BMP9有明显的增长,并且在磁场强度为2.4 mT时达到最高峰,初步证实PEMF(15 Hz、2.4 mT、2 h/d)辐照可以有效增强BMP9诱导的PDLSC成骨分化作用,并且存在“窗口效应”。
对于PEMF调控干细胞成骨分化和PEMF增强生长因子诱导干细胞成骨分化的机制,目前研究不多,有学者认为PEMF可改变细胞内外离子的分布并产生跨膜电位,进一步的作用机制可能与电压门控Ca2+通道有关,但是与PEMF成骨作用相关的跨膜受体,目前仍在进一步研究中[13, 44]。一系列研究表明,PEMF的生物学作用与细胞内环磷酸腺苷、Ca2+等第二信使参与的多种信号转导通路有关,从而促进成骨所需生长因子如类胰岛素一号增长因子、BMP、TGF-β等的表达[13, 45]。本研究发现PEMF可以增强BMP9诱导的PDLSC成骨分化效果,推测PEMF的物理刺激可能使得干细胞发生某些应激反应,或其下游信号通路与BMP蛋白通过串话机制来增强彼此之间的成骨能力,这也为后续探索细胞内信号转导机制提供了方向。
综上所述,本研究发现PEMF作为一种物理刺激,在适宜作用参数下可以有效增强BMP9诱导的PDLSC成骨分化,这将为促进骨骼生长发育和骨折愈合等临床应用提供重要理论基础和技术指导。目前关于PEMF诱导成骨的具体细胞内信号转导机制尚不明确,相信随着PEMF作用机制的进一步阐明,将为临床上骨组织的形成和发育提供一种安全、低刺激、辅助性的物理疗法。
| [1] |
王兴. 第四次全国口腔健康流行病学调查报告[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018: 17-26.
|
| [2] |
MICHAUD D S, FU Z X, SHI J, CHUNG M. Periodontal disease, tooth loss, and cancer risk[J]. Epidemiol Rev, 2017, 39: 49-58. DOI:10.1093/epirev/mxx006 |
| [3] |
李欣, 张潇, 解斯羽, 何祥一, 郭文巧, 杨罗, 等. 外科植入引导牙周组织再生载药PLGA/CS/nHA复合膜的制备及表征[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2017, 38: 194-200. LI X, ZHANG X, XIE S Y, HE X Y, GUO W Q, YANG L, et al. Preparation and characteristics of drug loaded PLGA/chitosan/nano-hydroxyapatite membrane for guided periodontal tissue regeneration in surgical implanting[J]. Acad J Sec Mil Med Univ, 2017, 38: 194-200. |
| [4] |
HAN J, MENICANIN D, GRONTHO S, BARTOLD P M. Stem cells, tissue engineering and periodontal regeneration[J]. Aust Dent J, 2014, 59: 117-130. DOI:10.1111/adj.12100 |
| [5] |
MORSCZECK C, REICHERT T E. Dental stem cells in tooth regeneration and repair in the future[J]. Expert Opin Biol Ther, 2018, 18: 187-196. DOI:10.1080/14712598.2018.1402004 |
| [6] |
SEO B M, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, BARTOLD P M, BATOULI S, BRAHIM J, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament[J]. Lancet, 2004, 364: 149-155. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16627-0 |
| [7] |
KANG Q, SUN M H, CHENG H, PENG Y, MONTAG A G, DEYRUP A T, et al. Characterization of the distinct orthotopic bone-forming activity of 14 BMPs using recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene delivery[J]. Gene Ther, 2004, 17: 1312-1320. |
| [8] |
MILLER A F, HARVEY S A, THIES R S, OLSON M S. Bone morphogenetic protein-9, An autocrine/paracrine cytokine in the liver[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275: 17937-17945. DOI:10.1074/jbc.275.24.17937 |
| [9] |
SLOBODAN V, LOVORKA G, MARKO P. Clinical need for bone morphogenetic proteins[J]. Int Orthop, 2017, 41: 2415-2416. DOI:10.1007/s00264-017-3550-y |
| [10] |
WANG T T, WANG P, CAO Z Z, WANG X X, WANG D L, SHEN Y X, et al. Effects of BMP9 and pulsed electromagnetic fields on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells[J]. Bioelectromagnetics, 2017, 38: 63-77. DOI:10.1002/bem.22018 |
| [11] |
DAISH C, BLANCHARD R, FOX K, PIVONKA P, PIROGOVA E. The application of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMFs) for bone fracture repair:past and perspective findings[J]. Ann Biomed Eng, 2018, 46: 525-542. DOI:10.1007/s10439-018-1982-1 |
| [12] |
SELVAMURUGAN N, KWOK S, VASILOV A, JEFCOAT S C, PARTRIDGE N C. Effects of BMP-2 and pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) on rat primary osteoblastic cell proliferation and gene expression[J]. J Orthop Res, 2007, 25: 1213-1220. DOI:10.1002/jor.20409 |
| [13] |
YUAN J, XIN F, JIANG W X. Underlying signaling pathways and therapeutic applications of pulsed electromagnetic fields in bone repair[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 46: 1581-1594. DOI:10.1159/000489206 |
| [14] |
WANG J, AN Y X, LI F J, LI D M, JING D, GUO T W. The effects of pulsed electromagnetic field on the functions of osteoblasts on implant surfaces with different topographies[J]. Acta Biomater, 2014, 10: 975-985. DOI:10.1016/j.actbio.2013.10.008 |
| [15] |
JING D, LI F J, JIANG M G, CAI J, WU Y, XIE K N, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields improve bone microstructure and strength in ovariectomized rats through a Wnt/Lrp5/b-catenin signaling-associated mechanism[J/OL]. PloS One, 2013, 8: e79377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079377.
|
| [16] |
LI J J, ZENG Z B, ZHAO Y T, JING D, TANG C H, DING Y, et al. Effects of low-intensity pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone microarchitecture, mechanical strength and bone turnover in type 2 diabetic db/db mice[J/OL]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 10834. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11090-7.
|
| [17] |
JING D, SHEN G H, HUANG J H, XIE K N, CAI J, XU Q L, et al. Circadian rhythm affects the preventive role of pulsed electromagnetic fields on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats[J]. Bone, 2010, 46: 487-495. DOI:10.1016/j.bone.2009.09.021 |
| [18] |
CHAUDHARY L R, HOFMEISTER A M, HRUSKA K A. Differential growth factor control of bone formation through osteoprogenitor differentiation[J]. Bone, 2004, 34: 402-411. DOI:10.1016/j.bone.2003.11.014 |
| [19] |
HEINO T J, HENTUNEN T A. Differentiation of osteoblasts and osteocytes from mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther, 2008, 3: 131-145. DOI:10.2174/157488808784223032 |
| [20] |
CAO X, CHEN D. The BMP signaling and in vivo bone formation[J]. Gene, 2005, 357: 1-8. DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2005.06.017 |
| [21] |
KOMORI T. Runx2, an inducer of osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation[J]. Histochem Cell Biol, 2018, 149: 313-323. DOI:10.1007/s00418-018-1640-6 |
| [22] |
SILLER A F, WHYTE M P. Alkaline phosphatase:discovery and naming of our favorite enzyme[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2018, 33: 362-364. DOI:10.1002/jbmr.3225 |
| [23] |
ICER M A, GEZMEN-KARADAG M. The multiple functions and mechanisms of osteopontin[J]. Clin Biochem, 2018, 59: 17-24. DOI:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.07.003 |
| [24] |
LI J Q, ZHANG H Y, YANG C, LI Y H, DAI Z Q. An overview of osteocalcin progress[J]. J Bone Miner Metab, 2016, 34: 367-379. DOI:10.1007/s00774-015-0734-7 |
| [25] |
黄美能, 李博, 蔚一博, 韩煦, 杨欣谕, 全知怎, 等. 降钙素促进人牙周膜干细胞的胶原合成和成骨作用[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2019, 40: 954-962. HUANG M N, LI B, WEI Y B, HAN X, YANG X Y, QUAN Z Z, et al. Calcitonin promotes collagen synthesis and osteogenesis in human periodontal ligament stem cells[J]. Acad J Sec Mil Med Univ, 2019, 40: 954-962. |
| [26] |
HU L, LIU Y, WANG S. Stem cell-based tooth and periodontal regeneration[J]. Oral Dis, 2018, 24: 696-705. DOI:10.1111/odi.12703 |
| [27] |
LIU L, LING J Q, WEI X, WU L P, XIAO Y. Stem cell regulatory gene expression in human adult dental pulp and periodontal ligament cells undergoing odontogenic/osteogenic differentiation[J]. J Endod, 2009, 35: 1368-1376. DOI:10.1016/j.joen.2009.07.005 |
| [28] |
CARREIRA A C, ALVES G G, ZAMBUZZI W F, SOGAYAR M C, GRANJEIRO J M. Bone morphogenetic proteins:structure, biological function and therapeutic applications[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2014, 561: 64-73. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2014.07.011 |
| [29] |
FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, MUSTAFA ABD EL R, SAULACIC N, KOBAYASHI E, ZHANG Y F, SCHALLER B, et al. Superior bone-inducing potential of rhBMP9 compared to rhBMP2[J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2018, 106: 1561-1574. DOI:10.1002/jbm.a.36359 |
| [30] |
GALLI C, PEDRAZZI G, GUIZZARDI S. The cellular effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on osteoblasts:a review[J]. Bioelectromagnetics, 2019, 40: 211-233. DOI:10.1002/bem.22187 |
| [31] |
AZADIAN E, ARJMAND B, KHODAII Z, ARDESHIRYLAJIMI A. A comprehensive overview on utilizing electromagnetic fields in bone regenerative medicine[J]. Electromagn Biol Med, 2019, 38: 1-20. DOI:10.1080/15368378.2019.1567527 |
| [32] |
CHANG K, CHANG W H, TSAI M T, SHIH C. Pulsed electromagnetic fields accelerate apoptotic rate in osteoclasts[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2006, 47: 222-228. DOI:10.1080/03008200600858783 |
| [33] |
TSAI M T, CHANG W H, CHANG K, HUO R J, WU T W. Pulsed electromagnetic fields affect osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in bone tissue engineering[J]. Bioelectromagnetics, 2007, 28: 519-528. DOI:10.1002/bem.20336 |
| [34] |
HUG K, RÖÖSLI M. Therapeutic effects of whole-body devices applying pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF):a systematic literature review[J]. Bioelectromagnetics, 2012, 33: 95-105. DOI:10.1002/bem.20703 |
| [35] |
JING D, ZHAI M M, TONG S C, XU F, CAI J, SHEN G H, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote osteogenesis and osseointegration of porous titanium implants in bone defect repair through a Wnt/β-catenin signaling-associated mechanism[J/OL]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 32045. doi: 10.1038/srep32045.
|
| [36] |
ZHAI M M, JING D, TONG S C, WU Y, WANG P, ZENG Z B, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote in vitro osteoblastogenesis through a Wnt/β-catenin signaling-associated mechanism[J]. Bioelectromagnetics, 2016, 37: 152-162. DOI:10.1002/bem.21961 |
| [37] |
LIM K T, JIN H X, KIN J H, SEONWOO H, CHO W J, CHOUNG P H, et al. Effects of electromagnetic fields on osteogenesis of human alveolar bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J/OL]. Biomed Res Int, 2013, 2013: 296019. doi: 10.1155/2013/296019.
|
| [38] |
SIMMONS J W Jr, MOONEY V, THACKER I. Pseudarthrosis after lumbar spine fusion:nonoperative salvage with pulsed electromagnetic fields[J]. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ), 2004, 33: 27-30. |
| [39] |
KANG K S, HONG J M, KANG J A, RHIE J W, JEONG Y H, CHO D W. Regulation of osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by controlling electromagnetic field conditions[J/OL]. Exp Mol Med, 2013, 45: e6. doi: 10.1038/emm.2013.11.
|
| [40] |
SONG M Y, YU J Z, ZHAO D M, WEI S, LIU Y, HU Y M, et al. The time-dependent manner of sinusoidal electromagnetic fields on rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2014, 69: 47-54. DOI:10.1007/s12013-013-9764-8 |
| [41] |
YU J Z, WU H, YANG Y, LIU C X, LIU Y, SONG M Y. Osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells regulated by osteoblasts under EMF exposure in a co-culture system[J]. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci, 2014, 34: 247-253. DOI:10.1007/s11596-014-1266-4 |
| [42] |
CECCARELLI G, BLOISE N, MANTELLI M, GASTALDI G, FASSINA L, GABRIELLA M, et al. A comparative analysis of the in vitro effects of pulsed electromagnetic field treatment on osteogenic differentiation of two different mesenchymal cell lineages[J]. Biores Open Access, 2013, 2: 283-294. DOI:10.1089/biores.2013.0016 |
| [43] |
OKADA M, KIM J H, YOON S T, HUTTON W C. Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) plus BMP-2 upregulates intervertebral disc-cell matrix synthesis more than either BMP-2 alone or PEMF alone[J/OL]. J Spinal Disord Tech, 2013, 26: E221-E226. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0b013e31827caeb7.
|
| [44] |
FUNK R H, MONSEES T K. Effects of electromagnetic fields on cells:physiological and therapeutical approaches andmolecular mechanisms of interaction[J]. Cells Tissues Organs, 2006, 182: 59-78. DOI:10.1159/000093061 |
| [45] |
PILLA A A, MUEHSAM D J, MARKOV M S, SISKEN B F. EMF signals and ion/ligand binding kinetics:prediction of bioeffective waveform parameters[J]. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg, 1999, 48: 27-34. DOI:10.1016/S0302-4598(98)00148-2 |
 2020, Vol. 41
2020, Vol. 41


