2. 海军军医大学(第二军医大学)长海医院整形外科, 上海 200433
2. Department of Plastic Surgery, Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University(Second Military Medical University), Shanghai 200433, China
乳头内陷是一种女性常见疾病,1849年由Cooper首次报道,1888年Kehrer首次报道了手术修复乳头内陷的病例。乳头内陷主要表现为乳头失去正常凸起,齐平或凹陷于乳晕平面之下,其影响女性乳房的形态和功能,容易诱发浆细胞性乳腺炎,严重危害女性的身心健康。为解决这一问题,国内外众多学者进行了大量的基础与临床研究并取得了一定进展[1-3]。目前,乳头内陷的主要治疗方法分为外科手术治疗和非手术治疗两大类,本文主要就国内外在其外科手术治疗方面的研究进展作一综述。
1 疾病概述乳头内陷既可以是因先天因素造成,也可由后天因素导致。以先天性乳头内陷多见,发病率为2%~10%[2-3],Schwager等[4]研究认为乳头中胚层的发育障碍使乳头下支撑组织缺乏、乳腺导管及其周围纤维组织减少是导致乳头内陷的直接原因。后天因素包括既往乳房手术、浸润性的输乳管肿瘤或乳腺炎等,这些因素均可不同程度地侵犯乳房的纤维组织导致其收缩而造成乳头内陷。乳头内陷的分类方法很多,根据临床表现的三级分类法并经过实践证明更有助于专科医师选择合适的治疗方法。
乳头内陷的三级分类法[5-6]为:一级,内陷的乳头可以手动提起并在无外力牵引作用下维持凸出状态,温柔按压乳晕周围皮肤可使乳头凸出。此级病例乳头下软组织基本完整,输乳管正常。
二级,内陷的乳头依然可以通过按压乳晕周围使其凸出,但凸出程度不如一级,乳头在按压凸出后有回陷趋势。此级病例的乳腺组织有轻度的纤维化及输乳管回缩,乳头下有丰富的胶原基质及很多光滑的肌肉结节。
三级,比较严重的乳头回缩及内陷,通过手动按压使乳头凸出比较困难,需要一个持续的牵引力才能使乳头保持凸出。此级病例乳头下组织纤维化明显,软组织量不足;组织学上,终末输乳管和小叶单位发生萎缩并被大量的纤维组织取代[5-6]。
2 乳头内陷外科治疗方法及进展国内外学者为矫治乳头内陷进行了大量的基础和临床研究,其中乳头内陷的外科治疗方法包括手术与非手术方法两大类。乳头内陷矫治原则:离断乳头下牵拉条带(去短缩),就近取材填充支撑乳头(防回缩),缩窄乳头基部(再塑形)。乳头内陷的根本原因在于乳头下乳腺导管纤维组织挛缩造成对乳头向内的一个牵引力,外科手术治疗乳头内陷的方法是通过对乳头基底部挛缩的纤维组织进行彻底松解,释放乳头使之保持凸出位置,并在松解后形成的空腔内置入填充物作为支撑,从而使乳头术后保持良好的形态。外科手术治疗方法主要包括真皮瓣法、牵引法和微创及内镜下纤维组织松解法3类。非手术方法则是利用各种牵引装置或吸引装置使凹陷的乳头恢复凸出状态。
2.1 真皮瓣法真皮瓣法是治疗乳头内陷的经典外科方法。该类方法在开展早期是通过手术松解纤维组织后在空腔置入硅胶板、聚四氟乙烯等填充物,但经过长期随访及术后观察,这些填充物会发生术后凸出、短时间乳头内陷复发等并发症[7],为避免此类并发症的发生,近年来越来越多的术者选择自体去表皮化真皮瓣作为乳头下填充支撑物。
皮瓣的设计方法不同,手术的固定方法及皮肤缝合的方法也不同。自1980年以来,各种基于基本手术方法的改良后皮瓣设计被国内外整形外科医师应用于乳头内陷的矫正治疗。Pitanguy[8]、邢新和焦向阳[9]在皮瓣形状和数量的设计上不断推陈出新,如组织瓣法、菱形瓣法、三角形乳晕真皮瓣法、一叶瓣、双叶瓣等,并在临床实践中获得了良好效果;Lee等[10]报道利用改进的去表皮化三角形皮瓣作为填充物修复乳头内陷取得满意的支撑效果;Ertaş等[11]报道皮下带蒂的菱形皮瓣可以有效地避免瘢痕形成。
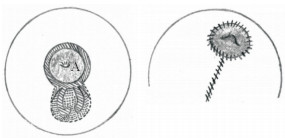
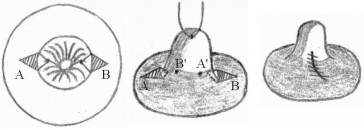
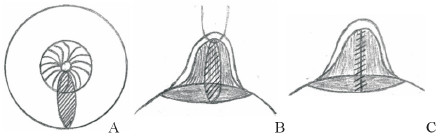
Karacaoglu[12]于2009年报道了在乳房固定术中去上皮化区域作双天线型皮瓣(图 1)固定乳房的同时矫正乳头内陷的病例,为隆乳同时治疗乳头内陷提供了新的思路;Jeong和Lee[13]在26例(47侧)乳头内陷患者的矫治中使用了乳头两侧的菱形皮瓣(图 2),独特设计的皮瓣在隐蔽切口、减少术后瘢痕形成的同时有效保护了术中真皮瓣的血供。术后患者平均随访14个月,所有患者均无复发,均未发生手术并发症。周信荣等[14]在2012年至2014年采用类似方法治疗24例(39侧)中重度先天性乳头内陷患者,术后平均随访1年,患者双侧乳头基本对称,均未出现乳头再次内陷,也均未出现皮肤感觉异常及乳头血运障碍等并发症。Mathur和Loh[15]报道了应用吊桥式皮瓣(图 3)治疗乳头内陷的病例,其设计的吊桥式真皮瓣可以直接观察乳头导管的解剖结构,便于选择性分离挛缩的输乳管,有利于避免对正常输乳管及乳头感觉的损伤。
|
图 1 Karacaoglu[12]行乳房固定术时为纠正乳头内陷设计的双天线型皮瓣 Fig 1 Karacaoglu[12] designed a double-antenna flap for correcting inverted nipple during mastopexy A is areola (center represents the inverted nipple). The surgical area is in the dotted line (the slash area is to remove the epidermis area), and extending downward is an antenna-shaped dermal flap. The punctate area removes the epidermis and dermis, and the double-antenna dermal flap is filled under the nipple and sutured along the dotted lines on both sides |
|
图 2 Jeong和Lee[13]为矫正乳头内陷设计的双侧菱形皮瓣 Fig 2 Jeong and Lee[13] designed a double-sided diamond flap for correcting inverted nipple A and B are pedicled diamond-shaped dermal flaps with epidermis removed, pulling the inverted nipple with a suture, loosening the contracture under the nipple to form a tunnel; the tip of the flap (A), is overturned and fixated to A'; the tip of the opposite flap (B) is then fixated to B'; and the incision after the separation flap is sutured to maintain the state of the nipple |
|
图 3 Mathur和Loh[15]为矫正乳头内陷设计的吊桥式皮瓣 Fig 3 Mathur and Loh[15] designed a drawbridge flap for correcting inverted nipple A: At 6 o'clock, mark a vertical ellipse. B: Suture the nipple to remove the epidermis of the labeled flap. Selectively loosen the contracture under the nipple to form a tunnel under direct vision, and then raise the dermal flap to a "drawbridge", filling the flap in the tunnel under the nipple. C: The incision after the separation of the flap is sutured to the position, so that the nipple cone is narrowed and the degree of protrusion is increased |
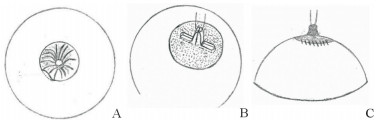
Bracaglia等[16]针对复发的三级乳头内陷患者,放弃了小切口的选择,而是在较大切口的情况下,用垂直方向的两条乳晕周围真皮瓣直接垂直于皮肤作U型缝合作为新生乳头的支柱(图 4),从而达到比小切口手术更佳的手术效果及对基底部纤维导管组织更彻底的松解。
|
图 4 Bracaglia等[16]设计的U型缝合作为新生乳头支柱的皮瓣 Fig 4 U-shaped suture flap designed by Bracaglia et al.[16] to support the corrected nipple A: Select the incision around the areola, separate the inferior papillary duct and fibrous tissue, and turn up the areola flap; B: Separate the two single-layer flaps and fold them under the nipple, and suture the incision after the separation of the flaps; C: After the areola flap is repositioned, two U-shaped nails are used to fix the 3 and 9 o'clock positions on the base of the nipple, which are tightened to form a stable nipple protrusion state, and the incision around the areola is sutured |
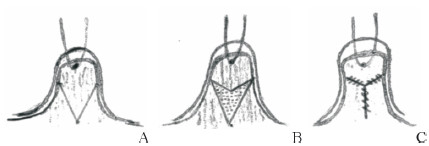
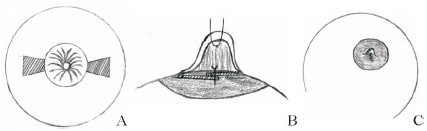
在真皮瓣的基础上,真皮乳腺瓣的手术设计也进行着不断的改良。相对于传统真皮瓣,真皮乳腺瓣虽然对纤维组织的松解程度较低,但其手术切口更小、术后恢复更快、瘢痕程度更轻。Persichetti等[17]报道直接将牵引状态下的乳头垂直切开,双侧同时作一个垂直于皮肤的V-Y推进皮瓣(图 5),不仅避免了在分离乳头基底部时对输乳管的损伤,同时也使手术更易于操作,时间缩短至30 min之内;McG Taylor等[18]在真皮瓣手术的基础上,直接用腔隙两侧的真皮乳腺瓣推进缝合填充乳头基底分离后形成的腔隙(图 6),再将恢复凸起的乳头置于其上方,彻底避免了可能因皮瓣折叠或扭曲而造成的血运障碍。
|
图 5 Persichetti等[17]报道的垂直于皮肤的V-Y推进缝合真皮乳腺瓣 Fig 5 V-Y advancement suture dermal flap perpendicular to skin reported by Persichetti et al.[17] A: Suture the nipple, make a vertical incision to divide the nipple into 2 flaps; B: Make 2 V-shaped incisions in the cut surface; C: The incision suture is closed into a Y shape |
|
图 6 McG Taylor等[18]使用的真皮乳腺瓣直接推进缝合方法 Fig 6 The method of dermal breast flap advancement suture used by McG Taylor et al.[18] A: Remove the dermal flap of the epidermis at 6 and 12 o'clock, respectively, the width is approximately 1/8 of the edge of the areola, and separate the catheter and fibrous tissue under the nipple; B: The 2 dermal flap tips are sutured in the cavity under the nipple; C: The incision after the separation of the flap is sutured and tightened to maintain the state of the nipple |
2.2 牵引法
为了更彻底地避免对输乳管的损伤,满足乳头内陷患者母乳喂养的需求及提供更多的临床手段选择,牵引法修复乳头内陷也常常被应用于育龄期女性患者。此类方法不会在乳头基底部做松解处理,而是用持续外力牵拉乳头使乳头恢复至凸出形状。
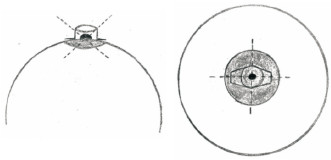
Long和Zhao[19]在2003年至2010年用自主设计的牵引器对95例乳头内陷病例实施了牵引矫正,该乳头牵引器用10 mL或5 mL注射器制作,即去掉活塞,切割至管口水平。牵拉内陷乳头至凸出位置后,用牵引器套住乳头并用金属线固定(图 7)。固定完成后佩戴牵引器6个月,每4周调整1次牵引器的张力。6个月后随访所有患者均无复发,并发症(包括乳晕区的褪色、溃疡及金属固定线的移位)的发生率也仅为5.25%。齐鑫等[20]在2017年应用改进后的“套管针穿刺”支架法完成了13例乳头内陷矫正术,先用静脉留置针穿刺贯穿乳头基底部,然后利用留置针管作通道穿过缝线,再牵引内陷乳头并悬吊固定在用注射器制作的牵引器上。术后随访6个月,13例矫治后的患者均未复发,且拆除支架后均未发生乳头感觉和血运障碍等并发症。“套管针穿刺”支架法在简化手术操作过程的同时避免了单纯使用金属线悬吊对乳头基底部造成的组织切割,还可在术后需要调节缝线悬吊张力时通过留置针管更换缝线而重新悬吊固定。
|
图 7 Long和Zhao[19]自制的乳头牵引器操作示意图 Fig 7 Schematic diagram of self-made nipple retractor made by Long and Zhao[19] After pulling the invaginated nipple up, the tractor is placed around the nipple with a wire through the base of the nipple and fixed on the tractor |
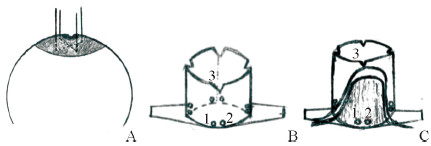
Liu等[21]回顾了用乳头牵拉器(图 8)矫正乳头内陷的10年经验。他们也是采用注射器的中空末端,在基底留置8个孔以便于乳头基底缝线牵拉,牵拉器高度由乳头乳晕复合体和乳房体积决定。乳头基底部“十”字交叉缝线提升乳头,固定于牵拉器预留孔洞并保持合适的张力。患者需佩戴牵拉器3~6个月。他们在2003年至2012年用该方法治疗了136例(257侧)患者,矫正成功率为90.7%。一、二级乳头内陷的矫正效果明显优于三级内陷患者,32例术后生育的患者均能正常哺乳。该方法的并发症包括拆线后瘘管形成(7.4%)、缝线断裂(3.1%)、乳头溃疡(10.9%)、慢性疼痛(3.4%),但均可治愈。
|
图 8 Liu等[21]制作的乳头牵拉器操作示意图 Fig 8 Schematic diagram of nipple retractor made by Liu et al.[21] A: Cross the nipple through the base of the nipple with two sutures to lift the nipple; B: Eight holes are made for the tractor base, such as hole 1 and hole 2, and 4 slits are made at the top edge, such as incision 3; C: Place the tractor on the areola, and pass the sutures through the adjacent two holes on the base respectively, such as the suture threading from the incision 3 to the hole 1, passing through the hole 2, and then respectively adjoining the two. The root suture is tightened and knotted to stabilize the nipple protrusion |
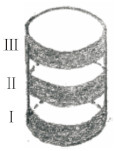
陈玥等[22]采用自行设计的梯级提升牵引器(图 9),对22例(44侧)乳头内陷患者进行矫正,术中先将患者内陷的乳头上提,然后用直径2 mm的牵引杆从乳头基底穿过,并固定在梯级提升牵引器的牵引环上。梯级提升牵引器分为3档调节(档距3 mm),术后每个月调节提升1档。根据每例患者乳头内陷的严重程度,分别在3~4个月完成牵引,然后保持3~6个月后拆除牵引器。术后随访6~18个月,在44侧乳头中有42侧乳头凸出高度≥15 mm,且术后均未发生感染、皮肤色素脱失、感觉障碍或乳头坏死等并发症。
|
图 9 陈玥等[22]为矫正乳头内陷设计的梯级提升牵引器 Fig 9 The elevator tractor designed by Chen et al.[22] for correcting inverted nipple Divided into three gears (Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ) for adjustment (gear distance 3 mm), adjust 1 gear every month after surgery |
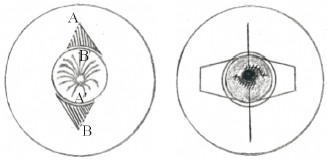
Durgun等[23]推荐采用真皮瓣术后辅以机械牵引混合法(图 10)治疗乳头内陷,该方法治疗后明显的瘢痕更少,且能保留哺乳功能和乳头感觉。他们在2010年至2013年用该方法治疗了16例(28侧)乳头内陷患者,瘢痕线性分布于乳头和乳晕交界处,术后采用50 mL的注射器底座牵引防止回缩。随访8~24个月,所有患者的乳头均保持足够的凸起,均未发生伤口裂开、感染等并发症。
|
图 10 Durgun等[23]采用真皮瓣术后辅以机械牵引混合法治疗乳头内陷 Fig 10 Mixed method of mechanical traction after operation of dermal flap for correcting inverted nipple used by Durgun et al.[23] Make 2 triangular de-epidermal dermal flaps A and B beside the areola, the flap on the solid side is completely separated, and the flap on the side of the dotted line is not separated, loosen the contracture under the nipple to form a tunnel. Pull the A flap on the side of the dotted line toward the areola, the tip of the flap (A) is overturned and fixated to A'. In the same way pull the B flap on the side of the dotted line toward the areola, the tip of the opposite flap (B), is then fixated to B', suture the incision along the areola, pull the nipple with sutures, and the traction sutures are placed in the grooves on both sides of the apparatus |
尹光迪等[24]则采用真皮脂肪瓣联合“十”字缝线法对15例(29侧)乳头内陷患者进行矫正治疗。采用真皮脂肪瓣交叉支撑乳头基底的同时,在皮瓣下以缝线作“十”字交叉并固定外接牵引器悬吊4周(即在Jeong和Lee[13]设计的菱形皮瓣手术基础上加用注射器自制的牵引器对乳头进行牵引)。应用该手术方式治疗的15例患者术后随访半年至1年,均未出现感染坏死、感觉障碍或血运障碍等并发症,其中1例患者出现左侧乳头感觉稍麻木,3个月后恢复正常。
2.3 微创及内镜下纤维组织松解法为了在松解挛缩纤维导管组织的同时减少对正常输乳管过多的损伤,使患者在治疗后尽可能保持正常的哺乳功能,近年一些微创及内镜辅助下乳头内陷修复技术被应用于临床。该类方法最大的优点在于以微小切口进入乳头基底部,以最小程度的损伤完成对挛缩纤维组织的松解,从而使乳头牵拉之后能够保持凸出位置。
微创法松解挛缩纤维组织的基础是各种可以在微小切口下进行操作的手术器械,包括18 G粗针、15号微刀等。基本手术步骤为:(1)局部麻醉完成后,首先通过挤压或牵拉使内陷的乳头在张力情况下恢复至凸出状态;(2)以1个或多个入口使用特制的手术器械直接进入乳头基底部对乳晕平面下的挛缩组织进行扫除式松解;(3)以环扎术或类似的荷包型缝合技术在乳头基底部作固定,使凸出的乳头能够维持本身的凸出状态。此类方法并不会在乳晕周围留下巨大切口及进行扫除式的松解动作,因此其对乳头下血管及导管系统的损伤明显小于开放式皮瓣手术。
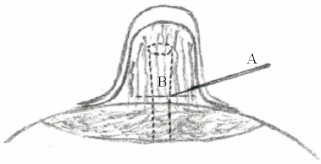
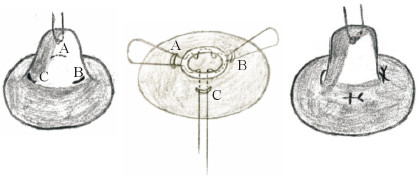
Kolker和Torina[25]报道了58例用18 G粗针松解的微创法修复手术(图 11),体表创面仅有单针的入口,最后获得长期肯定疗效且无需二期、三期手术的病例有45例,占总例数的78%;Cabalag等[26]报道了8例微刀法(图 12)修复的病例,手术使用了12、4、8点3个方向的入路,进一步降低了血管损伤的风险,用微刀将乳晕平面以下的保留组织分开后,再通过切口部位进行环切缝合,经过5年随访无一例发生并发症及复发。而Jeong等[27]采取双轨横移缝合法(图 13)矫正乳头内陷,先分别在3、9和12点方向做3个狭小切口和6点方向做1个5 mm的小切口,通过6点的小切口进行乳头下组织松解后用缝线进行双轨缝合,缝合的形状类似于圆形内的“十”字,既包括用于外翻力的荷包线针,也包括用于悬吊支撑效果的核心线针。应用该方法的患者共46例(75侧),平均术后随访22.4个月,所有患者矫正后的乳头均未再凹陷,乳头-乳晕交界处未见明显瘢痕,且均未发现血肿、感染等并发症。Liang等[28]采用交叉垂直垫状缝合法(图 14)为30例(55侧)乳头内陷患者进行矫治,在充分松解乳头下方的组织后将组织填充在乳头基底部,且双纵向缝合方式使乳头根部收紧以保持乳头外翻。交叉垂直垫状缝合法的优点是缝合的运行方向与乳腺导管相同,避免了乳腺导管损伤,对乳头血供和感觉的影响较小。术后患者均随访6个月至2年,仅2例患者复发,但经二次矫正后疗效满意。所有患者术后乳头均有足够的感觉功能引起收缩反应。因此,微创法的手术效果值得肯定。
|
图 11 Kolker和Torina[25]报道的矫正乳头内陷的微创法手术示意图 Fig 11 Schematic diagram of minimally invasive surgery for correcting inverted nipple reported by Kolker and Torina[25] A is 18-gauge needle, B is the scar under the nipple and fibrous tissue. Minimal-access release of fibro-ductal elements with an 18-gauge needle, the suture is looped at the base of the nipple, and the suture is tightened and knotted |
|
图 12 Cabalag等[26]报道的矫正乳头内陷的微刀法手术示意图 Fig 12 Schematic diagram of micro-knife surgery for correcting inverted nipple reported by Cabalag et al.[26] Make 3 incisions A, B, and C at 12, 4, and 8 o'clock at the base of the nipple, insert each incision with a micro-knife, and in a sweeping motion to divide the retaining tissues below the areolar plane, avoiding an excessive defect below the nipple. Through the incision site for circumcision suture, and through all the incisions A, B, C, the suture is tightened and knotted at the incision C, converting the horizontal cut into a vertical scar |
|
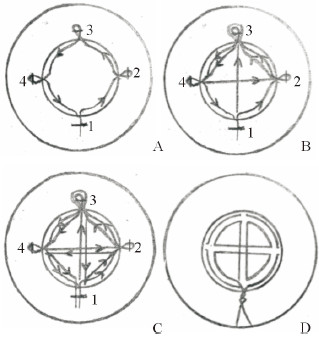
图 13 Jeong等[27]采取的双轨横移缝合法 Fig 13 The double-track sun-cross running suture technique used by Jeong et al.[27] A: Three slit incisions at 3, 9 and 12 o'clock (2, 3, 4) and one 5-mm incision at 6 o'clock were made (1). After the nipple tissue is released by a small incision at 6 o'clock, the stitch entered through the 5-mm incision, and then sutures pass through the outer circumference of the nipple in the direction of the arrow. B, C: The suture passes through the center of the nipple in the direction of the arrow, and finally is tightened at the incision 1, and the 4 incisions are closed. D: A schematic diagram of the complete double-track sun-cross running suture |
|
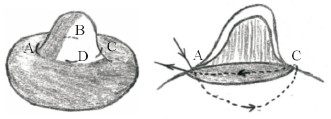
图 14 Liang等[28]采用的交叉垂直垫状缝合法 Fig 14 The method of cross vertical mattress suturing used by Liang et al.[28] Make 4 small incisions at 3, 6, 9 and 12 o'clock. Releasing the fibrous tissue under the nipple gives the nipple the desired projection and keep the lactiferous ducts intact. The method of cross vertical mattress suturing is about to suture the needle from the point A of the 9 o'clock in the direction of the arrow, after passing through the deep tissue under the nipple, it is pierced from the point C at the 3 o'clock position, and then the needle is inserted from the point C, and passes through the shallow tissue of the nipple and then passes through point A. The same form of vertical mattress suture is between point B and point D. Tighten and tie the sutures to stabilize the nipple protrusion |
Chen等[29]在腔镜辅助下的纤维组织松解(图 15)是在直视状态下操作,基本可以完全避免对正常血管及输乳管的损伤。手术切口长约8 mm,与真皮瓣的切口相当,然后置入4 mm的内镜引导微创手术器械对挛缩的纤维组织进行分离,最后完成乳头基底的环扎术。基本的手术过程与微创法类似,但是由于要引入内镜,因此皮肤切口稍大,其优点是最大程度地降低了对血管及输乳管的损伤。
|
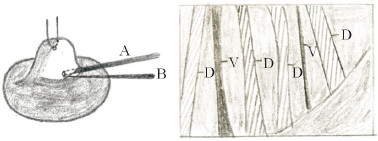
图 15 矫正乳头内陷的腔镜辅助下纤维组织松解法[29]示意图 Fig 15 Schematic diagram of fiber tissue release assisted by endoscope for correcting inverted nipple[29] A is a 4-mm endoscope and B is a separation device. The picture on the right is seen in the simulated endoscope, V stands for vein, and D stands for lactiferous duct |
3 小结
由以上可知,目前常用的乳头内陷外科治疗方法主要有真皮瓣法、各种持续牵引方法、微创及内镜下纤维组织松解等。由于每个级别乳头内陷患者的组织纤维化水平、软组织垫及输乳管结构各不相同,不同术者的手术习惯也有差异,虽然经报道的乳头内陷治疗方法很多,但是目前仍然没有任何一种单一手术方式可以矫正所有类型的乳头内陷[30]。
理想的乳头内陷矫正手术应当在最大程度松解分离乳头下挛缩纤维组织的前提下尽量使手术操作简化,减少手术创伤与术后瘢痕的形成,尽可能保护手术乳头的正常血运及哺乳功能。
单纯负压吸引或牵引的方法虽然能够在短期内恢复乳头的凸出状态,同时完整保留哺乳功能,但由于并未从根本上解决乳头内陷的病因,凸出的乳头仍存在回缩趋势,其远期的治疗效果还需要长期随访研究进一步观察,一般用于治疗轻度乳头内陷。
各类真皮瓣、真皮组织瓣手术由于其明确的治疗效果而逐渐获得推广,尤其适用于中重度乳头内陷。在对皮瓣的设计及缝合方法进行多年的改良,或术后辅助以机械牵引的方法[23-24],目前已能够将术后乳头内陷的复发率及并发症的发生率控制在较低的水平,该方法最大的问题依旧是如何在分离过程中避免对正常输乳管造成不必要的损伤。而近年Mathur和Loh[15]设计的吊桥式真皮瓣有利于避免对正常输乳管及乳头感觉的损伤。因此,未来需要更多研究及新的思路改良皮瓣设计,以达到有效避免对正常输乳管损伤的目的。
近年来,微创治疗乳头内陷越来越受到手术医师及患者的青睐[31],在诸多微创方法治疗乳头内陷的病例报道中,对二级以下乳头内陷治疗的有效率及并发症发生率已基本与传统手术方法接近。微创法是在腔镜的辅助下,借助先进的手术器械对挛缩的纤维组织进行精确分解,加之其对正常组织损伤小、术后恢复快和瘢痕小的特点,应当成为未来整形学科手术治疗乳头内陷的主流发展趋势。但需要注意的是,由于微创及内镜技术入路的局限性,对挛缩纤维组织的松解效果肯定不如开放式皮瓣手术,因此三级乳头内陷患者在实施此类术式时较易复发。Chen等[29]报道28例腔镜辅助下乳头内陷修复病例,术后6个月内复发的5例患者全部为三级,复发率为21%;Kolker和Torina[25]报道的58例粗针微创法修复的乳头内陷病例,三级乳头内陷的复发率达到了50%(5/10);但Cabalag等[26]、Jeong等[27]、Liang等[28]应用基于微创法的改良方法进行矫治的病例,预后均较好,复发率较低。因此,如何更彻底地分离挛缩纤维组织,以及更好地应用改良后的微创法避免三级重度乳头内陷患者术后复发是需要进一步研究和实践的方向。未来随着手术器械的改良及手术技术的不断完善,相信乳头内陷的治疗效果也将不断提高。
| [1] |
周瑾, 邢新. 乳头内陷的手术治疗进展[J]. 实用美容整形外科杂志, 2001, 12: 326-327. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7040.2001.06.020 |
| [2] |
HAN S, HONG Y G. The inverted nipple:its grading and surgical correction[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1999, 104: 389-397. DOI:10.1097/00006534-199908000-00010 |
| [3] |
LEE M J, DEPOLI P A, CASAS L A. Aesthetic and predictable correction of the inverted nipple[J]. Aesthet Surg J, 2003, 23: 353-356. DOI:10.1016/S1090-820X(03)00209-7 |
| [4] |
SCHWAGER R G, SMITH J W, GRAY G F, GOULIAN D Jr. Inversion of the human female nipple, with a simple method of treatment[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1974, 54: 564-569. DOI:10.1097/00006534-197411000-00007 |
| [5] |
ALEXANDER J M, CAMPBELL M J. Prevalence of inverted and non-protractile nipples in antenatal women who intend to breast-feed[J]. Breast, 1997, 6: 72-78. DOI:10.1016/S0960-9776(97)90177-6 |
| [6] |
KIM D Y, JEONG E C, EO S R, KIM K S, LEE S Y, CHO B H. Correction of inverted nipple:an alternative method using two triangular areolar dermal flaps[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2003, 51: 636-640. DOI:10.1097/01.sap.0000095722.82954.82 |
| [7] |
SERRA-RENOM J, FONTDEVILA J, MONNER J. Correction of the inverted nipple with an internal 5-point star suture[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2004, 53: 293-296. DOI:10.1097/01.sap.0000116281.28491.08 |
| [8] |
PITANGUY I. Aesthetic plastic surgery of head and body[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1981: 63.
|
| [9] |
邢新, 焦向阳. 去表皮乳晕三角瓣支撑法乳头内陷矫正术[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志, 1999, 10: 296-299. |
| [10] |
LEE H B, ROH T S, CHUNG Y K, KIM S W, KIM J B, SHIN K S. Correction of inverted nipple using strut reinforcement with deepithelialized triangular flaps[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1998, 102: 1253-1258. DOI:10.1097/00006534-199809020-00055 |
| [11] |
ERTAŞ NM, KÜÇÜKÇELEBI A, BOZDOĞAN N, KURTAY A, OZDIL K, CELEBIOĞLU S. Treatment of recontracture with the subcutaneous pedicle rhomboid flap[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2006, 117: 1590-1598. DOI:10.1097/01.prs.0000207399.68943.7c |
| [12] |
KARACAOGLU E. Correction of recurrent grade Ⅲ inverted nipple with antenna dermoadipose flap:case report[J]. Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2009, 33: 843-848. DOI:10.1007/s00266-009-9322-3 |
| [13] |
JEONG H S, LEE H K. Correction of inverted nipple using subcutaneous turn-over flaps to create a tent suspension-like effect[J/OL]. PLoS One, 2015, 10: e0133588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133588.
|
| [14] |
周信荣, 朱明兰, 孙波, 李川, 张冰玉, 陈康. 旋转-包埋瓣技术矫治中重度乳头内陷的疗效评价[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016, 30: 389-391. DOI:10.7507/1002-1892.20160077 |
| [15] |
MATHUR B, LOH C Y Y. Sensation-sparing correction of inverted nipples using the 'drawbridge' flap approach[J]. Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2019, 43: 348-353. DOI:10.1007/s00266-018-1260-5 |
| [16] |
BRACAGLIA R, TAMBASCO D, GENTILESCHI S, D'ETTORRE M. Recurrent inverted nipple:a reliable technique for the most difficult cases[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2012, 69: 24-26. DOI:10.1097/SAP.0b013e318221b52f |
| [17] |
PERSICHETTI P, POCCIA I, PALLARA T, DELLE FEMMINE P F, MARANGI G F. A new simple technique to correct nipple inversion using 2 V-Y advancement flaps[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2011, 67: 343-345. DOI:10.1097/SAP.0b013e318209a63e |
| [18] |
MCG TAYLOR D, LAHIRI A, LAITUNG J K. Correction of the severely inverted nipple: areola-based dermoglandular rhomboid advancement[J/OL]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2011, 64: e297-e302. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2011.05.002.
|
| [19] |
LONG X, ZHAO R. Nipple retractor to correct inverted nipples[J]. Breast Care (Basel), 2011, 6: 463-465. DOI:10.1159/000335221 |
| [20] |
齐鑫, 刘思源, 王亮, 折占飞. "套管针穿刺"支架法乳头内陷矫正术13例[J]. 中国现代普通外科进展, 2018, 21: 643-644, 649. |
| [21] |
LIU Y, GUO K, SUN J. Application of nipple retractor for correction of nipple inversion:a 10-year experience[J]. Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2016, 40: 707-715. DOI:10.1007/s00266-016-0675-0 |
| [22] |
陈玥, 陈小平, 王昕, 林金德, 郑翔宇. 梯级提升牵引器矫治乳头内陷的临床应用[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志, 2018, 29: 147-149. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7040.2018.03.007 |
| [23] |
DURGUN M, OZAKPINAR H R, SELÇUK C T, SARICI M, CERAN C, SEVEN E. Inverted nipple correction with dermal flaps and traction[J]. Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2014, 38: 533-539. DOI:10.1007/s00266-014-0317-3 |
| [24] |
尹光迪, 赵李平, 汪凯, 王明刚, 杜晓扬, 余刚, 等. 真皮脂肪瓣联合"十"字缝线矫正重度乳头内陷的效果[J]. 安徽医学, 2017, 38: 418-421. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0399.2017.04.007 |
| [25] |
KOLKER A R, TORINA P J. Minimally invasive correction of inverted nipples:a safe and simple technique for reliable, sustainable projection[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2009, 62: 549-553. DOI:10.1097/SAP.0b013e31819fb190 |
| [26] |
CABALAG M S, CHUI C H, TAN B K. Correction of nipple inversion using a micro-knife and transverse to longitudinal skin closure[J/OL]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2010, 63: e627-e630. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2010.03.021.
|
| [27] |
JEONG J H, PARK I, HAN J, PARK J U. Correction of inverted nipples with the double-track sun-cross running suture technique[J]. J Plast Surg Hand Surg, 2018, 52: 87-93. DOI:10.1080/2000656X.2017.1338184 |
| [28] |
LIANG W, ZHAO Z, LIU S, GU T. Cross vertical mattress suturing with basilar tightening during the correction of inverted nipple in 30 cases[J]. Aesthetic Plast Surg, 2017, 41: 782-787. DOI:10.1007/s00266-017-0856-5 |
| [29] |
CHEN S H, GEDEBOU T, CHEN P H. The endoscope as an adjunct to correction of nipple inversion deformity[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2007, 119: 1178-1182. DOI:10.1097/01.prs.0000258402.57900.87 |
| [30] |
ZHOU H, TAN Q, WU J, ZHENG D F, ZHOU H R, XU P, et al. Correction of inverted nipple with bilateral areolar rhomboid dermal flaps[J/OL]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2011, 64: e159-e161. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2011.01.022.
|
| [31] |
王伟, 杨琳. 微创治疗乳头内陷临床探讨[J]. 中国美容医学杂志, 2015, 24: 12-14. |
 2019, Vol. 40
2019, Vol. 40


