膀胱癌在全身常见的恶性肿瘤中位列第9位[1],最常见的病理类型是尿路上皮癌。目前对膀胱尿路上皮癌患者预后的评估主要依赖于临床病理分期和分级。然而,由于恶性肿瘤具有异质性,其内部不同部位极可能存在着不同发展阶段的肿瘤亚群[2];此外,肿瘤大小、数目和分级等均可反映肿瘤的生物学特点,并对肿瘤复发和进展的影响有明显差异[3]。因此,临床病理分期和分级在判断患者预后方面的价值有限,亟需更准确的方法对患者的病情进展和预后进行预测。
前白蛋白是一种重要的血清肿瘤标志物,其临床检测具有无创、简便和不易受人血白蛋白影响等优点。诸多研究已经发现术前血清前白蛋白水平降低与恶性肿瘤的不良预后有关[4-6],但仍未有确切报道证实其可以用于监测膀胱尿路上皮癌患者的预后。本研究旨在探讨术前血清前白蛋白评价膀胱尿路上皮癌患者预后的可行性。
1 资料和方法 1.1 研究对象回顾性分析2006年1月至2014年12月在海军军医大学(第二军医大学)长海医院行根治性膀胱切除术的膀胱尿路上皮癌患者的临床病理资料。纳入标准:(1)术前相关资料完整;(2)经术后病理证实病理类型为尿路上皮癌;(3)病历及随访资料完整。排除标准:(1)围手术期存在严重并发症;(2)术前接受过放射治疗或全身性化学治疗;(3)具有其他恶性肿瘤病史。最终符合纳入标准的320例患者中男278例(86.9%)、女42例(13.1%),年龄27~88岁,中位年龄65岁。本研究经海军军医大学(第二军医大学)长海医院伦理委员会审批。
1.2 研究方法收集纳入患者的性别、年龄、吸烟史、高血压病史、糖尿病史、术前肾积水、病理T分期、病理分级、淋巴结侵犯、远处转移、术中输血和术前血清前白蛋白水平等临床病理资料,其中血清前白蛋白检测均在术前2周内完成。患者术后接受门诊和电话随访,截止时间为2018年4月。
1.3 统计学处理应用SPSS 20.0软件进行统计学分析。以总生存状态作为观察终点绘制受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线,确定术前血清前白蛋白的最佳截断值,根据最佳截断值将320例患者分为高前白蛋白组和低前白蛋白组。采用χ2检验比较两组患者临床病理特征的差异。用log-rank检验和Kaplan-Meier法分析术前血清前白蛋白水平及其他临床病理因素与患者预后的关系,将筛选出的变量纳入Cox回归模型进行多因素分析。检验水准(α)为0.05。
2 结果 2.1 术前血清前白蛋白水平与临床病理特征的关系为了确定术前血清前白蛋白的最佳截断值,以总生存状态作为观察终点绘制ROC曲线,ROC曲线下面积为0.639(95%置信区间:0.571~0.706);当血清前白蛋白水平为249.5 mg/L时,约登指数最大,为0.244。采用249.5 mg/L作为最佳截断值,将320例患者分为高前白蛋白(≥249.5 mg/L)组162例和低前白蛋白(<249.5 mg/L)组158例。χ2检验结果提示,与高前白蛋白组比较,低前白蛋白组患者年龄更大(P<0.05),术前肾积水、高病理T分期、高病理分级、远处转移和术中输血的患者比例均较高(P均<0.05),见表 1。
|
|
表 1 不同术前血清前白蛋白水平膀胱尿路上皮癌患者临床病理特征的比较 Tab 1 Comparison of clinicopathological characteristics of bladder urothelial carcinoma patients with different preoperative serum pre-albumin levels |
2.2 术前血清前白蛋白水平与患者预后的关系
本研究中320例患者均获得随访,随访时间为41~145个月,中位随访时间为59个月。高前白蛋白组5年总生存率为80.4%,低前白蛋白组5年总生存率为62.4%;高前白蛋白组5年无复发生存率为88.5%,低前白蛋白组5年无复发生存率为68.4%。低前白蛋白组患者的总生存情况和无复发生存情况均较高前白蛋白组差(P均<0.05),见图 1。
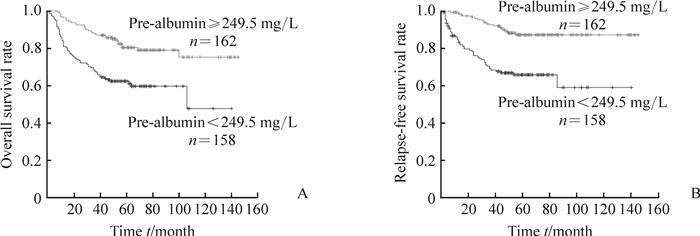
|
图 1 不同术前血清前白蛋白水平膀胱尿路上皮癌患者总生存(A)和无复发生存(B)情况的Kaplan-Meier曲线 Fig 1 Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival (A) and relapse-free survival (B) of bladder urothelial carcinoma patients with different preoperative serum pre-albumin levels |
2.3 患者预后危险因素分析
将log-rank检验和Kaplan-Meier法筛选得到的影响膀胱尿路上皮癌患者术后总生存时间和无复发生存时间的危险因素(年龄、术前肾积水、高病理T分期、高病理分级、淋巴结侵犯、远处转移、术中输血和术前血清前白蛋白水平)纳入Cox回归模型进行多因素分析,结果显示高病理T分期、淋巴结侵犯、远处转移、术中输血和术前血清前白蛋白水平降低是影响膀胱尿路上皮癌患者术后总生存时间的独立危险因素(HR=1.648、3.237、2.371、1.567、0.480,P均<0.05);高病理T分期、淋巴结侵犯、远处转移和术前血清前白蛋白水平降低是影响膀胱尿路上皮癌患者术后无复发生存时间的独立危险因素(HR=1.551、3.882、2.618、0.289,P均<0.05),见表 2。
|
|
表 2 膀胱尿路上皮癌患者总生存情况和无复发生存情况危险因素的多因素Cox回归模型分析 Tab 2 Multivariable Cox regression analysis of predicting factors for overall survival and relapse-free survival ofbladder urothelial carcinoma patients |
3 讨论
恶性肿瘤患者常出现营养不良症状,血清前白蛋白是一种由肝脏合成的负性急性时相蛋白,常被用于评价恶性肿瘤患者的营养状况[7]。目前术前前白蛋白逐渐成为血清肿瘤标志物研究的热点内容,其与白蛋白相比具有半衰期更短和敏感性更高等特点。尽管在泌尿系统恶性肿瘤中,已有多篇文献报道了术前低白蛋白在评价患者预后不良中的价值[8-12],但目前仍鲜见较为系统地研究其与膀胱尿路上皮癌患者预后关系的报道。
在本研究中,我们发现术前血清前白蛋白水平降低是膀胱尿路上皮癌患者临床病理特征进一步恶化的危险因素。低前白蛋白组高龄患者占比更高,这可能是因为随着患者年龄增加肝脏合成前白蛋白的功能减退。此外,低前白蛋白组更易出现术前肾积水、高病理T分期、高病理分级、远处转移和术中输血。这可能是因为较低的血清前白蛋白水平是患者肝脏功能受损的指标,且肝功能受损导致患者的自身免疫能力下降,使得肿瘤进展加快。Han等[4]在食管胃交界腺癌相关研究中也发现对于肿瘤呈现恶性分化状态的患者而言,其术前血清前白蛋白水平更低。
本研究还发现术前血清前白蛋白水平降低是影响患者总生存时间和无复发生存时间的独立危险因素。这意味着术前血清前白蛋白水平降低的膀胱尿路上皮癌患者在行根治性膀胱切除术后需要更重视术后复查,以便及时发现复发灶,并尽早进行后续治疗,以延长生存时间。有研究发现乳腺癌患者术前血清前白蛋白水平并不能预测患者复发情况[13];此外,在包括输尿管癌和前列腺癌等相关的多项研究中,术前血清前白蛋白水平在评价患者预后中的价值也有差异[5, 14]。这可能与研究人群和研究方法存在差异有关,也可能与前白蛋白在不同恶性肿瘤中的不同作用有关。因此,仍需要更大范围人群的研究进一步探索术前血清前白蛋白评估肿瘤预后的价值。
综上所述,根据本中心的研究结果,术前血清前白蛋白水平与膀胱尿路上皮癌患者术后远期生存情况密切相关,是良好的术后预测指标之一。此外,作为一种简便、低成本的术前常规检查项目,术前血清前白蛋白检测不仅为基于血清肿瘤生物标志物的膀胱癌研究提供了新思路,而且有助于指导膀胱尿路上皮癌患者术后的监测和治疗工作。
| [1] |
ANTONI S, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, ZNAOR A, JEMAL A, BRAY F. Bladder cancer incidence and mortality:a global overview and recent trends[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71: 96-108. DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.010 |
| [2] |
NAVIN N, KRASNITZ A, RODGERS L, COOK K, METH J, KENDALL J, et al. Inferring tumor progression from genomic heterogeneity[J]. Genome Res, 2010, 20: 68-80. DOI:10.1101/gr.099622.109 |
| [3] |
XYLINAS E, KENT M, KLUTH L, PYCHA A, COMPLOJ E, SVATEK R S, et al. Accuracy of the EORTC risk tables and of the CUETO scoring model to predict outcomes in non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder[J]. Br J Cancer, 2013, 109: 1460-1466. DOI:10.1038/bjc.2013.372 |
| [4] |
HAN W X, CHEN Z M, WEI Z J, XU A M. Preoperative pre-albumin predicts prognosis of patients after gastrectomy for adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction[J/OL]. World J Surg Oncol, 2016, 14: 279. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-1035-x.
|
| [5] |
HUANG J, WANG Y, YUAN Y, CHEN Y, KONG W, CHEN H, et al. Preoperative serum pre-albumin as an independent prognostic indicator in patients with localized upper tract urothelial carcinoma after radical nephroureterectomy[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8: 36772-36779. |
| [6] |
CAI W, KONG W, DONG B, ZHANG J, CHEN Y, XUE W, et al. Pretreatment serum prealbumin as an independent prognostic indicator in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma using tyrosine kinase inhibitors as first-line target therapy[J/OL]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2017, 15: e437-e446. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2017.01.008.
|
| [7] |
LEE J L, OH E S, LEE R W, FINUCANE T E. Serum albumin and prealbumin in calorically restricted, nondiseased individuals: a systematic review[J/OL]. Am J Med, 2015, 128: 1023.e1-1023.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.03.032.
|
| [8] |
CARAS R J, LUSTIK M B, KERN S Q, MCMANN L P, STERBIS J R. Preoperative albumin is predictive of early postoperative morbidity and mortality in common urologic oncologic surgeries[J/OL]. Clin Genitourin Cancer, 2017, 15: e255-e262. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2016.09.008.
|
| [9] |
CUI J, YU M, ZHANG N, WANG S, ZHU Y, CHEN S, et al. Prognostic scores based on the preoperative plasma fibrinogen and serum albumin level as a prognostic factor in patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8: 68964-68973. |
| [10] |
LIU J, DAI Y, ZHOU F, LONG Z, LI Y, LIU B, et al. The prognostic role of preoperative serum albumin/globulin ratio in patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma undergoing radical cystectomy[J/OL]. Urol Oncol, 2016, 34: 484.e1-484.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.05.024.
|
| [11] |
KRANE L S, RICHARDS K A, KADER A K, DAVIS R, BALAJI K C, HEMAL A K. Preoperative neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio predicts overall survival and extravesical disease in patients undergoing radical cystectomy[J]. J Endourol, 2013, 27: 1046-1050. DOI:10.1089/end.2012.0606 |
| [12] |
LIU J, WANG F, LI S, HUANG W, JIA Y, WEI C. The prognostic significance of preoperative serum albumin in urothelial carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J/OL]. Biosci Rep, 2018, 38. pii: BSR20180214. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180214.
|
| [13] |
FUJⅡ T, YAJIMA R, TAKADA T, SUTOH T, MORITA H, YAMAGUCHI S, et al. Serum albumin and prealbumin do not predict recurrence in patients with breast cancer[J]. Anticancer Res, 2014, 34: 3775-3779. |
| [14] |
FAN L, CHI C, GUO S, WANG Y, CAI W, SHAO X, et al. Serum pre-albumin predicts the clinical outcome in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with abiraterone[J]. J Cancer, 2017, 8: 3448-3455. DOI:10.7150/jca.21134 |
 2018, Vol. 39
2018, Vol. 39


