间充质干细胞(mesenchymal stem cell,MSC)是具有自我复制、自我更新和多分化潜能的成体干细胞,在体外特定的诱导条件下,可分化为脂肪、软骨、骨、肌肉、肌腱、神经、肝、心肌、胰岛β细胞和内皮等多种组织细胞,连续传代培养和冷冻保存后仍具有多向分化潜能[1]。不论是自体还是同种异源的MSC,一般都不会引起宿主的免疫反应,即MSC具有低免疫原性。MSC抑制同种异体T细胞活化和增殖的免疫调节作用也被不断证实[2, 3, 4, 5]。
多发性硬化症(multiple sclerosis,MS)是髓鞘特异性T细胞介导的自身免疫性疾病,机体产生自身反应性T细胞是MS发病的主要原因[6]。实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis,EAE)是MS的理想动物模型。本研究将分离纯化的MSC移植至EAE小鼠模型,观察MSC对EAE的疗效,探讨其免疫调节机制,为MSC治疗自身免疫病的机制研究提供理论依据。 1 材料和方法 1.1 试剂和仪器
胎牛血清(FBS)为Gibco公司产品;DMEM培养基为Invitrogen产品;髓鞘少突胶质细胞糖蛋白(myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein,MOG35-55;肽序列:Met-Glu-Val-Gly-Trp-Tyr- Arg-Ser-Pro-Phe-Ser-Arg-Val- Val-His-Leu-Tyr-Arg-Asn-Gly-Lys),纯度98%,购于上海吉尔生化公司;弗氏完全佐剂(CFA,灭活结核分枝杆菌含量5 mg/mL)购于上海三踏生物科技有限公司;百日咳毒素(PT)购于北京联立信生物技术有限公司;大鼠抗小鼠抗体anti-CD4-FITC和anti-Foxp3-Flu647均购于eBioscience公司; ELISA试剂盒购于上海科兴生化试剂有限公司;BD FACS Calibur流式细胞仪为美国BD公司产品;石蜡切片机为德国SLEE公司产品;ELISA酶标仪为Bio-Tek公司产品。 1.2 实验动物及分组
6~8周龄的雄性C57BL/6小鼠和GFP-C57BL/6小鼠,体质量20~25 g[北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司,动物生产许可证号:SCXK(京)2012-0001],饲养在河南省实验动物中心SPF级环境中。选用30只C57BL/6小鼠进行EAE诱导,至发病高峰期即诱导后第15天,除去2只死亡的小鼠,随机分为EAE组和MSC治疗组。 1.3 小鼠EAE模型的建立及临床评分标准
小鼠背部皮下多点免疫CFA和MOG35-55的乳化剂(5 mg/mL的CFA与1.5 mg/mL的MOG35-55溶液按等体积混合,使用注射器反复推拉成油包水的乳剂),200 μL/只,在免疫后第0天和第2天尾静脉注射PT试剂(稀释在200 μL PBS中),2 μL/只。按照如下标准对小鼠进行临床评分:0分,正常小鼠;0.5分,尾部无力;1.0分,尾部完全瘫痪;1.5分,一后肢无力;2.0分,两后肢均无力;2.5分,一后肢瘫痪,另一后肢无力;3.0分,两后肢均瘫痪;3.5分,部分前肢瘫痪;4.0分,前肢完全瘫痪;5.0分,死亡。 1.4 MSC的分离纯化和移植
颈椎脱臼处死20只正常GFP-C57BL/6小鼠,在无菌条件下剥离小鼠胫骨和股骨,暴露骨髓腔,使用PBS冲洗出骨髓腔中的细胞,394.2×g离心5 min收集细胞,使用含15% FBS的DMEM培养液重悬细胞,调整细胞密度为1×106/mL,放置在37℃、5%CO2培养箱中进行培养。4 h后换液,去除未贴壁的细胞,之后每12 h换液1次,3 d后显微镜下观察贴壁细胞的铺满率,若>80%就用胰酶消化进行传代培养。 MSC传代培养至第5代,镜下观察MSC纯度达95%。EAE诱导后的第15天,使用胰酶消化重悬MSC,调整MSC悬液的浓度,以每只1×106/400 μL的量经尾静脉注射至MSC治疗组小鼠体内。同时EAE组小鼠经尾静脉注射400 μL PBS作为对照。 1.5 脊髓组织病理切片分析
MSC移植后第15天,随机选取EAE 组和MSC治疗组小鼠各3只。用20 g/L戊巴比妥钠0.1 mL麻醉小鼠,用40 g/L多聚甲醛进行心脏灌注,解剖取出小鼠的脊髓。置于4%多聚甲醛中固定24 h后,送至郑州大学第一附属医院病理科进行切片及H-E染色。 1.6 ELISA检测血浆细胞因子的含量
MSC移植后第15天,各组小鼠取5只进行尾静脉取血,按照ELISA试剂盒说明书的要求检测血浆中细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、干扰素γ(IFN-γ)、白介素4(IL-4)和转化生长因子β (TGF-β)的含量。 1.7 流式细胞术分析Treg和MSC在受体小鼠体内的变化
MSC移植后第2天和第10天,分别颈椎脱臼处死小鼠3只,取出脑和脊髓,使用Ficoll分离液提取单个核细胞,采用流式细胞术检测GFP+细胞的比例。MSC移植后第15天,处死小鼠并获取脾脏细胞悬液,计数脾脏细胞数1.5×106,标记抗小鼠流式抗体CD4-FITC、Foxp3-Flu647,用FlowJo 软件分析两组小鼠脾脏CD4+Foxp3+ T细胞(Treg)的比例变化。 1.8 统计学处理
采用SPSS17.0统计软件进行数据分析,采用GraphPad Prism 5作为作图工具和辅助统计分析工具。计量资料数据用x±s表示,不同组间各指标的比较采用单因素方差分析和t检验,检验水准(α)为0.05。 2 结 果 2.1 MSC移植后对EAE小鼠的治疗效果
EAE诱导后,对EAE组和MSC治疗组小鼠进行临床评分,可见MSC治疗组小鼠的临床评分在MSC移植后的第2天就开始明显降低 (P<0.05),之后开始缓慢降低(图 1A)。
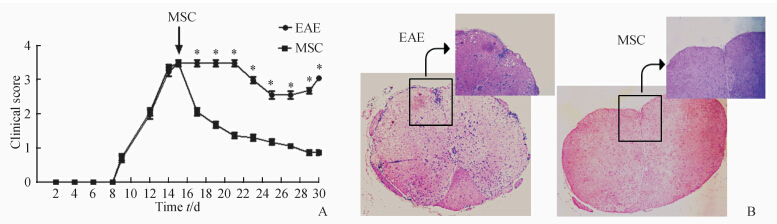 | 图 1 间充质干细胞(MSC)对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)的疗效 Fig 1 Effect of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) for treating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) A: The clinical score of the two groups (*P<0.05 vs MSC treated group,n=8,x±s); B: The spinal pathology at 15 d after MSC transplantation (H-E staining,original magnification: ×50,×100 [inclusion]) |
在MSC移植后第15天,两组小鼠的脊髓组织病理切片结果显示:EAE组小鼠脊髓组织有大量的T细胞浸润,MSC治疗组T细胞浸润情况明显改善(图 1B)。 2.2 MSC移植后对外周血中细胞因子的影响
ELISA结果显示,EAE组小鼠炎症细胞因子TNF-α和IFN-γ的含量高于正常小鼠(P<0.05);抗炎因子IL-4和TGF-β的表达则明显低于正常小鼠(P<0.05); 与EAE组小鼠相比,MSC治疗组小鼠炎症细胞因子TNF-α和IFN-γ的表达降低(P<0.05),而抗炎因子IL-4和TGF-β的表达升高(P<0.05)。见图 2。
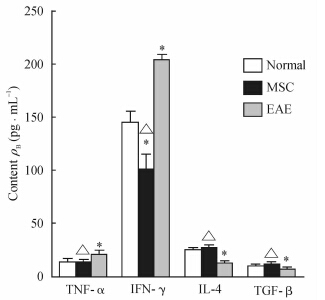 | 图 2 ELISA检测间充质干细胞(MSC)移植后15 d实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)小鼠外周血中细胞因子的含量 Fig 2 Cytokine contents in peripheral blood of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis(EAE) mice at 15 d after mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) transplantation by ELISA) *P<0.05 vs normal group; △P<0.05 vs EAE group. n=5,x±s |
对小鼠脾脏细胞进行流式细胞术分析,结果显示,与正常小鼠[(11.2±0.4)%]相比,MSC治疗组小鼠脾脏细胞中CD4+Foxp3+ Treg细胞的比例[(19.08±0.33)%]升高(P<0.05),而EAE组CD4+Foxp3+ Treg的比例[(6.32±0.19)%]稍有下降但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见图 3。
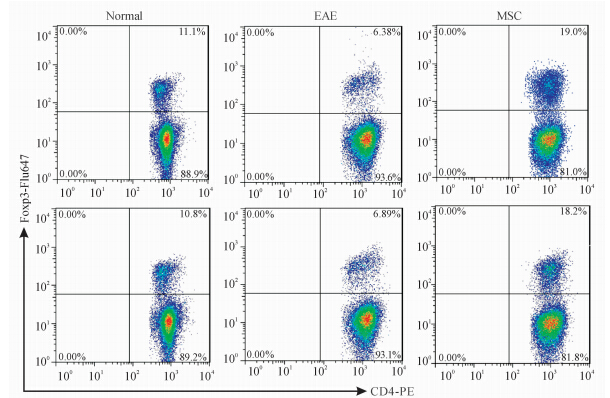 | 图 3 流式细胞术分析脾脏细胞中CD4+Foxp3+ Treg细胞的比例 Fig 3 Ratio of CD4+Foxp3+ Treg cells in splenic cells as determined by Flow cytometry MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells treated group; EAE: Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis group |
MSC移植2 d后小鼠脊髓单个核细胞中GFP+细胞的比例为(1.82±0.08)%,而10 d后发现GFP+ MSC细胞基本消失(图 4)。
 | 图 4 流式细胞术分析间充质干细胞(MSC)移植2 d和10 d后C57BL/6小鼠脊髓中GFP+细胞的比例 Fig 4 Ratio of GFP+ cells at 2 d and 10 d after mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) transplantation |
MS是一种以中枢神经系统(central nervous system,CNS)脱髓鞘为特征、CD4+T细胞介导的自身免疫性疾病[7, 8]。目前临床上对MS还没有一种有效的治疗方法,主要原因是在对患者进行髓鞘再生和修复的过程中,不能够有效地抑制患者体内自体反应性T细胞的产生[9]。所以研究在治疗MS过程中免疫调节的作用就显得尤为重要。MSC移植是一种潜在的治疗MS患者髓鞘再生和修复的有效手段。有研究发现来源于成人组织的MSC可通过抑制T淋巴细胞浸润CNS,有效地促使神经髓鞘细胞再生,并调节患者的神经炎症和损伤[10]。MSC可通过依赖CCL-2的途径抑制CD4 Th17细胞的生成而发挥对EAE的治疗作用[11]。有学者在研究原始细胞向Th1和Th17细胞分化的过程中,发现MSC通过抑制促炎性T细胞的生成和促使调节性细胞表型的表达,给细胞提供一个免疫反应受抑的生长环境[12]。人类脂肪组织来源的MSC可通过分泌IL-10来抑制APC细胞的功能,缓解CNS的自身免疫性疾病[13]。另外,近几年MSC的神经再生和神经营养作用机制也被学者不断阐述[14]。
本研究通过建立EAE 模型,并在EAE 小鼠发病高峰期进行GFP+ MSC移植,观察EAE 组小鼠和MSC治疗组小鼠的发病情况。数据显示在MSC治疗后第2天小鼠的临床症状明显减轻,之后仍旧以平缓的趋势改善。这些现象与前期报道[15] 一致。MSC移植后第15天,MSC治疗组小鼠血浆中促炎因子TNF-α和IFN-γ的含量明显降低,而抗炎因子IL-4和TGF-β的含量升高(P<0.05)。原始T细胞的分化受到细胞因子的影响,TNF-α和IFN-γ可以促使原始T细胞分化为Th1和Th17等致病细胞;IL-4可促使原始T细胞分化为Th2;TGF-β是促使向Treg细胞分化的主要细胞因子[16, 17]。通过流式细胞术分析发现,EAE组小鼠脾脏细胞中Treg细胞在CD4+ T细胞中的比例由正常小鼠的(11.2±0.37)%下降至(6.32±0.19)%;而MSC治疗组小鼠脾脏细胞中Treg的比例升高至(19.08±0.33)%。但是关于TGF-β升高是引起Treg细胞升高的原因还是结果,仍需进一步探讨。另外,本研究还发现,在MSC移植后第2天,小鼠CNS中仍存在GFP+细胞,但是10 d后,GFP+细胞基本消失,初步推测MSC在小鼠体内会随着时间的推移逐渐被吞噬掉,详细机制需要进一步研究。但是,我们继续观察至MSC移植后15 d,发现MSC治疗组小鼠的疾病症状仍旧在缓慢改善。对于这一现象,我们认为可作如下解释:MSC可以促使小鼠分泌细胞因子,而这些细胞因子本身就有抗炎作用,另外也可以促使原始细胞向免疫抑制细胞即Treg分化,从而发挥免疫抑制和调节作用;同时MSC的神经营养作用使小鼠受损神经再生和恢复,所以,MSC细胞在体内被吞噬消失后一定时间内,在部分恢复的血脑屏障的保护下致病细胞Th1/Th17不能大量进入CNS。 4 利益冲突
所有作者声明本文不涉及任何利益冲突。
| [1] | Pittenger M F, Mackay A M, Beck S C, Jaiswal R K, Douglas R, Mosca J D, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Science, 1999,284:143-147. |
| [2] | Di N M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, Milanesi M, Longoni P D, Matteucci P, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli[J]. Blood, 2002,99:3838-3843. |
| [3] | Augello A, Tasso R, Negrini S M, Amateis A, Indiveri F, Cancedda R, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells inhibit lymphocyte proliferation by activation of the programmed death 1 pathway[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2005,35:1482-1490. |
| [4] | Glennie S, Soeiro I, Dyson P J, Lam E W, Dazzi F. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells[J]. Blood, 2005,105:2821-2827. |
| [5] | Zappia E, Casazza S, Pedemonte E, Benvenuto F, Bonanni I, Gerdoni E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis inducing T-cell anergy[J]. Blood, 2005,106:1755-1761. |
| [6] | O'Connor R A, Prendergast C T, Sabatos C A, Lau C W, Leech M D, Wraith D C, et al. Cutting edge: Th1 cells facilitate the entry of Th17 cells to the central nervous system during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J]. J Immunol, 2008,181:3750-3754. |
| [7] | Noseworthy J H, Lucchinetti C, Rodriguez M, Weinshenker B G. Multiple sclerosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2000,343:938-952. |
| [8] | Anderson A C, Chandwaskar R, Lee D H, Sullivan J M, Solomon A, Rodriguez-Manzanet R, et al. A transgenic model of central nervous system autoimmunity mediated by CD4+ and CD8+ T and B cells[J]. J Immunol, 2012,188:2084-2092. |
| [9] | Karussis D, Grigoriadis S, Polyzoidou E, Grigoriadis N, Slavin S, Abramsky O. Neuroprotection in multiple sclerosis[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2006,108:250-254. |
| [10] | Matysiak M, Orlowski W, Fortak-Michalska M, Jurewicz A, Selmaj K. Immunoregulatory function of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in EAE depends on their differentiation state and secretion of PGE2[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2011,233:106-111. |
| [11] | Rafei M,Campeau P M,Aguilar-Mahecha A,Buchanan M, Williams P, Birman E, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting CD4 Th17 T cells in a CC chemokine ligand 2-dependent manner[J]. J Immunol, 2009,182:5994-6002. |
| [12] | Luz-Crawford P, Kurte M, Bravo-Alegria J, Contreras R, Nova-Lamperti E, Tejedor G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells generate a CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cell population during the differentiation process of Th1 and Th17 cells[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2013,4:65. |
| [13] | Payne N L, Sun G, McDonald C, Moussa L, Emerson-Webber A, Loisel-Meyer S, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells engineered to secrete IL-10 inhibit APC function and limit CNS autoimmunity[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2013,30:103-114. |
| [14] | Uccelli A, Benvenuto F, Laroni A, Giunti D. Neuroprotective features of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol, 2011,24:59-64. |
| [15] | Constantin G, Marconi S, Rossi B, Angiari S, Calderan L, Anghileri E, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J]. Stem Cells, 2009,27:2624-2635. |
| [16] | Sakaguchi S, Powrie F. Emerging challenges in regulatory T cell function and biology[J]. Science, 2007,317:627-629. |
| [17] | Ryu C H, Park K Y, Hou Y, Jeong C H, Kim S M, Jeun S S. Gene therapy of multiple sclerosis using interferon beta-secreting human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2013,2013:696738. |
 2015, Vol. 36
2015, Vol. 36


