2. 复旦大学放射医学研究所, 上海 200032
*通信作者
2. Radiation Medicine Research Institute, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
*Corresponding author.
近年来,大量研究证实64层CT、双源CT在探查冠状动脉狭窄方面具有很高的敏感性和特异度,冠状动脉CT血管成像(CT angiography,CTA)检查已经成为冠心病的首选筛查手段[1, 2, 3],但辐射剂量仍制约着CTA检查的临床应用。尽管通过降低管电压、管电流等技术可以部分降低辐射剂量,但目前CTA辐射剂量仍较大。因此,如何保证冠状动脉的图像质量又能降低辐射剂量显得尤为重要[4]。320排容积CT具有成像速度快、覆盖范围宽及时间分辨率高等特点,可以对心率<65次/min 患者进行单个心动周期前瞻性门控心脏扫描,包括容积扫描(volume)及螺旋扫描(helical)两种模式,成为目前研究的热点。因此,本研究初步尝试比较两种扫描模式下的冠脉图像质量、辐射剂量及造影剂用量,为临床应用选择提供参考。
1 资料和方法 1.1 病例选择及分组
2013年6月至8月,第二军医大学长海医院行冠状动脉CTA检查患者128例,男 80 例,女 48 例,年龄42~73岁,平均(58.34±12.95)岁。其中,6月至7月连续72例(男44例,女28例),为容积扫描组,采用前瞻性容积扫描法;7月至8月连续56例(男36例,女20例),为螺旋扫描组,采用前瞻性螺旋扫描法。心率>65次/min的患者检查前1 h服用酒石酸美托洛尔片25~50 mg以使患者心率适当降低并稳定。排除标准:既往对含碘造影剂过敏者,永久性心脏起搏器安置或人工心脏瓣膜置换者,服用酒石酸美托洛尔片后心率仍较快(>65次/min)者,严重心肺及肝肾功能不全及不能配合屏气的患者。两组患者年龄[(58.67±12.08)岁 vs (58.07±13.07)岁]、男女性别比(1.57 vs 1.80)、体质指数(body mass index,BMI; 24.57±2.30 vs 24.15±2.11)、心率(55.79±5.54 vs 58.32±3.04)等基线资料差异无统计学意义。所有患者均知情同意并签署知情同意书,本研究通过第二军医大学长海医院医学伦理委员会审批。 1.2 CTA扫描
采用东芝320排CT(东芝Aquilion One动态容积CT)机进行扫描。扫描方案:两组管电压均为120 kV,管电流为450~550 mA,探测器均选用320排,采集范围均为16 cm,球管转速均为350 ms/周。采用前瞻性心电门控扫描模式。两组患者均接受严格呼吸训练,扫描前3 min舌下含服硝酸甘油0.5 mg。容积扫描组采用容积扫描法的前瞻性心电门控扫描方案:扫描70%~80%心动周期时相。螺旋扫描组采用螺旋扫描法的前瞻性心电门控扫描方案:扫描65%~85%心动周期时相,螺距为0.2。在肘静脉埋置20 G静脉留置针,采用双通道高压注射器,以5 mL/s注入非离子对比剂碘普罗胺(优维显,Ultravist 370 mgI/mL)。因容积扫描法扫描速度较快,因此对比剂使用量少。容积扫描法对比剂用量为50~60 mL,螺旋扫描组对比剂用量为80~90 mL,两组均以对比剂同样流速后续30~40 mL生理盐水。采用SureStart软件智能触发扫描:容积扫描组触发点定于容积中心层面降主动脉,阈值达到300 HU开始扫描;螺旋扫描组触发点定于冠状动脉起始层面升主动脉,阈值达到120 HU嘱患者屏气后开始扫描。 1.3 图像分析
重组层厚0.5 mm,层间隔0.25 mm,CT重建函数选择软组织重建函数(FC03),重建容积数据包含预设的75%期相和计算机默认重建的最佳期相。重组的血管段不能满足诊断要求,进行心电编辑之后进行该血管段的高级重组,得到清晰显示冠状动脉节段的横断面图像,将该时相数据传至Vitrea FX图像后处理工作站,应用血管分析软件重组得到冠状动脉的容积再现(volume reconstruction,VR)、多平面重建 (multiplannar reconstruction,MPR )、曲面重建(curved multiplannar reconstruction ,CPR)图像。冠状动脉主要分支根据美国心脏协会(AHA)分为9个节段[5],即:左主干,前降支近、中、远段,左旋支近、远段,右冠状动脉近、中、远段进行分析 。按照4分法将图像质量分为4级[6]:1分(优)为走行连续,没有运动伪影,血管轮廓清晰;2分(良)为走行连续,有轻微伪影,对血管有轻度干扰;3分(中等)为中等程度伪影干扰,但血管走行连续;4分(差)为严重伪影干扰,血管呈现双影,或走行中断,血管轮廓不能分辨。1~3分为可评价图像,4分为不可评价图像(图 1)。
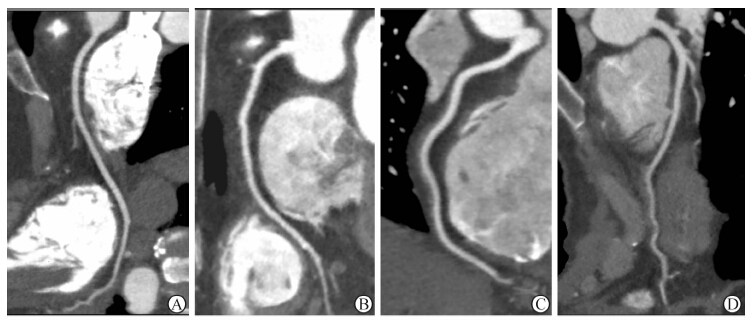
|
图 1 冠状动脉图像质量评分示意图 A: 1分; B: 2分; C: 3分; D: 4分 |
由两位经验丰富的放射科医师(从事冠状动脉CTA诊断5年以上)在不知扫描方式分组的情况下独立完成血管图像质量评价,评价不一致时两人共同阅片,协商达成一致结论。以图像质量优秀(1分)及合格(≤3分)节段数量占每例患者总节段数量的百分比为优秀率及合格率。放射剂量以剂量长度乘积(dose length product,DLP)乘以k换算求得,k为胸部特定的转换系数,参考欧盟委员会关于CT的质量标准指南,k=0.017 mSv·mGy-1·cm-1 [7]。 1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS19.0软件,计量资料以 x±s表示。两组间优秀率及合格率的比较采用χ2检验,其余各参数比较采用t检验。比较两组间图像质量及辐射剂量的差异。检验水准(α)为0.05。 2 结 果 2.1 冠状动脉图像质量比较
结果(表 1)表明:两组间图像质量均符合诊断要求,冠状动脉节段优秀率分别为97.5%(632/648)、96.8%(488/504),合格率分别为99.7%(646/648)、99.2%(500/504),差异无统计学意义;两组间主动脉根部CT值及图像噪声差异无统计学意义。
|
|
表 1 两组患者图像质量的比较 |
两种扫描方式辐射剂量差异有统计学意义。容积扫描组DLP值低于螺旋扫描组(188.89±12.14 vs 780.86±140.70 mGy/cm,P<0.001);容积扫描组有效辐射剂量(ED)较螺旋扫描组降低了75.7%,差异有统计学意义( 3.21±2.23 vs 13.27±2.39 mSv,P<0.001)。容积扫描组对比剂用量为50~60 mL,螺旋扫描组因扫描时间长,对比剂用量为80~90 mL。 3 讨 论
320排CT采用覆盖宽度达16 cm的大面积量子探测器,球管只需旋转1圈(最快0.35 s)即可获取全心范围扫描数据。在慢心率(<65次/min)的情况下,容积扫描法在1个心动周期内便能即时立体重构整个心脏及冠状动脉,无需移动检查床,因此没有层面间的拼接,从根本上解决了回顾性门控扫描造成的重叠曝光问题,并能提供高清晰影像[8]。新型320排CT螺旋扫描时球管旋转1周最大覆盖范围为160×0.5 m,在患者心率<65次/min时,一般全心扫描约为5个心动周期,约需4.2~4.9 s。本研究中的螺旋扫描法是指采用大准直(160×0.5 m)小螺距扫描。在患者心率<65次/min时,相同螺距的情况下较64层螺旋CT扫描速度快,但与容积扫描法相比其扫描时间依然长了很多。因此,容积扫描法可最大限度避免患者心律不齐和屏气欠佳所造成的图像质量下降。
心率超过65次/min时,可采用多节段采集的方法提高时间分辨率,但易造成图像质量下降,最常见的问题是运动伪影。本研究两组患者都为低心率,避免了心率快或心律不齐导致的心脏运动伪影[9, 10]。320排CT诊断冠状动脉狭窄的敏感性、特异度、阳性预测率、阴性预测率均大于90%[11, 12]。心率<65次/min时,容积扫描前瞻性门控(70%~81%心动周期)可以得到高质量的图像[13]。
减少辐射剂量是目前相关研究的热点,传统64排CT前瞻性门控冠脉成像的辐射剂量约为9 mSv[4, 14, 15]。因容积扫描法时间短,无重叠扫描,所以容积前瞻性门控扫描法辐射剂量远小于64排CT,与国内研究结果相近[16],但小于国外学者的研究结果[17]。这可能与国外患者体质量较大而采用更高的剂量有关。本研究中螺旋扫描模式与64排CT相比辐射剂量略大,可能是与没有采用个性化设计及操作人员的水平有关。目前,DSA冠脉造影仍是诊断冠状动脉狭窄的“金标准”。本研究中容积扫描组辐射剂量与DSA冠脉造影剂量[10]相当,但具有无创的优点。本研究不足之处在于图像质量评分有一定的主观性;其次未对冠状动脉的准确性与“金标准”DSA相比较。
综上所述,容积扫描法在低心率冠状动脉扫描时所得的图像质量与螺旋扫描法相当,且缩短了扫描时间,减少了对比剂用量及辐射剂量。因此,在对心率较低的患者行冠状动脉CT成像时,使用前瞻性门控容积扫描可能更有优势,值得深入研究。
4 利益冲突
所有作者声明本文不涉及任何利益冲突。
| [1] | Mollet N R,Cademartiri F,van Mieghem C A,Runza G,McFadden E P,Baks T,et al.High-resolution spiral computed tomography coronary angiography in patients referred for diagnostic conventional coronary angiography[J].Circulation,2005,112:2318-2323. |
| [2] | Alkadhi H,Scheffel H,Desbiolles L,Gaemperli O, Stolzmann P,Plass A,et al.Dual-source computed tomography coronary angiography:influence of obesity,calcium load,and heart rate on diagnostic accuracy[J].Eur Heart J,2008,29:766-776. |
| [3] | Achenbach S,Ropers U,Kuettner A,Anders K,Pflederer T,Komatsu S,et al.Randomized comparison of 64-slice single- and dual-source computed tomography coronary angiography for the detection of coronary artery disease[J].JACC Cardiovasc Imaging,2008,1:177-186. |
| [4] | Kim M J,Park C H,Choi S J,Hwang K H,Kim H S.Multidetector computed tomography chest examinations with low-kilovoltage protocols in adults:effect on image quality and radiation dose[J].J Comput Assist Tomogr,2009,33:416-421. |
| [5] | Fuster V,Alexander R W.Huster's the heart[M]. 10thed.Boston:Philadelphix McGraw-Hill Eduction,2002:422-429. |
| [6] | Shuman W P,Branch K R,May J M,Mitsumori L M,Lockhart D W,Dubinsky T J,et al.Prospective versus retrospective ECG gating for 64-detector CT of the coronary arteries:comparison of image quality and patient radiation dose[J].Radiology,2008,248:431-437. |
| [7] | Valentin J;International Commission on Radiation Protection.Managing patient dose in multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT).ICRP Publication 102[J].Ann ICRP,2007,37:1-79,Ⅲ. |
| [8] | Torres F S,Crean A M,Nguyen E T,Menezes R,Doyle D,Ayyappan A P,et al.Abolition of respiratory-motion artifact in computed tomography coronary angiography with ultrafast examinations:a comparison between 64-row and 320-row multidetector scanners[J].Can Assoc Radiol J,2010,61:5-12. |
| [9] | Dewey M,Zimmermann E,Deissenrieder F,Laule M,Dübel H P,Schlattmann P,et al.Noninvasive coronary angiography by 320-row computed tomography with lower radiation exposure and maintained diagnostic accuracy:comparison of results with cardiac catheterization in a head-to-head pilot investigation[J].Circulation,2009,120:867-875. |
| [10] | Dewey M,de Vries H,de Vries L,Haas D,Leidecker C.The present and future of cardiac CT in research and clinical practice:moderated discussion and scientific debate with representatives from the four main vendors[J].Rofo,2010,182:313-321. |
| [11] | 王治中,杨进华,万琪琳,程冠昌.应用320排CT评价冠状动脉狭窄的临床研究[J].中国医学计算机成像杂志,2012,18:205-208. |
| [12] | Alessandri N,Di Matteo A,Rondoni G,Petrassi M,Tufani F,Ferrari R,et al.Heart imaging:the accuracy of the 64-MSCT in the detection of coronary artery disease[J].Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2009,13:163-171. |
| [13] | Steigner M L,Otero H J,Cai T,Mitsouras D,Nallamshetty L,Whitmore A G,et al.Narrowing the phase window width in prospectively ECG-gated single heart beat 320-detector row coronary CT angiography[J].Int J Cardiovasc Imaging,2009,25:85-90. |
| [14] | Singh S,Kalra M K,Moore M A,Shailam R,Liu B,Toth T L,et al.Dose reduction and compliance with pediatric CT protocols adapted to patient size,clinical indication,and number of prior studies[J].Radiology,2009,252:200-208. |
| [15] | Park E A,Lee W,Kang J H,Yin Y H,Chung J W,Park J H.The image quality and radiation dose of 100-kVp versus 120-kVp ECG-gated 16-slice CT coronary angiography[J].Korean J Radiol,2009,10:235-243. |
| [16] | 覃杰,刘凌云,张建生,方圆,钱孝贤,朱洁明,等.320排CT前瞻性与回顾性心电门控一个心动周期内冠状动脉成像的对照研究[J].中国医师杂志,2010,12:1162-1165. |
| [17] | Hoe J,Toh K H.First experience with 320-row multidetector CT coronary angiography scanning with prospective electrocardiogram gating to reduce radiation dose[J].J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr,2009,3:257-261. |
 2014, Vol. 35
2014, Vol. 35


