2. 河南大学淮河医院超声科, 开封 475000;
3. 河南大学淮河医院病理科, 开封 475000;
4. 河南大学淮河医院普通外科, 开封 475000
2. Department of Ultrasound, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475000, Henan, China;
3. Department of Pathology, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475000, Henan, China;
4. Department of General Surgery, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng 475000, Henan, China
再生基因 (regenerating gene,Reg) 蛋白家族是钙依赖性凝集素超家族,高表达于部分胃肠道肿瘤,参与肿瘤细胞的增殖和分化,Reg Ⅳ是其中一个新成员 [1]。既往研究[2,3]表明:Reg Ⅳ在Crohn病和溃疡性结肠炎表达,并与大肠癌的恶性潜能和大肠腺瘤的恶性转化相关,且其能够通过增强Akt、Bcl-2、Bcl-xL及survivin的表达,维持大肠癌细胞的存活[4],但目前关于其在胃腺癌中的可能作用及机制尚不明确。因此,本研究采用免疫组织化学染色技术检测胃癌及癌旁正常组织中Reg Ⅳ蛋白的表达差异,分析其与磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)、Akt蛋白表达的相关性,探讨Reg Ⅳ在胃癌发生发展中的可能意义及机制,为进一步深入研究奠定基础。 1 材料和方法 1.1 一般资料
河南大学淮河医院普通外科2010年1月至2012年1月手术切除的新鲜胃腺癌标本63例,均经H-E染色病理证实,所有患者术前均未接受放疗或化疗,并排除其他脏器恶性肿瘤。选取同一病例的癌旁切缘正常组织63例作为对照组。63例胃腺癌患者,男33例,女30例;年龄28~77岁,平均(46.8±3.9)岁;高、中、低分化腺癌分别为15例、22例和26例;淋巴结转移43例,无转移20例;按TNM分期标准,Ⅰ期9例,Ⅱ期15例,Ⅲ期18例,Ⅳ期21例;按浸润深度分为T1 11例,T2 14例,T3 15例,T4 23例。 1.2 免疫组织化学染色
浓缩型鼠抗人单克隆抗体Reg Ⅳ、PI3K、Akt及免疫组化试剂盒,DAB试剂盒均购自北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司。免疫组化S-P法染色:取厚4 μm石蜡切片,常规脱蜡、水化后,采用电炉加热煮沸修复抗原;Reg Ⅳ与PI3K、Akt蛋白单克隆抗体均按1∶100稀释,操作参照产品说明书,以磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)代替一抗作为阴性对照。用已证实的RegⅣ、PI3K、Akt染色阳性胃腺癌切片作阳性对照。 1.3 结果判断
根据免疫组化染色程度及阳性细胞数来计算免疫组化染色评分。染色程度:0为阴性,1为弱阳性,2为中等阳性,3为强阳性;阳性细胞数:无阳性细胞计为0分,阳性细胞1%~25%计为1分,阳性细胞25%~50%计为2分,阳性细胞大于50%计为3分。两者之和为3~6分者评为免疫组化染色阳性。结果判定在双盲法下进行,每张切片由两名高年资病理科主治医师独立判断,不一致时交高年资主任医师仲裁并重新计数。 1.4 统计学处理 采用SPSS 13.0统计软件包,计数资料应用率或比表示,两组率的比较采用χ2检验,等级资料的比较采取非参数检验的秩和检验,双变量相关关系分析采用Spearman相关分析,检验水准(α)为0.05。 2 结 果 2.1 胃腺癌组织Reg Ⅳ、PI3K、Akt蛋白的表达
免疫组化结果(图 1)表明:63例胃腺癌组织中,Reg Ⅳ蛋白阳性表达率50.7% (32/63),其阳性表达部位为胞质;PI3K的阳性表达率68.3% (43/63),阳性表达部位为胞质;Akt的阳性表达率60.3% (38/63),阳性表达部位主要在胞质,部分在胞核,均呈强阳性过度表达现象。癌旁正常组织中,Reg Ⅳ、PI3K、Akt蛋白均为弱阳性低表达,阳性表达率分别为19.0% (12/63)、20.6% (13/63)、9.5% (6/63)。两组间表达差异有统计学意义(χ2=13.969、28.929、35.761,P值均<0.05)。
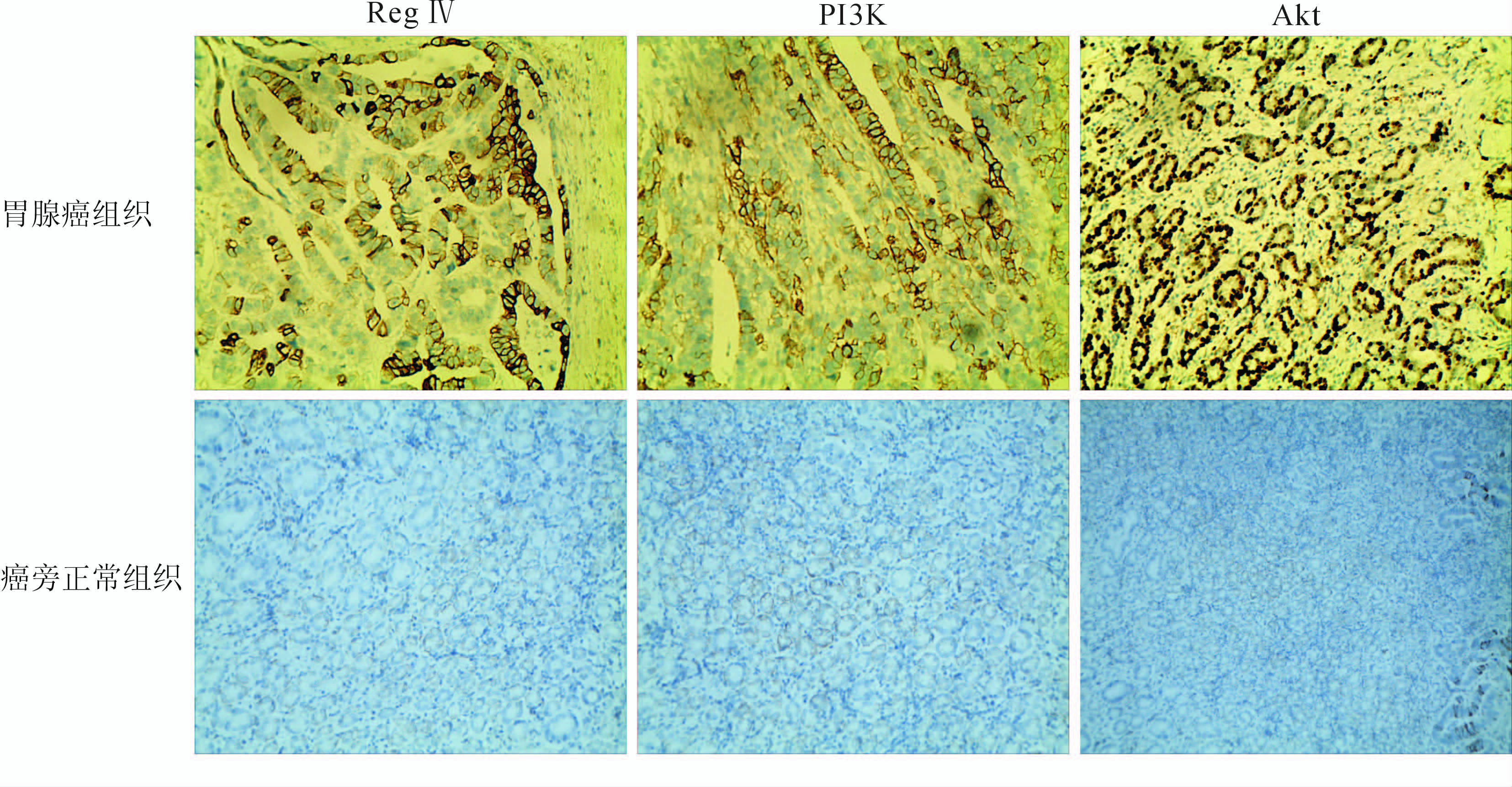
|
图 1 胃腺癌组织及癌旁正常组织Reg Ⅳ、PI3K、Akt蛋白的表达(S-P法) 胃腺癌组织Reg Ⅳ及其受体阳性表达,而癌旁正常组织弱阳性表达. Original magnification: ×200 |
结果(表 1)表明:不同肿瘤分化程度间RegⅣ蛋白表达差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);不同肿瘤分化程度、浸润深度、淋巴结转移与否、临床分期间PI3K蛋白表达差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);淋巴结转移与否胃癌组织Akt蛋白表达差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
|
|
表 1 胃腺癌不同临床病理特征下Reg Ⅳ及其受体的表达 |
配对资料的Spearman相关分析显示:胃腺癌组织中Reg Ⅳ蛋白与PI3K、Akt表达正相关(rs=0.284、0.305,P<0.05),PI3K蛋白与Akt蛋白表达正相关(rs=0.423,P<0.05)。 3 讨 论
人Reg Ⅳ基因位于1号染色体上[5,6],可在各种正常组织中表达,如胃、大肠、小肠和胰腺,但其表达水平较癌组织中要低得多[7]。Violette等[8]研究表明,Reg Ⅳ在大肠肿瘤(特别是在黏液癌)有较高表达。Oue 等[7]采用定量PCR技术测定胃癌组织Reg Ⅳ基因的表达显著高于正常组织。Reg Ⅳ的抗凋亡特性与大肠癌的进展和胃癌化疗耐药性密切相关[9],Reg Ⅳ有望成为一个标记高度恶性潜力的生物学标记物[10,11]。本研究发现,Reg Ⅳ在胃腺癌中高表达,显著高于癌旁正常组织,且与肿瘤分化程度相关,但与肿瘤临床分期、有无淋巴结转移、浸润深度等因素无关,提示Reg Ⅳ可能参与了胃腺癌的发展,值得深入研究。
PI3K是脂质激酶家族的一个成员,已被证明在调节细胞增殖、黏附、生存和活力等方面发挥了关键作用[12]。PI3K蛋白是细胞内信号转导的关键酶,能够磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇的肌醇环3-位上的羟基基团,是人类肿瘤最常见的激活途径之一[13,14,15]。PI3K非常适合于药物干预,是目前肿瘤治疗最具潜力的靶标。本研究发现,胃腺癌组织PI3K蛋白阳性表达率显著高于癌旁正常组织,且与肿瘤分化程度、浸润深度、淋巴结转移、临床分期正相关,与既往报道结果[16]类似。Akt蛋白属于蛋白激酶B族,是PI3K信号通路上游和下游的中心节点[17,18,19,20]。Akt蛋白在肿瘤发生发展过程中通过多种信号通路被激活[18,19,21] ,参与了肿瘤的发生和发展[17]。本研究表明,胃腺癌组织Akt蛋白高表达,显著高于癌旁正常组织,且与淋巴转移相关,与文献报道[16,22]类似,提示Akt参与了胃腺癌的发展。
目前对于Reg Ⅳ激活的信号转导通路知之甚少。Kuniyasu等[23]发现Reg Ⅳ可提高抗凋亡基因Bcl-2、Bcl-xL、survivin的表达,且Reg Ⅳ基因高效转染MKN28和TMK1胃癌细胞后可促进Akt磷酸化和EGFR磷酸化,而细胞的数量和侵袭能力未得到增长和增强。Takehara等[24]研究认为Reg Ⅳ可能通过PI3K/Akt信号通路刺激胰腺癌细胞的生长。本研究发现,Reg Ⅳ与PI3K、Akt蛋白在胃腺癌中的表达均呈正相关,进一步从蛋白水平证实了上述观点。PI3K和Akt蛋白作为PI3K/Akt信号系统的两个关键酶,为信号转导系统的上下游关系。本研究结果显示,PI3K和Akt蛋白的表达在胃腺癌组织中正相关,与既往报道相符[16]。限于研究时限及经费来源,本研究未能同期行基因水平研究,存在不足,后续研究会进一步补充。
综上所述,本研究从蛋白水平证实Reg Ⅳ高表达与胃腺癌分化程度相关,PI3K/Akt信号通路的激活可能参与其中,为后续基于Reg Ⅳ蛋白的肿瘤靶向治疗研究奠定了基础。
4 利益冲突
所有作者声明本文不涉及任何利益冲突。
| [1] | Li A,Crimmins D L,Luo Q,Hartupee J,Landt Y,Ladenson J H,et al.Expression of a novel regenerating gene product,Reg Ⅳ,by high density fermentation in Pichia pastoris: production,purification,and characterizationp[J].Protein Expr Purif,2003,31:197-206. |
| [2] | Nanakin A,Fukui H,Fujii S,Sekikawa A,Kanda N,Hisatsune H,et al.Expression of the REG Ⅳ gene in ulcerative colitis[J].Lab Invest,2007,87:304-314. |
| [3] | Zhang Y,Lai M,Lv B,Gu X,Wang H,Zhu Y,et al.Overexpression of Reg Ⅳ in colorectal adenoma[J].Cancer Lett,2003,200:69-76. |
| [4] | Bishnupuri K S,Luo Q,Murmu N,Houchen C W, Anant S,Dieckgraefe B K.Reg Ⅳ activates the epidermal growth factor receptor/Akt/AP-1 signaling pathway in colon adenocarcinomas[J].Gastroenterology,2006,130:137-149. |
| [5] | Broekaert D,Eyckerman S,Lavens D,Verhee A, Waelput W,Vandekerckhove J,et al.Comparison of leptin- and interleukin-6-regulated expression of the rPAP gene family:evidence for differential co-regulatory signals[J].Eur Cytokine Netw,2002,13:78-85. |
| [6] | Nata K,Liu Y,Xu L,Ikeda T,Akiyama T,Noguchi N,et al.Molecular cloning,expression and chromosomal localization of a novel human REG family gene,REG Ⅲ[J].Gene,2004,340:161- 170. |
| [7] | Oue N,Hamai Y,Mitani Y,Matsumura S,Oshimo Y,Aung P P,et al.Gene expression profile of gastric carcinoma:identification of genes and tags potentially involved in invasion,metastasis,and carcinogenesis by serial analysis of gene expression[J].Cancer Res,2004,64:2397-2405. |
| [8] | Violette S,Festor E,Pandrea-Vasile I,Mitchell V,Adida C,Dussaulx E,et al.Reg Ⅳ,a new member of the regenerating gene family,is overexpressed in colorectal carcinomas[J].Int J Cancer,2003,103:185-193. |
| [9] | Bishnupuri K S,Luo Q,Korzenik J R,Henderson J O,Houchen C W,Anant S,et al.Dysregulation of Reg gene expression occurs early in gastrointestinal tumorigenesis and regulates anti-apoptotic genes[J].Cancer Biol Ther,2006,5:1714-1720. |
| [10] | Pankova-Kholmyansky I,Arber N.Reg Ⅳ can serve for early diagnosis and therapy[J].Cancer Biol Ther,2007,6:123-124. |
| [11] | Oue N,Mitani Y,Aung P P,Sakakura C,Takeshima Y,Kaneko M,et al.Expression and localization of Reg Ⅳ in human neoplastic and non-neoplastic tissues:Reg Ⅳ expression is associated with intestinal and neuroendocrine differentiation in gastric adenocarcinoma[J].J Pathol,2005,207:185-198. |
| [12] | Bowles D W,Jimeno A.New phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer [J].Expert Opin Investig Drugs,2011,20:507-518. |
| [13] | Guillermet-Guibert J,Bjorklof K,Salpekar A,Gonella C, Ramadani F,Bilancio A,et al.The p110β isoform of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signals downstream of G protein-coupled receptors and is functionally redundant with p110γ[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2008,105:8292-8297. |
| [14] | Dbouk H A,Pang H,Fiser A,Backer J M.A biochemical mechanism for the oncogenic potential of the p110beta catalytic subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2010,107:19897-19902. |
| [15] | Edling C E,Selvaggi F,Buus R,Maffucci T,Di Sebastiano P,Friess H,et al.Key role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase class IB in pancreatic cancer[J].Clin Cancer Res,2010,16:4928-4937. |
| [16] | 邹绍静,陈兆峰,李敏,姬瑞,路红,郭庆红,等.PI3K/AKT2在胃癌组织表达及其与临床病理特征和生存期的关系[J].实用肿瘤杂志,2011,26:346-350. |
| [17] | Kirkegaard T,Witton C J,Edwards J,Nielsen K V,Jensen L B,Campbell F M,et al.Molecular alterations in AKT1,AKT2 and AKT3 detected in breast and prostatic cancer by FISH[J].Histopathology,2010,56:203-211. |
| [18] | Altomare D A,Testa J R.Perturbations of the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer [J].Oncogene,2005,24:7455-7464. |
| [19] | Chin Y R,Toker A.Function of Akt/PKB signaling to cell motility,invasion and the tumor stroma in cancer[J].Cell Signal,2009,21:470-476. |
| [20] | Shaw R J,Cantley L C.Ras,PI3K and mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth[J].Nature,2006,441:424-430. |
| [21] | Bellacosa A,Kumar C C,Di Cristofano A,Testa J R.Activation of AKT kinases in cancer:implications for therapeutic targeting[J].Adv Cancer Res,2005,94:29-86. |
| [22] | Zhang H Y,Tao H M,Chen H T.Expression and clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor and protein kinase B in gastric carcinoma [J].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi,2011,14:140-142. |
| [23] | Kuniyasu H,Oue N,Sasahira T,Yi L,Moriwaka Y,Shimomoto T,et al.Reg Ⅳ enhances peritoneal metastasis in gastric carcinomas[J].Cell Prolif,2009,42:110-121. |
| [24] | Takehara A,Eguchi H,Ohigashi H,Ishikawa O,Kasugai T,Hosokawa M,et al.Novel tumor marker REG4 detected in serum of patients with resectable pancreatic cancer and feasibility for antibody therapy targeting REG4[J].Cancer Sci,2006,97:1191-1197. |
 2014, Vol. 35
2014, Vol. 35


