2. 第二军医大学药学院海洋药物研究中心, 上海 200433
2. Research Center for Marine Drugs, School of Pharmacy, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China
软珊瑚是低等腔肠门(Coelenterata)珊瑚虫纲(Anthozoa)的海洋无脊椎动物,这类海洋生物广泛分布于从亚热带到两极、从潮间带到深达数千米深度的广大海域,仅我国境内就分布有100多种软珊瑚[1]。
肉芝软珊瑚(Sarcophyton)属于八放珊瑚亚纲(Octocorallia)软珊瑚目(Alcyonacea)软珊瑚科(Alcyoniidae)动物。作为珊瑚家族的重要成员之一,现已发现该属有41个物种[2]。二萜化合物是该属珊瑚中数目最多的一类次生代谢产物,它们在珊瑚的防御、竞争、繁殖等方面可能发挥着重要的生态学功能,这些化合物在体外活性筛选实验中表现出抗肿瘤、抗炎和抗菌等多种生物学活性[3],具有重要的药用研究价值。
对于肉芝软珊瑚的研究可以追溯到1974年从S. glaucum中分离得到sarcophine,标志着肉芝软珊瑚属珊瑚中二萜类化合物研究的开始[4]。在此后的近40年的时间里,此类化合物因其丰富的化学多样性和显著的生物活性逐步成为天然产物研究的热点之一。相关研究在Natural Product Reports海洋天然产物年度综述中有连续报道,印度学者1997年对肉芝软珊瑚属动物之前的研究概况进行了较为详细的综述[5],我国兰州大学学者在2006年出版的专著中对1970-1998年该属珊瑚中的西松烷型二萜化合物研究也给予了总结[3],最近郭跃伟小组[6]详细综述了肉芝软珊瑚属中西松烷型二萜二聚化合物的化学和生物活性(1982-2013)。本文综述了1998年之后肉芝软珊瑚中二萜化合物的研究进展,涉及化合物143个,从化学结构和生物活性两个方面进行论述,文献收录至2013年10月。
西松烷二萜最先发现于陆生植物美国白皮松Pinus albicaulis中[7],是肉芝软珊瑚属的主体代谢产物,数量约占二萜化合物的90%以上;由1个十四元碳环及相连1个异丙基和3个甲基取代组合而成,化学多样性主要是不同位置的双键取代及氧化所致,生物活性包括抗肿瘤、抗菌、抗炎、抗氧化和酶诱导活性等。
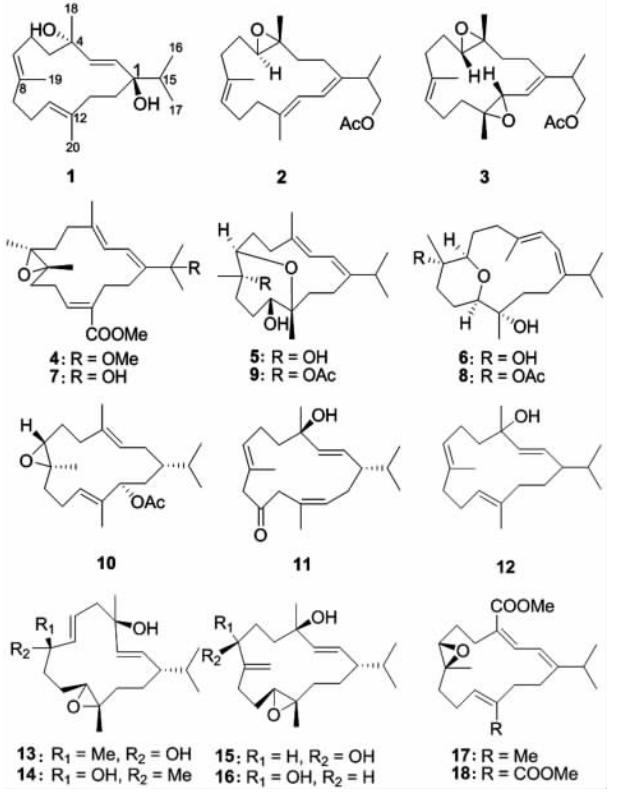
该类化合物共35个,从9种已得到鉴定及3种尚未鉴定到的软珊瑚中分离得到。1998年从澳大利亚肉芝软珊瑚S. ehrenbergi中分离得到化合物sarcophytol T (1)及类似物2和3[8];之后又从台湾同种珊瑚中分离得5个类似物ehrenberoxides A~C ( 4 ~ 6)、ehrenbergols A和B ( 7 和 8 ),以及acetyl ehrenberoxide B (9),体外实验中这6个化合物均显示抗病毒作用,其对人巨细胞病毒的IC50值分别为24.8、4.7、16.1、46.0、5.0、8.0 μmol/L[9 ,10,11],从日本肉芝软珊瑚S. acutangulum中先后报道了化合物epoxysartone B (10)、sartone E ( 11 )[12]及acutanol (12)[13];之后从澳大利亚同种肉芝软珊瑚中又得到类似物13~16,其中化合物13和14可以竞争性抑制8-环戊基-1,3-二丙基黄嘌呤与鼠的脑腺苷A1感受器结合,而化合物 15 和16多了1个环外双键导致与A1感受器的亲和力消失[14]。我国学者先后对4种中国南海肉芝软珊瑚进行了系统研究,从未鉴定种的肉芝软珊瑚中分离得到化合物sarcophytonolides A (17)和B ( 18 )[15]、从软珊瑚S. latum中分离得到化合物diepoxysarcophytonene (19)和sarconphytonol (20)、从软珊瑚S. trocheliophorum Marenzeller中分离得到化合物yalongenes A和B (21和23)和sarcophytonolide M (23)而从S. crassocaule中分离得到化合物sarcrassins A~C(24~26),化合物23的18-甲基氧化成酸并形成甲酯,而24~26中20-甲基也同时被羧甲基化,在分子中形成了18,20-二羧基甲酯的结构;体外活性筛选实验中,化合物19在对COX-2显示弱的抑制作用[16],化合物21可保护SH-SY5Y细胞免遭H2O2的氧化[17,18],而化合物24和25对KB肿瘤细胞有细胞毒性,其IC50值分别为19.0、5.0 μg/mL[19]。从肯尼亚软珊瑚S. elegans中分离得到2个化合物methyl tetrahydrosarcoate (27)和methyl tetrahydroisosarcoate ( 28 ),两者均含有2,6,13-三酮结构,化合物27在海虾活体鉴定中显示对卤虫有显著的毒性作用,LC50值为1.5 μmol/L[20]。从印度洋软珊瑚 S. flexuosum中分离得到了化合物flexusines A和B (29和30)和epimukulol (31),fexusines A (29)含有6,14-二酮结构, 但在flexusines B (30)和epimukulol (31)中二酮结构被全部或部分还原[21]。同年,从越南软珊瑚S. mililatensis中分离鉴定了化合物 32 ,其异丙基上的末端双键氧化形成邻二醇[22]。近年从软珊瑚S. glaucum中又分离得到化合物sarglaucol (33)及类似物34和35,化合物34的异丙基进一步氧化形成羧酸酯,而化合物35在G-4与C-12及C-8与C-11间则分别形成分子内醚键,体外活性筛选实验中只有化合物33显示弱的抗肿瘤活性[23,24,25]。
 |
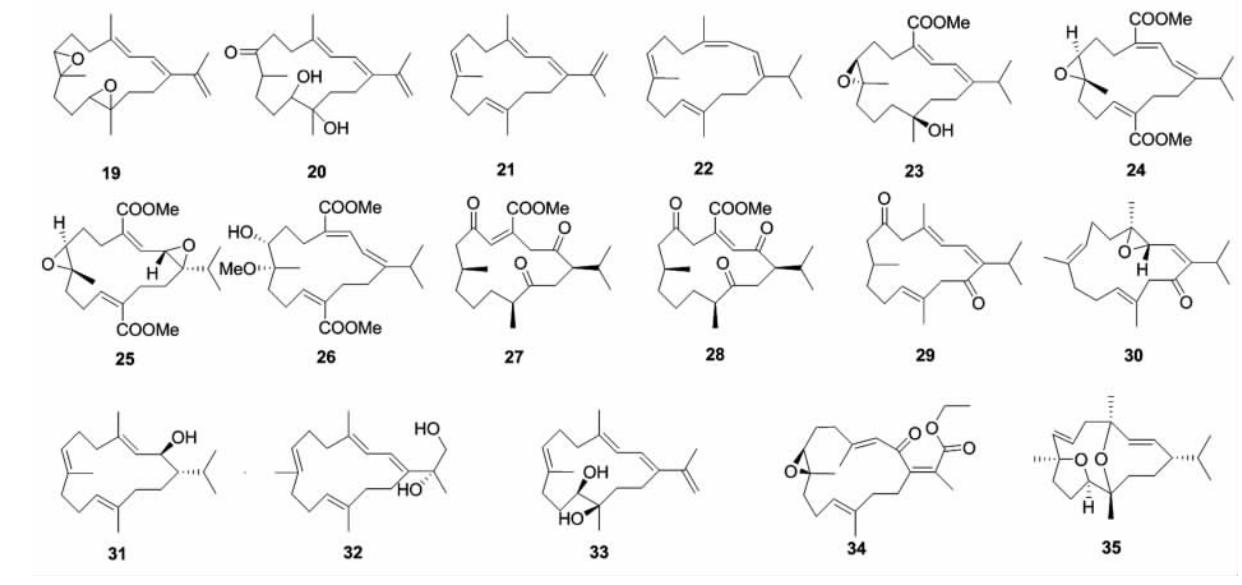 |
此类结构数目相对较少,共有8个化合物,涉及到5种珊瑚。从中国台湾软珊瑚S. ehrenbergi中分离得到的sarcophytoxide (36)和lobophynin C (37)具有7,8-环氧结构,且20-甲基被氧化成羧酸或羧基甲酯,在体外实验中均对人巨细胞病毒显示抗病毒作用[9]。化合物38来自澳大利亚软珊瑚S. cherbonnieri,其19-甲基也氧化生成羧基甲酯,可以适度抑制癌细胞HM02、HepG2和MCF7的生长[26]。从越南软珊瑚 S. mililatensis 中分离鉴定的化合物39~41[22],而从中国南海和埃及的2种未鉴定肉芝软珊瑚中分离得到的化合物 42~44[27,28],其中化合物40~42均为7,8-邻二醇衍生物,而化合物43的呋喃环上则具有过氧取代,化合物44具有7,8-环氧及C-16位的伯醇取代结构;化合物40在成骨细胞MC3T3-E1体外作用研究实验中可以显著提高磷酸酶活性、促进胶原蛋白量和根瘤矿化,说明其可以直接刺激骨形成,可能具有防御骨质疏松作用。
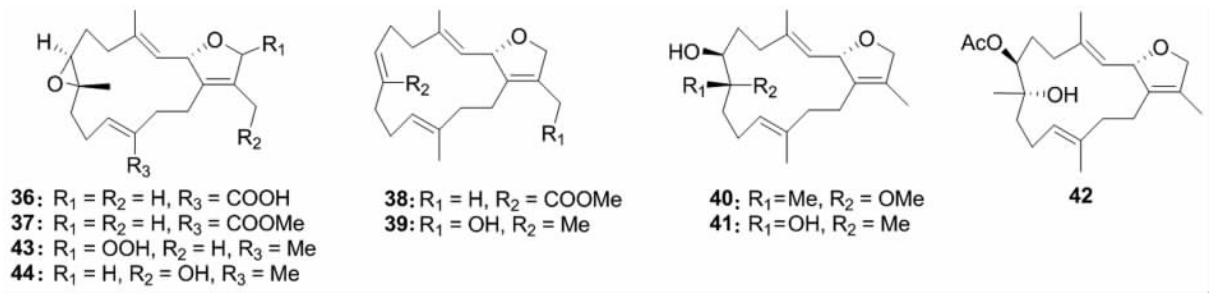 |
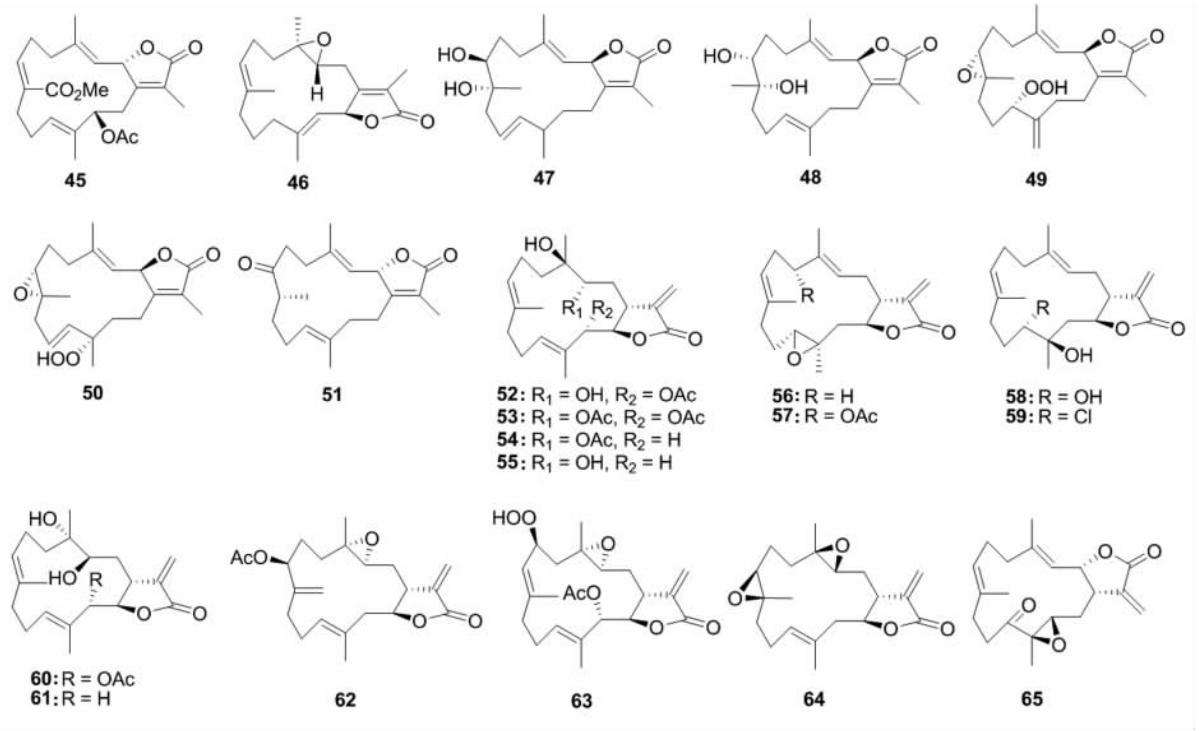
五元内酯环型西松烷二萜多具有细胞毒活性,五元内酯环是其重要的活性中心,分别由1-异丙基、18-甲基、19-甲基或20-甲基氧化形成的羧基与其γ羟基缩合而成。此类结构的化合物数目最多,共从9种已鉴定及5种未鉴定的肉芝软珊瑚中共分离得到74个化合物。从软珊瑚S. glaucum中分离得到化合物16-oxosarcoglaucol acetate (45)[29]及其类似物46 ~51[24,30,31,32],这些化合物的五元内酯环均由17-羧基与2-OH缩合而成,十四元环上3个甲基烯丙位是发生功能集团取代的重要位置,其中化合物46 具有3,4-环氧结构,化合物47及48含均有7,8-邻二醇,化合物49及50在C-11及C-12分别有过氧基取代,其绝对构型通过单晶X-衍射和CD法得到确定,而化合物51的C-7位则出现了羰基取代。之前的研究表明,谷氨酸盐可导致皮质神经元细胞的凋亡[33],而化合物46在 体外生物活性筛选实验显示不仅可抑制谷氨酸盐诱导的神经元细胞内Ca2+浓度升高,而且在预培养期可诱导抗细胞凋亡因子bcl-2的表达,因而对神经元细胞具有保护作用,可作为治疗神经紊乱性疾病的潜在药物[30];化合物50及51不但对细胞色素P450 1A有显著抑制作用(IC50值分别为2.7和3.7 nmol/L),而且对谷胱甘肽S-转移酶、醌还原酶也有显著的诱导作用,故具有一定的抗癌活性[32]。从软珊瑚S. crassocaule中分离得到化合物crassocolides A~P (52~67) [34,35,36]、sarcocrassocolides A~O (68~82)[37,38,,39]以及类似物83~86[40,41];化合物功能集团取代也主要发生在十四元环上3个甲基烯丙位或氧化成环氧,如化合物56、57、63~65及73~86,或进一步氧化开环形成邻二醇衍生物,如化合物52~55及58~61等,化合物68~71则在C-4及C-7间形成了少见的分子内醚键;其中化合物86的绝对构型是通过单晶X-衍射来确定的,此后,其他结构类似物在此基础上得以确定。在体外生物活性筛选实验中,化合物52、55和57对癌细胞HepG2、MCF7、MDA-MB-231和A-549有不同程度的抑制作用[34],化合物60~ 62 对癌细胞KB、HeLa和Daoy表现为不同程度的细胞毒性,而化合物59、63、66和67仅对癌细胞Daoy有不同程度的细胞毒性[35,36],83~86对癌细胞P-388有显著的细胞毒性[40 ,41],而68~71和73~82则有显著的抗炎活性,表现为抑制iNOS蛋白的表达从而抑制LPS去刺激巨噬细胞RAW264.7[37,38,39]。从澳大利亚珊瑚S.cherbonnieri中分离得到的化合物87和88均具有20-羧基甲酯结构,其中化合物88对癌细胞HM02、HepG2和MCF7有不同程度的抑制作用[26]。从埃及软珊瑚S. trocheliophorum中分离得到化合物化合物89~91,其中化合物89和91为7,8-邻二醇衍生物[42,43]。从中国南海软珊瑚S. ehrenbergi及S. elegans分离得到化合物 92 ~94,其中化合物 93 可抑制人巨细胞病毒活性[9,10],而化合物94具有抑制人类卵巢肿瘤细胞A2780的作用[44]。从中国海南软珊瑚S. latum及S. stolidotum中发现了isosarcophytonolide D (95)[45]、sarcophytonolides E~L (96~103) [46,47]及sarcostolides A~G (104~110),其五元内酯环均由18-羧基与2-OH缩合而成,化合物104~110中还含有3,13-二酮结构。化合物99的相对构型由波谱学分析得到解决,其绝对构型通过Mosher法进行了确定;类似物96~98的绝对构型也因此得以确定。体外活性筛选实验中 108 对人的WiDr和Daoy肿瘤细胞显示弱细胞毒性[48]。从中国南海软珊瑚S. infundibuliforme中分离得到的化合物sarcolactone A (111)具有20-羧基与10-OH形成的五元内酯结构,体外显示一定的海虾致死作用和防污浊功能[49]。最后,从5种未鉴定种的肉芝软珊瑚属珊瑚中分离得到一系列具有五元内酯结构的化合物112~118[15,28,50,51,52],其中化合物117和118中的C-19与6-OH形成的γ-丁内酯是西松烷二萜中极为罕见的内酯结构。
 |
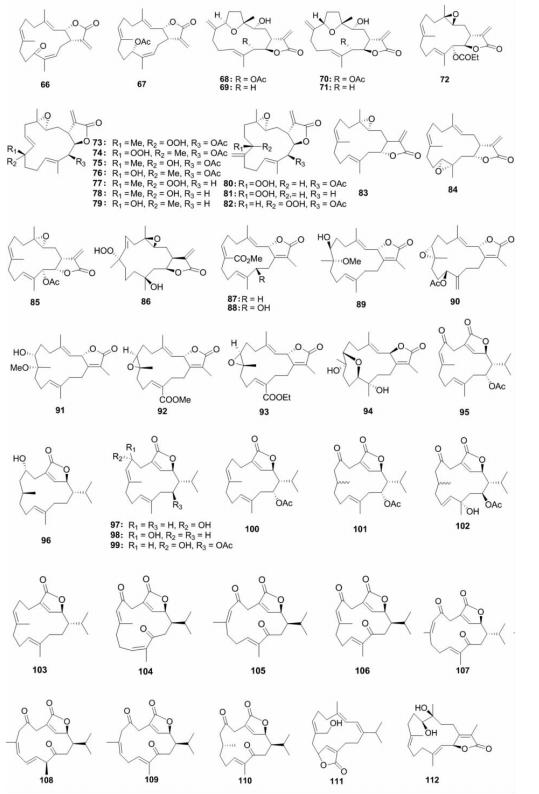 |
 |
已发现的七元内酯环型西松烷二萜的内酯结构均由20-羧基与8-OH缩合而成,结构变化主要来自C-1~C-7及C-18、C-19的氧化状态不同,包括环氧化、羟化、羧化及双键的位置、构型不同等。这类化合物数目相对较少,共从3种珊瑚中分离得到11个化合物,其中9个来自中国海南软珊瑚S. crassocaule[sarcrassins D和E (119和120)][53]及S. trocheliophorum Marenzeller[sartrolides A~G (121~127)][54],另外2个类似物(128和129)由未鉴定种的澳大利亚肉芝软珊瑚中分离得到。化合物128和129对癌细胞KB有细胞毒性[19]。
 |
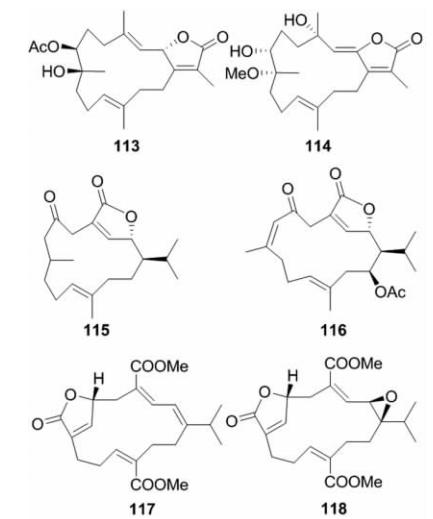
二聚西松烷二萜是自然界中一类罕见的西松烷二萜类化合物,仅发现于软珊瑚中。除sinulochmodin A由2分子西松烷二萜通过光自由基反应形成外,肉芝软珊瑚属珊瑚中的其他二聚西松烷型二萜均由2分子二萜通过Diels-Alder反应聚合而成。不仅骨架新颖、结构复杂而且具有显著的生物学活性,尤其表现为抗炎、抗肿瘤等。郭跃伟小组[6]已对二聚西松烷型二萜化合物的化学和生物活性已做了详细的总结(1986-2013年),从4个不同地域的4种肉芝软珊瑚属珊瑚中共发现的37个化合物,其中多数发现于1998年以后,共有35个化合物。
除上述西松烷二萜及其二聚体外,从肉芝软珊瑚中还发现有8种骨架类型的二萜,除Lobane型骨架外,其余7类在生源上均认为是在西松烷型结构基础上转化而来。
第一类是由西松烷二萜通过4,13-及5,10-位环合而成的三环骨架结构二萜,包括从印度洋软珊瑚S. elegans中分离得到的化合物sarcophytin (130)及类似物131~133,其中化合物130通过单晶X-衍射及相关波谱学数据分析确定其绝对构型,131~133的绝对构型则在130结构基础上得到确定[55,56,57]。
第二类Capnosane型二萜是由3,7-位相连形成五元与十一元环骈合的骨架结构,3个化合物sarcophyolides B~D (134~136)均从我国南海软珊瑚S. elegans中分离得到,其中化合物134具有抑制人卵巢癌细胞A2780的作用,其绝对构型是在波谱学研究的基础上由Mosher方法得到确定,类似物 135 和136的绝对构型也因此得以确定[44]。
第三类是由异丙基17-甲基与C-3位相连与原有的十四元环形成骈合五元环,这类化合物只有1个(ehrenbergol A, 137 ),是由台湾软珊瑚S. ehrenbergi中分离得到,体外对人巨细胞病毒显示抗病毒作用,其EC50 值为20 μg/mL[11];该类骨架首次发现于软珊瑚Lobophytum crassum中,其绝对构型通过改进的Mosher方法得以确定[58]。
从日本肉芝软珊瑚S. acutangulum中分离得到sartol acetate B (138)代表了第四类化合物骨架,是西松烷二萜位于十四元环C-11、C-12的环氧基团重排缩环形成十三元环结构,此类化合物的绝对构型是通过对其溴代苯衍生物的单晶X-衍射实验得以确定[59]。
第五及第六类骨架的sarcofuranocembrenolides A和B (139和140)都是从未鉴定种的印尼软珊瑚中分离得到的化合物, 化合物139可能是在19-甲基处形成3-羟基-2-丁酮或频哪醇重排后脱乙酰氧基形成的十三元环结构,而140的20-甲基则从原来的C-12位迁移到C-10位并与8-OH缩合成酯[60]。
 |
第七类是最近报道的化合物methyl sarcotroates A和B (141和142),由我国海南软珊瑚S. trocheliophorum中分离得到,化合物通过分子内[2+2]环加成形成了罕见的4元环结构,其绝对构型由ECD/TDDFT方法成功得以确定;化合物142对酪氨酸磷酸酯酶1B有显著的抑制作用[18]。
化合物carbomethoxyfuscol (143)是唯一一个Lobane型骨架的二萜,从马达加斯加西北部未鉴定种的肉芝软珊瑚中分离得到[61]。
肉芝软珊瑚属珊瑚中的次级代谢产物二萜类化合物数量丰富、结构多变,新化合物及新骨架不断地从中被分离鉴定。据统计,1970-1999年共19年间,从肉芝软珊瑚中分离得到的西松烷二萜化合物有近90个[3],而1998-2013年共15年间分离得到西松烷型二萜近170个,这些化合物在抗肿瘤、抗炎、抗菌等方面表现出多种生物活性。其中五元内酯环类二萜化合物在此方面活性尤为突出,部分化合物显示显著的抗病毒、抗氧化、诱导酶活性、抑制蛋白表达等活性,这不但为有机化学提供了很好的模式分子,而且对新药先导化合物的发现具有重要意义。随着多学科、多领域的合作交流以及研究的深入,相信这一珍贵生物资源会得到有效保护及合理研究开发,以期为人类的健康事业做出应有的贡献。
所有作者声明本文不涉及任何利益冲突。
| [1] | 黄宗国.中国海洋生物种类与分布[M].北京: 海军出版社, 2008:320-325. |
| [2] | Aratake S, Tomura T, Saitoh S, Yokokura R, Kawanishi Y, Shinjo R, et al.Soft coral Sarcophyton (Cnidaria:Anthozoa:Octocorallia) species diversity and chemotypes[J].PloS one, 2012, 7:e30410. |
| [3] | Liang X T, Fang W S.Medical chemistry of bioactive natural products[M].Hoboken:John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2006:257-300. |
| [4] | Ne'eman I, Fishelson L, Kashman Y.Sarcophine.New toxin from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum (Alcyonaria)[J].Toxicon, 1974, 12:593-598. |
| [5] | Anjaneyulu A S R, Rao G V.Chemical constituents of the soft coral species of Sarcophyton genus:a review[J]. J Indian Chem Soc, 1997, 74:272-278. |
| [6] | 李玉芬, 梁林富, 萧 伟, 梁敬钰, 郭跃伟, 等.肉芝软珊瑚属中二聚西松烷型二萜化合物的化学和生物活性研究进展[J].有机化学, 2013, 33:1157-1166. |
| [7] | Dauben W G, Thiessen W E, Resnich P R.Cembrene, a 14-membered ring diterpene hydrocarbon[J].J Am Chem Soc, 1962, 84:2015-2016. |
| [8] | Knig G M, Wright A D.New cembranoid diterpenes from the soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi[J].J Nat Prod, 1998, 61:494-496. |
| [9] | Cheng S Y, Wang S K, Chiou S F, Hsu C H, Dai C F, Chiang M Y, et al.Cembranoids from the octocoral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi[J].J Nat Prod, 2010, 73:197-203. |
| [10] | Wang S K, Hsieh M K, Duh C Y.Three new cembranoids from the Taiwanese soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi[J].Mar Drugs, 2012, 10:1433-1444. |
| [11] | Wang S K, Hsieg M K, Duh C Y.New diterpenoids from soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi[J].Mar Drugs, 2013, 11:4318-4327. |
| [12] | Iwagawa T, Nakashima R, Takayama K, Okamura H, Nakatani M, Doe M, et al.New cembranes from the soft coral Sarcophyton species[J]. J Nat Prod, 1999, 62:1046-1049. |
| [13] | Mada K, Ooi T, Kusumi T.NMR study of acutanol, a new cembrene alcohol, and sarcophytol A isolated from the soft coral Sarcophyton acutangulum[J].Spectroscopy, 2001, 15:177-182. |
| [14] | Phamn B, Butler M S, Quinn R J.Naturally occurring cembranes from an Australian Sarcophyton species[J].J Nat Prod, 2002, 65:1147-1150. |
| [15] | Jia R, Guo Y W, Mollo E, Mollo E, Cimino G.Sarcophytonolides A-D, Four new cembranolides from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton sp[J].Helv Chim Acta, 2005, 88:1028-1033. |
| [16] | Yan X H, Feng L Y, Guo Y W.Further new cembrane diterpenes from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton latum[J].Chin J Chem, 2008, 26:150-152. |
| [17] | Yao L G, Zhang H Y, Liang L F, Guo X J, Mao S C, Guo Y W.Yalongenes A and B, Two new cembranoids with cytoprotective effects from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum Marenzeller[J].Helv Chim Acta, 2012, 95:235-239. |
| [18] | Liang L F, Kurtn T, Mndi A, Yao L G, Li J, Zhang W, et al.Unprecedented diterpenoids as a PTP1B inhibitor from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum Marenzeller[J].Org Lett, 2013, 15:274-277. |
| [19] | Zang C X, Li J, Su J Y, Ling Y J, Yang X P, Zheng K C, et al.Cytotoxic diterpenoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule[J].J Nat Prod, 2006, 69:1476-1480. |
| [20] | Bishara A, Rudi A, Benayhu Y, Kashman Y.Three biscembranoids and their monomeric counterpart cembranoid, a biogenetic Diels Alder precursor, from the soft coral Sarcophyton elegans[J].J Nat Prod, 2007, 70:1951-1954. |
| [21] | Bensemhoum J, Rudi A, Bombarda I, Gaydou E M, Kashman Y, Aknin M.Flexusines A and B and epimukulol from the soft coral Sarcophyton flexuosum[J].J Nat Prod, 2008, 71:1262-1264. |
| [22] | Cuong N X, Tuan T A, Kiem P V, Minh C V, Choi E M, Kim Y H.New cembranoid diterpenes from the Vietnamese soft coral Sarcophyton mililatensis stimulate osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells[J].Chem Pharm Bull, 2008, 56:988-992. |
| [23] | Zhang C X, He X X, Zang J, Guo Q, Lei L F, Su J Y, et al.New precursor of tetraterpenoids from the soft coral Sarphyton glaucum[J].Nat Prod Res, 2013, 27:782-786. |
| [24] | Yao L G, Liu H L, Guo Y W, Mollo E.New cembranoids from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum[J].Helv Chim Acta, 2009, 92:1085-1091. |
| [25] | El-Ezz R F A, Ahmed S A, Radwan M M, Ayoub N A, Afifi M S, Ross S A, et al.Bioactive cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum[J].Tetrahedron Lett, 2013, 54:989-992. |
| [26] | Gross H, Kehraus S, Nett M, Knig G M, Beil W, Wright A D.New cytotoxic cembrane based diterpenes from the soft corals Sarcophyton cherbonnieri and Nephthea sp[J].Org Biomol Chem, 2003, 1:944-949. |
| [27] | Chen S P, Chen B W, Dai C F, Sung P J, Wu Y C, Sheu J H.Sarcophytonins F and G, new dihydrofuranocembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton sp[J].Bull Chem Soc Jpn, 2012, 85:920-922. |
| [28] | Daniela G, Shaker K H, Soliman H S M, Hegazi M M, Seifert K.Cembranoid diterpenes from the soft corals Sarcophyton sp.and Sarcophyton glaucum[J].Nat Prod Commun, 2008, 3:1473-1478. |
| [29] | Feller M, Rudi A, Berer N, Glidberg I, Stein Z, Benayahu Y, et al.Isoprenoids of the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum:nyalolide, a new biscembranoid, and other terpenoids[J].J Nat Prod, 2004, 67:1303-1308. |
| [30] | Badria F A, Guiriguis A N, Perovic S, Steffen R, MÜller W E G, Schrder H C.Sarcophytolide:a new neuroprotective compound from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum[J].Toxicology, 1998, 131:133-143. |
| [31] | Hegazy M E F, Ei-Beih A A, Moustafa A Y, Hamdy A A, Alhammady M A, Selim R M, et al.Cytotoxic cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum[J].Nat Prod Commun, 2011, 6:1809-1812. |
| [32] | Hegazy M E F, Eldeen A M G, Shahat A A, Abdel-Latif F F, Mohamed T A, Whittlesry B R, et al.Bioactive hydroperoxyl cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum[J].Mar Drugs, 2012, 10:209-222. |
| [33] | Kure S, Tominaga T, Yoshimoto T, Tada K, Naridawa K.Glutamate triggers internucleosomal DNA cleavage in neuronal cells[J].Biochim Biophys Res Commun, 1991, 179:39-45. |
| [34] | Huang H C, Ahmed A F, Su J H, Chao C H, Wu Y C, Micheal Y C, et al.Crassocolides A-F, cembranoids with a trans-fused lactone from the soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule[J].J Nat Prod, 2006, 69:1554-1559. |
| [35] | Huang H C, Chao C H, Kuo Y H, Sheu J H.Crassocolides G-M, cembranoids from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule[J].Chem Biodivers, 2009, 6:1232-1242. |
| [36] | Wang G H, Huang H C, Su J H, Huang C Y, Hsu C H, Kou Y H, et al.Crassocolides N-P, three cembranoids from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2011, 21:7201-7204. |
| [37] | Lin W Y, Su J H, Wen Z H, Dai C F, Kou Y H, et al.Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule[J].Bioorg Med Chem, 2010, 18:1936-1941. |
| [38] | Lin W Y, Su J H, Wen Z H, Dai C F, Kou Y H, et al.Bioactive cembranoids from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule[J].Mar Drugs, 2011, 9:994-1006. |
| [39] | Lin W Y, Lu Y, Chen B W, Huang C Y, Su J H, Wen Z H, et al.Sarcocrassocolides M-O, bioactive cembranoids from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule[J].Mar Drugs, 2012, 10:617-626. |
| [40] | Duh C Y, Wang S K, Chung S G, Chou G C, Dai C F.Cytotoxic cembrenolides and steroids from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule[J].J Nat Prod, 2000, 63:1634-1637. |
| [41] | Xu X H, Kong C H, Lin C J, Wang X, Zhu Y D, Yang H S.A novel diterpenoid from the soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule[J].Chin J Chem, 2003, 21:1506-1509. |
| [42] | Grote D, Soliman H S M, Shaker K H, Mohamed H, Seifert K.Cembranoid diterpenes and a briarane diterpene from corals[J].Nat Prod Res, 2006, 20:285-291. |
| [43] | Hegazy M E F, Mohamed T A, Abdel-Latif F F, Alsaid M S, Shahat A A, Par P W.Trochelioid A and B, new cembranoid diterpenes from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum[J].Phytochemistry Lett, 2013, 6:383-386. |
| [44] | Xi Z F, Bie W, Chen W, Liu D, Ofwegen L V, Proksch P, et al.Sarcophyolides B-E, new cembranoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton elegans[J].Mar Drugs, 2013, 11:3186-3196. |
| [45] | Yan X H, Gavagnin M, Cimino G, Guo Y W.Two new biscembranes with unprecedented carbon skeleton and their probable biogenetic precursor from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton latum[J].Tetrahedron Lett, 2007, 48:5313-5316. |
| [46] | Jia R, Guo Y W, Mollo E, Gavagnin M, Cimino G.Sarcophytonolides E-H, cembranolides from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton latum[J].J Nat Prod, 2006, 69, 819-822. |
| [47] | Yan X H, Li Z Y, Guo Y W.Further new cembranoid diterpenes from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton latum[J].Helv Chim Acta, 2007, 90:1574-1580. |
| [48] | Cheng Y B, Shen Y C, Kuo Y H, Khalil A T.Cembrane diterpenoids from the Taiwanese soft coral Sarcophyton stolidotum[J].J Nat Prod, 2008, 71:1141-1145. |
| [49] | Sun X P, Wang C Y, Shao C L, Li L, Li X B, Chen M, et al.Chemical constituents of the soft coral Sarcophyton infundibuliforme from the South China Sea[J].Nat Prod Commun, 2010, 5:1171-1174. |
| [50] | 马祥全, 闫素君, 苏镜娱, 曾陇梅.软珊瑚Sarcophyton sp.中一个新的西松烷二萜内酯的分离及结构测定[J].高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25:479-481. |
| [51] | Bie W, Deng Z W, Xu M J, Lin W H.Structural elucidation of a new cembranoid diterpene from the Chinese soft coral Sarcophyton sp[J].J Chin Pharm Sci, 2008, 17:221-224. |
| [52] | Longeon A, Bourguet-Kondracki M L, Guyot M.Two new cembrane diterpenes from a Madagascan soft coral of the genus Sarcophyton[J].Tetrahedron Lett, 2002, 43:5937-5939. |
| [53] | Gross H, Wright A D, Bei W, Knig G M.Two new bicyclic cembranolides from a new Sarcophyton species and determination of the absolute configuration of sarcoglaucol-16-one[J].Org Biomol Chem, 2004, 2:1133-1138. |
| [54] | Liang L F, Lan L F, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Guo Y W.Sartrolides A-G and bissartrolide, new cembranolides from the South China Sea soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum Marenzeller[J].Tetrahedron, 2013, 69:7381-7386. |
| [55] | Anjaneyulu A S R, Venugopal M J R V, Sarada P, Rao G V, Clardy J, Lobkovshy E.Sarcophyton, a novel tetracycline diterpenoid from the Indian Ocean soft coral Sarcophyton elegans[J].Tetrahedron Lett, 1998, 39:135-138. |
| [56] | Anjaneyulu A S R, Mangala G P, Murthy M V K.Δ7(15)-Dehydrosarcophytin, a new diterpenoid from the soft coral Sarcophyton elegans of the Indian Ocean[J].Indian J Chem, 1998, 37B:1090-1091. |
| [57] | Anjaneyulu V, Makarieva T, Ilyin S G, Dmitrenok A S, Rashika P, Subbarao P V, et al.Two new diterpenoids, sarcophytins B and C, from the Indian Ocean soft coral Sarcophyton species[J].J Nat Prod, 2000, 63:109-111. |
| [58] | Lin S T, Wang S K, Cheng S W, Duh C Y.Lobocrasol, a new diterpenoid from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum[J].Org Lett, 2009, 11:3012-3014. |
| [59] | Iwagawa T, Nakamura S, Masuda T, Okamura H, Nakatani M, Siro M.Irregular cembranoids containing a 13-membered carbocyclic skeleton isolated from a soft coral, Sarcophyton species[J].Tetrahedron, 1995, 51:5291-5298. |
| [60] | Kapojos M M, Lee J S, Oda T, Nakazawa T, Takahashi O, Ukai K, et al.Two unprecedented cembrene-type terpenes from an Indonesian soft coral Sarcophyton sp[J].Tetrahedron, 2010, 66:641-645. |
| [61] | Bonnard I, Jhaumeer-Laullo S B, Bontemps N, Banaigs B, Aknin M.New lobane and cembrane diterpenes from two Comorian soft corals[J].Mar Drugs, 2010, 8:359-372. |
 2014, Vol. 35
2014, Vol. 35


