文章信息
- 周宁, 杜祥博, 杨莉, 许怡, 孙博, 张琪, 戴二黑, 颜贤忠, 董方霆
- ZHOU Ning, DU Xiang-bo, YANG Li, XU Yi, SUN Bo, ZHANG Qi, DAI Er-hei, YAN Xian-zhong, DONG Fang-ting
- 不同病程的结核病患者的血浆代谢组学研究
- Plasma Metabonomics in Tuberculosis Patients at Different Stages
- 波谱学杂志, 2016, 33(2): 224-235
- Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 2016, 33(2): 224-235
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11938/cjmr20160205
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2016-01-04
修订日期: 2016-04-08


DOI:10.11938/cjmr20160205
2. 石家庄市第五医院 检验科, 河北 石家庄 050021

 , DONG Fang-ting1
, DONG Fang-ting1

2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shijiazhuang Fifth Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050021, China
结核病(tuberculosis,TB)是由结核杆菌(Mycobacterium tuberculosis,MTB)感染引起的慢性呼吸道传染病,也是第二大由单一病原菌感染引起的致死性疾病,致死率仅次于艾滋病[1].根据世界卫生组织(world health organization,WHO)的统计,2012年全球约有860万例TB患者和130万例TB死亡者,在发展中国家尤其严重.近年来,由于人口的急速增长和不断流动,以及多重耐药和广泛耐药型结核菌的出现,使得已趋于平缓的TB发病率又出现了回升的趋势,给TB病情控制带来了新的挑战[2].正确诊断是TB控制的重要环节.目前TB诊断的金标准是分支杆菌培养法,依靠检测MTB是否呈现阳性来判断是否感染,但MTB生长缓慢,耗时长且检出阳性率低,该法还需要辅助临床症状、胸部影像以及其它方法进行确认.血清学也可用于TB检测,而且诊断操作简单,但是其检测试剂的敏感性与特异性均有待提高[3].结核菌素皮肤试验(tuberculin skin test,TST)是结核病诊断常用的参考指标,但该法易受多种因素的影响,人群实验显示其假阳率极高[4].g-干扰素释放试验(interferon-gamma release assays,IGRA)是通过检测g-干扰素和效应T细胞的含量来判断是否存在MTB感染的检测方法,但由于实验材料与设备要求较高、成本较高,限制了其在发展中国家的应用[5].近几年发展起来的分子生物学诊断技术如聚合酶链反应(polymerose chain reaction,PCR)、DNA探针技术、DNA序列测定、基因芯片技术等也因操作要求较高、价格昂贵等问题使其使用受到限制[6].在TB发病率较高的地区,特别是发展中国家,约有40%的患者不能被正确诊断,误诊、漏诊以及延迟诊断都会造成更高的传染率与死亡率.因此,准确、敏感、特异、快速的早期鉴别与诊断对控制病菌感染、减少传播机会、抑制TB流行具有非常重要的意义.
后基因组时代发展起来的各种“组学”技术为人类认识从生物表型到各种内源性分子及其功能的发展提供了一个全局性的新角度.TB引起的系统性变化不仅反映在结核杆菌感染的部位,全身代谢也发生了变化.目前,已有很多报道应用基因组学、蛋白质组学技术对MTB以及TB进行了研究.例如结核分枝杆菌菌株H37Rv的全基因组测序工作已完成[7],载脂蛋白CⅡ、视黄醇结合蛋白4等一系列差异蛋白也陆续被发现[8-10].与基因组学和蛋白质组学不同,代谢组学揭示的小分子代谢变化是一系列生命活动的终端,直接反映生命活动的最终状态[11].疾病发展过程的各个阶段病理生理的变化都可由代谢变化反映出来,代谢组学可以根据这些变化筛选出相关的生物标志物,还可以在疾病早期就检测到代谢物含量的改变,借以揭示疾病发生发展过程中的代谢变化机制,为进一步探索疾病治疗靶点提供有用的信息.目前已有一些有关MTB的代谢组研究报道[12-17],也有几篇针对TB病人的代谢组学研究[18-22],发现了TB病人体内存在着各种代谢途径紊乱,并发现了氨基酸、有机酸、酮体等各种差异代谢物,但是目前还没有针对TB患者病情发展过程中代谢变化的研究.
本文采用基于核磁共振氢谱(1H NMR)的代谢组学技术研究了不同病程的TB患者与健康志愿者血浆代谢谱的差异,对TB发生发展过程中的代谢变化进行了研究,以寻找与病情进展阶段相关的差异代谢物,进一步探讨了相关的代谢紊乱机制,为TB早期诊断和筛查提供有用的信息.
1 实验部分 1.1 仪器及试剂Varian Unity INOVA 600型超导脉冲傅里叶变换NMR谱仪购自美国Varian公司.用于定标的2,2,3,3-氘代三甲基甲硅烷基丙酸钠(TSP)购自加拿大Merck公司,用于提供锁场频率信号的重水(D2O,99.8%氘代)购自美国Norell公司.
1.2 样品收集与制备选取就诊的TB患者64例,以及年龄无显著性差异(p>0.05)的健康志愿者23例作为对照组(CON).对TB患者做IGRA和TST检测,根据试验结果采用我国的通用标准[23]将TB患者分为4组,具体分组资料如表 1所示.抽取TB患者与健康志愿者血样置于EDTA抗凝管中获得血浆样品,置于-80 ℃冰箱保存.由于血浆中含有大分子蛋白等物质,我们在样品制备时用氯仿和甲醇对样品进行提取分离,以去除对谱峰有干扰的大分子信号,具体操作如下:取出300 mL解冻后的血浆样品与600 mL甲醇和600 mL氯仿混合;加入300 mL去离子水,并离心15 min(4 000 rpm)使其分层;取上层提取相用温和氮气吹干;再依次加入350 mL D2O、200 mL磷酸盐缓冲液(pH 7.4,0.2 mol/L)和50 mL TSP(1 mg/mL),振荡使其溶解;以13 000 rpm离心10 min;取上清580 mL到5 mm NMR样品管中待测.
| 组别 | 样本量 | IGRA | TST | 年龄 | 性别(男/女) |
| CON | 23 | 阴性(-) | 阴性(-);<5 mm | 40.3±13.3 | 8/15 |
| TB1 | 10 | 阴性(-) | 弱阳性(+);5~9 mm | 34.6±9.3 | 2/8 |
| TB2 | 11 | 阳性(+) | 弱阳性(+);5~9 mm | 35.1±11.5 | 9/2 |
| TB3 | 20 | 阳性(+) | 中度阳性(++);10~19 mm | 33.5±16.2 | 11/9 |
| TB4 | 12 | 阳性(+) | 强阳性(+++);>20 mm | 30.7±12.6 | 8/4 |
| TST 中的数字表示结核菌素皮肤试验注射部位产生硬结平均直径的大小;年龄以平均值 (x ) ±标准差(SD)的方式来表示 | |||||
样品1H NMR谱图由Varian Unity INOVA 600型NMR谱仪在27 ℃下采得,采用Presat单脉冲序列,预饱和方式抑制水峰信号.实验主要参数为:谱宽为8 000 Hz,弛豫延迟时间为2 s,采样点数为64 k,累加次数为64.自由感应衰减(free induction decay,FID)信号经傅里叶变换转换为频域谱,谱线增宽因子为0.3 Hz.经相位调整、基线校正以及内标峰定标后,以1.2 Hz的宽度将d 0.4~4.4范围内的谱图进行分段积分,并将抗凝剂EDTA(d 2.54~2.59、d 2.69~2.73、d 3.07~3.28、d 3.59~3.64)及提取溶剂甲醇(d 3.34~3.37)信号排除.按每张谱的总积分强度为10 000进行归一化,将所得数据输出并转换成Excel文件.
1.4 数据处理与统计分析应用icoshift[24]对积分数据进行谱峰对齐处理.处理后的数据导入多元统计分析软件SIMCA-P+ V12.0(Umetrics AB,Sweden)进行模式识别分析,并采用七倍交叉验证法对模型进行验证.对数据进行偏最小二乘法判别分析(PLS-DA)及正交偏最小二乘法判别分析(OPLS-DA),其中R2与Q2分别反映模型的拟合情况和预测能力.采用置换试验以及CV-ANOVA结果检验模型是否有效.CON组与TB各组两两比较时,数据在单位方差(UV scaling)中心化预处理后进行OPLS-DA分析.然后应用基于Matlab R2008a软件(Math Works Inc.,USA)的脚本绘制出OPLS-DA的相关系数载荷图,用灰度图来显示--即用黑白渐进色条来表征代谢物对组间区分的贡献大小[25].谱峰方向代表该信号含量的增加或减少.用皮尔森相关系数(Pearson correlation coefficient)的绝对值|r|来判定代谢物对组间区分的贡献,|r|大于临界值表示该代谢物对组间分离有贡献,组间差异有统计学意义;|r|越大,在相关系数载荷图中该信号的颜色越深,对组间区分的贡献也越大[26].使用SPSS V17.0软件(SPSS Inc. USA)对5组数据进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),找出存在显著性差异(p<0.05)的代谢物.将同时满足相关性分析(|r|>临界值)和方差分析(p<0.05)条件的代谢物作为差异代谢物列表.
2 结果与讨论 2.1 1H NMR 谱图分析CON组与TB各组血浆样品的代表性1H NMR谱见图 1.参考人类代谢组数据库(human metabolome database,HMDB)以及本实验室代谢物标准谱库共鉴别出21个代谢物.从谱图可以看出从CON到TB4组,在病情发生发展的进程中,乳酸水平逐渐升高,N-乙酰糖蛋白、缬氨酸、亮氨酸和丙氨酸等代谢物在TB各组水平均高于CON组.详细的比较则有赖于多元统计分析的结果.
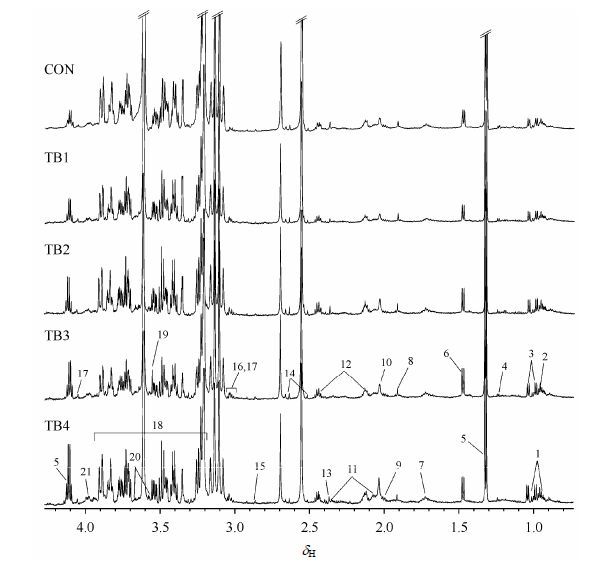
|
| 图1 健康CON组与TB各组血浆的代表性1H NMR谱图 Fig.1 Typical 1H NMR spectra of the plasma samples from health controls and TB patients |
为了分析各组间的细微代谢差别、发现差异代谢物,我们对数据进行了PLS-DA和OPLS-DA分析.图 2(a)显示了CON组与TB各组的PLS-DA模型的得分图,可以看出各组间虽显示了一定的分离趋势,但不是很明显.模型相应的置换试验验证图[图 2(b)]中R2回归线的截距值(0.066)不超过0.4,Q2回归线的截距值(-0.144)不超过0.05,R2与Q2模型左边的值均低于右边的初始值,证明模型不存在过度拟合,是有效的[27].由于临床样本受地域和饮食等多种因素的影响数据较为复杂,再加上样本分组较多,所以使得PLS-DA模型区分效果不显著,而OPLS-DA模型可以滤除无关组分,使组间差异更加明显.我们进一步采用OPLS-DA进行分析,其得分图[图 2(c)]显示各组呈现了较好的分离趋势,且CON组与TB组基本可以沿t[1]方向分开,而各TB组间也有一定的分离.通过CV-ANOVA分析所得的p值小于0.05,证明模型有效[28].

|
| 图2 健康CON组(°)与TB各组(TB1 ▲,TB2 ◆,TB3 ●,TB4 ■)的血浆1H NMR谱图数据分析.(a) PLS-DA模型得分图(p=0.01);(b) 置换检验图;(c) OPLS-DA模型得分图(p=0.04) Fig.2 Analysis of 1H NMR spectra for plasma from health controls (CON°) and TB patients (TB1 ▲, TB2 ◆, TB3 ●, TB4 ■).(a) PLS-DA score plot (p=0.01); (b) Validating plot of permutation test; (c) OPLS-DA score plot (p=0.04) |
箱形图可以更直观地呈现组间差异及组内变异,展现代谢物在各组间的变化趋势.各组代表性差异代谢物的箱形图见图 3,图中标注的p值为one-way ANOVA分析的结果:p<0.05表示该代谢物在组间差异具有统计学意义.由图 3可以看出,在疾病发生发展的进程中(CON→TB1→TB2→TB3→TB4),随着病情的加重,乳酸、丙酮酸、N-乙酰糖蛋白、亮氨酸和谷氨酸等代谢物基本呈逐渐增加的趋势;TCA循环的中间产物--柠檬酸基本呈逐渐降低的趋势.缬氨酸、丙氨酸、肌酸和3-羟基丁酸等代谢物虽没有呈现渐进性的变化,但在TB组与CON组之间产生差别,而且TB各组中含量普遍高于CON组.这些代谢物含量的变化均与疾病进程息息相关,可能承载着疾病发生发展以及疾病严重程度的相关信息.

|
| 图3 健康CON组与TB各组血浆的差异代谢物箱形图(one-way ANOVA) Fig.3 Boxplots of typical biomarkers between healthy controls and TB patients (one-way ANOVA) |
为了对CON组与TB组间的代谢情况更进一步的分析,寻找到TB病情发生发展过程中的差异代谢物,我们将TB各组与CON组分别进行两两比较分析.从图 4的OPLS-DA得分图可以看出TB各组与CON组均可明显分离,得分图结合相应的相关系数载荷图可以直观地反映代谢物在组间的变化趋势.可以看出从TB1到TB4病情由轻到重的过程中,对组间分离有统计学意义的信号(相关系数载荷图中颜色较深的信号)越来越多,表明随病情的发生发展,病人体内代谢紊乱越来越严重.相关分析(|r|>临界值)结合统计分析ANOVA(p<0.05)找到的差异代谢物见表 2.可以看出,与CON组相比,在TB组病情由轻到重(TB1→TB4)的进程中,多种代谢物含量发生显著性变化,且差异代谢物的数量也逐渐增多,主要表现为:与CON组相比,TB1组中1个代谢物含量变化(丙氨酸含量升高),TB2组中3个代谢物含量变化(3-羟基丁酸、缬氨酸、丙氨酸含量升高),TB3组中5个代谢物含量变化(乳酸、3-羟基丁酸、N-乙酰糖蛋白、缬氨酸、谷氨酸含量升高),TB4组中8个代谢物含量变化(乳酸、丙酮酸、肌酸、N-乙酰糖蛋白、亮氨酸、缬氨酸和谷氨酸含量升高,柠檬酸含量降低).

|
| 图4 健康CON组(°)与TB1(▲)、TB2(◆)、TB3(●)、TB4(■)各组血浆样品1H NMR谱图数据的OPLS-DA分析.左图为OPLS-DA得分图;右图为OPLS-DA相关系数载荷图 Fig.4 OPLS-DA results of 1H-NMR data of health controls (°) and TB patients TB1(▲),TB2(◆),TB3(●),TB4(■); left: cross-validated scores plots; right: coefficient-coded loadings plots |
| 代谢物 | TB1 vs. CON | TB2 vs. CON | TB3 vs. CON | TB4 vs. CON |
| |r|>0.602 | |r|>0.576 | |r|>0.433 | |r|>0.553 | |
| 乳酸 | +0.522** | +0.614** | ||
| 丙酮酸 | +0.556* | |||
| 肌酸 | +0.553* | |||
| 3-羟基丁酸 | +0.576* | +0.433* | ||
| N-乙酰糖蛋白 | +0.446* | +0.556* | ||
| 柠檬酸 | -0.571* | |||
| 缬氨酸 | +0.625* | +0.466* | +0.658* | |
| 亮氨酸 | +0.650** | |||
| 丙氨酸 | +0.632* | +0.580* | ||
| 谷氨酸 | +0.434* | +0.563* | ||
| + 表示与健康对照组相比,TB组相对含量较高;-表示与健康对照组相比,TB组相对含量较低.*表示采用ANOVA分析时,与健康对照组相比p<0.05,**表示表示采用ANOVA分析时,与健康对照组相比p<0.01 | ||||
研究结果显示,在TB发生发展的进程中,多种代谢物含量发生变化,涉及多条代谢通路.TB患者体内能量代谢、糖代谢、脂代谢和氨基酸代谢过程均发生紊乱;且在病情发生发展由轻到重的进程中(CON→TB1→TB2→TB3→TB4),代谢紊乱的情况也越来越严重.TB患者受结核杆菌感染诱发炎症反应,与炎症有关的血浆N-乙酰糖蛋白信号增强.TB是一种慢性消耗性疾病,机体能量需求增加导致脂解增强,脂肪酸生酮作用增强以提供能量,使得TB患者体内酮体(3-羟基丁酸)水平升高.TB患者血浆乳酸、丙酮酸含量的升高表明糖酵解作用的增强.TCA循环中间产物--柠檬酸含量的降低以及相关氨基酸(亮氨酸、缬氨酸)含量的升高暗示TCA循环受阻.氨基酸(缬氨酸、亮氨酸、丙氨酸、谷氨酸)含量的升高可能是由于蛋白质合成受阻造成,各种生糖氨基酸含量升高也表明糖异生途径受到抑制,氨基酸代谢途径发生紊乱.
能量代谢增强:肌酸可以通过合成ATP,维持体内ATP/ADP的平衡,给机体提供能量.我们的结果显示TB1、TB2和TB3各组内肌酸含量比CON组均略有升高,在TB4组升高明显.TB是一种慢性消耗性疾病,在TB病人体内能量需求增加的情况下,肌酸激酶会催化利用磷酸肌酸将ADP重新合成ATP的可逆反应[29].肌酸和它的磷酸形式被认为是能量代谢的关键中间体,肌酸含量的升高与能量代谢的增加有关.TCA循环是机体获得能量的关键环节,是糖、脂和氨基酸代谢联系的枢纽.我们的结果显示TCA循环的中间产物--柠檬酸在TB各组含量逐渐降低,在TB4组降低尤其明显,可能是在TB病情进展的过程中,由于机体长期慢性消耗能量,TCA循环提供的能量被消耗的越来越多,在病情最为严重的TB4组,能量被大量消耗,导致TCA循环中间体被大量消耗含量降低.之前也有研究[12, 15]发现柠檬酸、延胡索酸在结核杆菌感染的动物体内含量降低.丙酮酸是连接糖代谢、脂代谢和氨基酸代谢的中间产物,丙酮酸含量的升高也说明TB患者体内三大营养物质分解代谢增强以及能量 消耗的增加.
糖脂代谢紊乱:丙酮酸和乳酸分别是糖酵解的中间产物和终产物,由箱形图可以看出乳酸在TB1和TB2两组略有升高,在TB3和TB4两组明显升高;而丙酮酸在TB1、TB2和TB3组均略有升高,在TB4组明显升高,它们含量的增加以及葡萄糖含量的降低显示TB患者体内糖酵解的增强.结核杆菌感染的小鼠和豚鼠肺组织的相关研究[12, 13]也证实了糖酵解的增强.在TB患者以及结核杆菌感染的黄牛血清中也有同样的发现[15, 18, 21].已知结核分枝杆菌感染会诱发肺部肉芽肿性炎症与肺组织缺氧,而肺部损伤、组织缺氧和局部缺血均会导致无氧糖酵解的增强[30].我们的研究结果显示3-羟基丁酸在TB1组基本没有变化;在TB2~4组含量均比CON组要高,表明脂肪酸生酮作用增强.3-羟基丁酸与丙酮、乙酰乙酸盐合称酮体,是心脏和大脑能量的主要来源.脂肪酸通过生酮作用产生酮体,正常状态下酮体生产和利用达到一种稳态,当这种平衡被打破时,酮体含量即会升高.Zhou等人[21]的研究发现在TB病人血清中丙酮和乙酰乙酸盐含量升高,与我们的研究结果一致.另外,血浆N-乙酰糖蛋白信号的增强也与机体炎症和损伤有关[31],我们发现N-乙酰糖蛋白在TB各组均有所增加,说明TB各组均有不同程度的炎症存在.
氨基酸代谢紊乱:我们的研究结果显示在TB发生发展的过程中亮氨酸、丙氨酸、缬氨酸、谷氨酸含量升高,赖氨酸降低.氨基酸代谢非常复杂,涉及大量代谢通路,与蛋白质合成水解、糖异生、氨基酸的氧化分解等代谢过程均有关.支链氨基酸(缬氨酸、亮氨酸、异亮氨酸)以及丙氨酸是生糖氨基酸,游离氨基酸是蛋白质合成的前体物质,当糖异生被抑制或蛋白质合成受损时氨基酸的含量可能会升高,此时氨基酸不被蛋白质合成利用而是在受损的蛋白质合成过程中被氧化[32, 33].之前已经有研究[34]报道在患有TB和营养不良时,蛋白质被水解成氨基酸.流行病学研究[35]已经显示TB病人常伴有营养失调、体重降低以及代谢紊乱.能量消耗的增加、糖脂代谢紊乱、糖异生被抑制以及蛋白质合成受阻均会导致病人营养失调、体重降低等症状.有研究[36]显示谷氨酰胺/谷氨酸的比例是体重减轻的一个信号.我们的研究发现谷氨酰胺含量并没有太大变化,而谷氨酸含量在TB各组逐渐升高;在TB各组谷氨酰胺/谷氨酸的比例与CON组相比均有所降低,这与TB病人体重减轻的症状一致.
3 结论本研究利用基于1H NMR的代谢组学技术展示了TB病人血浆代谢组的改变,并对TB患者按病情轻重分组研究,找出了与病情进展阶段相关的差异代谢物,显示了TB病人体内包括能量代谢、糖代谢、脂代谢和氨基酸代谢等过程的紊乱.研究也显示了代谢组学技术在TB鉴别与诊断方面的优势,可以对结核杆菌感染的机体代谢情况进行全局性的研究,通过寻找相关的差异代谢物发现与疾病密切相关的异常代谢途径,并对TB病情进展的各个阶段代谢情况进行深入研究,有利于TB的早期鉴别与诊断,对减少传染、疾病控制以及探索新诊断与疗效评估新标志物等方面都有着非常重要的意义.
| [1] | Lawn S D, Zumla A I. Tuberculosis[J]. Lancet, 2011, 378(9785):57–72. |
| [2] | McNerney R, Maeurer M, Abubakar I, et al. Tuberculosis diagnostics and biomarkers:Needs, challenges, recent advances, and opportunities[J]. J Infect Dis, 2012, 205(Suppl 2):S147–S158. |
| [3] | Dowdy D W, Steingart K F, Pai M. Serological testing versus other strategies for diagnosis of active tuberculosis in India:A cost-effectiveness analysis[J]. PLoS Med, 2011, 8(8):e1001074. |
| [4] | Pai M, Zwerling A, Menzies D. Systematic review:T-cell-based assays for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection:an update[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2008, 149(3):177–184. |
| [5] | Brosch R, Vincent V. Cutting-edge science and the future of tuberculosis control[J]. Bull World Health Organ, 2007, 85(5):410–412. |
| [6] | Katoch V M. Newer diagnostic techniques for tuberculosis[J]. Indian J Med Res, 2004, 120(4):418–428. |
| [7] | Cole S T, Brosch R, Parkhill J, et al. Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence[J]. Nature, 1998, 393(6685):537–544. |
| [8] | Zhang J, Wu X F, Shi L L, et al. Diagnostic serum proteomic analysis in patients with active tuberculosis[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2012, 413(9, 10):883–887. |
| [9] | Xu D D, Deng D F, Li X, et al. Discovery and identification of serum potential biomarkers for pulmonary tuberculosis using iTRAQ-coupled two-dimensional LC-MS/MS[J]. Proteomics, 2014, 14(2, 3):322–331. |
| [10] | Zhang C, Song X, Zhao Y, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis secreted proteins as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis and latent tuberculosis infection[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2015, 29(5):375–382. |
| [11] | German J B, Bauman D E, Burrin D G, et al. Metabolomics in the opening decade of the 21st century:Building the roads to individualized health[J]. J Nutr, 2004, 134(10):2729–2732. |
| [12] | Shin J H, Yang J Y, Jeon B Y, et al. 1H-NMR-based metabolomic profiling in mice infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J]. J Proteome Res, 2011, 10(5):2238–2247. |
| [13] | Somashekar B S, Amin A G, Rithner C D, et al. Metabolic profiling of lung granuloma in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected guinea pigs:ex vivo 1H magic angle spinning NMR studies[J]. J Proteome Res, 2011, 10(9):4186–4195. |
| [14] | Somashekar B S, Amin A G, Tripathi P, et al. Metabolomic signatures in guinea pigs infected with epidemic-associated W-Beijing strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J]. J Proteome Res, 2012, 11(10):4873–4884. |
| [15] | Chen Y, Wu J, Tu L, et al. 1H NMR spectroscopy revealed Mycobacterium tuberculosis caused abnormal serum metabolic profile of cattle[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9):e74507. |
| [16] | Baughn A D, Rhee K Y. Metabolomics of central carbon metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2014, 2(3):323–329. |
| [17] | Nandakumar M, Prosser G A, de Carvalho L P, et al. Metabolomics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2015, 1285:105–115. |
| [18] | Weiner J, Parida S K, Maertzdorf J, et al. Biomarkers of inflammation,immunosuppression and stress with active disease are revealed by metabolomic profiling of tuberculosis patients[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(7):e40221. |
| [19] | du Preez I, Loots D T. New sputum metabolite markers implicating adaptations of the host to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and vice versa[J]. Tuberculosis (Edinb), 2013, 93(3):330–337. |
| [20] | Che N, Cheng J, Li H, et al. Decreased serum 5-oxoproline in TB patients is associated with pathological damage of the lung[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2013, 423(23):5–9. |
| [21] | Zhou A, Ni J, Xu Z, et al. Application of 1H NMR spectroscopy-based metabolomics to sera of tuberculosis patients[J]. J Proteome Res, 2013, 12(10):4642–4649. |
| [22] | Lau S K, Lee K C, Curreem S O, et al. Metabolomic profiling of plasma from patients with tuberculosis by use of untargeted mass spectrometry reveals novel biomarkers for diagnosis[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2015, 53(12):3750–3759. |
| [23] | 张贺秋, 赵雁林. 现代结核病诊断技术[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013 . Zhang He-qiu, Zhao Yan-lin. Modern Tuberculosis Diagnosis Techniques[M]. Beijing: People's Medical PublishingHouse, 2013 . |
| [24] | Savorani F, Tomasi G, Engelsen S B. Icoshift:A versatile tool for the rapid alignment of 1D NMR spectra[J]. J Magn Reson, 2010, 202:190–202. |
| [25] | 陈璐, 宋侃, 王玉兰. 感染减毒鼠伤寒沙门氏菌对小鼠粪样代谢组的影响[J].波谱学杂志, 2014, 31 (3) : 349–363 . Chen Lu, Song Kan, Wang Yu-lan. Effects of attenuated salmonella typhimurium infection on fecal metabonome in mice[J].Chinese J Magn Reson, 2014, 31(3):349–363. |
| [26] | Jiang L M, Huang J, Wang Y L, et al. Metabonomic analysis reveals the CCl4-induced systems alterations for multiple rat organs[J]. J Proteome Res, 2012, 11(7):3848–3859. |
| [27] | Eriksson L, Johansson E, Kettaneh-Wold N, et al. Multi- and Megavariate Data Analysis[M]. New York: MKS Umetrics AB, 2006 . |
| [28] | Eriksson L, Trygg J, Wold S. CV-ANOVA for significance testing of PLS and OPLS® models[J]. J Chemometr, 2008, 22(11, 12):594–600. |
| [29] | Wallimann T, Tokarska-Schlattner M, Schlattner U. The creatine kinase system and pleiotropic effects of creatine[J]. Amino Acids, 2011, 40(5):1271–1296. |
| [30] | de Backer D. Lactic acidosis[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2003, 29(5):699–702. |
| [31] | Sun L, Hu W, Liu Q, et al. Metabonomics reveals plasma metabolic changes and inflammatory marker in polycystic ovary syndrome patients[J]. J Proteome Res, 2012, 11(5):2937–2946. |
| [32] | Macallan D C. Malnutrition in tuberculosis[J]. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis, 1999, 34(2):153–157. |
| [33] | Schwenk A, Macallan D C. Tuberculosis, malnutrition and wasting[J]. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, 2000, 3(4):285–291. |
| [34] | Macallan D C, McNurlan M A, Kurpad A V, et al. Whole body protein metabolism in human pulmonary tuberculosis and undernutrition:Evidence for anabolic block in tuberculosis[J]. Clin Sci (Lond), 1998, 94(3):321–331. |
| [35] | Blumenthal A, Isovski F, Rhee K Y. Tuberculosis and host metabolism:ancient associations, fresh insights[J]. Transl Res, 2009, 154(1):7–14. |
| [36] | Kinscherf R, Hack V, Fischbach T, et al. Low plasma glutamine in combination with high glutamate levels indicate risk for loss of body cell mass in healthy individuals:the effect of N-acetyl-cysteine[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 1996, 74(7):393–400. |
 2016, Vol. 33
2016, Vol. 33

