文章信息
- piR-9994对胃癌细胞增殖、迁移及侵袭的影响及其机制
- Effect of piR-9994 on Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells and Its Mechanism
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(10): 922-928
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2021, 48(10): 922-928
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.21.0468
- 收稿日期: 2021-04-23
- 修回日期: 2021-07-22
2. 350014 福州,福建医科大学附属肿瘤医院,福建省肿瘤医院病理科;
3. 350014 福州,福建省肿瘤转化医学重点实验室
2. Department of Pathology, Fujian Medical University Cancer Hospital, Fujian Cancer Hospital, Fuzhou 350014, China;
3. Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Translational Cancer Medicine, Fuzhou 350014, China
胃癌是常见的消化道恶性肿瘤之一,对人类健康构成重大威胁。中国是胃癌的高发地区,发病率和死亡率持续上升,并呈显著的年轻化趋势[1]。胃癌的发生发展、侵袭转移及凋亡等机制仍未阐明[2-3],亟需深入探索其生物学机制。由于多数胃癌被发现时已处于中晚期,失去手术机会,生存率低,预后差,因此寻求新的胃癌标志物及有效的生物治疗靶点是进一步改善胃癌预后的关键。
piRNA是一类新发现的非编码小RNA,长25~31 nt,因与PIWI蛋白结合故命名为piRNA。通过与PIWI蛋白相互作用而发挥作用,其与保持基因组稳定性、调节表观遗传学、生殖干细胞分化、胚胎发育和多种疾病的发生发展密切相关[4]。近年有关piRNA与肿瘤的相关性已成为研究热点[5]。前期有实验通过测序技术筛选到多个胃癌特异性piRNAs, piR-9994便为其中之一[6];piR-9994在胃癌组织中过表达,并与肿瘤分期和神经侵犯密切相关[7]。本实验检测piR-9994在胃癌细胞中的表达,通过细胞学实验明确其对胃癌细胞增殖、周期及侵袭的影响,探讨piR-9994与胃癌生物学机制的相关性。
1 材料与方法 1.1 细胞和主要试剂人胃癌细胞株MGC803和AGS购自国家实验细胞资源共享平台,正常人胃黏膜上皮细胞株GES-1购于中科院上海细胞库,HyClone DMEM/HIGH GLUCOSE培养基(美国GE公司),胎牛血清(FBS, 美国Gibco公司),RNeasy Mini Kit(德国Qiagen公司),PCNA、CCND1(CyclinD1)、Bcl-2、c-PARP、N-cadherin、MMP7、Twist、Vimentin、E-cadherin、β-actin、抗兔/鼠HRP标记的IgG抗体(美国Cell Signaling Technology公司)。Transwell小室(美国Millipore公司),MTT细胞增殖检测试剂MCE Thiazolyl Blue(美国Promega公司)。MiDETECTATrackTMmiRNA qRT-PCR Stater Kit、Pir-has-9994单链mimics和Pir-has-9994 inhibitor(广州市锐博生物科技有限公司)。MUSE cell cycle Kit(美国Millipore公司)。LipofectamineRnaiMax(美国Invitrogen公司)。
1.2 细胞培养和Pir-has-9994质粒感染将GES-1、AGS、MGC803细胞分别培养于包含10%FBS、100 u/ml青霉素和100 µg/ml链霉素的培养基中,放置在37℃和5%CO2的湿度环境培养箱中,2~3 d传代一次,所有实验均采用对数生长细胞。MGC803细胞以5×105个/孔接种于6孔板中,待每孔细胞培养至单层60%~80%,将3 μl待转染的质粒(150 μl无血清培养基稀释)和9 μl Lipofectamine转染试剂(150 μl无血清培养基稀释)混匀后逐滴加至每孔,轻摇混匀,培养48 h。通过瞬转技术利用空载质粒和过表达质粒建立对照的MGC803细胞株(MGC803/NC(过表达))和高表达piR-9994的MGC803细胞株(MGC803/piR-9994-OE),利用空载质粒和干扰质粒建立对照的MGC803细胞株(MGC803/NC(敲低))和低表达piR-9994的MGC803细胞株(MGC803/piR-9994-IN)。
1.3 实验方法 1.3.1 MTT法检测细胞增殖能力将MGC803细胞、MGC803/NC(过表达)细胞和MGC803/piR-9994-OE细胞/MGC803/NC(敲低)细胞和MGC803/piR-9994-IN细胞以5×103个/孔接种到96孔板中,各设3个复孔,共3个96孔板,分别培养24、48、72 h后,去掉上清液,加入2 mg/ml的MTT液50 μl,置于37℃和5%CO2的培养箱中孵育4 h,每孔加入150 μl的二甲基亚酚,振荡仪上振荡混匀,用仅含血清的DMEM/高葡萄糖200 μl培养液作为背景消减,用BIO-RADModel680检测490 nm的吸光度值。实验重复三次。
1.3.2 细胞划痕实验检测细胞迁移能力收集MGC803细胞、MGC803/NC(过表达)细胞和MGC803/piR-9994-OE细胞/MGC803/NC(敲低)细胞和MGC803/piR-9994-IN细胞以8×105个/孔接种到6孔板中,各设3个复孔,放置在37℃和5%CO2的培养箱中培养24 h,细胞单层铺满。用无菌的10 μl枪头沿着直尺在孔正中划一根从上到下的直线,去掉上清液及漂浮的细胞,用PBS洗涤细胞3次,拍照后,加入5 ml无血清培养基,置于37℃和5%CO2的培养箱中培养24 h,拍照。实验重复三次。
1.3.3 Transwell实验检测细胞侵袭能力把各组细胞浓度调整为8×105个/毫升,取100 µl接种于Transwell上室,下方用1 mg/ml的基质胶(美国Millipore公司)进行包被,下室用含30%FBS的培养基作为趋化吸引条件,将小室悬挂在24孔板中。置于37℃和5%CO2的培养箱中孵育48 h,上室细胞用棉签擦除,小室用甲醇固定15 min,用0.1%的结晶紫进行染色。随机选择5个视野进行观察,使用×200倒置显微镜下观察计数,确定各组细胞的平均数。实验重复三次。
1.3.4 细胞集落实验检测细胞增殖能力收集各组细胞以500个/孔接种到6孔板中,各设3个复孔,放置在37℃和5%CO2的培养箱中培养10~14天,期间根据培养液pH变化适时更换新鲜培养液,当出现肉眼可见克隆时,终止培养,弃去培养液,PBS液小心浸洗两次,晾干。甲醇固定15 min,弃甲醇后晾干。Giemsa染液染色10 min,用流水缓慢洗去染液,晾干,计数细胞集落个数。实验重复三次。
1.3.5 Western blot检测蛋白表达将细胞在冰上裂解,超声离心后取上清液,BCA法测定蛋白浓度,并进行聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳,湿法转印至硝酸纤维素膜上。2%BSA封闭1 h后分别加入1:1 000稀释的一抗4℃环境过夜,1×TBST洗涤3次,加入二抗封闭120 min,1×TBST洗涤3次后ECL发光试剂盒显色,凝胶成像系统照相,分析灰度值。
1.3.6 实时定量荧光PCR检测piR-9994含量检测GES-1、AGS、MGC803细胞、MGC803/NC(过表达)细胞和MGC803/piR-9994-OE细胞/ MGC803/NC(敲低)细胞和MGC803/piR-9994-IN细胞piR-9994含量。收集常规培养的对数生长期的细胞,提取细胞总RNA,反转录cDNA。利用荧光定量qRT-PCR(miDETECT A TrackTMmiRNA qRT-PCR Starter Kit试剂盒)进行检测,具体步骤简述如下:取2 µl cDNA进行qPCR扩增,扩增程序为:95℃ 10 min;95℃2 s,60℃ 20 s,70℃10 s,40个循环;进行熔解曲线检测。每个样本重复3次取平均值。以5S为内参基因。mRNA的相对定量用2-ΔΔCt法。piR-9994和5S引物购自广州锐博公司。
1.4 统计学方法采用SPSS17.0统计软件进行数据分析。配对资料的比较采用配对t检验;两组间比较先进行正态性检验及方差齐性分析,后进行两独立样本t检验。计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,两组之间均数比较采用t检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 qRT-PCR检测胃癌细胞系中piR-9994的表达情况及piR-9994过表达、敲低的MGC803细胞的构建结果显示piR-9994在MGC803和AGS细胞中的表达水平高于GES-1(P < 0.001),见图 1A。根据前期预实验结果,后续研究选择MGC803细胞系进行过表达/敲低实验。piR-9994在MGC803/piR-9994-OE表达水平显著高于MGC803/NC(过表达)(P < 0.001),见图 1B。piR-9994在MGC803/piR-9994-IN表达水平显著低于MGC803/NC(敲低)(P < 0.0001),见图 1C。以上结果表明MGC803/piR-9994-OE和MGC803/piR-9994-IN胃癌细胞株构建成功。
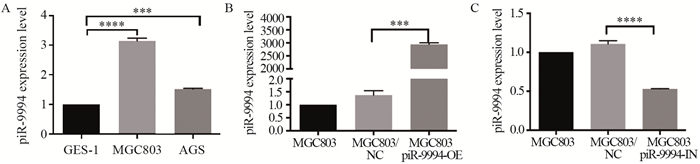
|
| A: qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of piR-9994 in normal gastric epithelial cells and gastric cancer cell lines; B, C: qRT-PCR was used to detect piR-9994 expression in constructed MGC803 cell lines with piR-9994 overexpression or knockdown; ***: P < 0.001, ****: P < 0.0001. 图 1 piR-9994在胃癌细胞系中的表达以及构建piR-9994过表达或敲除MGC803细胞株 Figure 1 Expression of piR-9994 in gastric cancer cell lines and construction of MGC803 cell line with piR-9994 overexpression or knockdown |
MTT结果显示,相比对照组MGC803/NC(过表达), MGC803/piR-9994-OE细胞的增殖能力增强(P < 0.01),见图 2A。细胞集落实验结果显示,MGC803/piR-9994-OE细胞形成集落数显著高于MGC803/NC(过表达)(32.78±2.75 vs. 70.56±4.92, P=0.0026),见图 2B。细胞划痕实验结果显示,MGC803/piR-9994-OE细胞迁移能力高于MGC803/NC(过表达),差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01),见图 2C~D。Transwell侵袭实验结果显示,MGC803/piR-9994-OE细胞迁移个数增加,明显高于MGC803/NC(过表达)(122.80±2.28 vs. 168.60±2.45, P=0.0002),见图 2E。以上结果表明,piR-9994过表达可促进胃癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和迁移。
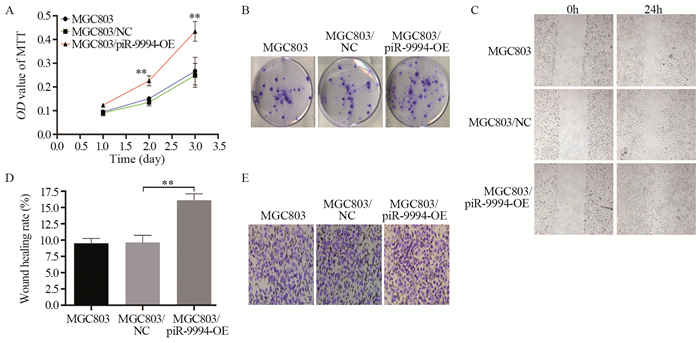
|
| A: effect of piR-9994 overexpression on the proliferation of MGC803 cells was determined by MTT assay; B: effect of piR-9994 overexpression on the proliferation of MGC803 cells was determined by colony formation method; C, D: effect of piR-9994 overexpression on migration ability of MGC803 cells was detected by scratch test; E: Transwell invasion assay was used to detect the effect of piR-9994 overexpression on the invasion ability of MGC803 cells; **: P < 0.01. 图 2 piR-9994过表达对MGC803细胞增殖生长和迁移侵袭的影响 Figure 2 Effect of piR-9994 overexpression on proliferation, migration and invasion of MGC803 cells |
MTT结果显示,相比对照组MGC803/NC(敲低),MGC803/piR-9994-IN细胞增殖能力显著减弱(P < 0.05),见图 3A。细胞集落实验结果显示,MGC803/piR-9994-IN细胞形成集落数低于MGC803/NC(敲低)(30.67±3.22 vs. 13.56±0.40, P=0.0062),见图 3B。细胞划痕实验结果显示,MGC803/piR-9994-IN细胞迁移能力相比于MGC803/NC(敲低)显著下降(P < 0.01),见图 3C~D。Transwell侵袭实验结果显示,MGC803/piR-9994-IN细胞穿膜个数减少,显著低于MGC803/NC(敲低)(149.1±7.50 vs. 85.07±2.28, P=0.0012),见图 3E。以上结果表明,piR-9994敲低可抑制胃癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和转移。
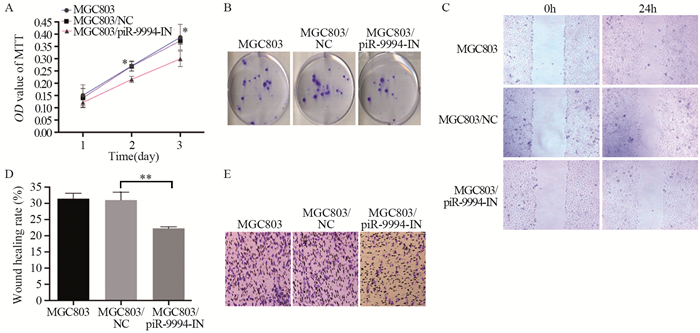
|
| A: effect of piR-9994 knockdown on the proliferation of MGC803 cells was determined by MTT assay; B: effect of piR-9994 knockdown on the proliferation of MGC803 cells was determined by colony formation method; C, D: effect of piR-9994 knockdown on the migration ability of MGC803 cells was detected by scratch test; E: Transwell invasion assay was used to detect the effect of piR-9994 knockdown on the invasion ability of MGC803 cells; *: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01. 图 3 piR-9994的敲低对MGC803细胞增殖生长和迁移侵袭的影响 Figure 3 Effect of piR-9994 knockdown on proliferation, migration and invasion of MGC803 cells |
流式细胞术检测结果显示,MGC803/piR-9994-OE组S期细胞百分比明显高于MGC803/NC(过表达),见图 4A(P < 0.05),而MGC803/piR-9994-IN组S期细胞百分比明显低于MGC803/NC(敲低),见图 4B(P < 0.05)。S期为DNA复制期,提示piR-9994表达与细胞周期密切相关,piR-9994异常表达可能导致周期改变。
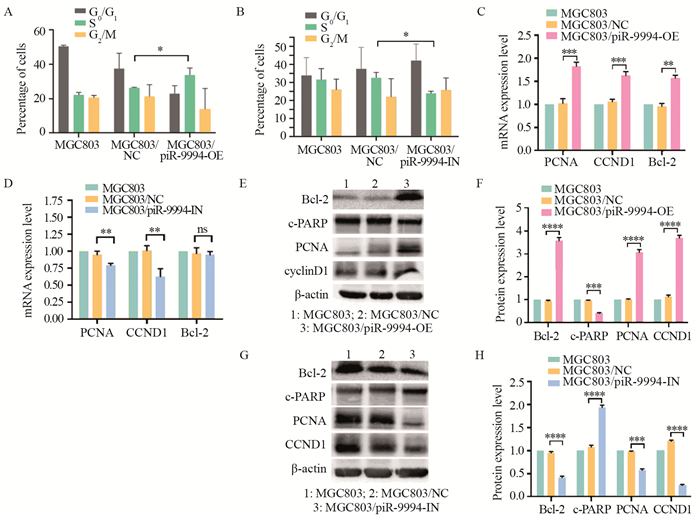
|
| A, B: effect of piR-9994 overexpression or knockdown on MGC803 cell cycle was detected by flow cytometry; C, D: effect of piR-9994 overexpression or knockdown on the expression of proliferation-related genes PCNA, CCND1 and Bcl-2 in MGC803 cells was detected by qRT-PCR; E, F: effect of piR-9994 overexpression on proliferation-related genes Bcl-2, c-PARP, PCNA and CCND1 was detected by Western blot; G, H: effect of piR-9994 knockdown on proliferation-related genes Bcl-2, c-PARP, PCNA and CCND1 was detected by Western blot; *: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001, ****: P < 0.0001; ns: no significance. 图 4 piR-9994表达对MGC803细胞周期和增殖相关基因表达的影响 Figure 4 Effect of piR-9994 expression on cell cycle and proliferation-related genes expression of MGC803 cells |
qRT-PCR和Western blot结果显示,在MGC803/piR-9994-OE中PCNA、CCND1、Bcl-2表达水平显著高于MGC803/NC(过表达)(P < 0.01),c-PARP表达水平低于MGC803/NC(过表达)(P < 0.001)。而在MGC803/piR-9994-IN中PCNA、CCND1、Bcl-2表达水平显著低于MGC803/NC(敲低)(P < 0.05),c-PARP表达水平高于MGC803/NC(敲低)(P < 0.05),见图 4。PCNA、CCND1、Bcl-2表达与细胞增殖正相关,c-PARP表达与细胞增殖负相关,以上结果提示piR-9994促进MGC803细胞增殖和抑制其凋亡。
2.5 piR-9994对胃癌细胞EMT进展的影响结果显示:piR-9994过表达时,N-cadherin、MMP7、Twist和Vimentin高表达,E-cadherin低表达(P < 0.05),见图 5A~C;piR-9994敲低时,E-cadherin高表达,N-cadherin、MMP7、Twist和Vimentin低表达(P < 0.05),见图 5D~F。以上结果表明,piR-9994过表达增加细胞的运动及侵袭、转移能力,诱导细胞发生EMT现象。
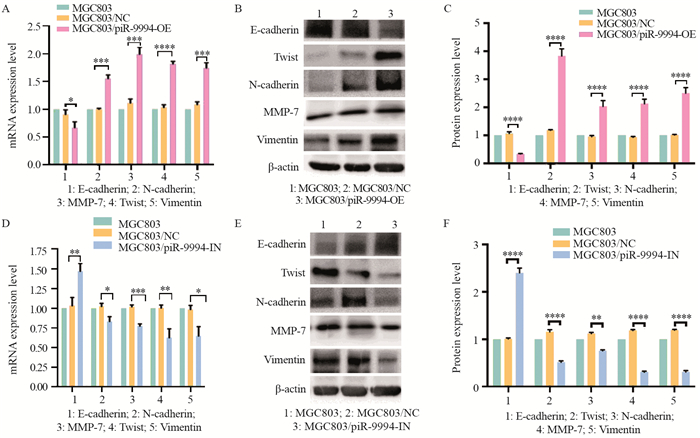
|
| A: effect of piR-9994 overexpression on the expression of EMT-related gene expression in MGC803 cells was detected by qRT-PCR; B, C: Effect of piR-9994 overexpression on the expression of EMT-related genes in MGC803 cells was detected by Western blot; D: Effect of piR-9994 knockdown on the expression of EMT-related genes in MGC803 cells was detected by qRT-PCR; E, F: effect of piR-9994 knockdown on the expression of EMT-related genes in MGC803 cells was detected by Western blot; *: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001, ****: P < 0.0001. 图 5 piR-9994表达与MGC803细胞EMT相关基因表达的关系 Figure 5 Relation between piR-9994 expression and EMT-related genes expression in MGC803 cells |
piRNA是一种特异性表达的内源性小分子RNA,长25~31nt,与PIWI蛋白结合形成piRNA/PIWI复合物,影响转座子沉默、精子发生、基因重排、表观遗传调控、蛋白质调控和生殖干细胞维持。研究表明piRNA在乳腺癌、食管癌、胰腺癌、肝癌、肺癌、肾母细胞瘤等多种实体肿瘤中有差异表达[7-10];食管癌中piR-823通过异常的DNA甲基化产生致癌作用,且与淋巴结的转移密切相关[8]。非小细胞肺癌中piR-651异常表达与肿瘤进展有关,体内体外实验表明piR-651的过表达促进肺癌细胞的侵袭和转移[11]。
本项目的前期研究通过测序技术和生物信息学技术构建piRNA在胃癌中的表达谱,同时筛选出50个在胃癌及癌旁组织中有差异性表达的piRNAs,其中17个在胃癌组织中高表达,33个低表达,piR-9994为高表达的piRNA之一[6];进一步通过大样本胃癌组织标本分析表明,piR-9994在胃癌组织高表达,piR-9994在胃癌组织中的表达比癌旁组织上调2.3倍(P=0.002),而且与肿瘤分期、神经侵犯密切相关(P < 0.05)[7]。本实验在此基础上,构建piR-9994过表达与敲低的胃癌细胞株MGC803,进行生物学功能研究。研究表明,piR-9994过表达促进胃癌细胞增殖、侵袭、迁移,而piR-9994敲低抑制胃癌细胞增殖、侵袭、迁移。同时piR-9994与细胞周期密切相关。以上结果,从组织学和细胞学层面分析表明,piR-9994参与胃癌发展进程并发挥重要作用。
上皮间质转化(epithelial mesenchymal transition, EMT)是指上皮细胞失去其顶端-基底极性和细胞间黏附特性,转变成具有侵袭性的间充质细胞的过程。大量研究表明EMT是肿瘤细胞侵袭转移的重要机制之一,与胃癌的发生、发展密切相关[12],EMT的激活使胃癌上皮细胞具有间质细胞的特征,上皮极性减少,而且间质细胞获得干细胞侵袭、转移、抗凋亡及耐药等特征。前期研究工作显示,piR-9994在胃癌组织中异常表达与EMT密切相关[13]。本实验进一步发现,piR-9994过表达胃癌细胞组中Twist、N-cadherin、MMP-7、Vimentin高表达,而E-cadherin低表达。piR-9994敲低胃癌细胞组中Twist、N-cadherin、MMP-7、Vimentin低表达,而E-cadherin高表达。以上结果表明,piR-9994异常表达影响EMT进程,但具体机制仍需进一步研究。
综上所述,piR-9994参与胃癌发展进程并发挥重要作用,其异常表达影响胃癌细胞增殖、侵袭、转移及EMT进程。piR-9994可能是胃癌的新的标志物和治疗靶点。
作者贡献
林华妹:实验设计、实施及文章撰写
邹长棪、廖锦容、林可焴、何火聪:部分生物学功能研究
苏颖:实验实施及文章执笔
胡丹、郑雄伟:临床资料收集
林贤东:实验设计、评估及文章审校
| [1] |
Shi WJ, Gao JB. Molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance in gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastrointest Oncol, 2016, 8(9): 673-681. DOI:10.4251/wjgo.v8.i9.673 |
| [2] |
Cheng J, Fan XM. Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in gastric cancer development and progression[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(42): 7361-7368. DOI:10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7361 |
| [3] |
Wadhwa R, Song S, Lee JS, et al. Gastric cancer-molecular and clinical dimensions[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2013, 10(11): 643-655. DOI:10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.170 |
| [4] |
Liu Y, Dou M, Song X, et al. The emerging role of the piRNA/piwi complex in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 123. DOI:10.1186/s12943-019-1052-9 |
| [5] |
姚婕. PIWI/piRNA在癌症中作用研究进展[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2015, 29(11): 1050-1052. [Yao J. Research progress of PIWI/piRNA in cancer[J]. Zhonghua Shi Yong Zhen Duan Yu Zhi Liao Za Zhi, 2015, 29(11): 1050-1052.] |
| [6] |
Lin X, Xia Y, Hu D, et al. TranscriptomewidepiRNA profiling in human gastric cancer[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 41(5): 3089-3099. |
| [7] |
夏言, 林贤东, 胡丹, 等. 胃癌组织中piR-9994的表达及其与PIWIL4表达的相关性[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志, 2019, 35(2): 155-160. [Xia Y, Lin XD, Hu D, et al. Expression of piR-9994 in gastric carcinoma and its correlation with PIWIL4[J]. Lin Chuang Yu Shi Yan Bing Li Xue Za Zhi, 2019, 35(2): 155-160.] |
| [8] |
Huang G, Hu H, Xue X, et al. Altered expression of piRNAs and their relation with clinicopathologic featuresof breast cancer[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2013, 15(7): 563-568. DOI:10.1007/s12094-012-0966-0 |
| [9] |
Su JF, Zhao F, Gao ZW, et al. piR-823 demonstrates tumor oncogenic activity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through DNA methylation induction via DNA methyltransferase 3B[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2020, 216(4): 152848. DOI:10.1016/j.prp.2020.152848 |
| [10] |
Navarro A, Tejero R, Vinolas N, et al. The significance of PIWI family expression in human lung embryogenesis and non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6(31): 31544-31556. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.3003 |
| [11] |
Al-Janabi O, Wach S, Nolte E, et al. Piwi-like 1 and 4 gene transcript levels are associated with clinicopathological parameters in renal cell carcinomas[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014, 1842(5): 686-890. DOI:10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.01.014 |
| [12] |
Pearson GW. Control of Invasion by Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Programs during Metastasis[J]. J Clin Med, 2019, 8(5): 646. DOI:10.3390/jcm8050646 |
| [13] |
Li D, Luo Y, Gao Y, et al. piR-651 promotes tumor formation in non-small cell lung carcinoma through the upregulation of cyclin D1 and CDK4[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 38(3): 927-936. DOI:10.3892/ijmm.2016.2671 |
 2021, Vol. 48
2021, Vol. 48


