文章信息
- LncRNA-p21调控Notch信号通路对非小细胞肺癌A549细胞增殖、迁移及侵袭的影响
- Effect of LncRNA-p21 Regulating Notch Signaling Pathway on Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cells
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2021, 48(2): 121-126
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2021, 48(2): 121-126
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2021.20.0730
- 收稿日期: 2020-06-28
- 修回日期: 2020-11-12
2. 450000 郑州,郑州大学第一附属医院肿瘤科
2. Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450000, China
非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)占肺癌类型的80%以上,具有发病率高、病死率高的特点,近年来发病率有逐渐升高的趋势[1]。NSCLC病情隐匿,早期极易误诊或漏诊,贻误病情,使患者失去最佳手术时机,预后生存期短[2]。因此,了解NSCLC发生发展机制,寻找有效干预手段,对患者治疗至关重要。近年来研究表明,NSCLC与多基因、多环节异常改变有关,其中长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA, LncRNA)表达调控与其改变关系紧密,参与肿瘤发生及发展的多个环节[3-4]。研究发现,LncRNA-p21具有抑制胃癌、肺癌等癌细胞侵袭、转移的作用,但具体调控机制尚不清楚[5-6]。本研究通过脂质体转染过表达LncRNA-p21质粒载体,上调A549细胞中LncRNA-p21基因表达,观察过表达LncRNA-p21基因对A549细胞增殖和侵袭等能力的影响及作用机制,为临床NSCLC靶向治疗提供参考依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料非小细胞肺癌A549细胞系购自上海生科院细胞库;pcDNA-lincRNA-p21、空载质粒pcDNA(上海吉玛公司);Notch信号通路特异性激活剂Jagged1蛋白(美国R & D Systems公司);LipofectamineTM 2000试剂盒、TRIzol(美国Invitrogen公司);二喹啉甲酸(bicinchoninic acid, BCA)试剂盒(美国Sigma-Aldrich公司);细胞裂解液(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);一步法实时荧光定量PCR试剂盒(美国QIAGEN公司);二喹啉甲酸蛋白定量分析试剂盒(美国Thermo公司);兔抗人Notch1、转录因子HES-1、Notch1胞内结构域(Notch 1 intracellular domain, NICD)、E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)、波形蛋白(Vimentin)单抗(一抗)、HRP标记二抗(美国Santa Cruz公司);StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR仪(美国Thermo Fisher公司);ELx800TS酶标仪(美国BioTek公司)。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 细胞培养非小细胞肺癌A549细胞置于含10%FBS的DMEM培养基,于5%CO2、37℃恒温箱培养,每两天换液一次,3~5天传代1次。
1.2.2 细胞转染及分组取对数期细胞常规消化并接种至6孔板,细胞再次贴壁至70%左右时,更换无血清培养基同条件孵育12 h,严格按照LipofectamineTM 2000脂质体转染试剂盒操作,继续培养6 h,更换无双抗培养基,继续培养32 h,获得稳定转染细胞设为过表达组,同法获得转染空载质粒pcDNA A549细胞,获得稳定转染细胞设为空载组,同时取未经处理的A549细胞株为对照组。取稳定转染过表达组细胞,加入Jagged1蛋白(终浓度5 mg/L),设为Notch激活剂组。
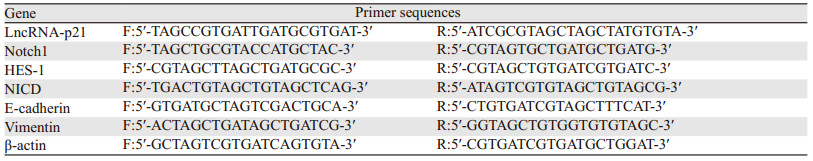
1.2.3 转染后LncRNA-p21基因表达检测取稳定转染的各组细胞,胰蛋白酶消化后,离心收集各组细胞,RT-qPCR法检测各组LncRNA-p21基因表达情况。TRIzol法提取总RNA,反转录获取cDNA;根据SYBR Green PCR试剂盒设定反应体系:SYBR Green PCR buffer 5 μl,10 μmol/L上下游引物各0.2 μl,dNTP酶10.0 μl,ddH2O 4.6 μl;反应条件:95℃预变性3 min;95℃变性20 s,59℃退火40 s,72℃延伸30 s,重复42个循环。以内参β-actin作对照物,按照2-ΔΔCT计算LncRNA-p21相对表达强度,引物序列见表 1。
|
取稳定转染空载组、过表达组、空白组及Notch激活剂组细胞,调整细胞密度,以每毫升1×105个接种于96孔板,每组5个复孔。培养至24、48及72 h时,加入20 μl浓度为5 mg/ml MTT溶液,继续孵育4 h,倾倒上层培养液,各孔加入DMSO溶液150 μl,混匀后,酶标仪测定570 nm波长处吸光度(A)值。
1.2.5 划痕实验检测细胞迁移能力取稳定转染空载组、过表达组、空白组及Notch激活剂组细胞,以每毫升5×104个重新接种于6孔板,每组5个复孔;同条件下继续培养,待细胞再次融合完整后,用50 μl无菌枪头于培养板中间划直线,移液管吸取细胞培养液轻轻吹洗,确认划痕边缘整齐,加入完全培养基,48 h后于倒置显微镜下观察并拍照。细胞迁移率(%)=(初始划痕宽度-48 h划痕宽度)/初始划痕宽度×100%。
1.2.6 Transwell法检测细胞侵袭能力收集各组细胞,Transwell小室滤膜由1:6稀释的DMEM人工基质均匀涂布,37℃恒温培养箱放置40 min左右胶干;下层小室加入培养12 h后的无细胞上清液,上层小室加入培养12 h的单细胞悬液。继续孵育48 h后,用手术镊取下中间滤膜,置于质量分数3.7%甲醇固定,经结晶紫染色后,于显微镜下随机取5个视野,计数并统计平均穿膜细胞数。
1.2.7 Notch1、HES-1、NICD、E-cadherin和Vimentin基因表达检测取稳定转染空载组、过表达组、空白组及Notch激活剂组细胞,调整细胞密度,以每毫升1×105个接种于96孔板,培养48 h。胰蛋白酶消化后,离心收集各组细胞,RT-qPCR法检测各组细胞中Notch1、HES-1、NICD、E-cadherin、Vimentin基因表达情况。TRIzol法提取总RNA,反转录法获得cDNA;严格按照SYBR Green PCR试剂盒进行试验。以2-ΔΔCT计算目的基因的相对表达强度。各基因上下游引物序列见表 1。
1.2.8 Notch1、HES-1、NICD、E-cadherin、和Vimentin蛋白表达检测取稳定转染空载组、过表达组、空白组及Notch激活剂组细胞,调整细胞密度以1×105个/毫升接种于96孔板,培养48 h。胰蛋白酶消化后,离心收集各组细胞,加入0.5 ml细胞裂解液,于冰上裂解20 min,12 000 r/min离心10 min取上清液,BCA试剂盒测定蛋白总量。取50 μg样品进样,进行SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳,然后电转、封闭,按要求加入稀释一抗4℃摇床孵育过夜,TBST洗涤3次×5 min后,加入稀释二抗,室温孵育2 h,TBST洗涤3次×5 min,于暗室中显影、定影,扫描拍照后采用Image J软件分析各条带灰度值,蛋白相对表达量用Notch1、HES-1、NICD、E-cadherin、Vimentin蛋白与内参β-actin灰度值比值表示。
1.3 统计学方法采用SPSS21.0统计软件,计量资料均以x±s表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两样本间比较采用LSD-t检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
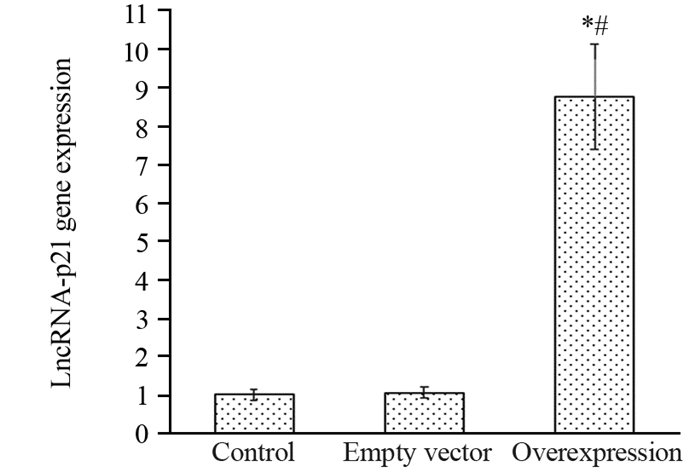
2 结果 2.1 各组细胞中LncRNA-p21基因表达比较过表达组、空载组及对照组LncRNA-p21基因相对表达量分别为8.57±1.36、1.07±0.15、1.02±0.14,组间比较差异有统计学意义(F=146.674, P < 0.001);过表达组LncRNA-p21基因相对表达量高于空载组和对照组(t=12.257、12.348, 均P < 0.001);空载组与对照组比较,差异无统计学意义(t=0.545, P=0.601),见图 1。
|
| *: P < 0.05, compared with control group; #: P < 0.05, compared with empty vector group. 图 1 各组细胞中LncRNA-p21基因表达比较 Figure 1 Comparison of LncRNA-p21 gene expression in each group |
不同时间四组间MTT实验A值比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);过表达组培养24、48、72 h MTT实验A值均低于对照组、空载组和Notch激活剂组,Notch激活剂组低于对照组和空载组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05);对照组与空载组培养24、48、72 h MTT实验A值比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);四组培养48 h MTT实验A值均高于培养24 h(P < 0.05),且培养72 h MTT实验A值高于48 h(P < 0.05),见表 2。

|
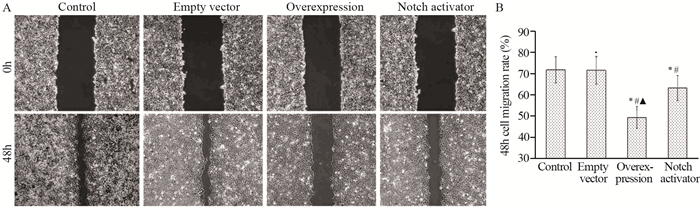
对照组、空载组、过表达组和Notch激活剂组48 h细胞迁移率分别为(71.69±6.20)%、(71.50± 6.53)%、(49.32±5.20)%、(63.17±5.92)%,四组间比较差异有统计学意义(F=15.544, P < 0.001);过表达组48 h细胞迁移率低于空载组、对照组和Notch激活剂组(t=6.182、5.941、3.647, 均P < 0.05),Notch激活剂组低于对照组和空载组(t=2.483、2.367, 均P < 0.05);空载组与对照组间差异无统计学意义(t=0.047, P=0.964),见图 2。
|
| *: P < 0.05, compared with control group; #: P < 0.05, compared with empty vector group; ▲: P < 0.05, compared with Notch activator group. 图 2 各组划痕实验48 h细胞迁移率结果 Figure 2 Cell migration rates of each group at 48 hours detected by scratch test |
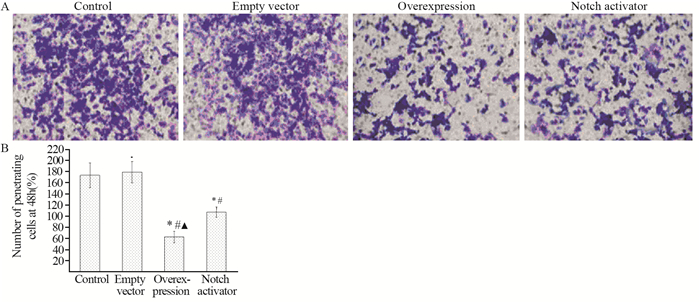
对照组、空载组、过表达组和Notch激活剂组48 h穿膜细胞数分别为173.33±22.00个、179.00±19.33个、62.33±10.33个、107.00±9.33个,四组间比较差异有统计学意义(F=59.514, P < 0.001);过表达组48 h穿膜细胞数少于空载组、对照组和Notch激活剂组(t=10.212、11.903、7.176, 均P < 0.001),Notch激活剂组少于对照组和空载组(t=6.207、7.501, 均P < 0.001);空载组与对照组间差异无统计学意义(t=0.433, P=0.677),见图 3。
|
| *: P < 0.05, compared with control group; #: P < 0.05, compared with empty vector group; ▲: P < 0.05, compared with Notch activator group. 图 3 Transwell实验48 h穿膜细胞数结果 Figure 3 Number of transmembrane cells at 48 hours detected by Transwell test |
Notch1、HES-1、NICD、E-cadherin和Vimentin mRNA相对表达量在四组间比较,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05);过表达组Notch1、HES-1、NICD、Vimentin mRNA相对表达量低于空载组、对照组和Notch激活剂组,Notch激活剂组低于对照组和空载组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05);过表达组中E-cadherin mRNA相对表达量高于空载组、对照组和Notch激活剂组,Notch激活剂组高于对照组和空载组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05);空载组与对照组间差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 3。
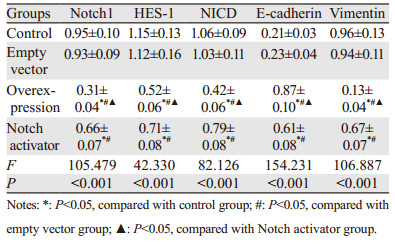
|
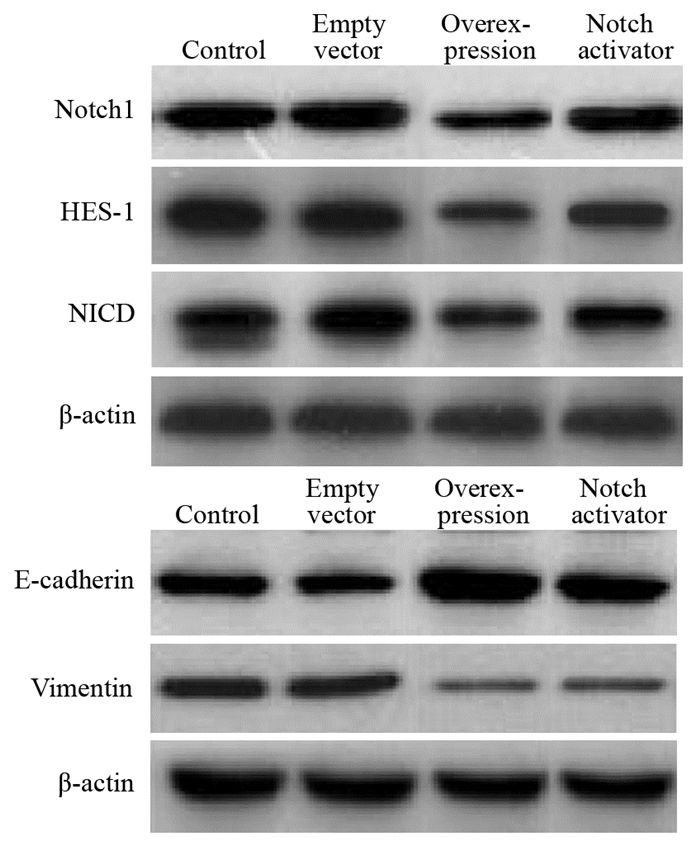
Notch1、HES-1、NICD、E-cadherin和Vimentin蛋白相对表达量组间比较,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05);过表达组Notch1、HES-1、NICD、Vimentin蛋白相对表达量低于空载组、对照组和Notch激活剂组,Notch激活剂组低于空载组和对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05);过表达组中E-cadherin蛋白相对表达量高于空载组、对照组和Notch激活剂组,Notch激活剂组高于空载组和对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05);空载组与对照组间差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表 4、图 4。
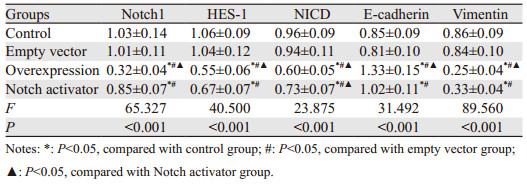
|
|
| 图 4 各组蛋白免疫印迹图 Figure 4 Immunoblotting diagrams of proteins in each group |
近年来,尽管手术及其他综合治疗手段不断进步,NSCLC治疗成功率有所提高,但仍有部分患者预后不佳,寻找新的治疗靶点意义重大。近年来研究表明,LncRNA可通过调控微小RNA或下游编码区RNA参与肿瘤的发生、发展,目前已成为肿瘤发生、发展机制相关研究的热点[7]。LncRNA-p21在多种恶性肿瘤组织或细胞中异常表达,且与肿瘤增殖、侵袭及迁移相关[8-9]。Notch信号通路是存在于多种动物体内的信号交点通路,在上皮间质转化(EMT)、细胞增殖、迁移及分化等多种肿瘤生物学活动中发挥重要调控作用[10-11]。因此,探讨LncRNA-p21能否通过调控Notch信号通路对NSCLC细胞的EMT过程产生影响,从而影响癌细胞的增殖、侵袭及迁移能力有重要意义。
本研究采用脂质体转染法上调A549细胞中LncRNA-p21基因的表达,结果显示过表达组LncRNA-p21基因相对表达量高于空载组和对照组,说明成功上调该基因的表达。基因组测序分析显示,人类基因组非编码区存在大量LncRNA,其中约2.4万个LncRNA参与转录、干扰、染色质修饰等多项生物学活动[12]。Han等[13]研究发现,LncRNA-p21在恶性骨肉瘤组织中表达受到抑制,体外试验表明,上调LncRNA-p21表达可抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖,与本结果一致。Isin等[14]发现LncRNA-p21在前列腺癌患者中异常低表达,可作为鉴别诊断前列腺癌和良性前列腺增生的可靠标志物。本研究结果提示LncRNA-p21基因过表达可抑制非小细胞肺癌A549细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭能力。
本研究结果显示,Notch激活剂组A549细胞增殖、迁移及侵袭能力较过表达组增强,Notch1信号通路相关基因和蛋白表达较过表达组均有上调,过表达组Notch1信号通路相关基因和蛋白表达较对照组和空载组均下调,提示过表达LncRNA-p21基因对非小细胞肺癌的增殖、迁移、侵袭能力的抑制作用可能与抑制Notch信号通路、阻断A549细胞上皮间质转化过程有关。人类Notch信号通路主要由Notch受体(1-4)、Notch配体(DSL蛋白)及相关靶基因HES-1、同型半胱氨酸诱导的内质网蛋白等组成[15]。Notch1信号通路在多种恶性肿瘤组织中检测出激活状态,参与肿瘤化疗耐药、侵袭及转移过程[16-17]。Notch1信号通路中受体与配体结合后激活,受体蛋白水解,继而释放出NICD易位于细胞核,与核内多种转录因子结合调控下游靶基因转录和表达。HES-1是Notch1信号通路下游靶基因,有抑制细胞增殖作用[18-19]。E-cadherin及Vimentin分别是上皮及间质标记基因,两者在维持细胞形态、结构完整、细胞间黏附作用等方面起重要作用[20]。研究显示,活化Notch1片段NICD可诱导转录性抑制体大量表达,继而与E-cadherin结合,增加细胞间接触抑制从而抑制EMT,抑制细胞侵袭及迁移能力[21]。
综上,本研究得出LncRNA-p21基因过表达可抑制非小细胞肺癌A549细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,其调控机制可能与抑制Notch信号通路,从而阻断A549细胞上皮间质转化过程有关,为临床通过靶向干扰LncRNA-p21基因表达治疗NSCLC提供理论支持。
作者贡献:
张冠磊:文献收集整理、实验设计及操作、统计分析、论文撰写与修改
马苗苗:收集和资料汇总分析
兰文静:文章审校、修改和指导
王琳:论文指导
| [1] |
季新强. 北京大学肿瘤医院2000-2013年3733例肺癌手术患者临床病理特征动态变化分析[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2017, 24(24): 1687-1692. [Ji XQ. Dynamic analysis of clinical epidemiology and the distribution of pathology types of patients with primary lung cancer in Peking University Cancer Hospital from 2000 to 2013[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Za Zhi, 2017, 24(24): 1687-1692.] |
| [2] |
Sakin A, Sahin S, Atci MM, et al. The effect of different treatment modalities on survival in elderly patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Pulmonology, 2019, pii: S2531-0437(19): 30215-6. |
| [3] |
Niazi Z, Garazhian E, Esfandi F, et al. Expression Analysis of the Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01433 in Lung Cancer[J]. Klin Onkol, 2019, 32(6): 453-455. |
| [4] |
Chen X, Shi Y, Zhou K, et al. A bibliometric analysis of long non-coding RNA and chemotherapeutic resistance research[J]. Oncotarget, 2019, 10(35): 3267-3275. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.26938 |
| [5] |
裴洪利, 白尚星. 过表达lncRNA-p21通过介导Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制胃癌MGC-803细胞的生长与转移[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2019, 39(8): 1615-1621. [Pei HL, Bai SX. Over-expression of lncRNA-p21 inhibits the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer MGC-803 cells by mediating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Lin Chuang Yu Bing Li Za Zhi, 2019, 39(8): 1615-1621.] |
| [6] |
Guo L, Gu J, Hou S, et al. Long non-coding RNA DANCR promotes the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by inhibiting p21 expression[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2018, 12: 135-146. DOI:10.2147/OTT.S186607 |
| [7] |
Dahariya S, Paddibhatla I, Kumar S, et al. Long non-coding RNA: Classification, biogenesis and functions in blood cells[J]. Mol Immunol, 2019, 112: 82-92. DOI:10.1016/j.molimm.2019.04.011 |
| [8] |
张勇, 张启发, 田长海, 等. 长链非编码RNA-p21通过调节Warburg效应促进前列腺癌细胞侵袭[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2017, 34(6): 1014-1016. [Zhang Y, Zhang QF, Tian CH, et al. Long non-coding RNA-p21 induced by hypoxia promotes the invasion of prostate cancer by enhancing Warburg effect[J]. Zhonghua Shi Yan Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2017, 34(6): 1014-1016.] |
| [9] |
朱克祥, 张正聪, 袁得峰, 等. lincRNA-p21通过STAT3信号抑制结直肠癌HCT116细胞增殖[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2019, 35(5): 797-803. [Zhu KX, Zhang ZC, Yuan DF, et al. Growth inhibition of colorectal cancer HCT116 cells by lincRNA-p21 through STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Zhongguo Bing Li Sheng Li Za Zhi, 2019, 35(5): 797-803.] |
| [10] |
Zhou P, Wang C, Hu Z, et al. Genistein induces apoptosis of colon cancer cells by reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal via a Notch1/NF-κB/slug/E-cadherin pathway[J]. BMC Cancer, 2017, 17(1): 813. DOI:10.1186/s12885-017-3829-9 |
| [11] |
Fukusumi T, Guo TW, Sakai A, et al. The NOTCH4-HEY1 Pathway Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24(3): 619-633. DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1366 |
| [12] |
Li N, Shi R. Expression alteration of long non-coding RNAs and their target genes in the intestinal mucosa of patients with Crohn's disease[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2019, 494: 14-21. DOI:10.1016/j.cca.2019.02.031 |
| [13] |
Han W, Liu J. LncRNA-p21 inhibited the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells via the miR-130b/PTEN/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 97: 911-918. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.014 |
| [14] |
Işın M, Uysaler E, Özgür E, et al. Exosomal lncRNA-p21 levels may help to distinguish prostate cancer from benign disease[J]. Front Genet, 2015, 6: 168. |
| [15] |
张欣, 林雨, 海龙, 等. NOTCH通路依赖PI3K/AKT通路调控胶质瘤干细胞增殖和自我更新能力[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2018, 45(9): 640-646. [Zhang X, Lin Y, Hai L, et al. NOTCH Signaling Pathway Regulates Glioma Stem-like Cell Proliferation and Self-renewal Abilities via PI3K/AKT Activity[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2018, 45(9): 640-646.] |
| [16] |
Vázquez-Ulloa E, Ramos-Cruz AC, Prada D, et al. Loss of nuclear NOTCH1, but not its negative regulator NUMB, is an independent predictor of cervical malignancy[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(27): 18916-18928. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.24828 |
| [17] |
Jiang B, Chen J, Yuan W, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-D promotes colorectal cancer cell migration, invasion and proliferation by regulating Notch1 and matrix metalloproteinase-9[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15(2): 1573-1579. |
| [18] |
李美玲, 陈美琼, 张鹏, 等. 靶向沉默Notch1基因对骨髓瘤细胞增殖的影响[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2017, 25(6): 1707-1712. [Li ML, Chen MQ, Zhang P, et al. Targeting Notch1 Gene Inhibits the Proliferation of Multiple Myeloma Cells[J]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 2017, 25(6): 1707-1712.] |
| [19] |
Pizza FX, Martin RA, Springer EM, et al. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 augments myoblast adhesion and fusion through homophilic trans-interactions[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 5094. |
| [20] |
Zhang HS, Zhang ZG, Du GY, et al. Nrf2 promotes breast cancer cell migration via up-regulation of G6PD/HIF-1α/Notch1 axis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2019, 23(5): 3451-3463. |
| [21] |
Gao YP, Li Y, Li HJ, et al. LncRNA NBR2 inhibits EMT progression by regulating Notch1 pathway in NSCLC[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(18): 7950-7958. |
 2021, Vol. 48
2021, Vol. 48
