文章信息
- S-poly(T)plus荧光定量PCR技术在检测肝癌相关miR-199中的临床应用价值
- Clinical Value of S-poly (T) plus Real-time PCR in Detection of Liver Cancer-related miR-199
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2020, 47(10): 761-765
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2020, 47(10): 761-765
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2020.19.1618
- 收稿日期: 2019-12-30
- 修回日期: 2020-07-03
2. 350001 福州,福建医科大学附属协和医院检验科;
3. 350005 福州,福建医科大学附属第一医院检验科
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou 350001, China;
3. Department of Clinical Laboratory, The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350005, China
微小RNA(microRNA, miRNA)是长度在22个核苷酸左右(19~25 nt)的非编码RNA,多数对基因表达水平发挥负向调控作用[1]。研究证实,肿瘤组织包括肝癌可释放miRNA至外周血,其种类、含量与肿瘤有一定关系[2],所以循环miRNA的检测对于肿瘤诊断和预后监测具有良好的前景,如血浆miR-34a可作为食管癌的诊断标志物,miR-199有潜力成为肝癌患者的诊断标志物[3]。由于循环miRNA检测具有非侵入性以及检测方便等优点,近年来循环miRNA的检测在临床的应用价值受到越来越多的关注[4]。
miRNA检测方法多样,包括微阵列芯片、RNA深度测序、实时定量PCR(qRT-PCR)等技术,其中qRT-PCR由于操作简单且价格便宜得到广泛应用[5]。Poly(A)加尾法qRT-PCR技术是检测miRNA表达的常用方法之一,然而由于血清miRNA含量低,需要较高敏感度的检测方法,Poly(A)加尾法在血清miRNA检测仍有待于进一步改善[6-7]。
S-poly(T) plus法基于Poly(A)加尾法进行改良,利用特异性引物和探针,将加尾法和反转录cDNA同步进行,具有检验时间更短、重复性更好、敏感度更高等特点[8],研究表明S-poly(T) plus法检测肺动脉高压和缺氧治疗相关miRNA具有更高的敏感度[8-9],但该方法在检测肝癌相关miRNA方面是否有优势尚且未知。因此,我们以检测与肝癌密切相关的miR-199为例,比较S-poly(T) plus法与Poly(A)加尾法检测肝癌患者血清和健康人miR-199的结果,对S-poly(T) plus法进行方法学评价,为血清miRNA定量检测提供高敏感度和高稳定性的快速检测方法。
1 资料与方法 1.1 资料选择2017年8月—10月福建医科大学附属第一医院初诊为肝癌患者血清标本15例和年龄、性别与患者相匹配的体检健康者(各项体检结果正常,无乙肝携带及肝功能障碍)血清标本50例,该研究经福建医科大学伦理审查委员会同意,所有患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 主要试剂及实验仪器主要试剂:RNA提取试剂盒(康为世纪北京生物技术有限公司,CW0581),S/P RNAiso kit(深圳今发展生物有限公司,No. AB-MIS-001)、miRNA cDNA合成试剂盒(康为世纪北京生物技术有限公司,CW2141),miRNA Poly(A)检测试剂盒(康为世纪北京生物科技有限公司,CW2142)。
主要实验仪器:低速台式离心机(湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发公司,L500-A),台式高速冷冻离心机(香港力康公司,Neofuge 23R),超净工作台(香港力康公司,AlphaClean 1300),磁力加热搅拌器(常州国华仪器公司,78-1),实时荧光定量PCR仪(美国ABI公司,7500)。
1.3 方法 1.3.1 血清RNA提取按照RNA提取试剂盒说明书操作步骤,提取总RNA。
1.3.2 引物设计与合成使用miRBase数据库查找miRNA的序列,利用Primer Premier6.0软件进行引物设计,于上海生工有限公司合成,见表 1。cel-miR54为预混于miRNA提取试剂RNAiso中的Spiked-in RNA,作为miRNA定量检测的内参。
S-poly(T) plus法:如文献[8]所述,取500 ng总RNA,首先利用S-Poly(T) plus法特异性反转录引物合成cDNA,加Poly(A)尾和反转录同时进行,反应条件:37℃ 30 min,42℃ 30 min,75℃ 5 min。使用miR-199特异上游引物及下游通用引物完成qPCR。扩增条件:预变性95℃ 3 min,95℃ 10 s,60℃ 30 s,40个循环。
poly(A)加尾法:取500 ng总RNA,进行poly(A)加尾,poly(A)加尾反应条件为37℃ 15 min,混匀Poly(A)加尾反应液,利用随机引物反转录合成cDNA,反应条件为:42℃ 50 min,85℃ 5 min。用miR-199特异上游引物及下游通用引物进行qPCR。扩增条件:95℃ 3 min,95℃ 10 s,60℃ 30 s,40个循环。
1.4 统计学方法采用Graph prism 6软件进行统计分析,计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
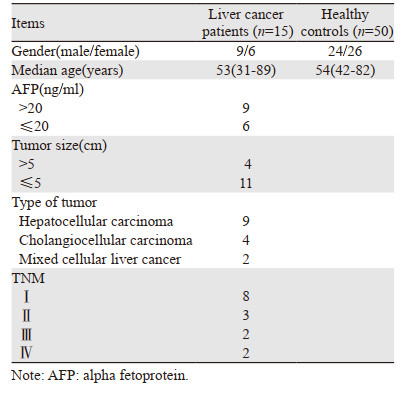
2 结果 2.1 临床资料本实验中,共有15例初次确诊的肝癌患者纳入实验组,肝癌患者及健康对照者临床资料见表 2。
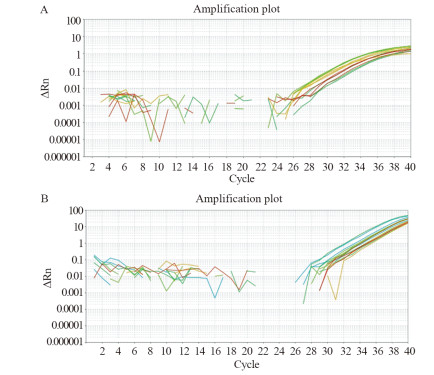
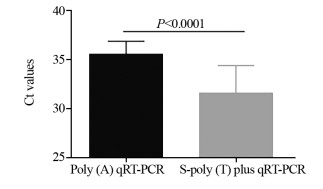
分别用S-poly(T) plus法和Poly(A)加尾法对50例健康者血清miR-199进行检测,扩增曲线,见图 1,其Ct值分析结果,见图 2。S-poly(T) plus法检测miR-199的Ct值较Poly(A)加尾法显著性降低(30.32±0.72 vs. 35.42±0.67, P < 0.0001),说明S-poly(T) plus法的敏感度较高。
|
| 图 1 S-poly(T) plus法(A)和Poly(A)尾法(B)qRT-PCR检测miR-199扩增曲线 Figure 1 Amplification curves of S-poly(T) plus qRT-PCR method(A) and Poly(A) qRT-PCR method(B) for miR-199 |
|
| 图 2 S-poly(T) plus法和Poly(A)加尾法qRT-PCR测定miR-199的Ct值 Figure 2 Ct values of S-poly(T) plus qRT-PCR method and Poly(A) qRT-PCR method for miR-199 |
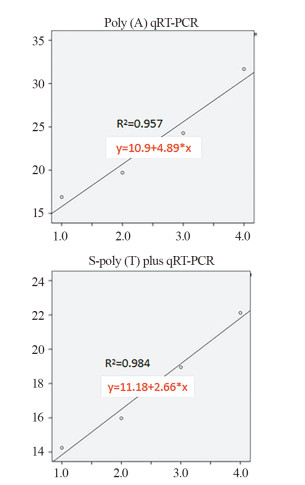
随机选取1例肝癌患者血清miR-199标本(初始浓度约450 ng/μl)按照101、102、103和104的倍数进行梯度稀释,分别用两种方法检测梯度稀释的血清miR-199浓度,并分别计算S-poly(T) plus和Poly(A)加尾法的线性相关系数,见图 3。同时再随机选取2例肝癌患者血清样本,进行上述重复实验,分别计算出R2值,发现S-poly(T) plus线性相关系数显著大于Poly(A)加尾法(0.9843±0.0047 vs. 0.9573±0.0045, P=0.0027),说明S-poly(T) plus法检测血清miR-199线性关系更好。
|
| 图 3 S-poly(T) plus法(A)和Poly(A)加尾法(B)qRT-PCR分别检测同1例肝癌患者血清miR-199的线性梯度关系比较 Figure 3 Comparison of linear gradient relation between S-poly(T) plus qRT-PCR method(A) and Poly(A) qRT-PCR method(B) for detecting serum miR-199 from the same patients |
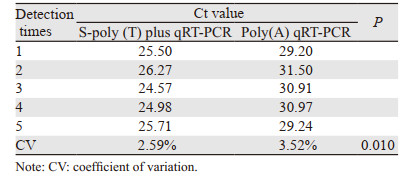
取同一份标本进行miR-199检测重复5次,计算其变异系数(coefficient of variation, CV),CV=标准差/均数×100%。S-poly(T)plus法的CV值为2.59%,Poly(A)加尾法的CV值为3.52%,可见在重复性上,S-poly(T) plus法优于Poly(A)加尾法(P=0.010),见表 3。
|
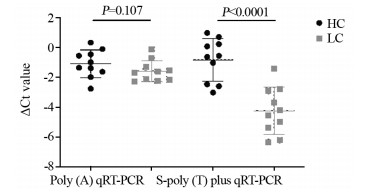
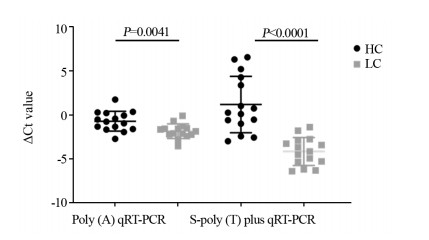
随机选取10例原发性肝癌患者和10例健康者的miR-199表达水平进行检测,并且以合成的外源cel-miR-54-5p为对照。Poly(A)加尾法检测结果显示患者与健康者血清miR-199差异无统计学意义(P=0.107),而S-poly(T) plus法检测发现肝癌患者miR-199的Ct值显著降低(P < 0.0001),提示S-poly(T) plus法在检测肝癌患者miR-199具有更好的敏感度,见图 4。在原来10例的基础上增加5例肝癌患者和相对应的健康者作为对照,共计15例肝癌患者和15例健康者进行S-poly(T) plus法和S-poly(T)加尾法检测血清miR-199水平。两种方法检测结果肝癌患者血清miR-199水平均显著高于健康者,但S-poly(T) plus法检测结果差异更为显著(P < 0.0001 vs. P=0.0041),见图 5。综上所述,S-poly (T) plus法检测肝癌患者外周血血清的miR-199敏感度较Poly(A)加尾法更好。
|
| HC: healthy controls; LC: liver cancer patients; Ct: Cycle threshold. 图 4 S-poly(T) plus法(A)和Poly(A)加尾法(B)qRT-PCR检测肝癌患者与健康人的血清miR-199相对表达水平 Figure 4 Relative expression levels of miR-199 in liver cancer patients and healthy controls detected by S-poly(T) plus qRT-PCR method(A) and Poly(A) qRT-PCR method(B) |
|
| 图 5 S-poly(T) plus法(A)和Poly(A)加尾法(B)qRT-PCR检测15例肝癌患者与15例健康人的miR-199相对表达水平 Figure 5 Relative expression levels of miR-199 in 15 liver cancer patients and 15 healthy controls detected by S-poly(T) plus qRT-PCR method(A) and Poly(A) qRT-PCR method(B) |
原发性肝癌是目前最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,每年有超过80万例的新发病例和死亡病例。早期发现肝癌,术后五年生存率可提高至70%,因此肝癌的早期诊断以及早期治疗对患者的治疗效果具有重要意义[10]。目前常用于诊断肝癌的方法是影像学检测和血清甲胎蛋白(alpha-fetoprotein, AFP)。然而在肝癌早期,依靠影像学和AFP的检测常常导致肝癌漏诊[11-12]。血清miRNA稳定性高,与疾病相关性较好,在肝癌的早期临床诊断方面具有巨大的应用前景[2, 8]。
本研究通过对比试验发现,S-poly(T) plus法检测miR-199平均Ct值显著低于Poly(A)加尾法,即S-poly(T) plus法具有更好的敏感度,这是因为Poly(A)加尾法用的是通用oligo引物,而S-poly(T) plus法在反转录时使用的是能够与对应的miRNA牢固地互补结合的特异性引物,这将大大增强与目的miRNA分子结合的热稳定性和锚定力度,从而使反转录效率更高,大幅提高目的miRNA第一链cDNA的合成和qPCR效率,使扩增产物增多[8]。同时S-poly(T) plus法稳定性显著优于Poly(A)加尾法,具有更好的重复性,在临床样本检测中更具有可靠性。此外,该方法同时进行Poly(A)加尾和反转录,简化操作、缩短时间,提高了实验效率。利用S-poly(T) plus法检测与肝癌密切相关的血清miR-199时,发现S-poly(T) plus法检测结果差异更显著,更容易区别肝癌患者和健康体检者血清标本,本团队前期基础利用ROC曲线分析外周血miR-199a诊断肝癌的临床价值,发现当△Ct截断值为1.02时,其敏感度和特异性分别为91.7%和62.0%[13]。以上结果说明S-poly(T) plus法在肝癌血清miRNA检测具有一定的临床应用价值。另一方面,文献表明肝炎和肝硬化的患者miR-199存在下降的现象,暗示肝炎和肝硬化患者会一定程度影响到此方法的准确性[14]。
然而,S-poly(T) plus法也有其缺陷,由于运用的反转录引物为特异性的,因此不能像Poly(A)加尾法一样一次性进行所有miRNA合成cDNA,每一个miRNA都要进行一次反转录反应,虽然提高了实验敏感度和特异性,但是降低了实验效率和增加了实验成本。同时在本实验中只针对miR-199,还需要对肝癌相关的其他血清miRNA进行研究。所以S-poly(T) plus法虽然在检测肝癌血清miRNA具有更好的敏感度和稳定性以及一定的临床应用价值,但是有待进一步研究解决提高其实验效率和降低实验成本。
综上所述,S-poly(T) plus法利用特异性反转录引物进行特定miRNA的反转录和PCR反应,较普通的加尾法有更好的敏感度,在肝癌血清特定miRNA的检测有着巨大的应用前景。
作者贡献
吴娟:实验实施及论文撰写
张雅琴、吴云彬:提供实验技术,数据处理
陈敏:提供实验平台,写作指导
于洲:样本收集
曹颖平:项目指导及论文撰写
| [1] |
Mohr AM, Mott JL. Overview of microRNA biology[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2015, 35(1): 3-11. |
| [2] |
Carpi S, Polini B, Fogli S, et al. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for early diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma[J]. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2020, 20(1): 19-30. |
| [3] |
Lin Y, Lin Z, Fang Z, et al. Plasma MicroRNA-34a as a Potential Biomarker for Early Diagnosis of Esophageal Cancer[J]. Clin Lab, 2019, 65(11). |
| [4] |
Wang WT, Chen YQ. Circulating miRNAs in cancer: from detection to therapy[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2014, 7: 86. DOI:10.1186/s13045-014-0086-0 |
| [5] |
Luo M, Gao Z, Li H, et al. Selection of reference genes for miRNA qRT-PCR under abiotic stress in grapevine[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 4444. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-22743-6 |
| [6] |
Dellett M, Simpson DA. Considerations for optimization of microRNA PCR assays for molecular diagnosis[J]. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2016, 16(4): 407-414. DOI:10.1586/14737159.2016.1152184 |
| [7] |
Luo X, Zhang J, Wang H, et al. PolyA RT-PCR-based quantification of microRNA by using universal TaqMan probe[J]. Biotechnol Lett, 2012, 34(4): 627-633. DOI:10.1007/s10529-011-0813-3 |
| [8] |
Niu Y, Zhang L, Qiu H, et al. An improved method for detecting circulating microRNAs with S-Poly(T) Plus real-time PCR[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5(1): 15100. DOI:10.1038/srep15100 |
| [9] |
Kang K, Zhang X, Liu H, et al. A novel real-time PCR assay of microRNAs using S-Poly(T), a specific oligo(dT) reverse transcription primer with excellent sensitivity and specificity[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(11): e48536. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0048536 |
| [10] |
Villanueva A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380(15): 1450-1462. DOI:10.1056/NEJMra1713263 |
| [11] |
Omran MM, Farid K, Omar MA, et al. A combination of alpha-fetoprotein, midkine, thioredoxin and a metabolite for predicting hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2019, 19(2): 179-185. |
| [12] |
Sun C, Xu A, Liu D, et al. Deep Learning-Based Classification of Liver Cancer Histopathology Images Using Only Global Labels[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2020, 24(6): 1643-1651. DOI:10.1109/JBHI.2019.2949837 |
| [13] |
Wu J, Wu Y, Luo Y, et al. Circulating miRNA-199a and miRNA-122 Levels as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. Ann Clin Lab Sci, 2020, 50(2): 219-227. |
| [14] |
Zhan Y, Zheng N, Teng F, et al. MiR-199a/b-5p inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by post-transcriptionally suppressing ROCK1[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(40): 67169-67180. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.18052 |
 2020, Vol. 47
2020, Vol. 47