文章信息
- 环状RNA:肺癌的潜在生物标志物
- Circular RNA: A Potential Biomarker for Lung Cancer
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2019, 46(7): 654-657
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2019, 46(7): 654-657
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2019.18.1589
- 收稿日期: 2018-12-14
- 修回日期: 2019-03-18
2. 511436 广州,广州医科大学卫生管理学院
2. School of Medicine and Health Management, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511436, China
环状RNA(circular RNA, circ RNA)起初于植物类病毒中发现的单链环状RNA[1-2]。随后发现人体细胞也存在大量circRNA。环状RNA的含量在一些组织中比线性RNA多,可达10倍以上; circRNA是没有5'末端和3'末端的闭合环状,通过3′, 5′-磷酸二酯键首尾相连接,这样的特殊结构使得环状RNA比线性RNA更具有稳定性[3]; 环状内含子RNA中含有少量miRNA应答元件,含有大量miRNA结合位点,可通过与miRNA结合,调控mRNA的表达和蛋白质的翻译[4]。
环状RNA有几个显著的特征使它们具有成为人类疾病生物标志物的潜能:(1)稳定性:环状RNA分子缺乏的游离5'和3'末端共价闭环结构,具有抗核酸外切酶的RNaseR的能力[5-6]。血浆中环状RNA的平均半衰期超过48 h,远远长于mRNA 10 h的平均值[7],这使环状RNA相比线性RNA更稳定,更适合作为生物标志物。(2)普遍性:有研究认为环状RNA是分布在人类细胞中最普遍的分子[8-9]。(3)特异性:环状RNA以组织特异性和发育阶段特异性方式表达,这使其具有成为特定疾病的潜在生物标志物的能力[10]。许多研究也表明,环状RNA在癌组织和非癌组织之间有明显的差异表达[11]。(4)保守性:研究发现环状RNA在不同物种中具有进化保守性,这意味着在其他动物模型中鉴定的一些环状RNA生物标志物具有转化为人类临床应用的潜力[1, 12]。
环状RNA与线性RNA不同,不是通过RNA剪接的典型模式产生的[13]。环状RNA可以分为三类:外显子环状RNA(ecircRNA)、内含子环状RNA(ciRNA)、外显子-内含子环状RNA(EIciRNAs)[14]。Jeck等提出了两种不同的外显子环化模型,称为“套索驱动的环化”和“内含子驱动的环化”[3]。前一模型与“外显子跳跃”相关,其导致从剪接供体的3'末端到剪接受体的5'末端的共价剪接,产生含有外显子的套索结构。然后通过剪接体连接套索,并在移除内含子后形成ecircRNA。后者则认为侧翼内含子通过反向互补序列配对形成环状结构,然后剪切去除内含子并连接外显子,最终形成ecircRNA或EIciRNA[7, 15]。在随后的研究中,在人类细胞中发现了一种来自内含子的新型环状RNA即ciRNA,并提出了由于脱支失败导致ciRNA形成的新模型[4]。
1 环状RNA与肿瘤在肿瘤的发生过程中,不同的miRNA分别有类似抑癌基因和原癌基因的作用[16]。Yang等[17]发现循环RNA circ-ITCH通过海绵状miR-17/miR-224抑制膀胱癌进展并调节p21、PTEN的表达; Zhang等[18]发现hsa_circ_0007534的沉默抑制了结肠直肠癌细胞的增殖并诱导细胞凋亡; Xu等[19]发现环状RNA hsa_circ_0001649可调节胆管癌的增殖、迁移和侵袭; Zhu等[20]证实通过调节miR-1324/FZD5/Wnt/β-catenin轴,circRNA circ_0067934可促进肝癌细胞的生长和转移。
环状RNA可通过内源性竞争与miRNA上的靶位点结合,从而增强或抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖、分化和侵袭。Huang等[21]发现circRNA-100338与miR-141-3p结合,可调节乙型肝炎相关肝细胞癌; Han等[22]发现环状RNA circMTO1作为microRNA-9的海绵起到抑制肝细胞癌进展的作用。
环状RNA因其数量多、稳定性好、组织特异性且易提取等特点,成为当前肿瘤界的研究热点。虽然还没有实际应用到疾病诊断中,但随着研究对象的深入及扩展,可以为肿瘤的治疗和预后提供更多的可能性。
2 环状RNA作为肺癌的生物分子标志物最近的研究表明,环状RNA可能在肺癌的发生发展和预后中起重要作用,可以作为肺癌的生物标志物[23-42]。在这些研究中,hsa_circ_0046264[23]、circRNA-FOXO3[24]、circ_0001649[25]、circRNF13[26]、cir-ITCH[27]被证实在肺癌组织中表达下调,而hsa_circ_0079530[28]、circRNA_100876[29]、hsa_circ_0007385[30]、hsa_circ_0014130[31]、hsa_circ_0012673[32]、circPRKCI[33]、circ_001569[34]、hsa_circ_0007534[35]、circMAN2B2[36]、hsa_circ_0000064[37]、circUBAP2[38]、hsa_circ RNA_103809[39]、circ-BANP[40]、hsa_circ_0013958[41]、circRNA_102231[42]则被证实在肺癌组织中表达上调,这些分子同时也被证实在肿瘤的诊断和预后或进程中具有生物标志物的作用。
2.1 环状RNA作为诊断的生物标志物Li等[28]分析了92例NSCLC患者样本,发现hsa_circ_0079530在肺癌组织中表达显著上调(P < 0.01),其高表达在肿瘤大小(P=0.001)和淋巴结转移(P=0.038)中差异具有统计学意义,并且hsa_circ_0079530在NSCLC中的诊断ROC曲线下面积为0.756(95%CI: 0.649~0.864; P < 0.01),说明hsa_circ_0079530对肺癌的诊断具有一定的价值。hsa_circ_0013958[41]在49例患者的肺腺癌组织、细胞和血浆中的表达均显著上调,促进癌细胞增殖和侵袭,被认为是早期检测和筛查肺癌的潜在非侵入性生物标志物。circRNA_102231[42]和hsa_circ_0014130[31]也被证实在肺癌组织表达上调,且都具有对肺癌的潜在诊断价值。Zong等[42]对57例肺腺癌患者样本进行分析,诊断的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.897,敏感度和特异性分别为81.2%和88.7%。Zhang等[31]对46例非小细胞肺癌患者进行分析,发现hsa_circ_0014130诊断的ROC曲线下面积为0.878,最佳截断值为0.573,敏感度和特异性分别为87.0%和84.8%。
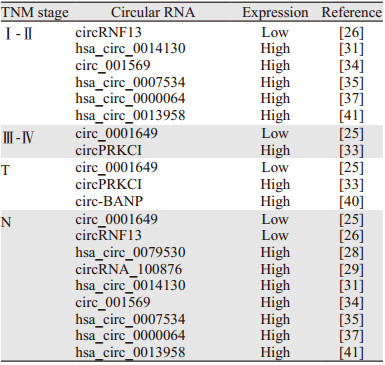
2.2 环状RNA与TNM分期研究显示,差异表达的环状RNA与TNM分期系统有着密切联系,有望成为肺癌TNM分期的生物标志物[25-26, 28-29, 31, 33-35, 37, 40-41],见表 1。
现阶段的研究中,差异表达的环状RNA与肺癌TNM分期中的N分期以及Ⅰ~Ⅱ期相关性较强,环状RNA的差异表达可能与肺癌的淋巴结受累情况有关。因此,环状RNA很有可能参与了肺癌的进展、转移,环状RNA也有望成为肺癌TNM分期的生物标志物。
2.3 环状RNA作为预后的生物标志物Liu等[39]发现hsa_circRNA_103809在肺癌组织中显著上调,进行Kaplan-Meier曲线分析,发现患者中hsa_circRNA_103809的较高表达与较低的存活率相关,说明hsa_circRNA_103809可作为肺癌预后的生物标志物。同时,另一项研究也发现[29],circRNA_100876在肺癌组织中的表达显著上调,并且具有高circRNA_100876表达的NSCLC患者的总存活时间显著短于具有低circRNA_100876表达的患者。circ-BANP[40]、circ_001569[34]、hsa_circ_0007534[35]也被证实可以作为NSCLC患者预后检测的潜在生物标志物。
2.4 环状RNA与增殖、凋亡、侵袭和迁移环状RNA与肺癌的侵袭和迁移的相关性较强,可能参与了肺癌侵袭和迁移相关的信号通路,影响了肺癌的侵袭和迁移[23-28, 30, 33-41],因此,环状RNA也有望成为肺癌治疗的靶点,成为肺癌治疗的生物标志物,见表 2。

|
环状RNA大量的研究目前仍停留在基础研究中,尚缺乏转化性研究的报道。现阶段尚未将肺癌患者中差异表达的环状RNA或其他肺癌生物标志物进行联合研究。肺癌研究领域环状RNA研究利用的标本种类过于单一,大部分研究者采用的仍是肺癌患者的癌组织以及癌旁组织,目前尚缺乏大范围大样本的肺癌环状RNA研究。环状RNA也尚无统一的命名系统,极易出现不同领域学者在研究同一个环状RNA时采用不同的称呼,从而造成混乱。
在临床应用方面,环状RNA也有更多研究价值,其闭合环结构在体液中更稳定,在血浆[43]、唾液[44-45]以及外泌体中都稳定存在[46-47],在多种疾病的发生发展中发挥重要作用,并且在肿瘤诊断、治疗和预后等方面有巨大潜能[48],因此具有成为诊断生物标志物的可能。环状RNA也有一些诊断方面的缺点:一些环状RNA需要患者的组织进行诊断,这会给患者带来创伤。其次,检测组织或外泌体中的环状RNA比现有检查更昂贵,限制了环状RNA作为生物标志物的广泛使用。虽然环状RNA的产生及其确定的功能尚不完全清楚,但随着环状RNA对肿瘤的影响机制的进一步研究,更多在肺癌中差异表达的环状RNA将被发现,未来将在疾病预防、诊断和治疗中发挥越来越重要的作用。
作者贡献
萧志昊:收集资料、撰写论文
肖瑶:承担论文的经费、设计、质量把关
卢晓丹:撰写及修改论文
李文丹:收集资料、撰写论文
| [1] | Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency[J]. Nature, 2013, 495(7441): 333–338. DOI:10.1038/nature11928 |
| [2] | Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, et al. Viroids are Single-Stranded Covalently Closed Circular RNA Molecules Existing as Highly Base-Paired Rod-Like Structures[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1976, 73(11): 3852–3856. DOI:10.1073/pnas.73.11.3852 |
| [3] | Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats[J]. RNA, 2013, 19(2): 141–157. DOI:10.1261/rna.035667.112 |
| [4] | Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, et al. Circular Intronic Long Noncoding RNAs[J]. Mol Cell, 2013, 51(6): 792–806. DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.017 |
| [5] | Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, et al. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs[J]. Cell, 2015, 160(6): 1125–1134. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.014 |
| [6] | Enuka Y, Lauriola M, Feldman ME, et al. Circular RNAs are long-lived and display only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2016, 44(3): 1370–1383. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkv1367 |
| [7] | Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2014, 32(5): 453–461. DOI:10.1038/nbt.2890 |
| [8] | Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17(1): 79. DOI:10.1186/s12943-018-0827-8 |
| [9] | Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, et al. Circular RNAs Are the Predominant Transcript Isoform from Hundreds of Human Genes in Diverse Cell Types[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(2): e30733. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0030733 |
| [10] | Petar Glažar, Panagiotis Papavasileiou, Rajewsky N. circBase: a database for circular RNAs[J]. RNA, 2014, 20(11): 1666–1670. DOI:10.1261/rna.043687.113 |
| [11] | Li M, Ding W, Sun T, et al. Biogenesis of circular RNAs and their roles in cardiovascular development and pathology[J]. FEBS J, 2018, 285(2): 220–232. DOI:10.1111/febs.2018.285.issue-2 |
| [12] | Floris G, Zhang L, Follesa P, et al. Regulatory Role of Circular RNAs and Neurological Disorders[J]. Molecular Neurobiology, 2017, 54(7): 5156–5165. DOI:10.1007/s12035-016-0055-4 |
| [13] | Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, et al. circRNA Biogenesis Competes with Pre-mRNA Splicing[J]. Mol Cell, 2014, 56(1): 55–66. DOI:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.019 |
| [14] | Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus[J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2015, 22(3): 256–264. DOI:10.1038/nsmb.2959 |
| [15] | Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, et al. Complementary Sequence-Mediated Exon Circularization[J]. Cell, 2014, 159(1): 134–147. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.001 |
| [16] | Karreth FA, Pandolfi PP. ceRNA Cross-Talk in Cancer: When ce-bling Rivalries Go Awry[J]. Cancer Dis, 2013, 3(10): 1113–1121. DOI:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0202 |
| [17] | Yang C, Yuan W, Yang X, et al. Circular RNA circ-ITCH inhibits bladder cancer progression by sponging miR-17/miR-224 and regulating p21, PTEN expression[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17(1): 19. DOI:10.1186/s12943-018-0771-7 |
| [18] | Zhang R, Xu J, Zhao J, et al. Silencing of hsa_circ_0007534 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(1): 118–126. |
| [19] | Xu Y, Yao Y, Zhong X, et al. Downregulated circular RNA hsa_circ_0001649 regulates proliferation, migration and invasion in cholangiocarcinoma cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 496(2): 455–461. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.077 |
| [20] | Zhu Q, Lu G, Luo Z, et al. CircRNA circ_0067934 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulation of miR-1324/FZD5/Wnt/β-catenin axis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 497(2): 626–632. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.119 |
| [21] | Huang XY, Huang ZL, Xu YH, et al. Comprehensive circular RNA profiling reveals the regulatory role of the circRNA-100338/miR-141-3p pathway in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 5428. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-05432-8 |
| [22] | Han D, Li J, Wang H, et al. Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as the sponge of microRNA-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(4): 1151–1164. DOI:10.1002/hep.29270 |
| [23] | Yang L, Wang J, Fan Y, et al. Hsa_circ_0046264 up-regulated BRCA2 to suppress lung cancer through targeting hsa-miR-1245[J]. Respir Res, 2018, 19(1): 115. DOI:10.1186/s12931-018-0819-7 |
| [24] | Zhang Y, Zhao H, Zhang L. Identification of the tumor-suppressive function of circular RNA FOXO3 in non-small cell lung cancer through sponging miR-155[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 17(6): 7692–7700. |
| [25] | Liu T, Song Z, Gai Y. Circular RNA circ_0001649 acts as a prognostic biomarker and inhibits NSCLC progression via sponging miR-331-3p and miR-338-5p[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 503(3): 1503–1509. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.070 |
| [26] | Wang L, Liu S, Mao Y, et al. CircRNF13 regulates the invasion and metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting miR-93-5p[J]. Gene, 2018, pii: S0378-1119(18)30443-8. |
| [27] | Wan L, Zhang L, Fan K, et al. Circular RNA-ITCH Suppresses Lung Cancer Proliferation via Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2016, 2016: 1579490. |
| [28] | Li J, Wang J, Chen Z, et al. Hsa_circ_0079530 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Gene, 2018, 665: 1–5. DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2018.04.059 |
| [29] | Yao JT, Zhao SH, Liu QP, et al. Over-expression of circRNA_100876 in non-small cell lung cancer and its prognostic value[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2017, 213(5): 453–456. DOI:10.1016/j.prp.2017.02.011 |
| [30] | Jiang MM, Mai ZT, Wan SZ, et al. Microarray profiles reveal that circular RNA hsa_circ_0007385 functions as an oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2018, 144(4): 667–674. DOI:10.1007/s00432-017-2576-2 |
| [31] | Zhang S, Zeng X, Ding T, et al. Microarray profile of circular RNAs identifies hsa_circ_0014130 as a new circular RNA biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 2878. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-21300-5 |
| [32] | Wang X, Zhu X, Zhang H, et al. Increased circular RNA hsa_circ_0012673 acts as a sponge of miR-22 to promote lung adenocarcinoma proliferation[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 496(4): 1069–1075. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.126 |
| [33] | Qiu M, Xia W, Chen R, et al. The circular RNA circPRKCI promotes tumor growth in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2018, 78(11): 2839–2851. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2808 |
| [34] | Ding L, Yao W, Lu J, et al. Upregulation of circ_001569 predicts poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 16(1): 453–458. |
| [35] | Qi Y, Zhang B, Wang J, et al. Upregulation of circular RNA hsa_circ_0007534 predicts unfavorable prognosis for NSCLC and exerts oncogenic properties in vitro and in vivo[J]. Gene, 2018, 676: 79–85. DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2018.07.028 |
| [36] | Ma X, Yang X, Bao W, et al. Circular RNA circMAN2B2 facilitates lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion via miR-1275/FOXK1 axis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 498(4): 1009–1015. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.105 |
| [37] | Luo YH, Zhu XZ, Huang KW, et al. Emerging roles of circular RNA hsa_circ_0000064 in the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 96: 892–898. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.015 |
| [38] | 殷玉敬, 高辉, 郭佳, 等. 环状RNA UBAP2沉默对肺癌A549细胞体外增殖和侵袭的影响及机制[J]. 中国肺癌杂志, 2017, 20(12): 800–807. [ Yin Y, Gao H, Guo J, et al. Effect of Circular RNA UBAP2 Silencing on Proliferation and Invasion of Human Lung Cancer A549 Cells and Its Mechanism[J]. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi, 2017, 20(12): 800–807. DOI:10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.12.02 ] |
| [39] | Liu W, Ma W, Yuan Y, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circRNA_103809 promotes lung cancer progression via facilitating ZNF121-dependent MYC expression by sequestering miR-4302[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 500(4): 846–851. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.172 |
| [40] | Han J, Zhao G, Mao X, et al. CircRNA circ-BANP-mediated miR-503/LARP1 signaling contributes to lung cancer progression[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 503(4): 2429–2435. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.172 |
| [41] | Zhu X, Wang X, Wei S, et al. hsa_circ_0013958: a circular RNA and potential novel biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma[J]. FEBS J, 2017, 284(14): 2170–2182. DOI:10.1111/febs.2017.284.issue-14 |
| [42] | Zong L, Sun Q, Zhang H, et al. Increased expression of circRNA_102231 in lung cancer and its clinical significance[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 102: 639–644. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.084 |
| [43] | Koh W, Pan W, Gawad C, et al. Noninvasive in vivo monitoring of tissue-specific global gene expression in humans[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2014, 111(20): 7361–7366. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1405528111 |
| [44] | Bahn JH, Zhang Q, Li F, et al. The Landscape of MicroRNA, Piwi-Interacting RNA, and Circular RNA in Human Saliva[J]. Clin Chem, 2015, 61(1): 221–230. DOI:10.1373/clinchem.2014.230433 |
| [45] | Lin X, Lo HC, Wong DT, et al. Noncoding RNAs in human saliva as potential disease biomarkers[J]. Front Genet, 2015, 6: 175. |
| [46] | Dou Y, Cha DJ, Franklin JL, et al. Circular RNAs are down-regulated in KRAS mutant colon cancer cells and can be transferred to exosomes[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 37982. DOI:10.1038/srep37982 |
| [47] | Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, et al. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis[J]. Cell Res, 2015, 25(8): 981–984. DOI:10.1038/cr.2015.82 |
| [48] | 郭佳妮, 何敬东. circRNAs在肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2016, 43(8): 728–730. [ Guo JN, He JD. Research progress of circRNAs in cancer[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2016, 43(8): 728–730. DOI:10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2016.08.016 ] |
 2019, Vol. 46
2019, Vol. 46