文章信息
- Integrinβ1和CARMA-3蛋白在膀胱癌组织中的表达与经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术后复发的相关性
- Relationship of Integrinβ1 and CARMA-3 Protein Expressions with Recurrence of Bladder Cancer After Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2019, 46(3): 239-242
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2019, 46(3): 239-242
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2019.18.1182
- 收稿日期: 2018-08-17
- 修回日期: 2018-10-29
膀胱癌(bladder cancer)是泌尿肿瘤系常见的恶性肿瘤,近90%的膀胱癌患者属于移行细胞癌。尽管患者可进行相应的手术治疗,但因其具有侵袭、转移的特性,使患者术后易复发,造成患者预后困难,因此探索膀胱癌术后复发的相关分子生物学特性,有助于更好地对患者进行预后评估和个体化治疗[1]。肿瘤细胞黏附是肿瘤转移和复发的关键环节[2],因此研究肿瘤细胞黏附有助于研究肿瘤预后。整合素β1(Integrinβ1)是整合素(Integrins)家族成员,具有介导细胞与细胞外基质、细胞与细胞之间的黏附反应,进而调控细胞增殖、迁移、分化等生物学行为。目前Integrinβ1已被报道在结直肠癌[3]、食管鳞癌[4]、乳腺癌[5]等多种肿瘤中过度表达。含半胱天冬酶募集结构域的膜相关鸟苷酸激酶蛋白3(CARD recruited membrane associated protein 3, CARMA-3)主要参与G蛋白偶联受体(G protein coupled receptor,GPCR)或表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR)诱导的NF-κB异常活化的过程。NF-κB异常活化与炎性反应、肿瘤的发生发展有关[6-8]。研究还发现,CARMA-3在多种肿瘤细胞高表达[8-9],抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖与浸润[10],并且与肿瘤生长、分期相关[11]。但关于Integrinβ1及CARMA-3表达与膀胱癌经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术后预后关系的系统性研究报道甚少。本研究检测膀胱癌组织中Integrinβ1及CARMA-3蛋白的表达情况,并探讨其与经膀胱癌电切术后预后的关系。
1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料选取2012年1月—2013年12月我院收治的160例经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术治疗的膀胱癌患者,保留患者的癌旁组织(距膀胱癌边缘3 cm)和膀胱癌组织标本,并对患者随访5年。其中,20例失访,10例死于其他疾病,2例中途退出,20例无复发,共纳入108例复发患者。根据患者尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术后复发时间分为短期复发组50例(6月内复发的患者)和长期首次复发组58例(3年以上第一次复发的患者)。本研究经患者知情同意,并通过了伦理委员会的认定(编号:201112A03)。
1.2 方法将纳入患者的膀胱癌组织和癌旁组织的石蜡标本,制作5 μm厚度的石蜡切片。参照免疫组织化学试剂盒(购自深圳宝安康生物公司)说明书进行免疫组织化学分析。实验步骤如下:常规脱蜡至水,抗原修复液(0.01 mol/L枸橼酸钠缓冲液)98℃修复20 min,室温下3%H2O2封闭内源性过氧化物酶30 min,水洗2次,晾干; 山羊血清封闭30 min; 甩除封闭液,加入Integrinβ1单克隆抗体(1:100稀释; Cat: sc-9970; Santa Cruz; 美国)或CARMA-3单克隆抗体(1:100稀释; Cat:SAB4501342; Sigma; 美国),4℃孵育过夜,PBS洗2次,孵育相应二抗室温孵育40 min,PBS洗2次; DAB显色3 min,Mayer's苏木精对比染色细胞核,1%盐酸酒精分化3秒,水洗2次,逐级酒精脱水,二甲苯透明,中性树胶封片。
1.3 判断标准Integrinβ1及CARMA-3进入细胞质或者细胞膜变为棕色,视为阳性。Integrinβ1及CARMA-3都依据阳性细胞数比例和染色强度参考相关半定量评分标准:(1)依据阳性细胞所占比例区分:没有阳性细胞记为0分; 阳性细胞所占比例<30%记为1分; 阳性细胞≥30%记为2分。(2)依据着色情况区分:没有着色记为0分; 表现为淡黄色记为1分; 表现为棕黄色记为2分; 表现为棕褐色记为3分。计算以上所得评分的乘积,若为0分,则为阴性; 若为1~2分,则为弱阳性; 若为3~4分,则为中阳性; 若为5~6分,则为强阳性。阅片的积分是由病理科两名高年资同事对评分一致的切片直接通过; 评分不一致的切片商讨通过; 商讨不一致的切片经第三人判定通过。
1.4 统计学方法采用SPSS20.0统计软件进行分析,计数资料行χ2检验,计量资料行t检验,相关性分析采用Spearman等级相关分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 患者一般资料分析两组患者在年龄和性别上比较,差异无统计学意义,但在T分期和病理分级上比较,差异有统计学意义(均P < 0.05); 短期复发组T1期和T2期所占比例大于长期首次复发组; 且低分化所占比例大于长期首次复发组,见表 1。

|
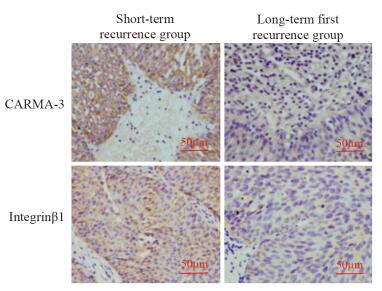
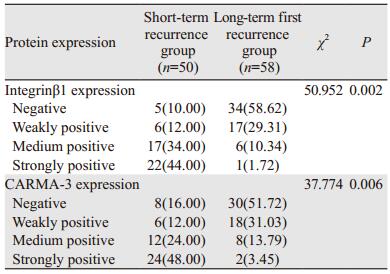
两组膀胱癌组织中Integrinβ1和CARMA-3蛋白均位于细胞质与细胞膜,见图 1,其中短期复发组患者的Integrinβ1和CARMA-3蛋白表达显著高于长期复发组(P < 0.05),见表 2。
|
| 图 1 短期复发组和长期首次复发组CARMA-3和Integrinβ1蛋白的表达(IHC ×200) Figure 1 Integrinβ1 and CARMA-3 expressions in short-term recurrence group and long-term first recurrence group (IHC ×200) |
|
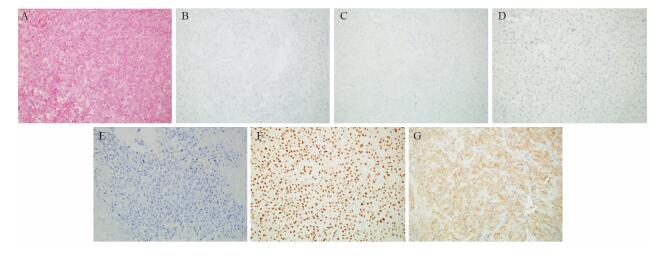
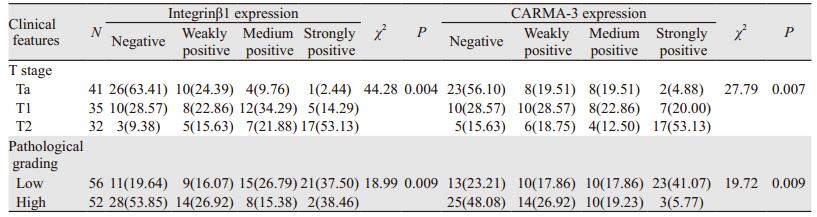
不同T分期Integrinβ1和CARMA-3蛋白表达的免疫组织化学结果,见图 2;Integrinβ1、CARMA-3蛋白的表达与T分期和分级成正相关,即:分期以及分级越高,患者的Integrinβ1蛋白和CARMA-3阳性表达越高(P < 0.05),见表 3。
|
| 图 2 不同T分期膀胱癌组织中CARMA-3和Integrinβ1蛋白的表达(IHC ×200) Figure 2 Integrinβ1 and CARMA-3 expressions in different T stages of bladder cancer (IHC ×200) |
|
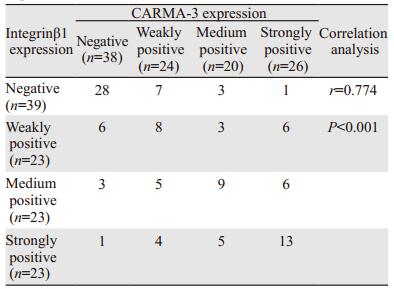
Integrinβ1和CARMA-3两种蛋白的表达呈明显正相关(r=0.774, P < 0.001),见表 4。
|
膀胱癌是泌尿生殖肿瘤中常见的恶性肿瘤之一,其发病率居泌尿系统恶性肿瘤的首位,且呈明显上升趋势[12]。膀胱癌根据其临床特征大致分为表浅性膀胱癌、肌层浸润性膀胱癌和转移性膀胱癌。表浅性膀胱癌是较早期的膀胱癌,首选经尿道膀胱肿瘤切除术治疗,该手术创伤小、恢复快。但目前为止,关于尿道肿瘤电切术后膀胱癌复发和预后方面的研究尚不全面。
研究表明,肿瘤的复发是一个多因素共同参与的复杂过程,而肿瘤细胞黏附是参与这个过程的一个重要环节[2]。Vallo等[13]发现,抑制Integrinβ1表达能抑制尿路上皮肿瘤细胞(包含膀胱癌细胞)黏附。Integrinβ1高表达与胰腺癌[14]、结直肠癌[15]、乳腺癌[16]等多种肿瘤的不良预后相关。本研究发现Integrinβ1蛋白在经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术后短期复发组明显高于远期首次复发组(P < 0.05),且Integrinβ1的表达与膀胱癌的T分期和分级明显相关(P < 0.05),结果暗示Integrinβ1蛋白是经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术后膀胱癌复发的危险因子。
而肿瘤的复发和转移一般伴随着G蛋白偶联受体(G protein coupled receptor, GPCR)和表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR)异常表达和失调[17]。CARMA-3主要参与GPCR及EGFR诱导的NF-κB激活肿瘤生长、转移、复发过程[6-8]。且众多研究表明CARMA-3在多种肿瘤细胞中高表达,可导致肿瘤的不良预后[8-10]。本研究发现CARMA-3蛋白在经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术后短期复发组明显高于远期首次复发组(P < 0.05)且与膀胱癌的T分期和分级明显相关(P < 0.05)。进一步分析膀胱癌中Integrinβ1和CARMA-3蛋白表达的相关性,结果显示两者的表达呈正相关(r=0.774, P < 0.05),提示Integrinβ1和CARMA-3在经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术后膀胱癌的复发中可能具有协同作用,但是两者参与调控肿瘤复发的具体作用机制还有待进一步研究。
综上所述,表明Integrinβ1及CARMA-3表达与经膀胱癌经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术后复发相关,且两者的表达呈正相关,由此推测Integrinβ1和CARMA-3可作为新的衡量经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术后膀胱癌复发的分子标志物。
作者贡献
李群秀:收集资料,设计实验与撰写论文
付凤林:监督实验进展
张胜利:统计数据
| [1] | Giulietti M, Occhipinti G, Righetti A, et al. Emerging biomarkers in bladder cancer identified by network analysis of transcriptomic data[J]. Front Oncol, 2018, 8: 450. DOI:10.3389/fonc.2018.00450 |
| [2] | Zhang H, Fredericks T, Xiong G, et al. Membrane associated collagen ⅩⅢ promotes cancer metastasis and enhances anoikis resistance[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2018, 20(1): 116. DOI:10.1186/s13058-018-1030-y |
| [3] | Takei N, Yoneda A, Sakai-Sawada K, et al. Hypoxia-inducible ERO1α promotes cancer progression through modulation of integrinβ1 modification and signalling in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 9389. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-09976-7 |
| [4] | Xu Z, Zou L, Ma G, et al. Integrin β1 is a critical effector in promoting metastasis and chemo-resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2017, 7(3): 531–42. |
| [5] | Hamurcu Z, Kahraman N, Ashour A, et al. FOXM1 transcriptionally regulates expression of integrinβ1 in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2017, 163(3): 485–93. DOI:10.1007/s10549-017-4207-7 |
| [6] | Spirina LV, Usynin YA, Yurmazov ZA, et al. Transcription factors NF-κB, HIF-1, HIF-2, growth factor VEGF, VEGFR2 and carboanhydrase Ⅸ mRNA and protein level in the development of kidney cancer metastasis[J]. Mol Biol, 2017, 51(2): 328–32. DOI:10.1134/S0026893317020194 |
| [7] | Li Y, Lin Z, Chen B, et al. Ezrin/NF-κB activation regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by EGF and promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 92: 140–8. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.058 |
| [8] | Hu YC, Yi ZJ, Zhou Y, et al. Overexpression of RIP140 suppresses the malignant potential of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated alternative polarization of macrophages[J]. Oncol Rep, 2017, 37(5): 2971–9. DOI:10.3892/or.2017.5551 |
| [9] | Xia ZX, Li ZX, Zhang M, et al. CARMA3 regulates the invasion, migration, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by activating NF-κB and suppressing the P38 MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Exp Mol Pathol, 2016, 100(2): 353–60. DOI:10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.10.004 |
| [10] | Zhang S, Zhang C, Liu W, et al. MicroRNA-24 upregulation inhibits proliferation, metastasis and induces apoptosis in bladder cancercells by targeting CARMA3[J]. Int J Oncol, 2015, 47(4): 1351–60. DOI:10.3892/ijo.2015.3117 |
| [11] | Xie C, Han Y, Fu L, et al. Overexpression of CARMA3 is associated with advanced tumor stage, cell cycle progression, and cisplatin resistance in human epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35(8): 7957–64. DOI:10.1007/s13277-014-2070-2 |
| [12] | Choi E, Lee S, Nhung BC, et al. Cancer mortality-to-incidence ratio as an indicator of cancer management outcomes in Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development countries[J]. Epidemiol Health, 2017, 39: e2017006. DOI:10.4178/epih.e2017006 |
| [13] | Vallo S, Rutz J, Kautsch M, et al. Blocking integrin β1 decreases adhesion in chemoresistant urothelial cancer cell lines[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(5): 5513–8. |
| [14] | Yang D, Tang Y, Fu H, et al. Integrin β1 promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer through Cdc42 activation of PI3K p110β signaling[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 505(1): 215–21. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.061 |
| [15] | Qiu X, Feng JR, Qiu J, et al. ITGBL1 promotes migration, invasion and predicts a poor prognosis in colorectal cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 104: 172–80. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.033 |
| [16] | Liu B, Zheng X, Meng F, et al. Overexpression of β1 integrin contributes to polarity reversal and a poor prognosis of breast invasive micropapillary carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 9(4): 4338–53. |
| [17] | Dho SH, Lee KP, Jeong D, et al. GPR171 expression enhances proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer cells[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(7): 7856–65. |
 2019, Vol. 46
2019, Vol. 46
