文章信息
- 蛇葡萄素通过Dermcidin蛋白调节肝癌细胞株HepG2侵袭活力及侵袭基因表达的实验
- Ampelopsis Regulates Invasive Activity and Invasion Gene Expression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cell Line Through Dermcidin Protein
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2019, 46(3): 218-221
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2019, 46(3): 218-221
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2019.18.1175
- 收稿日期: 2018-08-17
- 修回日期: 2018-10-22
肝癌是我国常见的消化系统恶性肿瘤,肿瘤病灶的血供丰富、癌细胞的增殖和侵袭活力旺盛,确诊时多已发展至中晚期、预后较差。目前,临床上用于肝癌治疗的手段包括手术切除、放化疗、热疗、射频消融、靶向药物等,但疗效并不理想[1-2]。因此,探寻肝癌治疗的新药具有迫切的临床价值。近年来,中药材的抗肿瘤价值受到了越来越多的关注。蛇葡萄素(ampelopsin, AMP)是从粤蛇葡萄及显齿蛇葡萄中提取得到的黄酮类化合物,已经在多种恶性肿瘤中被证实具有抗癌活性[3]。Dermcidin蛋白是新发现的与肝癌病理进程密切相关的一种蛋白,由dermcidin基因编码并且在肝癌组织中呈高表达的趋势[4]。本研究拟通过离体培养的肝癌细胞株HepG2来验证AMP对细胞侵袭活力及侵袭基因表达的调节作用,进一步通过转染小干扰RNA(siRNA)的方式来敲低dermcidin基因的表达并明确AMP在肝癌细胞内的生物学效应是否由dermcidin基因介导。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料肝癌细胞株HepG2购于美国ATCC细胞公司,细胞培养基RPMI 1640及胎牛血清购于美国Gibco公司,AMP购于成都曼斯特公司,Transwell小室购于美国Millipore公司,Matrigel基质胶购于美国BD公司,LipofectamineTM2000转染试剂购于美国Invitrogen公司,dermcidin基因的siRNA及阴性对照(NC)siRNA购于上海吉玛公司,荧光定量PCR检测所用引物购于上海生工公司、试剂盒购于北京天根公司。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 细胞培养肝癌细胞株HepG2用含有10%胎牛血清的RPMI 1640在培养瓶内进行培养,培养条件为100%饱和湿度、5CO2、37℃,细胞密度生长至90%后用胰蛋白酶进行消化,消化后的细胞继续传代并用于后续实验。
1.2.2 细胞处理细胞接种在培养板内,待细胞密度生长至80%~90%后进行处理,对照组处理条件为不含血清及药物的RPMI 1640,AMP组处理条件为含有不同剂量AMP的无血清RPMI 1640(AMP终浓度为20、40、60、80 μmol/L); siRNA转染采用LipofectamineTM2000转染试剂,在含有80 μmol/L AMP的无血清RPMI 1640中转染dermcidin基因的siRNA。
1.2.3 细胞迁移及侵袭的Transwell检测将细胞接种在预先涂有Matrigel基质胶的Transwell小室及未涂Matrigel基质胶的Transwell小室,不同条件处理后24 h用棉签擦拭Transwell小室内膜的细胞,结晶紫染色15 min后在40倍的高倍视野下随机观察4个视野,计数后计算平均数。
1.2.4 基因mRNA表达量的检测将细胞接种在12孔细胞板内,不同条件处理后24 h弃去培养液,保留细胞并用PBS缓冲液清洗2遍。采用试剂盒抽提细胞内的RNA并反转录为cDNA,按照cDNA 2 μl、含酶的PCR反应混合液10 μl、5 μmol/L的引物混合液0.8 μl、去离子水7.2 μl的方案配置反应体系,按照95℃ 20 s、基因特异性退火温度15 s、72℃ 25 s的反应程序重复40次,在软件中生成反应曲线后读取循环阈值(cycle threshold, Ct),根据2-ΔΔCt计算基因的mRNA表达量。
1.3 统计学方法采用SPSS19.0软件录入数据,计量资料的两组间比较采用t检验,多组间比较采用方差分析,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
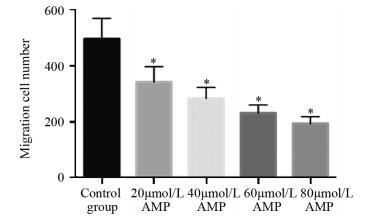
2 结果 2.1 AMP对HepG2细胞迁移和侵袭的调节作用在不含Matrigel基质胶的Transwell小室内,不同剂量AMP处理后细胞的迁移数目均低于对照组,且AMP剂量越大、细胞的迁移数目越少,20、40、60、80 μmol/L AMP组与对照组相比,P值依次为0.002、9.777×10-5、9.678×10-6、2.401×10-6,差异有统计学意义,见图 1;在含有Matrigel基质胶的Transwell小室内,不同剂量AMP处理后细胞的侵袭数目均低于对照组且AMP剂量越大、细胞的侵袭数目越少,20、40、60、80 μmol/L AMP组与对照组相比,P值依次为0.002、2.390×10-5、2.585×10-6、6.013×10-7,差异有统计学意义,见图 2。
|
| *: P < 0.05, compared with control group 图 1 AMP处理后HepG2细胞在不含Matrigel基质胶的Transwell小室内的迁移数目 Figure 1 Number of migration HepG2 cells treated with AMP in Transwell chamber without Matrigel |

|
| *: P < 0.05, compared with control group 图 2 AMP处理后HepG2细胞在含有Matrigel基质胶的Transwell小室内的侵袭数目 Figure 2 Number of invadsion HepG2 cells treated with AMP in Transwell chamber without Matrigel |
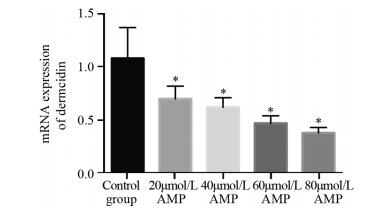
对照组中Dermcidin mRNA水平为(1.09±0.17),20、40、60和80 μmol/L剂量AMP处理后细胞中Dermcidin mRNA水平分别为(0.85±0.12)、(0.67±0.07)、(0.51±0.07)和(0.39±0.05)。不同剂量AMP处理后,细胞中Dermcidin mRNA水平均降低,且AMP剂量越大、细胞Dermcidin mRNA水平越低,20、40、60、80 μmol/L AMP组与对照组相比,P值依次为0.018、0.0002、1.583×10-5、2.147×10-6,差异有统计学意义,见图 3。
|
| *: P < 0.05, compared with control group 图 3 AMP处理后HepG2细胞中Dermcidin mRNA的表达水平 Figure 3 Expression of Dermcidin mRNA in HepG2 cells treated with AMP |
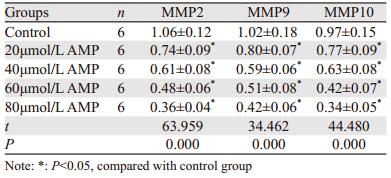
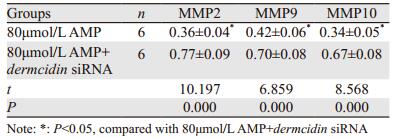
不同剂量AMP处理后,细胞中MMP2、MMP9和MMP10 mRNA水平均降低,且AMP剂量越大,细胞中MMP2、MMP9和MMP10 mRNA水平越低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表 1。
|
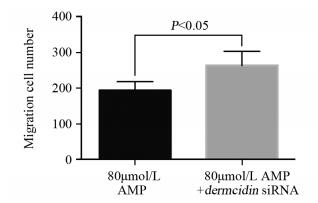
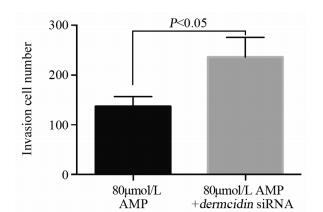
在含有80 μmol/L AMP的RPMI 1640中转染dermcidin基因的siRNA,与80 μmol/L AMP处理组比较,细胞的迁移、侵袭数目以及细胞内MMP2、MMP9和MMP10 mRNA的表达水平均增多,见图 4~5、表 2。
|
| 图 4 AMP联合dermcidin siRNA后HepG2细胞的迁移数目 Figure 4 Number of migration HepG2 cells treated with AMP combined with dermcidin gene siRNA transfection |
|
| 图 5 AMP联合dermcidin siRNA后HepG2细胞的侵袭数目 Figure 5 Number of invasion HepG2 cells treated with AMP combined with dermcidin gene siRNA transfection |
|
肝癌具有恶性程度高、容易发生远处转移,5年生存率较低、预后较差的特点,病灶内癌细胞侵袭活力的过度增强是与肝癌预后密切相关的病理环节,抑制肝癌细胞的侵袭活力被认为是治疗疾病的潜在靶点[5-6]。AMP是从粤蛇葡萄及显齿蛇葡萄中提取的抗癌活性物质,在乳腺癌、卵巢癌等多种恶性肿瘤中被证实具有确切的抗癌活性[7-8]。本研究在Transwell小室内培养肝癌细胞并用AMP进行处理,肝癌细胞在预先涂有Matrigel基质胶的Transwell小室及未涂Matrigel基质胶的Transwell小室内的移动分别能够反应细胞的侵袭和迁移,分析结果显示:AMP能够以剂量依赖性的方式降低肝癌细胞在Transwell小室内的侵袭和迁移数目,AMP剂量越大、肝癌细胞侵袭和迁移受抑制的效应越显著,进而也表明AMP能够有效抑制肝癌细胞的侵袭活力。
肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭过程依赖多种蛋白酶的水解活性,MMP2、MMP9和MMP10是目前已知与肝癌侵袭密切相关的MMPs成员[9-11],本研究进一步分析了AMP处理对肝癌细胞中MMP2、MMP9和MMP10表达的影响并发现:AMP能够以剂量依赖性的方式降低肝癌细胞中MMP2、MMP9和MMP10 mRNA表达水平,且AMP剂量越大,肝癌细胞中MMP2、MMP9和MMP10表达受抑制的效应越显著。MMP2、MMP9和MMP10的生物学活性是参与细胞外基质及基底膜中胶原蛋白、层黏连蛋白、弹性蛋白等成分的水解; 在生理条件下,细胞外基质及基底膜内含有丰富的蛋白成分,能够使细胞锚定于局部组织、抑制细胞向远处移动; 而在本实验中,AMP以剂量依赖性的方式降低MMP2、MMP9和MMP10的表达后,蛋白酶水解细胞外基质的能力减弱,进而使细胞的迁移和侵袭过程受到阻碍。以上MMPs相关的结果表明,AMP能够有效抑制肝癌细胞中多种MMPs的表达,进而使MMP所介导的细胞外基质及基底膜水解效应受阻并降低肝癌细胞的侵袭活力。
在明确AMP能够降低肝癌细胞侵袭活力后,需要进一步明确AMP发生该效应的分子机制。dermcidin基因所编码的Dermcidin蛋白是在肝癌病灶内高表达的蛋白,且参与了肝癌的病理进程[12-13],我们通过分析AMP处理后细胞内dermcidin基因表达的变化可知:AMP能够以剂量依赖性的方式降低肝癌细胞中Dermcidin的mRNA表达水平且AMP剂量越大,肝癌细胞中Dermcidin表达受抑制的效应越显著。这一结果表明AMP能够降低肝癌细胞中Dermcidin的表达,结合Dermcidin的生物学功能提示AMP能够通过下调Dermcidin的表达来影响肝癌细胞的侵袭活力。为了进一步验证这一推测,我们通过转染siRNA的方式来抑制肝癌细胞中Dermcidin的表达,在AMP处理的同时抑制Dermcidin的表达并观察侵袭活力的变化可知:转染Dermcidin siRNA能够使AMP降低肝癌细胞迁移侵袭能力、侵袭基因表达的效应发生逆转。由此提示AMP抑制肝癌细胞侵袭活力的效应部分由Dermcidin介导,也说明AMP能够通过下调Dermcidin蛋白的表达来降低肝癌细胞的侵袭活力。
以上研究结果表明,AMP对肝癌细胞的侵袭活力以及细胞内侵袭基因的表达具有显著的抑制作用,且抑制Dermcidin蛋白的表达是AMP发挥侵袭抑制活性的分子途径之一。
作者贡献
李关宁:课题的规划和设计,数据分析
杨振淮:课题指导、疑难问题处理
耿燚:统计分析、资料整理
| [1] | Hsu YC, Ho HJ, Lee TY, et al. Temporal trend and risk determinants of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients on entecavir or tenofovir[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2018, 25(5): 543–51. DOI:10.1111/jvh.2018.25.issue-5 |
| [2] | Bai L, Liu Z, Fang Q, et al. The trends and projections in the incidence and mortality of liver cancer in urban Shanghai: a population-based study from 1973 to 2020[J]. Clin Epidemiol, 2018, 9(10): 277–88. |
| [3] | Kou X, Fan J, Chen N. Potential molecular targets of ampelopsin in prevention and treatment of cancers[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2017, 17(12): 1610–6. |
| [4] | 薛志锋, 肖洪广, 邱芳华, 等. Dermcidin作为原发性肝细胞癌诊断标志物的临床研究[J]. 中国热带医学, 2016, 16(7): 633–6. [ Xue ZF, Xiao HG, Qiu FH, et al. Dermcidin as a novel biomarker in diagnosis of primary hepatocellular carcinoma: a preliminary clinical study[J]. Zhongguo Re Dai Yi Xue, 2016, 16(7): 633–6. ] |
| [5] | Wang X, Zhang Q, Wang Y, et al. clinical significance of ubiquitin specific protease 7 (usp7) in predicting prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and its functional mechanisms[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24: 1742–50. DOI:10.12659/MSM.909368 |
| [6] | Gao PT, Ding GY, Yang X, et al. Invasive potential of hepatocellular carcinoma is enhanced by loss of selenium-binding protein 1 and subsequent upregulation of CXCR4[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2018, 8(6): 1040–9. |
| [7] | Liu T, Liu P, Ding F, et al. Ampelopsin reduces the migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells via inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Oncol Rep, 2015, 33(2): 861–7. DOI:10.3892/or.2014.3672 |
| [8] | 周永, 郑金英, 金小玲, 等. PPARγ激活在蛇葡萄素抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖和诱导凋亡中的作用[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2018, 40(13): 1185–91. [ Zhou Y, Zheng JY, Jin XL, et al. Role of PPARγ activation in cell growth inhibition and apoptosis inducement by ampelopsin in breast cancer cells[J]. Di San Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao, 2018, 40(13): 1185–91. ] |
| [9] | Tan W, Zhu S, Cao J, et al. Inhibition of MMP-2 expression enhances the antitumor effect of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Oncol Res, 2017, 25(9): 1543–3. DOI:10.3727/096504017X14886444100783 |
| [10] | Li Z, Takino T, Endo Y, et al. Activation of MMP-9 by membrane type-1 MMP/MMP-2 axis stimulates tumor metastasis[J]. Cancer Sci, 2017, 108(3): 347–53. DOI:10.1111/cas.13134 |
| [11] | Wang B, Hsu CJ, Lee HL, et al. Impact of matrix metalloproteinase-11 gene polymorphisms upon the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2018, 15(6): 653–8. DOI:10.7150/ijms.23733 |
| [12] | 邱芳华, 薛志锋, 李秋明, 等. Dermcidin在原发性肝癌诊断及病情评估中的意义[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2016, 13(19): 2706–8. [ Qiu FH, Xue ZF, Li QM, et al. Significant of Dermcidin in the diagnosis of hepatocelular carcinoma and metastasis[J]. Jian Yan Yi Xue Yu Lin Chuang, 2016, 13(19): 2706–8. ] |
| [13] | Qiu F, Qiu F, Liu L, et al. The role of dermcidin in the diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers, 2018, 22(4): 218–23. DOI:10.1089/gtmb.2017.0230 |
 2019, Vol. 46
2019, Vol. 46


