文章信息
- miR-145通过靶向AP4对非小细胞肺癌A549细胞迁移侵袭的影响
- miR-145 Attenuates Migration and Invasion of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer A549 Cells by Targeting AP4
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2019, 46(2): 110-114
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2019, 46(2): 110-114
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2019.18.1160
- 收稿日期: 2018-08-05
- 修回日期: 2018-09-10
非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC)是一种死亡率较高的恶性肿瘤,占全部肺癌的85%,流行病学显示患者的五年生存率低于16%[1],由于很多肺癌患者就诊时已属中晚期,治疗效果与预后不理想,目前,临床上仍缺乏有效的早期诊断和治疗的方法,主要采用放化疗结合的手段。
miRNA是一类长约18~25个核苷酸的小分子非编码单链RNA,广泛存在于高等哺乳动物、植物及病毒中,参与不同的生物学过程,如细胞分化、增殖、代谢与凋亡等一系列细胞生命活动[1-2]。研究发现miR-145在多种肿瘤组织中的表达明显减少,如胃癌、食管癌、肝癌等[3-5]。有报道指出体外实验中miR-145在胃癌细胞中低表达,miR-145能够抑制细胞侵袭和转移,并可能作为转移抑制基因,体内自发转移试验分析进一步证实了miR-145对细胞的侵袭具有抑制功能[6]。目前miR-145对非小细胞肺癌迁移与侵袭的作用及其相关机制的研究尚未完善,因此本实验就此展开,为研究以miR-145作为肺癌的靶点提供更多的实验依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 实验材料40例非小细胞肺癌肺组织与癌旁正常肺组织(经病理科验证)来自南阳医学高等专科学校第一附属医院病理科;非小细胞肺癌细胞株A549购自中国科学院上海细胞库;miR-145 mimic、miR-145 NC、NC siRNA和AP4 siRNA由广州锐博技术有限公司合成;胎牛血清和DMEM培养基购自美国Gibco公司;LipofectamineTM2000转染试剂盒购自美国Invitrogen公司;Transwell小室购自美国Corning公司;mirVana miRNA分离试剂盒、miRNeasy mini试剂盒、Omniscript逆转录试剂盒、TRIzol试剂盒均购自美国Qiagen公司;AP4和α-tublin抗体购自美国Abcam公司;其他试剂为国产分析纯。
1.2 细胞培养将A549细胞株培养于含10%胎牛血清的DMEM完全培养基中,37℃、5%CO2培养箱中培养,2天换液一次,每6天按照1:3传代。
1.3 miR-145 mimic转染取生长状态良好的A549细胞融合至80%~90%左右时进行转染,按照LipofectamineTM2000试剂盒说明书操作,用移液枪吸取5 μl的LipofectamineTM2000转染试剂,加入100 µl无血清的OPTI-MEM培养基中,同时将调整好浓度为5 nmol/L的miR-145 mimic和miR阴性对照(miR-145 NC)加入无血清的OPTI-MEM培养基中,混匀,孵育5 min,将转染复合物加入培养基中,混匀,6 h后更换含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,37℃培养箱培养48 h。
1.4 AP4 siRNA转染取生长状态良好的A549细胞融合至80%~90%左右时进行转染,LipofectamineTM2000试剂盒说明书操作,用移液枪吸取5 μl的LipofectamineTM2000转染试剂,加入100 µl无血清的DMEM培养基中,再取20 nmol/L的AP4 siRNA和阴性对照siRNA(NC-siRNA),分别加入无血清的DMEM培养基混匀,孵育5 min,将转染复合物加入培养基中,混匀,6 h后更换含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基,37℃孵箱培养48 h。
1.5 划痕实验取各组生长良好的细胞,待细胞在板上孵育至密度约为90%时,用无菌枪头轻轻划细胞培养板,划痕后漂浮的细胞用PBS轻轻洗涤,换成完全培养基继续培养,在倒置显微镜下观察拍摄,并在24 h后于同一部位进行拍摄,观察细胞的移动情况。
1.6 Transwell小室侵袭实验将Matrigel 1:8稀释,包被Transwell小室底部膜的上室,37℃培养30 min;待细胞在无血清培养基中培养24 h后,消化细胞,弃去培养基,重悬,调整密度为5×105个细胞每毫升,将细胞悬液加入Transwell小室,在下室加入600 μl含20%胎牛血清的培养基,常规培养24 h,取出Transwell小室,弃去孔中培养液,PBS洗涤,甲醛固定30 min,0.1%结晶紫染色20 min,轻轻擦去上层细胞,于显微镜下观察,计数。
1.7 qRT-PCR实验对于miR-145 qRT-PCR检测,按照mirVana miRNA分离试剂盒说明书提取细胞或者组织中总RNA,按照miRNeasy mini kit说明书采用QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR system进行qRT-PCR,U6为内参。对于AP4 qRT-PCR检测,按照TRIzol试剂盒说明书操作,提取各组组织或者已处理细胞的总RNA,Omniscript反转录试剂盒说明书操作进行反转录成为cDNA,将反转录产物采用QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR system进行qRT-PCR。反应条件:95℃变性2 min;94 1 min℃,60℃ 30 s,72℃ 1 min,共35个循环;72℃ 10 min。按2-ΔΔCt法分析各组基因相对表达,重复实验三次,取平均值。其中上述利用的引物序列为:miR-145引物:上游:5’-GTCCAGTTTTCCCAGGAAT-3’,下游:5’-TGGTGTCGTGGAGTCG-3’;U6引物:上游:5’-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3’,下游:5’-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3’;AP4上游:5’-AACAGGGGCAGAGTGAGTTG-3’,下游:5’-GGGAAGTGCCTTCGACAGTG-3’;α-tublin上游:5’-TTCCTGGGCATGGAGTCCT-3’,下游:5’-AGGAGGAGCAATGATCTTGATC-3’。
1.8 Western blot检测相关蛋白表达收集各组A549细胞,加入适量蛋白裂解液裂解RIPA,提取细胞总蛋白,BCA法检测蛋白浓度,进行SDS-PAGE电泳,电转至PVDF膜,TBST液洗膜2次,将PVDF膜转移至5%脱脂奶粉中,封闭2 h,TBST液洗膜三次,加入一抗,4℃摇床孵育过夜,TBST液洗膜三次,加入相应二抗室温孵育1 h,TBST液洗涤三次,ECL化学发光法显色,暗室曝光,以α-tublin为内参,成像扫描分析系统保存图像。
1.9 双荧光素酶报告基因检测靶基因预测数据库miRanda显示miRNA-145与AP4存在靶向结合序列。进一步构建AP4野生型WT-3’UTR-荧光素酶表达载体和突变型Mutant-3’UTR-荧光素酶表达载体,并将其和miR-145 mimic转入细胞中。转染48 h后,按照双荧光素酶报告基因说明书进行操作,使用荧光素酶报告基因检测仪进行双荧光素酶报告实验测定。实验结果以荧光素酶活性与海肾荧光素酶活性的比值来进行统计学分析。
1.10 统计学方法采用SPSS17.0统计软件对所有数据进行统计学分析,所有数据均以均值±标准差(x±s)表示,两组比较采用t检验,三组数据的两两比较比较采用方差分析后再接受Bonferroni-t修正,组间比较以P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 miR-145和AP4在非小细胞肺癌组织的表达qRT-PCR结果显示,与癌旁正常组织相比,非小细胞肺癌组织中miR-145表达显著降低(t=10.235, P=0.000),AP4 mRNA明显增高(t=8.367, P=0.000),同时Western blot检测显示AP4在非小细胞肺癌组织中高表达(t=6.415, P=0.000)。进一步通过相关性分析显示,AP4蛋白表达与miR-145呈负相关(t=3.551, P=0.000),见图 1。
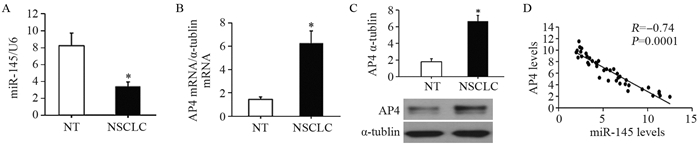
|
| A: the level of miR-145 was detected by qRT-PCR; B: The mRNA levels of AP4 was detected by qRT-PCR; C: the protein level of AP4 was detected by Western blot; D: AP4 mRNA was negatively correlated with miR-145. NT: normal tissue; NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer. *: P < 0.05, compared with NT group 图 1 miR-145在非小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及其与AP4表达的相关性(n=40) Figure 1 miR-145 was widely down-regulated in NSCLC tissues and negatively correlated with AP4 expression (n=40) |
qRT-PCR实验显示,与对照组相比,A549细胞转染miR-145 mimic后,miR-145表达明显增加(F=39.452, t=5.412, P=0.000),见图 2A;同时Transwell小室侵袭实验结果显示,转染miR-145 mimic后A549细胞的侵袭能力显著下降(F=123.162, t=8.543, P=0.000),见图 2B~C;划痕实验结果显示,转染miR-145 mimic后A549细胞的迁移能力显著下降(F=89.745, t=6.384, P=0.000),见图 2D~E。
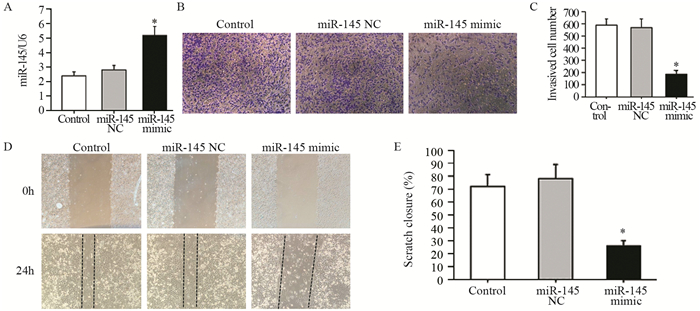
|
| A: the levels of miR-145 was detected by qRT-PCR; B, C: transwell invasion assay were performed to determine cell invasion; D, E: would healing assay were performed to determine cell migration. *: P < 0.05, compared with control group 图 2 miR-145过表达抑制A549细胞侵袭与迁移(n=3) Figure 2 miR-145 overexpression inhibited migration and invasion of A549 cells (n=3) |
qRT-PCR实验显示,与对照组相比,A549细胞转染miR-145 mimic后,AP4 mRNA表达明显降低(F=56.383, t=7.256, P=0.000),见图 3A;同时Western blot结果显示,A549细胞转染miR-145 mimic后,AP4蛋白表达明显降低(F=42.195, t=4.679, P=0.000),见图 3B~C;进一步,靶基因预测数据库miRanda显示miR-145与AP4 3' UTR存在靶向结合片段,见图 3D,双荧光素酶报告基因验证AP4是miR-145的靶基因,见图 3E。
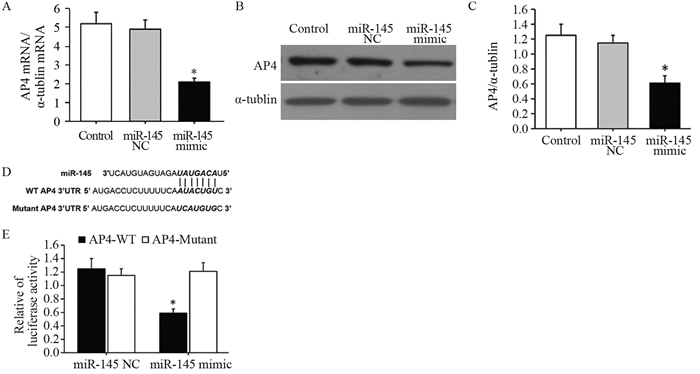
|
| A: after transfected with miR-145 mimic and miR-145 NC mRNA, the level of AP4 was determined by qRT-PCR; B, C: after transfected with miR-145 mimic and miR-145 NC mRNA, the protein level of AP4 was determined by Western blot; D: The predicted binding sites for miR-145 in the 3' UTR of AP4 and the mutations in the binding sites were shown; E: The luciferase activity of the wild-type AP4 3-UTR (Wt) and mutant AP4 3' UTR (Mut) co-transfected with miR-145 NC or miR-145 mimic measured using the dual-luciferase reporter gene assay kit. *: P < 0.05, compared with control group or miR-145 NC group 图 3 AP4是miR-145直接靶基因(n=3) Figure 3 AP4 was a direct target gene of miR-145 (n=3) |
Western blot实验结果显示,与对照组相比,A549细胞转染AP4 siRNA后,AP4蛋白表达明显降低(F=114.192, t=13.725, P=0.000),见图 4A;同时Transwell小室侵袭实验结果显示,转染AP4 siRNA后A549细胞的侵袭数显著下降(t=9.675, P=0.000),见图 4B;划痕实验结果显示,转染AP4 siRNA后A549细胞的迁移能力显著下降(t=8.347; P=0.000),见图 4C~D。
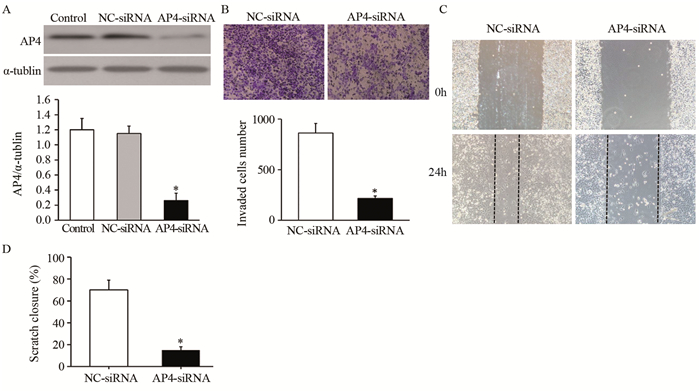
|
| A: After transfected with AP4 siRNA or NC siRNA, the mRNA level of AP4 was determined by qRT-PCR; B: AP4 siRNA inhibited the invasion of A549 cells; C, D: AP4 siRNA inhibited the migration of A549 cells; *: P < 0.05, compared with NC siRNA group 图 4 AP4 siRNA抑制A549细胞侵袭和迁移(n=3) Figure 4 AP4 siRNA inhibited migration and invasion of A549 cells (n=3) |
miRNA-145是近年来发现的具有抑制肿瘤细胞作用的mircoRNA,国外学者研究发现miR-145不但抑制乳腺癌细胞MCF-7和结肠癌细胞HCT-116的增殖,还能抑制其侵袭能力[7]。王寰昱等[8]研究发现miR-145通过改变肿瘤细胞表面黏附因子的表达从而抑制肝癌细胞的迁移与侵袭,但miR-145对非小细胞肺癌的研究尚不完善。本研究结果显示,miR-145在非小细胞肺癌组织中低表达。进一步对A549细胞采用过表达miR-145后,A549细胞的迁移与侵袭能力明显下降,随后,我们进行了其可能机制的研究。
激活增强子结合蛋白4(activating enhancer binding protein 4, AP4)是近年来发现的一种核转录因子,碱性螺旋-环-螺旋-亮氨酸拉链转录因子家族的成员,主要与转录因子AP1协同调控脊椎动物的生长发育、细胞增殖和凋亡的过程,病理状态下参与肿瘤的发生与发展过程[9-10]。大量研究证实,转录因子AP4在多种肿瘤组织中呈高表达,如肺癌、肝癌、胃癌等[11-13]。研究发现AP4在侵袭性甲状腺乳头状癌细胞株和组织中显示高表达,提示AP4在侵袭性甲状腺乳头状癌转移的过程中具有重要的作用[14]。已有报道证实当沉默子宫内膜癌细胞中的AP4因子后,增加细胞凋亡率,并抑制细胞上皮间质转化[15]。而关于AP4抑制肿瘤细胞的迁移与侵袭的机制,已有报道多与p53通路以及EMT改变相关[16-17],比如报道AP4通过激活p53依赖性通路促进MDA-MB-231细胞发生EMT[16];上调AP4直接结合上皮型钙黏附素(E-cadherin)启动子CACCTG序列,降低E-cadherin,促进结直肠癌细胞发生EMT,进一步发生侵袭和迁移。本实验发现AP4在非小细胞肺癌组织中高表达;AP4 siRNA转染后,非小细胞肺癌A549细胞的迁移与侵袭能力明显下降;另外,过表达miR-145后,非小细胞肺癌A549细胞中AP4因子的表达显著下降,提示过表达miR-145可能是通过下调靶基因AP4表达来抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞的迁移与侵袭。而关于AP4是通过何种机制影响非细胞肺癌侵袭与迁移,将是我们下一步研究的重点。
综上所述,上调miR-145的表达能明显抑制非小细胞肺癌A549细胞的迁移与侵袭能力,可能是通过抑制靶基因AP4的表达实现的。本研究为miR-145作为非小细胞肺癌治疗靶标提供了实验基础。
作者贡献
赵天增:设计课题、实施实验与文章撰写 杨金华:实施实验 刘向前:参与临床样本收集和进行数据统计 徐萌博:进行数据统计
| [1] | Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide:sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012[J]. Int J Cancer, 2015, 136(5): E359–86. DOI:10.1002/ijc.29210 |
| [2] | Balça-Silva J, Sousa Neves S, Gonçalves AC, et al. Effect of miR-34b overexpression on the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines[J]. Anticancer Res, 2012, 32(5): 1603–9. |
| [3] | Ostenfeld MS, Bramsen JB, Lamy P, et al. miR-145 induces caspase-dependent and independent cell death in urothelial cancer cell lines with targeting of an expression signature present in Tabladder tumors[J]. Oncologene, 2010, 29(7): 1073–84. |
| [4] | 孙嘉伟, 刘凤霞, 刘文雅, 等. MicroRNA-145对食管鳞状细胞癌细胞增殖的影响[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2013, 36(6): 756–8, 762. [ Sun JW, Liu FX, Liu WY, et al. The effect of microRNA-145 on proliferation of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells[J]. Xinjiang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 2013, 36(6): 756–8, 762. ] |
| [5] | Ding W, Tan H, Zhao C, , et al. MiR-145 suppresses cell proliferation and motility by inhibiting ROCK1 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(5): 6255–60. DOI:10.1007/s13277-015-4462-3 |
| [6] | Gao P, Xing AY, Zhou GY, et al. The molecular mechanism of microRNA-145 to suppress invasion-metastasis cascade in gastric cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32(4): 491–501. DOI:10.1038/onc.2012.61 |
| [7] | Sachdeva M, Mo YY. MicroRNA-145 suppresses cell invasion and metastasis by directly targeting mucin 1[J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(1): 378–87. |
| [8] | 王寰昱, 王亚峰, 张昆松, 等. 上调miRNA-145对肝癌细胞的作用及其机制研究[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2015, 31(6): 1019–25. [ Wang HY, Wang YF, Zhang KS, et al. Role of up-regulated microRNA145 in viability, apoptosis, invasion and metastasis of hepatoma cells[J]. Zhongguo Bing Li Sheng Li Za Zhi, 2015, 31(6): 1019–25. ] |
| [9] | 孙政, 曹杰, 杨平, 等. 转录因子激活蛋白-4在结直肠癌中的表达及与细胞凋亡的相关性[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2008, 25(7): 891–3. [ Sun Z, Cao J, Yang P, et al. Expression of activator protein-4 in colorectal carcinoma and its relationship with apoptosis[J]. Zhonghua Shi Yan Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2008, 25(7): 891–3. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-9030.2008.07.028 ] |
| [10] | Jung P, Hermeking H. The c-MYC-AP4-p21 cascade[J]. Cell Cycle, 2009, 8(7): 982–9. DOI:10.4161/cc.8.7.7949 |
| [11] | Hu X, Guo W, Chen S, et al. Silencing of AP-4 inhibits proliferation, induces cell cycle arrest and promotes apoptosis in human lung cancer cells[J]. Oncol Lett, 2016, 11(6): 3735–42. DOI:10.3892/ol.2016.4451 |
| [12] | Xinghua L, Bo Z, Yan G, et al. The overexpression of AP-4 as a prognostic indicator for gastric carcinoma[J]. Med Oncol, 2012, 29(2): 871–7. DOI:10.1007/s12032-011-9845-8 |
| [13] | Hu BS, Zhao G, Yu HF, et al. High expression of AP-4 predicts poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatectomy[J]. Tumour Biol, 2013, 34(1): 271–6. DOI:10.1007/s13277-012-0547-4 |
| [14] | 王小康, 解绪红, 陈文全, 等. 转录因子激活蛋白4、血管内皮生长因子C在甲状腺乳头癌中的表达及意义[J]. 中华普通外科学文献(电子版), 2013, 7(1): 36–9. [ Wang XK, Xie XH, Chen WQ, et al. Expression and clinical values of AP-4 and VEGF-C in papillary carcinoma of thyroid[J]. Zhonghua Pu Tong Wai Ke Xue Wen Xian (Dian Zi Ban), 2013, 7(1): 36–9. ] |
| [15] | 别延红, 李纳, 吴又明, 等. 转录因子增强结合蛋白-4基因沉默对子宫内膜癌细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 山东医药, 2017, 57(2): 5–9. [ Bie YH, Li N, Wu YM, et al. Effects of silencing transcription factor AP-4 gene on apoptosis of endometrial cancer cells[J]. Shandong Yi Yao, 2017, 57(2): 5–9. ] |
| [16] | Chen S, Chiu SK. AP4 activates cell migration and EMT mediated by p53 in MDA-MB-231 breast carcinoma cells[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2015, 407(1-2): 57–68. DOI:10.1007/s11010-015-2454-7 |
| [17] | Jackstadt R, Röh S, Neumann J, , et al. AP4 is a mediator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in colorectal cancer[J]. J Exp Med, 2013, 210(7): 1331–50. DOI:10.1084/jem.20120812 |
 2019, Vol. 46
2019, Vol. 46
