文章信息
- Garcinone E抑制鼻咽癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的研究
- Garcinone E Inhibits Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2018, 45(9): 617-622
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2018, 45(9): 617-622
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.18.0161
- 收稿日期: 2018-01-31
- 修回日期: 2018-06-06
2. 518055 深圳,南方科技大学医学院
2. Southern University of Science and Technology School of Medicine, Shenzhen 518055, China
鼻咽癌是头颈部肿瘤中发病率较高的癌症,在东南亚和我国华南地区较为常见[1]。鼻咽癌的主要治疗方法是放疗结合化疗,疗效相对显著,但仍有不少比例的患者因为癌细胞远处转移而无法治愈[2]。所以明确鼻咽癌细胞远处转移机制并针对性研发新型药物,对鼻咽癌患者的治疗具有重要意义。
氧杂蒽酮类化合物是在化学结构上拥有独特含氧杂环的一类化合物,研究表明,它具有广泛的药理作用,诸如抗肿瘤、抗抑郁、抗HIV、抗菌、神经保护作用及治疗糖尿病等[3-8]。Garcinone E是从岭南山竹果壳中提取的一种氧杂蒽酮类化合物,最近有研究显示,其对部分肿瘤细胞生长有抑制作用,且可抑制卵巢癌细胞的侵袭和迁移能力[9-10]。然而其对鼻咽癌细胞的作用及机制尚不清楚,本研究以鼻咽癌细胞HK1和HONE1为研究对象,通过检测Garcinone E对细胞增殖、迁移及侵袭能力的影响,初步探讨相关机制,为Garcinone E在鼻咽癌治疗中的应用提供实验和理论依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料 1.1.1 细胞鼻咽癌细胞HK1和HONE1为中山大学肿瘤防治中心钱朝南教授惠赠。前者属于高分化,不易远处转移的癌细胞;后者属于低分化,易远处转移的癌细胞。
1.1.2 主要试剂及仪器Garcinone E、RIPA蛋白裂解液、30%聚丙烯酰胺、过硫酸铵、四甲基乙二胺、蛋白上样缓冲液(×2)、蛋白质预染Marker、Tween-20购自美国Sigma公司,蛋白酶抑制剂和磷酸酶抑制剂购自美国Thermo公司,DMEM培养基、胎牛血清购自美国Gibco公司;三羟甲基氨基甲烷、十二烷基硫酸钠购自美国Genbase Bioscience公司,聚偏二氟乙烯膜(0.22 μm PVDF膜)购自美国Millipore公司,ECL化学发光检测试剂盒购自美国Thermo公司,细胞增殖检测试剂盒(MTS)美国Promega公司,BCA蛋白定量试剂盒购自中国碧云天生物公司,电动移液器、可调式移液器、低温高速离心机购自德国Eppendorf公司,细胞培养孵箱、生物安全柜、-80℃生物超低温冰箱购自美国Thermo科学公司,倒置荧光显微镜购自日本OLYMPUS公司,碎冰制冰机购自日本Sanyo公司,NanoDrop 2000分光光度计购自美国Thermo Scientific公司,E-cadherin、Vimentin、p-Vimentin、Snail、Slug和GAPDH抗体购自美国Cell Signaling Technology公司。反转录试剂盒和PowerUpTM SYBR Green PCR Master Mix Qty购自美国Thermo公司。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 细胞培养鼻咽癌细胞HK1和HONE1常规培养于含有10%胎牛血清、100 u/ml青霉素和100 μg/ml链霉素的DMEM培养基中,并置于37℃、5%CO2细胞培养箱。
1.2.2 MTS法检测细胞增殖率取对数生长期的HK1和HONE细胞,0.05%的胰酶消化、离心和重悬后,均匀接种于96孔板中。待细胞贴壁后,分别用含有不同浓度的Garcinone E(0、1.25、1.875、2.5、3.75、5、7.5、10、15、20 µmol/L)的完全培养基处理细胞,每个浓度设置5个复孔。培养24 h后,每孔加入20 μl MTS并继续放置培养箱中孵育2 h,用酶标仪测在波长为490 nm读取的吸光度(OD)值。细胞增殖率=(实验组OD490-空白组OD490)/(对照组OD490-空白组OD490)×100%,实验重复3次。
1.2.3 Transwell细胞迁移分析常规培养鼻咽癌细胞,消化、离心后用含有0.1% BSA的无血清培养基重悬细胞,细胞浓度调至2.5×105个/毫升(HONE1)或5×105个/毫升(HK1),取500 μl细胞悬液加入上层小室,然后取750 μl含有10%胎牛血清的完全培养基加入下层小室,注意上层小室与24孔板之间不能有气泡存在,细胞悬液和下室的完全培养基皆含有7.5 μmol/L Garcinone E。同时设置另外一组不加药的空白对照,进行同样的处理。放置孵箱24 h后,吸弃废液,DPBS涮洗两次,甲醇固定15 min,DPBS洗两次,1%结晶紫染色15 min,DPBS洗两次,棉签小心擦除上室染色的细胞,倒置显微镜观察拍照并计数。
1.2.4 Transwell细胞侵袭分析实验步骤与迁移相似,只是细胞小室底部膜上含有Matrigel,在进行实验前需要将含有Matrigel的小室进行再水化:在细胞小室内及所在的小孔中加入500 μl无血清培养基并放入细胞培养孵箱2 h。
1.2.5 Western blot分析相关蛋白表达用含有蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA提取细胞总蛋白,采用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒来测量蛋白浓度,将各组蛋白浓度调到相同浓度后进行加热变性,之后进行垂直电泳,用12%的SDS-PAGE分离样品,90 V转膜3 h,含有5%脱脂奶粉的TBST封闭1 h,TBST洗膜三次,每次10 min。于4℃冰箱过夜孵育1:1 000的一抗,洗膜三次,1:10 000的辣根过氧化物酶孵育1 h,洗膜三次,运用化学发光成像系统显影。以GAPDH作为内参。
1.2.6 Real-time PCR检测EMT相关基因的表达不同浓度药物(0、5、7.5、10 µmol/L)处理细胞24 h后,用TRIzol提取RNA,依照逆转录试剂盒说明获取cDNA,其中每管RNA的总量是2 μg,总反应体积为20 μl,反应条件为25℃,10 min;37℃,120 min;85℃,5min;待温度降至4℃后放于-20℃冰箱保存。将cDNA稀释10倍后,按照SYBR Green说明配置反应体系,并在ABI 7300仪器上进行Real-time PCR。引物具体信息见表 1。
SPSS17.0统计软件进行数据统计分析,数值由平均值±标准误表示。两组间比较运用配对t检验;三组及以上的组间比较运用单因素方差分析和邓肯事后多重比较,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
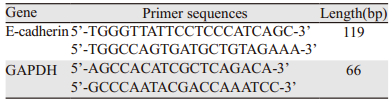
2 结果 2.1 Garcinone E对两种鼻咽癌细胞HK1和HONE1生长抑制作用体外细胞增殖实验结果显示,随着Garcinone E的浓度增加(1.25、1.875、2.5、3.75、5、7.5、10、15、20 μmol/L),其对鼻咽癌细胞HK1和HONE1的抑制作用也越来越明显,即呈浓度依赖性。HK1细胞中7.5、10、15、20 μmol/L组与0 μmol/L组比较,差异均有统计学意义(P=0.0369、0.0004、0.0009、0.0003);HONE1细胞中1.25、1.875、7.5、10、15、20 μmol/L组与0 μmol/L组比较,差异均有统计学意义(P=0.0015、0.0306、0.0094、0.0061、0.0001、0.0004)。HK1和HONE1细胞的IC50值分别为(12.57±0.01)和(10.91±0.89)μmol/L,见图 1。
|
| NPC cells were treated with 0-20 μmol/L of Garcinone E for 24h, then the cell viability was assessed by MTS method. With the increasing dose of Garcinone E, the cell proliferation was distinctly inhibited(*:P < 0.05,**: P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001, compared with 0 μmol/L Garcinone E) 图 1 不同浓度的Garcinone E对HK1和HONE1细胞增殖的抑制作用 Figure 1 Inhibitory effect of Garcinone E on proliferation of HK1 and HONE1 cells lines |
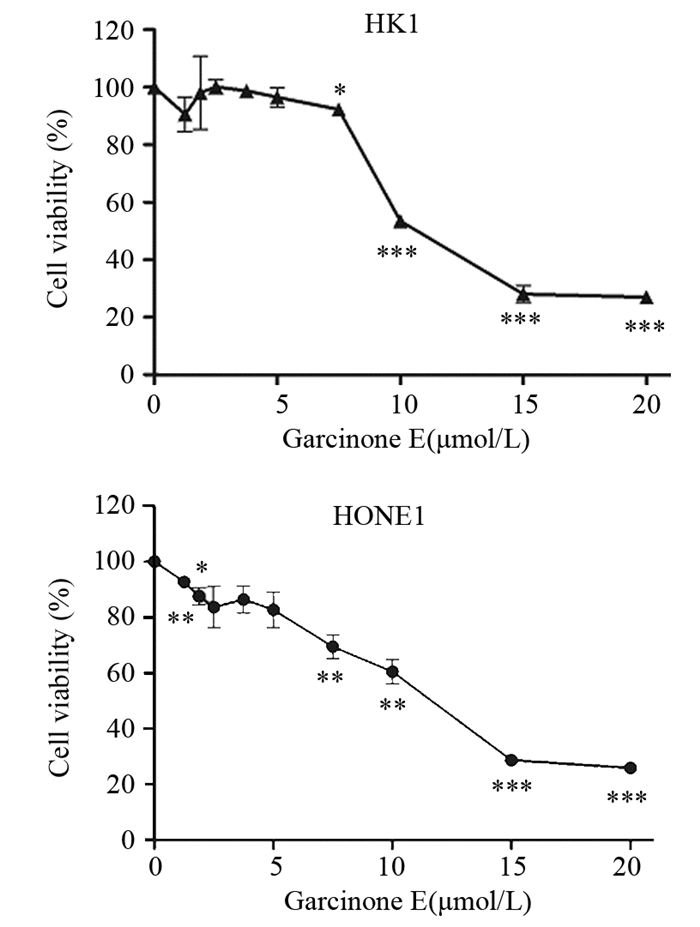
Transwell迁移结果显示,将HK1和HONE1接种到24孔板的Transwell迁移小室并加药,24 h后与对照组相比,HK1和HONE1细胞加药组细胞平均穿膜细胞数明显降低,且差异均有统计学意义(P=9.9894E-09和P=3.01265E-05),见图 2。
|
| 图 2 Transwell细胞小室检测7.5μmol/L Garcinone E对HK1和HONE1细胞迁移的抑制作用 Figure 2 Inhibitory effect of 7.5μmol/L Garcinone E on migration of HK1 and HONE1 cells examined by Transwell assay |
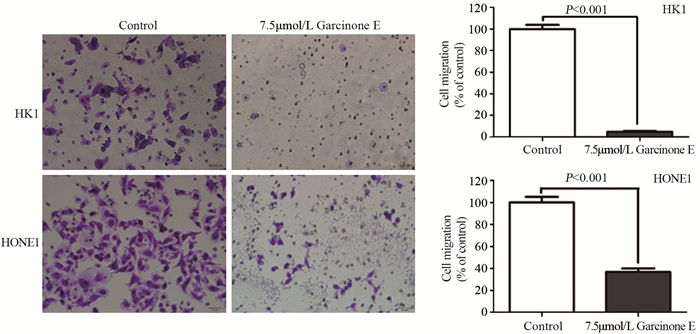
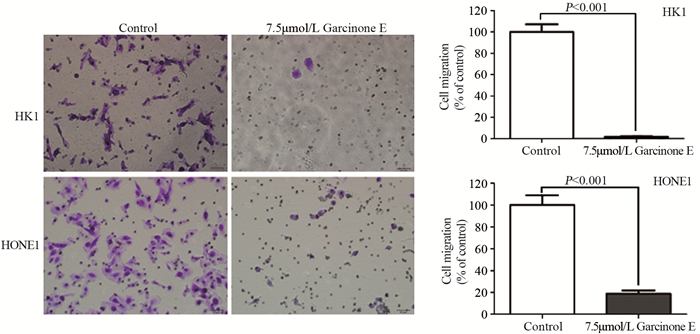
细胞侵袭结果显示,7.5 μmol/L Garcinone E可以显著降低HK1和HONE1细胞侵袭穿过膜下的细胞数。与对照组相比,HK1和HONE1细胞加药组细胞平均穿膜细胞数明显减少,且差异均有统计学意义(P=4.03E-04和P=6.15038E-06),见图 3。
|
| 图 3 Transwell细胞小室检测7.5μmol/L Garcinone E对HK1和HONE1细胞侵袭的抑制作用 Figure 3 Inhibitory effect of 7.5μmol/L Garcinone E on invasion of HK1 and HONE1 cells examined by Transwell assay |
Western blot检测结果发现:Garcinone E可显著降低HK1细胞中p-Vimentin(7.5、10 μmol/L vs. control,P=0.0161、0.0165)、Snail(7.5、10 μmol/L vs. control,P=0.0359、0.0156;10 μmol/L vs. 5 μmol/L,P=0.0467)和Slug(7.5、10 μmol/L vs. control,P=0.0240,0.0144)的蛋白表达以及HONE1中p-Vimentin(7.5、10 μmol/L vs. control,P=0.0015、0.0011,7.5、10 μmol/L vs. 5 μmol/L,P=0.0343、0.0244)和Slug(5、7.5、10 μmol/L vs. control,P=0.0369、0.0013、0.0001,7.5、10 μmol/L vs. 5 μmol/L,P=0.0496、0.0028)的蛋白表达。当Garcinone E浓度增加到10 μmol/L时,两细胞的E-cadherin蛋白表达显著增加(HK1细胞中10 μmol/L vs. control和5 μmol/L,P=0.0067和0.0273;HONE1细胞中7.5、10 μmol/L vs. control,P=0.0007、0.0266,5、10 μmol/L vs. 7.5 μmol/L,P=0.0013、0.0327),p-vimentin、Snail(10 μmol/L vs. control,P=0.0440)和Slug则明显降低。而在既定药物浓度范围内,Garcinone E对两株鼻咽癌细胞的Vimentin表达均无明显的调控作用,见图 4。
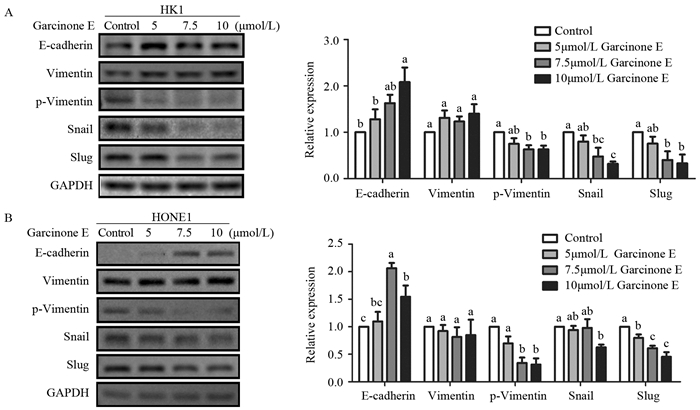
|
| A: Western blot analysis of EMT-related proteins in HK1 cells and statistical analysis of proteins expression level after the treatment of Garcinone E for 24h; B: Western blot analysis of EMT-related proteins in HONE1 cells and statistical analysis of proteins expression level after the treatment of Garcinone E for 24h; P < 0.05, compared between two groups with different letters(a, b, c) above error bars 图 4 Garcinone E促使鼻咽癌细胞HK1和HONE1表达更强的上皮样特性 Figure 4 Garcinone E promoted more epithelial characteristics in HK1 and HONE1 cells |
为了进一步验证Garcinone E对鼻咽癌细胞中EMT相关基因的影响,我们通过q-PCR检测其对E-cadherin转录水平上的作用。10 μmol/L Garcinone E作用鼻咽癌细胞24 h后,两株鼻咽癌细胞的E-cadherin(HK1细胞中control、5、7.5 μmol/L vs. 10 μmol/L,P=0.0041、0.0013、0.0099;HONE1细胞中control、5 μmol/L vs. 10 μmol/L,P=0.0308、0.0127)的mRNA表达明显比对照组高,见图 5。
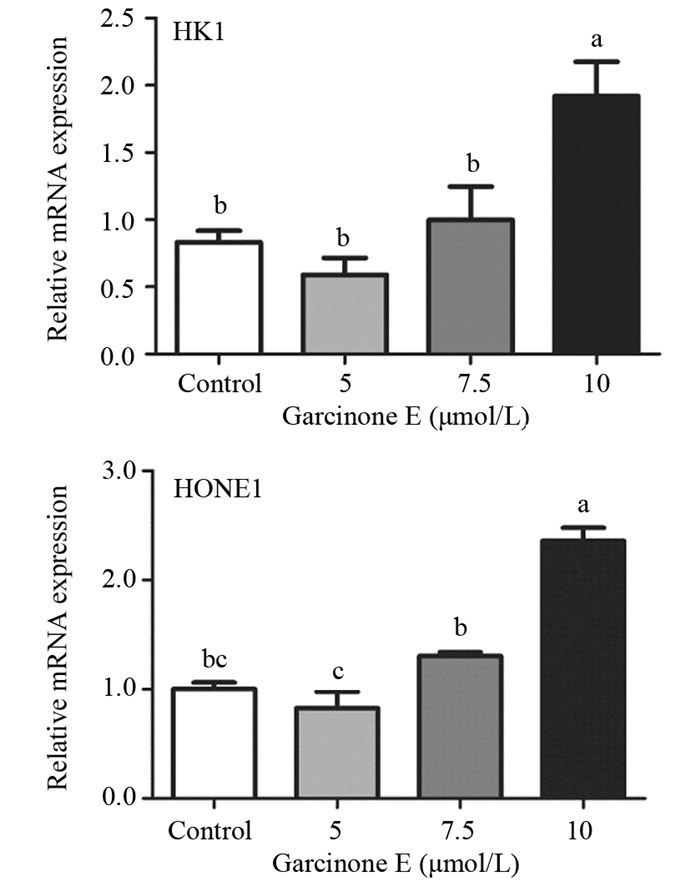
|
| P < 0.05, compared between two groups with different letters(a, b, c) above error bars 图 5 q-PCR检测Garcinone E对HK1和HONE1细胞中E-cadherin的影响 Figure 5 Effects of Garcinone E on E-cadherin in HK1 and HONE1 cells detected by q-PCR |
天然产物近年在抗肿瘤方面取得显著效果,氧杂蒽酮类化合物主要从山竹植物中提取的一类天然化合物,一系列的研究表明其具有广泛的药理作用,尤其是在抗肿瘤方面疗效显著[11-13]。最近研究显示一种氧杂蒽酮类化合物Garcinone E具有抗各种肿瘤细胞增殖的作用[9],然而其在鼻咽癌中的作用尚未有见报道。我们通过两种分化程度不同的鼻咽癌细胞HK1和HONE1来检测Garcinone E是否有抑制鼻咽癌作用,结果表明Garcinone E浓度依赖性抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖。
转移是肿瘤细胞通过特定程序从原发部位扩散到新的继发部位的过程[14],其中Ⅲ型EMT在肿瘤的远处转移中扮演着重要的角色,而很多上皮性肿瘤也存在EMT现象[15]。主要表现有细胞极性及细胞连接消失、脱离基底膜、具有迁移能力[16]。在分子标志物方面,上皮标志物的E-cadherin表达降低、调控E-cadherin表达的锌指转录因子Snail和Slug升高是EMT过程的常见表现[17-19]。本研究发现Garcinone E可显著降低鼻咽癌细胞穿过细胞小室的细胞数量,即抑制其迁移和侵袭能力,这与之前Xu等[10]做的关于Garcinone E抑制卵巢癌细胞迁移能力的研究相符合。
在Garcinone E抑制卵巢癌迁移和侵袭能力的机制方面,Xu等[10]发现Garcinone E可以抑制Rho家族GTP酶的表达,但是关于Garcinone E对鼻咽癌迁移和侵袭能力的影响,是否涉及到通过调控锌指转录因子Snail、Slug及钙依赖性跨膜蛋白E-cadherin却尚未有相关报道。本研究Western blot结果显示,Garcinone E可通过增加E-cadherin的表达,同时降低Snail和Slug的表达来逆转鼻咽癌EMT过程,进而抑制鼻咽癌的迁移和侵袭能力。有趣的是,在抗乳腺癌和胃癌方面,有研究表明通过施加一定的因素使得细胞骨架蛋白之一的Vimentin表达不变而其磷酸化p-Vimentin(Ser56)、p-Vimentin(Ser83)的表达升高,从而抑制或逆转相关肿瘤细胞的EMT过程[20-21];本研究结果却显示Garcinone E在不影响Vimentin表达的情况下,能够随着药物剂量的增加而愈发抑制鼻咽癌细胞中p-Vimentin(Ser56)的表达,进而抑制其EMT过程。这种磷酸化水平表达趋势不一致的情况可能是由于肿瘤细胞的种类不同,及其他细胞内的信号通路相互作用机制综合形成的结果。
为了进一步探讨Garcinone E对EMT相关基因在转录水平上的作用情况,本研究分别选取E-cadherin作为研究对象,通过实时定量荧光PCR检测其mRNA的表达水平。结果显示Garcinone E呈剂量依赖性提高鼻咽癌细胞中E-cadherin的表达,此结果与蛋白结果相同,表明Garcinone E可能是通过转录水平的调节作用促进E-cadherin的表达,进而促进其翻译产物蛋白的表达并抑制细胞的迁移和侵袭能力。
综上所述,Garcinone E可以显著抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖,同时通过调节E-caherin、Slug、Snail和p-Vimentin抑制鼻咽癌细胞的迁移和侵袭能力,逆转其EMT过程。这些研究结果提示Garcinone E具有潜在的抗鼻咽癌作用,而其抗鼻咽癌的具体机制尚需要深入研究。我们将在今后的研究中使用动物模型进一步验证Garcinone E抗鼻咽癌的作用及其机制。
| [1] | Lee KT, Tan JK, Lam AK, et al. MicroRNAs serving as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A critical review[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2016, 103: 1–9. DOI:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2016.04.006 |
| [2] | Jiang F, Jin T, Feng XL, et al. Long-term outcomes and failure patterns of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma staged by magnetic resonance imaging in intensity-modulated radiotherapy era: The Zhejiang Cancer Hospital's experience[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2015, 11(Suppl 2): C179–84. |
| [3] | Li C, Qi Q, Lu N, et al. Gambogic acid promotes apoptosis and resistance to metastatic potential in MDA-MB-231 human breast carcinoma cells[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2012, 90(6): 718–30. DOI:10.1139/o2012-030 |
| [4] | Zhao X, Chen Q, Liu Y, et al. Effect of xanthone derivatives on animal models of depression[J]. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp, 2014, 76: 45–50. DOI:10.1016/j.curtheres.2014.04.003 |
| [5] | Tan S, Yang B, Liu J, et al. Penicillixanthone A, a marine-derived dual-coreceptor antagonist as anti-HIV-1 agent[J]. Nat Prod Res, 2017, 19: 1–5. |
| [6] | Wang W, Liao Y, Huang X, et al. A novel xanthone dimer derivative with antibacterial activity isolated from the bark of Garcinia mangostana[J]. Nat Prod Res, 2017, 13: 1–6. |
| [7] | Phyu MP, Tangpong J. Neuroprotective effects of xanthone derivative of Garcinia mangostana against lead-induced acetylcholinesterase dysfunction and cognitive impairment[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2014, 70: 151–6. DOI:10.1016/j.fct.2014.04.035 |
| [8] | Zheng HH, Luo CT, Chen H, et al. Xanthones from Swertia mussotii as multitarget-directed antidiabetic agents[J]. Chem Med Chem, 2014, 9(7): 1374–7. DOI:10.1002/cmdc.v9.7 |
| [9] | Mohamed GA, Al-Abd AM, El-Halawany AM, et al. New xanthones and cytotoxic constituents from Garcinia mangostana fruit hulls against human hepatocellular, breast, and colorectal cancer cell lines[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2017, 198: 302–12. DOI:10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.030 |
| [10] | Xu XH, Liu QY, Li T, et al. Garcinone E induces apoptosis and inhibits migration and invasion in ovarian cancer cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 10718. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-11417-4 |
| [11] | Kumazaki M, Noguchi S, Yasui Y, et al. Anti-cancer effects of naturally occurring compounds through modulation of signal transduction and miRNA expression in human colon cancer cells[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2013, 24(11): 1849–58. DOI:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.04.006 |
| [12] | Xu Q, Ma J, Lei J, et al. α-Mangostin suppresses the viability and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells by downregulating the PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2014, 2014: 546353. |
| [13] | Li M, Ma H, Yang L, et al. Mangiferin inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells is correlated with downregulation of B-cell lymphoma-2 and upregulation of microRNA-182[J]. Oncol Lett, 2016, 11(1): 817–22. DOI:10.3892/ol.2015.3924 |
| [14] | Singh M, Manoranjan B, Mahendram S, et al. Brain metastasis-initiating cells: survival of the fittest[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15(5): 9117–33. DOI:10.3390/ijms15059117 |
| [15] | Geiger TR, Peeper DS. Metastasis mechanisms[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2009, 1796(2): 293–308. |
| [16] | Savagner P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: from cell plasticity to concept elasticity[J]. Curr Top Dev Biol, 2015, 112: 273–300. DOI:10.1016/bs.ctdb.2014.11.021 |
| [17] | Wang X, Wang H, Li G, et al. Activated macrophages down-regulate expression of E-cadherin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via NF-kappaB/Slug pathway[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35(9): 8893–901. DOI:10.1007/s13277-014-2159-7 |
| [18] | Liu YN, Yin JJ, Abou-Kheir W, et al. MiR-1 and miR-200 inhibit EMT via Slug-dependent and tumorigenesis via Slug-independent mechanisms[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32(3): 296–306. DOI:10.1038/onc.2012.58 |
| [19] | Chiang SP, Cabrera RM, Segall JE. Tumor cell intravasation[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2016, 311(1): C1–14. DOI:10.1152/ajpcell.00238.2015 |
| [20] | Thaiparambil JT, Bender L, Ganesh T, et al. Withaferin A inhibits breast cancer invasion and metastasis at sub-cytotoxic doses by inducing vimentin disassembly and serine 56 phosphorylation[J]. Int J Cancer, 2011, 129(11): 2744–55. DOI:10.1002/ijc.25938 |
| [21] | Zeng S, Xie X, Xiao YF, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00675 enhances phosphorylation of vimentin on Ser83 to suppress gastric cancer progression[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 412: 179–87. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.10.026 |
 2018, Vol. 45
2018, Vol. 45