文章信息
- 叶黄素对人前列腺癌PC3细胞增殖和凋亡影响的机制
- Effect of Lutein on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Prostate Cancer PC3 Cell Line and Related Mechanism
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2018, 45(5): 274-279
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2018, 45(5): 274-279
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.17.1303
- 收稿日期: 2017-10-16
- 修回日期: 2018-01-22
2. 450001 郑州, 郑州大学基础医学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室
2. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Basic Medical College, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450001, China
前列腺癌在许多西方国家是最常见的男性恶性肿瘤,占男性癌症死因的第二位。我国前列腺癌发病率较低,但近年来随着人口老龄化及生活条件的改善,发病率有明显增加的趋势。针对前列腺癌的防治,寻找高效、低毒的抗肿瘤药物、积极开展有关国人前列腺癌发生、发展的分子生物学研究对临床研究具有重要价值[1-2]。叶黄素(Lutein)作为一种新的抗肿瘤药物进入人们的视线[3-4]。它是一种天然色素,广泛存在于自然界的植物体中,其中万寿菊中含量最多,近年来一些研究表明叶黄素具有保护视力、降低白内障的发生率、延缓动脉硬化、抑制癌症等药理活性[5-7]。本课题以PC3细胞作为研究对象,旨在探讨叶黄素对其增殖抑制的影响和诱导凋亡效应等方面的作用机制。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料人前列腺癌细胞株由河南省医药科学研究院惠赠。叶黄素由加拿大农业与农业食品部食品研究中心提供。GAPDH抗体、Bax抗体(兔抗人)、Bcl-2抗体(兔抗人)、辣根过氧化物酶标记山羊抗兔二抗购自美国CST公司。Annexin V-FITC/PI凋亡试剂盒购自北京索莱宝生物有限公司,细胞RNA提取试剂盒(DNaseⅠ)购自北京康为世纪生物公司。Matrigel基质胶购自美国BD公司,Bcl-2、Bax上下游引物购自上海生工生物工程公司。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 细胞培养将PC3细胞株常规培养于含10%胎牛血清的RPMI 1640培养液中,在5%CO2和饱和湿度的培养箱中37℃恒温培养。
1.2.2 增殖抑制试验选取对数期的PC3细胞,以1.0×104个每毫升的浓度接种于96孔培养板,每孔200 μl。待24 h细胞重新贴壁后,分别加入浓度为20、40、80、120、160 μg/ml的叶黄素溶液,同时设DMSO溶剂对照组,每组6个复孔,重复3次。分别在24、48和72 h后用CCK8法染色。用酶标仪于515 nm波长处测得各孔OD值,并计算抑制率。生长抑制率GI(%)=(1-OD实验组/OD对照组)×100%。
1.2.3 细胞周期实验选取对数期生长的细胞,以每孔5×105个细胞接种于六孔板中。培养箱中培养24 h贴壁后,加入浓度为40、80和120 μg/ml的叶黄素溶液,同时设DMSO对照组。药物作用48 h后,离心收集细胞,用预冷的PBS洗两遍,重悬细胞。加入70%预冷乙醇500 μl固定2 h至过夜,4℃保存。染色前先用冰PBS洗去固定液,细胞沉淀中加入100 μl RNaseA溶液,重悬细胞,37℃水浴30 min,再加入400 μl PI染色液混匀,4℃避光孵育30 min。先用300目筛网过滤,然后用流式细胞仪于激发波长488 nm处检测。
1.2.4 细胞凋亡实验按周期方法加药处理细胞,用不含EDTA的胰酶进行消化(防止出现假阳性),收集细胞,用预冷的PBS洗两遍。加入500 μl 1×结合缓冲液重悬细胞,加入5 μl Annexin V-FITC,室温避光,轻轻混匀,室温避光10 min, 加入5 μl PI,轻轻吹匀,室温避光5 min,在1 h内进行BD LSRFortessaTM流式细胞仪检测。
1.2.5 细胞迁移与侵袭实验六孔板中每孔铺约5×105个PC3细胞。第二天待细胞贴壁用10 μl枪头划出宽度基本相同的一道无细胞区域,用PBS洗细胞3次,加入无血清培养液,并设置对照组和药物浓度组。放入37℃、5%CO2培养箱中培养。按0、24 h取样,倒置显微镜下拍照;在Transwell板中,每孔加入600 μl含10%血清的完全培养液,将小室移入孔中,注意不要产生气泡。在上室加入200 μl细胞悬液(含有1.0×105个细胞,药物浓度80 μg/ml, 160 μg/ml),将板移到培养箱里继续培养24 h。取出小室,擦掉上室细胞,将小室移入含500 μl 4%多聚甲醛固定液中固定20 min。将小室倒置风干,移入500 μl 0.1%结晶紫染色液中,染色30 min,用流水冲干净。在倒置显微镜下观察,拍照,随机数10个高倍镜视野细胞数(×200)。
1.2.6 RT-PCR检测技术按周期凋亡方法加药处理细胞后提取总RNA,在GenBank数据库中检索得到需要扩增的引物序列。
GAPDH-mRNA上游引物:5' -GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT-3' ,下游引物:5' -GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG-3' ;Bcl-2-mRNA上游引物:5' -GCCACTTACCTGAATGACCACC-3' ,下游引物:5' -AACCAGCGGTTGAAGCGTTCCT-3' ;Bax-mRNA上游引物:5' -TTTGCTTCAGGGTTTCATCCA-3' ,下游引物:5' -CTCCATGTTACTGTCCAGTTCGT-3' 。
所得RNA溶液进行浓度和纯度检测,快速一步法cDNA合成,将反转录得到的cDNA样本放入LightCycler®96反应仪中,采用SYBR GreenⅠ嵌合荧光法进行RT-PCR扩增。
1.2.7 Western blot检测技术按PCR技术处理细胞,48 h后,收集细胞,1 ml预冷的PBS洗涤3次,加入细胞裂解液,冰上裂解30 min。于4℃,12 000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液,即为总蛋白。BCA蛋白试剂盒测总蛋白浓度。总蛋白与SDS-PAGE蛋白上样缓冲液以4:1混合,煮沸5 min,-20℃保存备用。以每孔30 μg上样,恒压电泳80 V 30 min,120 V 90 min,恒流转膜300 mA 2 h。5%脱脂牛奶封闭2 h,4℃孵育一抗(1:1 000),过夜。PBST洗膜,5 min×3遍,室温孵育二抗(1:10 000)2 h。ECL超敏发光液曝光显影,Image-J软件比较条带的积分光密度。
1.3 统计学方法实验结果重复3次以上,用均数±标准偏差(x±s)表示,SPSS17.0软件进行统计分析,两样本均数比较采用t检验,Graphpad Prim 6.0进行图表分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 叶黄素对PC3细胞增殖的抑制作用叶黄素作用于PC3细胞后,可明显抑制其增殖,并呈时间和剂量依赖性,药物浓度为160 μg/ml时抑制率可达66.45%,且差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01),见图 1。
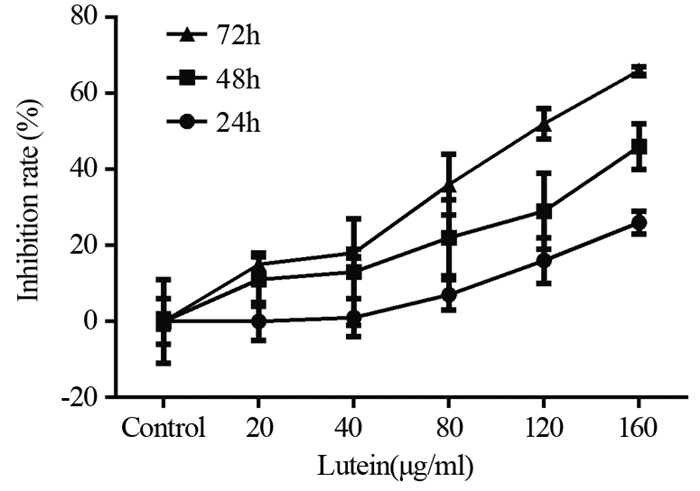
|
| 图 1 叶黄素对PC3细胞增殖的影响(n=6) Figure 1 Effect of lutein on proliferation of PC3 cells (n=6) |
叶黄素作用于PC3细胞48 h后,G0/G1期细胞比例由59.53%升至78.16%,表现为显著的G1期阻滞(P < 0.01),且随叶黄素浓度的增加,G2/M期细胞显著减少,S期细胞则变化不明显。结果显示,叶黄素可将PC3细胞阻滞于G0/G1期,见表 1、图 2。
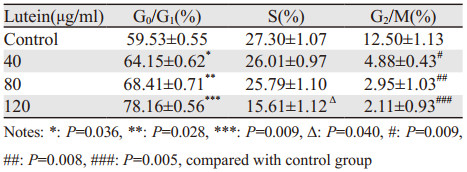
|
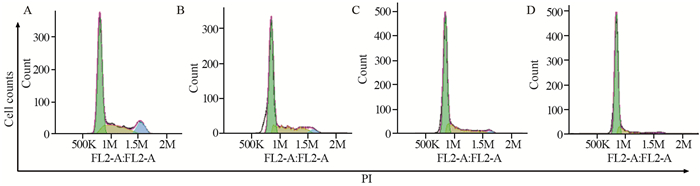
|
| A: control group; B: 40 μg/ml lutein; C: 80 μg/ml lutein; D:120 μg/ml lutein; 1K=1000, 1M=1000K, 500K=0.5M 图 2 叶黄素对PC3细胞周期分布的影响 Figure 2 Effect of lutein on cell cycle of PC3 cells |
叶黄素作用于PC3细胞48 h后,细胞凋亡数明显增多,凋亡率明显提高(早期+晚期)。对照组、40、80、120 μg/ml叶黄素组凋亡率分别是0.6%、10.4%、23.6%、36.1%,且随着浓度的升高,凋亡率显著增加,见图 3。
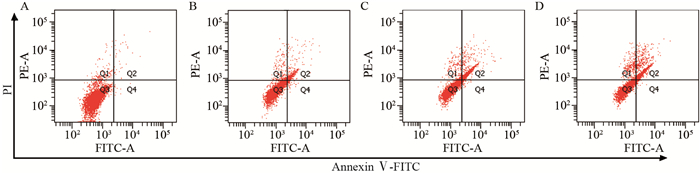
|
| A: control group; B: 40 μg/ml lutein; C: 80 μg/ml lutein; D: 120 μg/ml lutein 图 3 叶黄素对PC3细胞凋亡的影响 Figure 3 Effect of lutein on apoptosis of PC3 cells |
不同浓度的药物处理PC3细胞24 h后,细胞的迁移和侵袭能力明显降低,并且浓度为160 μg/ml时明显抑制(P < 0.01),见表 2、图 4~5。
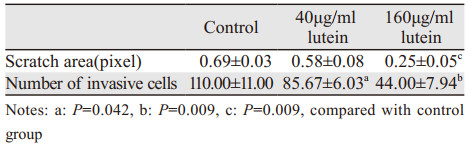
|

|
| 图 4 叶黄素对PC3细胞迁移能力的影响 Figure 4 Effect of lutein on migration ability of PC3 cells |
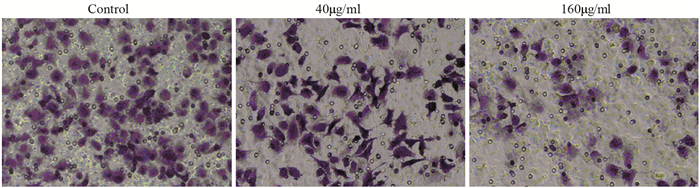
|
| 图 5 叶黄素对PC3细胞侵袭能力的影响 Figure 5 Effect of lutein on invasion ability of PC3 cells |
叶黄素干预组中细胞内Bax的mRNA含量均显著增加,Bcl-2含量显著下调,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);且随着药物浓度逐渐增加,呈剂量-时间效应关系,见图 6~7。
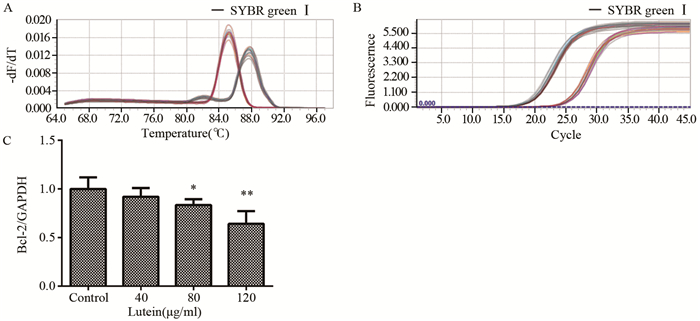
|
| A: melting peaks; B: amplification curves; C: column graph; *: P =0.038, **: P=0.009, compared with control group 图 6 叶黄素对Bcl-2 mRNA水平的影响(n=3) Figure 6 Effects of lutein on Bcl-2 mRNA (n=3) |
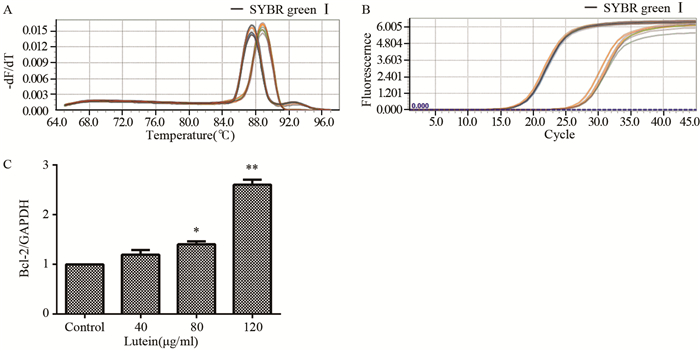
|
| A: melting peaks; B: amplification curves; C: column graph; *: P=0.019, **: P=0.001, compared with control group 图 7 叶黄素对Bax mRNA水平的影响(n=3) Figure 7 Effects of lutein on Bax mRNA (n=3) |
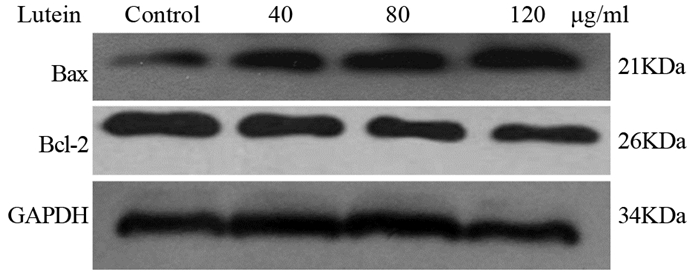
叶黄素作用细胞48 h后,Bax的蛋白表达水平均表现为上升,Bcl-2表达量下降,且随着叶黄素浓度的增加,呈剂量效应关系,见图 8。
|
| 图 8 不同剂量叶黄素对PC3细胞Bax和Bcl-2蛋白表达的影响 Figure 8 Effects of lutein on Bcl-2 and Bax protein expression in PC3 cells |
叶黄素有作为生命延长剂、皮肤保护剂、溃疡抵制剂、冠状动脉疾病抵制剂、癌症预防剂的潜在治疗用途。本研究结果显示叶黄素能够显著抑制PC3细胞的增殖。已有研究表明细胞周期调控系统功能的异常是肿瘤发生,发展的重要原因[8]。本研究发现叶黄素可以通过将PC3细胞周期进程阻滞在G0/G1期,进而抑制癌细胞的无节制分裂,并且呈剂量依赖性。前列腺癌的发生、发展是多基因、多步骤的过程,常规的化疗、放疗、免疫方法只能杀死原位的肿瘤细胞,却无法完全控制肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移过程,而肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移往往又是肿瘤复发的根本原因[9-11]。本实验表明叶黄素处理后,PC3细胞的迁移和侵袭受到明显抑制。
细胞凋亡的研究是目前肿瘤研究的热点,Bcl-2家族在线粒体途径细胞凋亡调控中有重要的作用,是目前凋亡研究的热点之一[12-13],Bcl-2家族中最重要的两个成员Bcl-2和Bax与肿瘤有明显相关性,Bcl-2和Bax分别是Bcl-2家族中最主要的抑制凋亡和促进凋亡蛋白[14-16]。Bax一方面能够与Bcl-2形成异源二聚体从而拮抗Bcl-2的抗凋亡作用,另一方面它自身还能形成同源二聚体诱导凋亡,通过调控细胞凋亡来发挥调节肿瘤细胞生长状态的作用[17-18]。多数肿瘤的Bcl-2表达升高,而Bax表达下降[19]。对Bcl-2和Bax的相互关系及其在体内外对肿瘤细胞凋亡的调控作用的进一步研究对阐明肿瘤发病机制、指导肿瘤治疗都将产生重要影响。本研究结果显示,叶黄素作用PC3细胞48 h后,凋亡比率明显升高,Bcl-2表达下降,Bax表达上升,通过改变两者的比例来促进凋亡,并呈浓度依赖性。
总之,本研究表明叶黄素能有效抑制人前列腺癌细胞增殖并诱导凋亡,为其临床应用提供了理论依据。但前列腺癌的发生发展是一个多因素共同作用的过程,发生凋亡机制也十分复杂,仍需进一步研究阐明叶黄素促凋亡机制。
| [1] | Vandekerkhove G, Chi KN, Wyatt AW. Clinical utility of emerging liquid biomarkers in advanced prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Genet, 2017, pii: S2210-7762(17): 30303–4. |
| [2] | Haworth A, Williams S. Focal therapy for prostate cancer: the technical challenges[J]. J Contemp Brachytherapy, 2017, 9(4): 383–9. |
| [3] | Eisenhauer B, Natoli S, Liew G, et al. Lutein and zeaxanthin-food sources, bioavailability and dietary variety in age-related macular degeneration protection[J]. Nutrients, 2017, 9(2): pii: E120. DOI:10.3390/nu9020120 |
| [4] | Fung FK, Law BY, Lo AC. Lutein attenuates both apoptosis and autophagy upon cobalt (ii) chloride-induced hypoxia in rat muller cells[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(12): e0167828. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0167828 |
| [5] | Sahli MW, Mares JA, Meyers KJ, et al. Dietary intake of lutein and diabetic retinopathy in the atherosclerosis risk in communities study (ARIC)[J]. Ophthalmic Epidemiol, 2016, 23(2): 99–108. DOI:10.3109/09286586.2015.1129426 |
| [6] | 刘志方, 吴凤秀, 王丽平, 等. 叶黄素介导Nrf-2/ARE信号通路途径抑制人结肠癌HT29细胞增殖的作用机制[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2016, 24(6): 858–65. [ Liu ZF, Wu FX, Wang LP, et al. Lutein suppresses cell proliferation in human colon cancer cell line HT29 via Nrf-2/ARE signal transduction pathway[J]. Shi Jie Hua Ren Xiao Hua Za Zhi, 2016, 24(6): 858–65. ] |
| [7] | 付蕾, 陈晓哲, 张慧娟, 等. 叶黄素对人结肠癌HT29细胞增殖的抑制及其机制[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2013, 21(13): 1239–44. [ Fu L, Chen XZ, Zhang HJ, et al. Mechanisms underlying suppressive effect of lutein on cell proliferation in human colon cancer cell line HT29[J]. Shi Jie Hua Ren Xiao Hua Za Zhi, 2013, 21(13): 1239–44. ] |
| [8] | Li X, Liu S. Suppression of HBXIP reduces cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro, and tumorigenesis in vivo in human urothelial carcinoma of the bladder[J]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm, 2016, 31(9): 311–6. DOI:10.1089/cbr.2016.2038 |
| [9] | Wang WC, Wang LH, Mizokami A, et al. Down-regulation of E-cadherin enhances prostate cancer chemoresistance via Notch signaling[J]. Chin J Cancer, 2017, 36(3): 150–62. |
| [10] | Vandsemb EN, Bertilsson H, Abdollahi P, et al. Phosphatase of regenerating liver 3 (PRL-3) is overexpressed in human prostate cancer tissue and promotes growth and migration[J]. J Transl Med, 2016, 14: 71. DOI:10.1186/s12967-016-0830-z |
| [11] | Hoyne G, Rudnicka C, Sang QX, et al. Genetic and cellular studies highlight that A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase 19 is a protective biomarker in human prostate cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2016, 16: 151. DOI:10.1186/s12885-016-2178-4 |
| [12] | Zhang C, Wang Z, Zhao J, et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Lutein on NMDA-Induced Retinal Ganglion Cell Injury in Rat Retina[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2016, 36(4): 531–40. DOI:10.1007/s10571-015-0231-5 |
| [13] | Maiyo FC, Moodley R, Singh M. Cytotoxicity, antioxidant and apoptosis studies of quercetin-3-o glucoside and 4-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl-1-- > 4-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyloxy)-benzyl isothiocyanate from moringa oleifera[J]. Anticancer Agents Medl Chem, 2016, 16(5): 648–56. DOI:10.2174/1871520615666151002110424 |
| [14] | Sowmya PR, Arathi BP, Vijay K, et al. Astaxanthin from shrimp efficiently modulates oxidative stress and allied cell death progression in MCF-7 cells treated synergistically with beta-carotene and lutein from greens[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2017, 106(Pt A): 58–69. |
| [15] | Nataraj J, Manivasagam T, Thenmozhi AJ, et al. Lutein protects dopaminergic neurons against MPTP-induced apoptotic death and motor dysfunction by ameliorating mitochondrial disruption and oxidative stress[J]. Nutr Neurosci, 2016, 19(6): 237–46. DOI:10.1179/1476830515Y.0000000010 |
| [16] | 李军, 回丽媛, 战仕胜, 等. 抗菌肽17BIPHE2对人肺腺癌细胞A549的抑制作用[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2017, 44(10): 659–64. [ Li J, Hui LY, Zhan SS, et al. Inhibition of antimicrobial peptide 17BIPHE2 on lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells and related mechanism[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2017, 44(10): 659–64. DOI:10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2017.17.0287 ] |
| [17] | Behbahani M. Evaluation of in vitro anticancer activity of Ocimum basilicum, Alhagi maurorum, Calendula officinalis and their parasite Cuscuta campestris[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(12): e116049. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0116049 |
| [18] | Irusta G, Pazos MC, Abramovich D, et al. Effects of an inhibitor of the gamma-secretase complex on proliferation and apoptotic parameters in a FOXL2-mutated granulosa tumor cell line (KGN)[J]. Biol Reprod, 2013, 89(1): 9. |
| [19] | 裴迎新, 衡正昌, 段广才, 等. 叶黄素对食管癌细胞凋亡的影响及其作用机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2007, 32(4): 332–4, 354. [ Pei YX, Heng ZC, Duan GC, et al. Effects and mechanism of lutein on apoptosis of esophageal carcinoma EC9706 cells[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 2007, 32(4): 332–4, 354. ] |
 2018, Vol. 45
2018, Vol. 45


