文章信息
- Gab2通过调节EMT促进胃癌的侵袭转移
- Gab2 Promotes Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via Regulating EMT
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2018, 45(6): 381-385
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2018, 45(6): 381-385
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2018.17.0881
- 收稿日期: 2017-10-12
- 修回日期: 2017-12-26
2. 261041 潍坊,潍坊人民医院放射治疗科;
3. 261053 潍坊,潍坊医学院病原微生物实验室;
4. 261042 潍坊,潍坊医学院附属医院胃肠科;
5. 261053 潍坊,潍坊医学院病理学实验室
2. Department of Radiotherapy, Weifang People's Hospital, Weifang 261041, China;
3. Department of Pathogeny Microbiology, Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261053, China;
4. Department of Gastroenterology, Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261042, China;
5. Department of Pathology, Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261053, China
胃癌是我国常见的恶性肿瘤之一,其导致患者死亡的主要原因是原发灶的浸润和转移。近来的研究发现Grb2协同结合蛋白2(Grb2 binding protein-2, Gab2)可能是一个重要的肿瘤转移调控蛋白,其高表达与某些肿瘤的恶性程度、侵袭转移能力密切相关[1-3]。但到目前为止,Gab2在胃癌组织中的表达及其对胃癌侵袭迁移的影响尚未见报道。本研究应用免疫组织化学技术检测胃癌组织中Gab2的表达,并通过基因干扰技术抑制胃癌细胞株SGC7901细胞Gab2的表达,观察Gab2对SGC7901细胞体外侵袭转移能力的影响,并初步探讨其可能的机制。
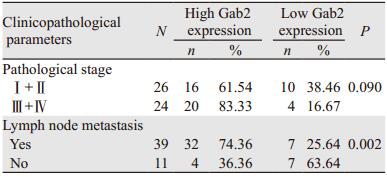
1 资料与方法 1.1 资料 1.1.1 病例资料收集潍坊医学院病理学教研室2013年3月1日至2016年11月30日有完整病理资料的胃癌蜡块标本50例,病理诊断均为腺癌,其中高分化5例,中分化12例,低分化33例;侵犯肌层36例,侵犯浆膜层14例;有淋巴结转移39例,未发生转移11例;Ⅰ期5例,Ⅱ期21例,Ⅲ期20例,Ⅳ期4例。患者年龄34~78岁,中位年龄56岁,其中男36例,女14例。所有患者术前均未接受任何抗肿瘤治疗。
1.1.2 主要试剂细胞培养产品购自美国Hyclone公司;Lipofectamin2000购自上海Invitrogen公司;细胞培养板和Transwell小室购自上海玉博生物科技有限公司;Matrigel膜基质购自北京威格拉斯生物技术有限公司;0.1%Fibronectin、HEPES和BSA购自美国Sigma公司;RT-PCR引物与试剂盒购自上海生工公司;Gab2、E-cadherin、N-cadherin、MMP-9一抗购自美国Santa Cruz公司;二抗及免疫组织化学试剂盒购自北京中杉金桥公司。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 免疫组织化学采用免疫组织化学SP法,操作方法按试剂说明书,胃癌组织免疫组织化学染色在显微镜下观察,Gab2和MMP-9以胞质出现浅黄到棕色颗粒沉淀为阳性,E-cadherin及N-cadherin以胞膜呈现浅黄到棕色为阳性。高倍镜(×400)下每张切片至少选择5个随机视野,随机计数500个细胞,阳性细胞占同类计数细胞的百分比为阳性细胞率。阳性结果的判定根据阳性细胞率及显色深浅分级:无细胞显色为0分,< 10%细胞显色为1分,10%~50%细胞显色为2分,> 50%细胞显色为3分。显色深浅:不显色或显色不清为0分,浅黄色为1分,黄棕色为2分,棕色为3分。两项乘积≥6分为高表达,≤4分为低表达。
1.2.2 细胞培养人胃癌细胞株SGC7901购自美国ATCC细胞库。SGC7901细胞常规培养于10%胎牛血清中,加入终浓度各为100 u/ml的青霉素和0.1 mg/ml的链霉素,置37℃、5%CO2培养箱中传代培养。采用对数生长期的细胞进行实验。当细胞密度达到80%时分别转染插入Gab2目标片段5'-GTGAGAACGATGAGAAATA-3'的小RNA干扰质粒和空白对照序列的小RNA干扰质粒,转染步骤参照转染试剂说明书。转染细胞株分别命名为实验组siGab2/SGC7901细胞和对照组NC/SGC7901细胞。
1.2.3 MTT细胞增殖实验取对数生长期细胞,以1×103个/孔接种于96孔板,培养24 h,待其贴壁后用无血清培养液洗涤3次,继续培养12 h后开始实验。将实验组和对照组细胞分别培养1、2、3、4、5 d后加入MTT溶液20 μl,37℃孵育4 h,弃去培养液,加入二甲基亚砜(DMSO),振荡10 min后在570 nm波长处测定吸光度值,实验重复3次。
1.2.4 RT-PCR实验用TRIzol抽提细胞总RNA,内参β-actin扩增片段长度为491 bp,Gab2扩增片段长度为240 bp。Gab2引物:上游:5'-CTGAGACTGATAACGAGGAT-3',下游:5'-GAGGTGTTTCTGCTTGAC-3';β-actin引物:上游:5'-ATGTTTG AGACCTTCAACAC-3',下游:5'-CACGTCACACTTCATGATGG-3'。PCR产物在2%琼脂糖进行凝胶电泳,于Bio-Rad凝胶成像仪下观察并照相,用Quantity One进行定量分析。
1.2.5 体外侵袭实验应用8 μm滤膜Transwell小室,用前铺上Matrigel膜基质并干燥,将NC/SGC7901和siGab2/SGC7901细胞悬液各200 μl(5×105cells/ml)加入Boyden小室上室。下室加入300 μl BM(RPMI 1640培养液,0.1%BSA,25 mmol/L HEPES)。5%CO2、37℃培养24 h。然后取出培养板弃去Boyden小室内培养液,用棉签擦净上室面的人工基底胶和细胞,下室面用甲醇固定10 min,苏木精对比染色,置400倍光学显微镜下观察,计数小室下室面的细胞数即为穿透人工基膜的细胞数,计数5个高倍镜视野。每个实验重复3次。
1.2.6 Western blot实验将转染后的siGab2/SGC7901和NC/SGC7901细胞培养72 h后提取蛋白,制备SDS-PAGE凝胶,蛋白质变性后电泳,转膜、封闭,分别滴加Gab2、E-cadherin、N-cadherin及MMP-9一抗、二抗孵育后显影。以目的蛋白条带的灰度值与内参照β-actin蛋白条带的灰度值的比值表示蛋白的相对表达量,实验重复3次。
1.3 统计学方法运用SPSS13.0做统计学处理。对所有定量资料数据结果用(x±s)表示,进行χ2检验、Spearman相关分析和两独立样本的t检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
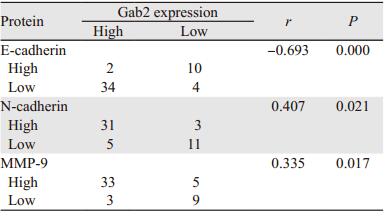
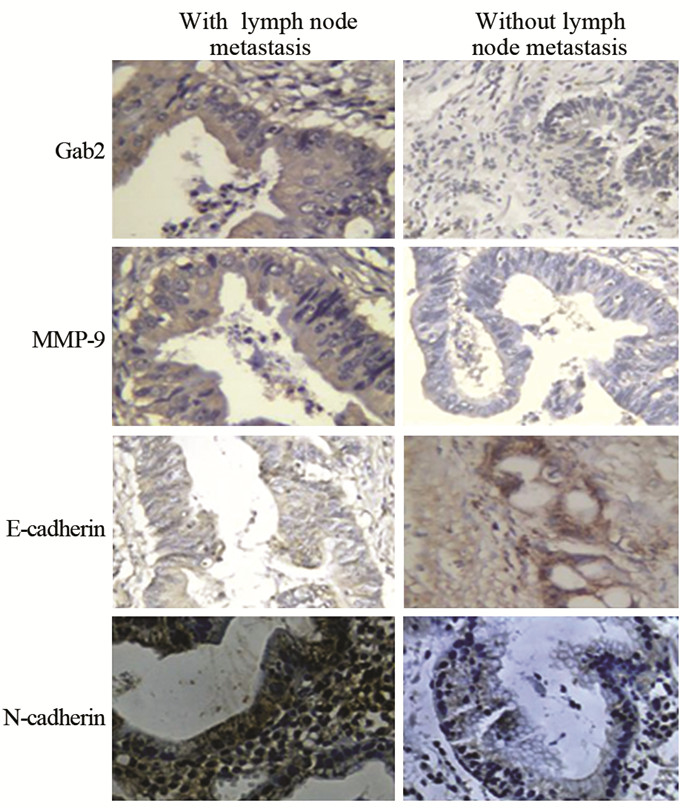
2 结果 2.1 胃癌组织中Gab2、E-cadherin、N-cadherin和MMP-9蛋白的表达Gab2在50例胃癌组织中的阳性表达率为100%,而且72%胃癌组织中Gab2高表达。癌旁非肿瘤组织的Gab2阳性表达率仅为14%,且全部为低表达。Gab2表达与病理分期无显著相关性(P=0.090),与淋巴结转移情况显著相关,(P=0.002),见表 1。四种蛋白在胃癌中的表达有相关性,Gab2高表达时,N-cadherin与MMP-9在胃癌中也呈高表达,E-cadherin则低表达;Gab2低表达时,N-cadherin与MMP-9也呈低表达,E-cadherin则高表达,见表 2、图 1。
|
|
|
| There were high expression of Gab2, MMP-9, N-cadherin and low expression of E-cadherin in gastric cancer tissues with lymph node metastasis, while low expression of Gab2, MMP-9, N-cadherin and high expression of E-cadherin in gastric cancer tissues without lymph node metastasis (IHC×200) 图 1 Gab2、MMP-9、E-cadherin和N-cadherin在胃癌组织中的表达与淋巴结转移的关系 Figure 1 Correlation of Gab2, MMP-9, E-cadherin and N-cadherin expression with lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer tissues |
RT-PCR结果显示siRNA干扰明显降低了siGab2/SGC7901细胞中Gab2 mRNA及蛋白的表达,与对照组NC/SGC7901细胞比较差异有统计学意义(P=0.003, P < 0.01),见图 2,表明通过基因沉默获得了Gab2低表达的细胞,为后续实验奠定了基础。

|
| RT-PCR and Western blot results showed that after microRNA interference, the mRNA and protein expressions of Gab2 in siGab2/SGC7901 cells were decreased obviously, while no significant difference was observed in SGC7901 or NC/SGC7901 cells 图 2 SGC7901、NC/SGC7901和siGab2/SGC7901细胞中Gab2 mRNA与蛋白的表达 Figure 2 Expression of Gab2 mRNA and protein in SGC7901, NC/SGC7901 and siGab2/SGC7901 cells |
MTT结果显示,小RNA干扰后siRNA/SGC7901细胞增殖显著减慢,OD值与对照组相比差异有统计学意义(P=0.048, P < 0.05)。说明Gab2表达下降后细胞增殖能力明显下降,见图 3。

|
| 图 3 Gab2表达降低对SGC7901细胞增殖的影响 Figure 3 Effect of decreased Gab2 expression on proliferation of SGC7901 cells |
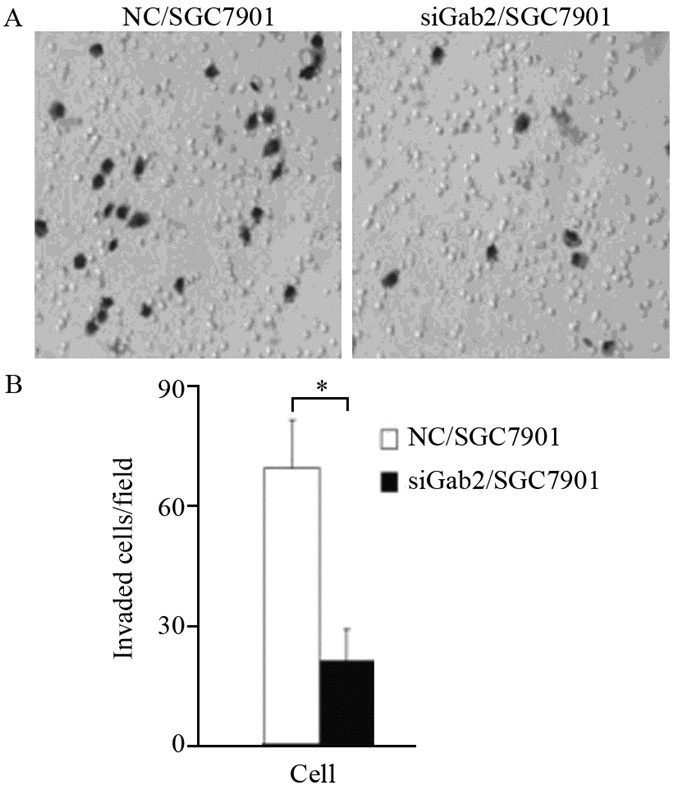
siGab2/SGC7901穿过8 μm微孔滤膜的细胞数与NC/SGC7901细胞数目比较明显减少,差异有统计学意义(P=0.005, P < 0.01),说明Gab2表达降低后细胞的侵袭能力明显下降,见图 4。
|
| In vitro matrigel invasion assay results showed that reduced expression of Gab2 could inhibit the invasion of SGC7901 cells and the quantity of gastric cancer siGab2/SGC7901cells which invaded and penetrated matrigel membrane was decreased; *: P < 0.01 图 4 Gab2表达降低对SGC7901细胞侵袭能力的影响 Figure 4 Effect of decreased Gab2 expression on invasiveness of SGC7901 cells |
为了进一步探究Gab2蛋白影响胃癌细胞侵袭性的机制,应用Western blot法检测E-cadherin、N-cadherin、MMP-9和Snail蛋白的表达。结果显示siGab2/SGC7901细胞中E-cadherin蛋白表达上调,N-cadherin、Snail和MMP-9蛋白表达下调,与NC/SGC7901细胞比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01),见图 5。

|
| Western blot showed that the expressions of N-cadherin and MMP-9 and Snail were decreased while E-cadherin expression was increased in siGab2/SGC7901 cells 图 5 Gab2表达降低对SGC7901细胞E-cadherin、N-cadherin、MMP-9与Snail蛋白表达的影响 Figure 5 Effect of decreased Gab2 expression on expression of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, MMP-9 and Snail in SGC7901 cells |
胃癌的浸润和转移是导致患者死亡的主要原因,从分子水平深入研究其浸润转移的机制,具有重要意义[4]。作为一类连接蛋白,生长因子受体结合蛋白2(Grb2)的相关结合蛋白家族参与了细胞内多种信号转导通路,是酪氨酸激酶(PTKs)激活的下游信号转导通路的关键分子。Gab2是这个家族的重要成员,接受胞外多种因子刺激后被PTKs磷酸化激活,招募富含SH2结构域的信号转运分子,活化下游PI3K/AKT和SHP2/Ras/ERK等一系列信号转导途径,在细胞增殖、分化及迁移等生理过程中发挥重要作用[5-6]。近年研究发现,Gab2在乳腺癌、卵巢癌、肺癌、脑胶质细胞瘤等恶性肿瘤中高表达,并参与调控肿瘤的发生及转移[7-11]。本研究结果显示,Gab2在胃癌组织中的表达较癌旁组织明显升高,并且与淋巴结转移显著相关。有淋巴结转移的胃癌组织中Gab2高表达,而无淋巴结转移的胃癌组织中Gab2表达较低。体外细胞实验也发现特异性siRNA沉默Gab2后,胃癌SGC7901细胞迁移侵袭能力明显降低,与Lee等的结果一致[12],进一步证实了Gab2参与调节肿瘤的迁移侵袭过程,提示Gab2在胃癌的侵袭转移中发挥重要作用。
肿瘤细胞从原发部位脱落是肿瘤浸润和转移的第一步,这与细胞黏附性减低有关,而上皮间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition, EMT)是肿瘤细胞黏附性降低的重要原因。有研究表明,Snail的表达诱导了EMT过程,增强了肿瘤细胞的运动和侵袭能力[13]。此外,E-cadherin是上皮细胞表型的标记分子,而N-cadherin是间质细胞表型的标记分子,E-cadherin表达降低及N-cadherin表达增高均可以增强肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移能力[14]。本研究结果表明,在有淋巴结转移的胃癌中E-cadherin低表达或缺失,而无淋巴结转移的胃癌组织中表达较高,与Gab2的表达呈负相关。恰恰相反,N-cadherin在有淋巴结转移的胃癌中高表达,在无淋巴结转移的胃癌组织中则表达较低,与Gab2的表达呈正相关,提示Gab2可能通过调控EMT在胃癌的浸润和转移过程中发挥重要作用。Ding等的研究表明Gab2的过表达能够促进EMT,抑制肿瘤细胞E-cadherin的表达[14-15],与本研究的结果相一致。
另外,MMP-9作为基质金属蛋白酶家族的重要成员之一,与肿瘤侵袭、转移关系最为密切。有研究显示,PI3K/Akt信号通路能够被酪氨酸磷酸化的Gab2激活,活化的PI3K/Akt信号通路会抑制E-cadherin表达,促进MMP-9的表达,而MMP-9对EMT有辅助作用,进一步增强肿瘤细胞的侵袭转移能力[14]。本研究结果表明,在有淋巴结转移的胃癌组织中,MMP-9高表达,而无淋巴结转移的胃癌组织中MMP-9表达较低,与Gab2的表达呈正相关,提示MMP-9高表达后胃癌的侵袭能力增强。为进一步探究Gab2对胃癌侵袭转移的作用机制,本组实验检测了siRNA沉默Gab2后SGC7901细胞中MMP-9蛋白和转录因子Snail的表达水平。结果显示MMP-9和Snail的表达在Gab2沉默的SGC7901细胞中显著减少,提示Gab2可能通过促进上皮间质转化,降低E-cadherin的表达,增高MMP-9和Snail的表达来促进细胞的侵袭和转移。
综上所述,本研究结果提示Gab2可能通过调控EMT在胃癌的侵袭转移中发挥重要作用,有可能成为胃癌治疗的一个潜在靶点。
| [1] | Ding CB, Yu WN, Feng JH, et al. Structure and function of Gab2 and its role in cancer(Review)[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2015, 12(3): 4007–14. DOI:10.3892/mmr.2015.3951 |
| [2] | Luo LY, Hahn WC. Oncogenic Signaling Adaptor Proteins[J]. J Genet Genomics, 2015, 42(10): 521–9. DOI:10.1016/j.jgg.2015.09.001 |
| [3] | Ma J, Yu J, Liu J, et al. MicroRNA-302a targets GAB2 to suppress cell proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma[J]. Oncol Rep, 2017, 37(2): 1159–67. DOI:10.3892/or.2016.5320 |
| [4] | Özer İ, Bostancı EB, Ulaş M, et al. Changing Trends in Gastric Cancer Surgery[J]. Balkan Med J, 2017, 34(1): 10–20. DOI:10.4274/balkanmedj |
| [5] | Adams SJ, Aydin IT, Celebi JT. GAB2-a Scaffolding Protein in Cancer[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2012, 10(10): 1265–70. DOI:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0352 |
| [6] | Vaughan TY, Verma S, Bunting KD. Gab2-associated binding(Gab) proteins in hematopoitic and immune cell biology[J]. Am J Blood Res, 2011, 1(2): 130–4. |
| [7] | Xu LJ, Wang YC, Lan HW, et al. Grb2-associated binder-2 gene promotes migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells via Akt signaling pathway[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2016, 8(2): 1208–17. |
| [8] | Ding C, Luo J, Fan X, et al. Elevated Gab2 induces tumor growth and angiogenesis in colorectal cancer through upregulating VEGF levels[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2017, 36(1): 56. DOI:10.1186/s13046-017-0524-2 |
| [9] | Shi L, Sun X, Zhang J, et al. Gab2 expression in glioma and its implications for tumor invasion[J]. 2013, 52(8): 1739-50. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23231021 |
| [10] | Zhang X, Dong Z, Zhang Z, et al. Critical Role for GAB2 in Neuroblastoma Pathogenesis Through the Promotion of SHP2/MYCN Cooperation[J]. Cell Rep, 2017, 18(12): 2932–42. DOI:10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.065 |
| [11] | Duckworth C, Zhang L, Carroll SL, et al. Overexpression of GAB2 in ovarian cancer cells promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by upregulating chemokine expression[J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(31): 4036–47. DOI:10.1038/onc.2015.472 |
| [12] | Lee SH, Jeong EG, Nam SW, et al. Increased expression of Gab2, a scaffolding adaptor of the tyrosine kinase signalling, in gastric carcinomas[J]. Pathology, 2007, 39(3): 326–9. |
| [13] | Wieczorek K, Wiktorska M, Sacewiczhofman I, et al. Filamin A upregulation correlates with Snail-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cell adhesion but its inhibition increases the migration of colon adenocarcinoma HT29 cells[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2017, 359(1): 163–70. DOI:10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.07.035 |
| [14] | Ding C, Luo J, Li L, et al. Gab2 facilitates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the MEK/ERK/MMP signaling in colorectal cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2016, 35: 5. DOI:10.1186/s13046-015-0280-0 |
| [15] | Yip WK, Seow HF. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling by EGF downregulates membranous E-cadherin and b-catenin and enhances invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells[J]. Cancer Lett, 2012, 318(2): 162–72. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.12.018 |
 2018, Vol. 45
2018, Vol. 45


