文章信息
- 隐丹参酮通过抑制帽子依赖的翻译促进人肺癌细胞A549的凋亡
- Cryptotanshinone Promotes Apoptosis of A549 Cells via Inhibiting Cap-dependent mRNA Translation
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2016, 43(7): 550-554
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2016, 43(7): 550-554
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2016.07.002
- 收稿日期: 2015-08-27
- 修回日期: 2015-09-27
2. 300222 天津,天津市胸科医院心内科
2. Department of Cardiology, Tianjin Chest Hospital, Tianjin 300222, China
eIF4F蛋白复合物由eIF4E、eIF4A和eIF4G组成,其形成能力决定了细胞内帽子依赖翻译的强弱[1]。eIF4F蛋白复合物的生成受mTOR激酶和4EBP1调控,非磷酸化的4EBP1通过与eIF4G竞争性结合eIF4E抑制eIF4F蛋白复合物的生成,当4EBP1被mTOR激酶磷酸化后,其与eIF4E的结合能力减弱,促进eIF4F蛋白复合物的生成[2-3]。在肺癌临床标本中mTOR激酶异常激活且eIF4E高表达[4-5],表明帽子依赖的翻译在肺癌的发生发展中发挥着重要的作用。
隐丹参酮是从中药丹参中分离得到的重要成分,具有抗炎、抗血管生成、抗氧化等多种生物学功能,在抗菌消炎、抗心血管疾病和神经退行性疾病中均展示了良好的应用前景[6-7]。隐丹参酮能够抑制黑色素瘤[8]、乳腺癌[9]、肝癌[10]、前列腺癌[11]、胶质瘤[12]等多种肿瘤细胞的存活。最近研究发现隐丹参酮能够通过促进细胞凋亡,抑制肺癌细胞的体外存活能力和体内成瘤能力[13],但其发挥作用的分子机制依然不清楚。基于帽子依赖翻译在肺癌恶性进展中的重要性,本研究探索了隐丹参酮对人肺癌细胞A549中帽子依赖翻译的影响及其在隐丹参酮促A549细胞凋亡中的作用。
1 材料与方法 1.1 细胞株及主要试剂人肺癌细胞A549由河北大学综合实验中心保存。隐丹参酮为西安合健生物科技有限公司产品。Phospho-m-TOR(Ser2481)抗体、Phospho-4EBP1(Ser65)抗体、eIF4E抗体和eIF4G抗体均为美国Cell Signaling Technology公司产品;mTOR抗体、4EBP1抗体、Bcl-2抗体和Tubulin抗体为美国Santa Cruz公司产品。m7GTP Sepharose beads为美国GE Healthcare公司产品;转染试剂Lipofectamine RNAiMAX为美国Invitrogen公司产品;Annexin V-FITC细胞凋亡检测试剂盒为天津三箭生物技术有限公司产品;Cell Counting Kit-8(cck8)试剂盒为日本同仁化学研究所产品;对照siRNA control和si-4EBP1为美国Invitrogen公司产品,引物序列见表 1。
将A549细胞以2×105每孔的密度接种到6孔板中,24 h后分别用DMSO和不同浓度的隐丹参酮(5、10、20μmol/L)处理细胞24 h,提取蛋白后使用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒对蛋白进行定量,取50μg蛋白添加SDS上样缓冲液沸水浴5 min后进行SDS-PAGE电泳,电泳结束后采用半干转膜法将蛋白转移到硝酸纤维素膜上,转好的膜使用5%脱脂奶粉封闭2 h后孵育一抗4℃过夜(mTOR抗体1:2 000稀释,Phospho-mTOR(Ser2481)抗体1:400稀释,4EBP1抗体1:3 000稀释,Phospho-4EBP1(Ser65)抗体1:400稀释,Bcl-2抗体1:1 000稀释,Tubulin抗体1:1 000稀释),使用TBST缓冲液洗膜3次(每次5 min)后孵育辣根过氧化物酶标记的二抗(羊抗兔二抗和羊抗鼠二抗均1:5 000稀释),使用TBST缓冲液洗膜3次(每次5 min)后使用ECL底物发光显色试剂盒压片显影。采用Image J软件对条带进行灰度分析,以Tubulin作内参,对蛋白表达水平进行相对定量分析。
1.3 m7GTP pull down实验检测将A549细胞以2×105每孔的密度接种到6孔板中,24 h后分别用DMSO和不同浓度的隐丹参酮(5、10、20μmol/L)处理细胞24 h,提取蛋白后使用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒对蛋白进行定量,取500μg蛋白添加400μl蛋白裂解液和20μl m7GTP Sepharose beads在4℃冰箱中翻转孵育2 h,离心弃上清液后用蛋白裂解液洗沉淀物3次,每次8 min,离心收集沉淀物添加SDS上样缓冲液沸水浴5 min进行Western blot实验,检测eIF4G、4EBP1和eIF4E的蛋白表达,通过eIF4G和4EBP1蛋白水平的变化分析隐丹参酮eIF4F蛋白复合物生成的影响。分别取40μg不同浓度隐丹参酮(5、10、20μmol/L)处理组的蛋白进行Western blot实验,检测eIF4G、4EBP1和eIF4E的蛋白表达作为对照,以检测隐丹参酮处理对细胞中相关蛋白表达的影响。采用Image J软件对条带进行灰度分析,以eIF4E作为内参,对eIF4G和4EBP1蛋白表达水平进行相对定量分析。
1.4 细胞凋亡检测将A549细胞以1×105每孔的密度接种到6孔板中,24 h后分别用对照siRNA control和si-4EBP1转染细胞,转染方法按Lipofectamine RNAiMAX转染试剂说明书进行。转染36 h后分别用DMSO和10μmol/L隐丹参酮处理细胞24 h,收集细胞后用预冷的PBS洗涤细胞2次,离心后添加100μl的结合缓冲液重悬细胞,分别加入碘化丙啶和Annexin V-FITC各5μl后混匀室温避光反应15 min。添加400μl的结合缓冲液后进行流式检测分析。
1.5 CCK8细胞活性检测将A549细胞以1×105每孔的密度接种到6孔板中,待其生长融合度至60%左右时分别用siRNA control和si-4EBP1转染细胞,转染方法按Lipofectamine RNAiMAX转染试剂说明书进行。转染36 h后收集细胞并以1 500细胞每孔的密度转接种至96孔细胞培养板中,24 h后分别用DMSO和10μmol/L隐丹参酮处理细胞48 h,每孔添加10μl CCK8后孵育1 h。用酶标仪测定在450 nm处的吸光度。每个时间点平行做3个孔,实验重复3次。
1.6 统计学方法数据使用SPSS11.5统计软件进行分析,以(x±s)表示,采用t检验进行组间比较,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 隐丹参酮以剂量依赖方式抑制A549细胞中mTOR及4EBP1的磷酸化Western blot结果显示:隐丹参酮抑制mTOR及其下游底物4EBP1的磷酸化,且这种抑制作用具有剂量依赖性,DMSO组pmTOR-2481和p4EBP1-65相对值分别为(1±0.07)和(1±0.09),而5、10、20μmol/L隐丹参酮处理组pmTOR-2481的相对值分别为(0.81±0.08),(0.52±0.11)和(0.22±0.08),p4EBP1-65的相对值分别为(0.77±0.08),(0.48±0.09)和(0.28±0.07),见图 1。
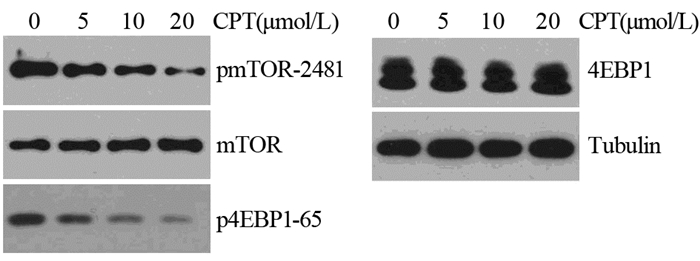
|
| CPT: cryptotanshinone 图 1 隐丹参酮对A549细胞中mTOR及4EBP1磷酸化的影响 Figure 1 Effect of Cryptotanshinone on phosphorylation of mTOR and 4EBP1 in A549 cells |
m7GTP pull down实验结果显示:隐丹参酮抑制A549细胞中eIF4E和eIF4G之间的相互作用, 且这种抑制作用具有剂量依赖性,DMSO组与eIF4E相互作用的eIF4G的相对值为(1±0.06),而5、10、20μmol/L隐丹参酮处理组相对值分别为(0.78±0.06)、(0.55±0.07)和(0.25±0.09),见图 2。
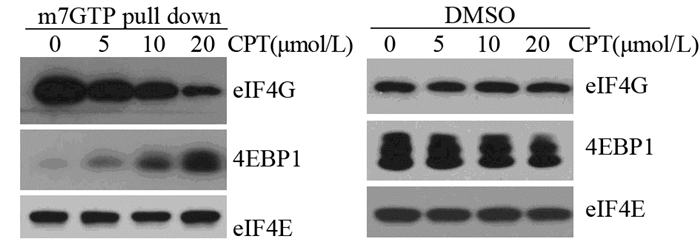
|
| 图 2 隐丹参酮对A549细胞中eIF4F蛋白复合物生成的影响 Figure 2 Effect of Cryptotanshinone on formation of eIF4F complex in A549 cells |
Bcl-2是肿瘤细胞中重要的抗凋亡蛋白,且Bcl-2蛋白的翻译受帽子依赖翻译的调控。Western blot分析结果显示:隐丹参酮抑制A549细胞中Bcl-2蛋白的表达,且这种抑制作用具有剂量依赖性,DMSO组Bcl-2蛋白表达的相对值为(1±0.05),而5、10、20μmol/L隐丹参酮处理组相对值分别为(0.78±0.08)、(0.41±0.07)和(0.20±0.11),见图 3。

|
| 图 3 隐丹参酮对A549细胞中Bcl-2蛋白表达的影响 Figure 3 Effect of Cryptotanshinone on Bcl-2 protein expression in A549 cells |
由于隐丹参酮是通过抑制4EBP1的磷酸化抑制帽子依赖翻译,因此通过敲低4EBP1的表达解除隐丹参酮对帽子依赖翻译的抑制作用后检测Bcl-2蛋白的表达,结果显示:隐丹参酮显著抑制了A549细胞中Bcl-2蛋白的表达[(1±0.06)vs.(0.25±0.09),P=0.0006],但敲低4EBP1表达拮抗了隐丹参酮对Bcl-2蛋白表达的抑制作用[(0.25±0. 09)vs.(0.85±0.11),P=0.0004],见图 4。
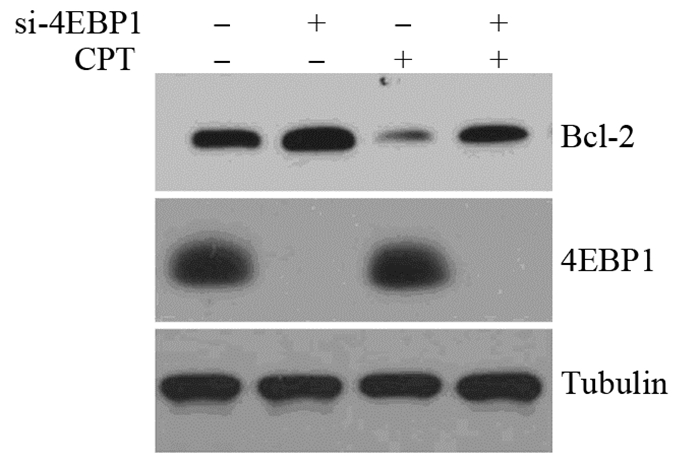
|
| 图 4 敲低4EBP1表达后隐丹参酮对A549细胞Bcl-2蛋白表达的影响 Figure 4 Effect of Cryptotanshinone on Bcl-2 expression in A549 cells after silencing 4EBP1 expression |
细胞凋亡检测结果显示:对照组中隐丹参酮显著地促进了A549细胞的凋亡,(4.68±0.77)% vs.(31.1±4.1)%,P=0.0009,但敲低4EBP1的表达显著抑制了隐丹参酮的促凋亡作用,(31.1±4.1)% vs.(8.85±1.2)%,P=0.0018,见图 5。
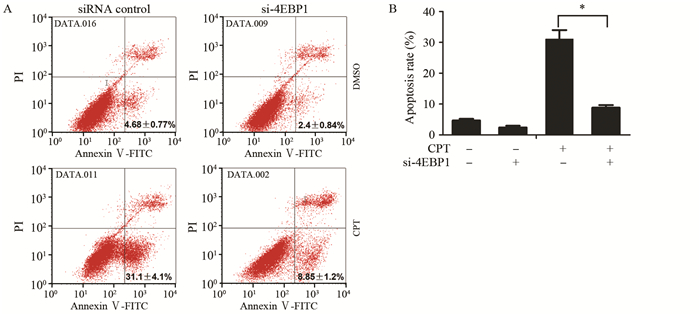
|
| 图 5 敲低4EBP1表达后隐丹参酮对A549细胞凋亡的影响(x±s, n=3) Figure 5 Effect of Cryptotanshinone on apoptosis of A549 cells after silencing 4EBP1 expression (x±s, n=3) |
CCK8检测结果显示:隐丹参酮显著地抑制了A549细胞的存活,(1±0.09)vs.(0.43±0.05),P=0.0012,但敲低4EBP1的表达拮抗了隐丹参酮的抑存活作用,(0.43±0.05)vs.(0.87±0.06),P=0.0011,见图 6。

|
| 图 6 敲低4EBP1表达后隐丹参酮对A549细胞存活的影响(x±s, n=3) Figure 6 Effect of Cryptotanshinone on survival of A549 cells after silencing 4EBP1 expression (x±s, n=3) |
细胞凋亡受到抑制将导致肿瘤细胞的恶性生长,肿瘤细胞中最重要的抗凋亡蛋白之一Bcl-2,它通过抑制促凋亡蛋白Caspase蛋白酶的活性抑制细胞的凋亡[14]。Bcl-2蛋白在多种肿瘤组织中过表达使其成为一个重要的抗肿瘤靶点[15]。研究发现Bcl-2蛋白的翻译受帽子依赖翻译的调控,而帽子依赖的翻译受mTOR信号通路调控[16],因此可以通过靶向mTOR信号通路抑制eIF4F蛋白复合物的生成从而抑制Bcl-2蛋白的表达进而促进肿瘤细胞的凋亡。
隐丹参酮是从中药丹参中分离得到的重要成分,在多种肿瘤细胞中显示了良好的抗肿瘤效果。最近研究发现隐丹参酮能够促进肺癌细胞的凋亡,但其作用机制仍不明确。之前有研究发现隐丹参酮通过抑制人骨髓横纹肌肉癌细胞和前列腺癌细胞中mTOR信号通路抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖[17],因此我们推测隐丹参酮可能通过抑制mTOR信号通路促进肺癌细胞的凋亡。为验证这一推测,我们首先检测了隐丹参酮对mTOR及下游底物4EBP1磷酸化的影响,发现隐丹参酮能够以剂量依赖方式抑制A549细胞中mTOR及4EBP1的磷酸化。由于eIF4F蛋白复合物的生成受4EBP1磷酸化的调控,因此随后检测了隐丹参酮对eIF4F蛋白复合物生成的影响,发现隐丹参酮以剂量依赖方式抑制A549细胞中eIF4F蛋白复合物的生成。由于抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2的翻译起始受帽子依赖翻译的调控,这提示隐丹参酮可能通过抑制Bcl-2蛋白的表达促进肺癌细胞的凋亡。为了验证这一推测,我们通过敲低4EBP1的表达解除了隐丹参酮对A549细胞中帽子依赖翻译的抑制作用后进行了Bcl-2蛋白表达、细胞凋亡和细胞存活相关分析,结果发现解除隐丹参酮对帽子依赖翻译的抑制作用后,隐丹参酮对Bcl-2蛋白表达和细胞存活的抑制作用显著减弱,而对细胞凋亡的促进作用被显著抑制,说明隐丹参酮通过抑制mTOR信号通路从而抑制帽子依赖的翻译,进而促进肺癌细胞的凋亡。至于隐丹参酮在肺癌细胞中如何调控mTOR激酶的活性目前还不清楚,研究表明隐丹参酮在肝癌细胞中能够激活AMPK激酶[18],而AMPK激酶能够磷酸化TSC2抑制抑制mTOR激酶的活性,隐丹参酮是否通过激活AMPK抑制肺癌细胞中mTOR激酶的活性是我们将来的研究方向。
总之,本研究发现隐丹参酮通过抑制帽子依赖的翻译进而促进肺癌细胞的凋亡,提示将来可以使用隐丹参酮治疗mTOR激酶过高或eIF4E过表达的肺癌患者。
| [1] | Spilka R, Ernst C, Mehta AK, et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factors in cancer development and progression[J]. Cancer Lett, 2013, 340 (1) : 9–21. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.06.019 |
| [2] | Pelletier J, Graff J, Ruggero D, et al. Targeting the eIF4F translation initiation complex: a critical nexus for cancer development[J]. Cancer Res, 2015, 75 (2) : 250–63. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2789 |
| [3] | Loreni F, Mancino M, Biffo S. Translation factors and ribosomal proteins control tumor onset and progression: how?[J]. Oncogene, 2014, 33 (17) : 2145–56. DOI:10.1038/onc.2013.153 |
| [4] | Fumarola C, Bonelli MA, Petronini PG, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in non small cell lung cancer[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2014, 90 (3) : 197–207. DOI:10.1016/j.bcp.2014.05.011 |
| [5] | Li BD, Liu L, Dawson M, et al. Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) in breast carcinoma[J]. Cancer, 1997, 79 (12) : 2385–90. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0142 |
| [6] | Chen X, Guo J, Bao J, et al. The anticancer properties of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge (Danshen): a systematic review[J]. Med Res Rev, 2014, 34 (4) : 768–94. DOI:10.1002/med.2014.34.issue-4 |
| [7] | Su CY, Ming QL, Rahman K, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza: Traditional medicinal uses, chemistry, and pharmacology[J]. Chin J Nat Med, 2015, 13 (3) : 163–82. |
| [8] | Chen L, Zheng SZ, Sun ZG, et al. Cryptotanshinone has diverse effects on cell cycle events in melanoma cell lines with different metastatic capacity[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2011, 68 (1) : 17–27. DOI:10.1007/s00280-010-1440-8 |
| [9] | Li S, Wang H, Hong L, et al. Cryptotanshinone inhibits breast cancer cell growth by suppressing estrogen receptor signaling[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2015, 16 (1) : 176–84. DOI:10.4161/15384047.2014.962960 |
| [10] | Park IJ, Kim MJ, Park OJ, et al. Cryptotanshinone induces ER stress-mediated apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF7 cells[J]. Apoptosis, 2012, 17 (3) : 248–57. DOI:10.1007/s10495-011-0680-3 |
| [11] | Xu D, Lin TH, Li S, et al. Cryptotanshinone suppresses androgen receptor-mediated growth in androgen dependent and castration resistant prostate cancer cells[J]. Cancer Lett, 2012, 316 (1) : 11–22. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.10.006 |
| [12] | Lu L, Li C, Li D, et al. Cryptotanshinone inhibits human glioma cell proliferation by suppressing STAT3 signaling[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2013, 381 (1-2) : 273–82. DOI:10.1007/s11010-013-1711-x |
| [13] | Chen L, Wang HJ, Xie W, et al. Cryptotanshinone inhibits lung tumorigenesis and induces apoptosis in cancer cells in vitro and in vivo[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2014, 9 (6) : 2447–52. |
| [14] | Kelly PN, Strasser A. The role of Bcl-2 and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer therapy[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2011, 18 (9) : 1414–24. DOI:10.1038/cdd.2011.17 |
| [15] | Juin P, Geneste O, Gautier F, et al. Decoding and unlocking the BCL-2 dependency of cancer cells[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2013, 13 (7) : 455–65. DOI:10.1038/nrc3538 |
| [16] | Kong J, Lasko P. Translational control in cellular and developmental processes[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2012, 13 (6) : 383–94. |
| [17] | Chen W, Luo Y, Liu L, et al. Cryptotanshinone Inhibits Cancer Cell Proliferation by Suppressing Mammalian Target of Rapamycin–Mediated Cyclin D1 Expression and Rb Phosphorylation[J]. Cancer Prev Res (Phila), 2010, 3 (8) : 1015–25. DOI:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0020 |
| [18] | Park IJ, Yang WK, Nam SH, et al. Cryptotanshinone induces G1 cell cycle arrest and autophagic cell death by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase signal pathway in HepG2 hepatoma[J]. Apoptosis, 2014, 19 (4) : 615–28. DOI:10.1007/s10495-013-0929-0 |
 2016, Vol. 43
2016, Vol. 43



