文章信息
- 高利娜, 王光, 袁慧雅, 刘俊亭
- GAO Lina, WANG Guang, YUAN Huiya, LIU Junting
- 5-羟基-1-甲基海因对百草枯中毒所致肺损伤保护作用的代谢组学研究
- Protective mechanism of 5-hydroxy-1-methylhydantoin against lung injury induced by paraquat poisoning
- 中国医科大学学报, 2020, 49(8): 679-684
- Journal of China Medical University, 2020, 49(8): 679-684
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2019-06-03
- 网络出版时间:2020-07-28 15:54
2. 中国医科大学 实验动物部, 沈阳 110122
2. Department of Laboratory Animal Science, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, China
5-羟基-1-甲基海因(5-hydroxy-1-methylhydantoin,HMH)是内源性的抗氧化剂[1-2],能够清除羟基自由基,抑制慢性肾脏疾病的进展,对高糖和缓激肽刺激的血管提供保护,改善血管损伤和重构[3-5]。百草枯(paraquat,PQ)是广泛应用的非选择性广谱除草剂,具有极强的毒性,口服中毒致死率为60%~80%[6-7]。PQ的中毒机制不清,多认为其肺损伤机制主要是线粒体功能障碍及氧自由基损伤[8]。前期研究[9-10]发现,HMH可通过其抗氧化特性保护PQ所致肾损伤。PQ中毒的靶器官是肺脏,中毒后可出现呼吸窘迫,中毒者多死于急性肺损伤及中毒后进行性肺纤维化。本研究拟通过检测超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)活性、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量、血红素氧合酶1(heme oxygenase-1,HO-1)及代谢产物,探讨HMH对PQ中毒模型小鼠肺组织的保护作用。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料 1.1.1 主要试剂HMH(上海一研生物技术有限公司),PQ(麦克林上海生物有限公司),SOD活性检测试剂盒(碧云天生物试剂有限公司),MDA检测试剂盒(贝博生物试剂有限公司),山羊抗小鼠IgG、山羊抗兔IgG、小鼠抗β-actin单克隆抗体(中杉金桥生物科技公司),ECL发光液、BCA蛋白定量试剂盒、HO-1兔多克隆抗体(武汉三鹰生物技术有限公司)。
1.1.2 实验动物分组及模型制备SPF级4周龄雄性昆明小鼠30只,体质量(30±2)g,购自辽宁长生生物技术股份有限公司,动物合格证号SYXK(辽)2018-0008。采用随机数字表法将小鼠分为生理盐水(NS)组、PQ组、HMH组,每组10只。采用PQ一次性灌胃(20 mg/kg)制备PQ中毒动物模型;NS组灌胃等量生理盐水;HMH组于造模后每天同一时间腹腔注射HMH(100 mg/kg),连续5 d。于第6天处死全部小鼠,留取肺组织备检。本研究中动物处置符合动物伦理学标准,获得中国医科大学实验动物福利与伦理委员会审批(审批号2018072)。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 肺组织形态学观察4%多聚甲醛固定肺组织48 h,脱水、浸蜡、包埋、切片,行HE染色,光镜下观察肺组织形态学改变。
1.2.2 肺组织MDA含量及SOD活性测定冰浴状态下剖取肺组织,捣碎匀浆,按照试剂盒说明书操作检测肺组织中MDA含量及SOD活性。
1.2.3 Western blotting检测肺组织中HO-1蛋白表达提取肺组织胞质蛋白20 μg,煮沸5 min变性,行聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳,转至PVDF膜,用TBST洗涤3次,5%脱脂牛奶室温封闭2 h;加入一抗(1:1 000),4 ℃摇床过夜,洗涤3次,加入二抗(1:3 000)室温孵育2 h,洗涤3次后,采用化学发光试剂检测,图像分析系统定量分析,以目的蛋白与内参β-actin的灰度比值作为目的蛋白的相对表达量。
1.2.4 液相色谱质谱联用检测肺组织代谢产物取0.1 mg肺组织(液氮研磨)置于EP管中,加入80%甲醇水溶液400 μL(4倍体积甲醇),涡旋震荡,置-20 ℃静置60 min,14 000 g、4 ℃离心20 min,取上清液置于1.5 mL离心管中,真空冷冻干燥,将残留物溶于100 μL复溶剂,涡旋振荡,14 000 g、4 ℃离心15 min,取上清液进行LC-MS分析。色谱条件:色谱柱Accucore HILIC column,柱温40 ℃,流速0.3 mL/min。正模式:流动相A(0.1%甲酸,95%乙腈,10 mmol/L醋酸铵),流动相B(0.1%甲酸,50%乙腈,10 mmol/L醋酸铵)。负模式:流动相A(95%乙腈,10 mmol/L醋酸铵,pH9),流动相B(50%乙腈,10 mmol/L醋酸铵,pH9)。色谱梯度洗脱程序:0~1 min,A%:B%=98:2;17~17.5 min,A%:B%=50:50;18~20 min,A%:B%=98:2。质谱条件:扫描范围选择m/z 100~1 500;ESI源设置为喷雾电压3.2 kV;鞘气流速35 arb;尾气流速10 arb;毛细管温度320 ℃。正负模式下扫描。MS/MS扫描为数据依赖性全扫描。
1.3 统计学分析炎性细胞因子的表达水平以x±s表示,组间比较采用Student’s t检验。采用主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)观察各组代谢产物的整体分布状况。采用多维分析方法偏最小二乘法-判别分析(partial least squares discriminant analysis,PLS-DA)法评价模型的准确性。以重要性投影(variable importance in the projection,VIP)值﹥1筛选差异代谢物。采用SPSS 20.0软件进行统计学分析,正态分布的计量资料以x±s表示,总体比较采用方差分析,组间比较采用Student’s t检验。以双侧P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。对每个代谢物差异倍数以2为底取对数,将P值以10为底取对数的绝对值,制火山图。
2 结果 2.1 各组肺组织病理改变光镜下可见,NS组肺泡结构清晰,肺泡壁薄,肺血管规则,无明显炎症细胞浸润(图 1A)。PQ组肺泡结构紊乱,肺间质明显增加,肺泡内可见水肿液,肺血管内皮肿胀、出血,可见炎症细胞浸润,部分肺泡腔形成透明膜(图 1B);HMH组肺泡水肿及炎症细胞浸润明显减轻,少量炎性渗出及出血(图 1C)。
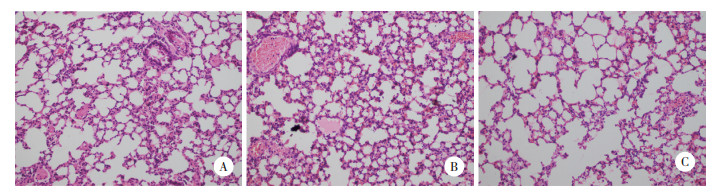
|
| 图 1 光镜下观察各组大鼠肺组织病理改变HE ×200 Fig.1 Pathological changes of lung tissues in each group were observed under light microscope HE ×200 |
2.2 各组肺组织SOD活性及MDA含量
与NS组比较,PQ组和HMH组肺组织MDA含量均显著升高(均P < 0.001),SOD活性均显著下降(均P < 0.001);且HMH组MDA含量低于PQ组,SOD活性高于PQ组,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.001)。见表 1。
| Group | n | SOD(U/mg prot) | MDA(μmol/mg prot) | HO-1/β-actin |
| NS | 10 | 272.8±2.54 | 0.13±0.05 | 0.61±0.07 |
| HMH | 10 | 182.5±5.651), 2) | 0.29±0.101), 2) | 1.19±0.151), 2) |
| PQ | 10 | 172.2±2.541) | 0.54±0.061) | 1.55±0.261) |
| 1)P < 0.001 vs NS group;2)P < 0.001 vs PQ group. SOD,superoxide dismutase;MDA,malondialdehyde;HO-1,heme-oxygenase-1. | ||||
2.3 各组肺组织HO-1蛋白表达变化
与NS组比较,PQ组和HMH组肺组织HO-1表达水平均增高,且PQ组表达水平高于HMH组,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.001)。见图 2。
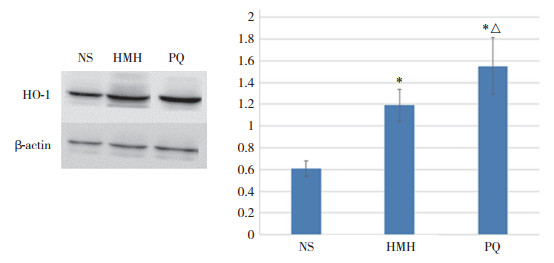
|
| *P < 0.001 vs NS group; △P < 0.001 vs HMH group. 图 2 Western blotting检测各组小鼠肺组织HO-1蛋白表达 Fig.2 HO-1 protein expression in lung tissues of mice in each group was detected by Western blotting |
2.4 代谢组学分析结果 2.4.1 差异代谢产物火山图
在质谱仪的正负离子模式下观察代谢产物的变化情况,如图 3所示,在质谱仪的正模式下,筛选出87个具有显著性差异的代谢物;在质谱仪的负离子模式下,筛选出59个显著性差异代谢物(P < 0.05,VIP > 1)。
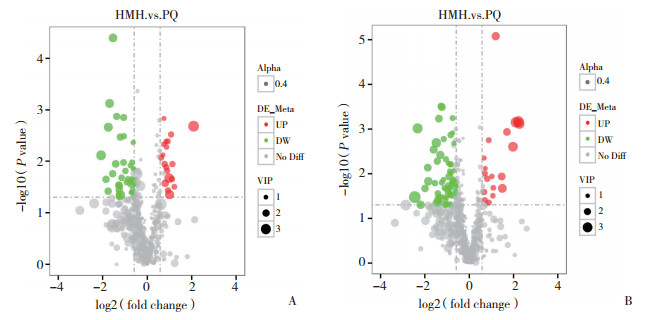
|
| A, in the negative ion mode; B, in the positive ion mode. Red represents up-regulation, green represents down-regulation, gray represents no change, and VIP represents the variable importance in the projection of the substance in the opls-da model. 图 3 差异代谢物火山图 Fig.3 The volcano map of different metabolites |
2.4.2 PCA和PLS-DA
为了得到有意义的统计结果,进行了PCA及PLS-PCA。结果如图 4、5所示,HMH组和PQ组均在95%置信区间里得到很好的分离。

|
| A, PCA was obtained in negative ion mode; B, PCA was obtained in positive mode. In the figure, the abscissa t[1] and the ordinate t[2] represent the scores of the principal components ranked first and second, respectively. The blue dots represent the samples of the PQ group, and the red dots represent the samples of the HMH group. 图 4 主成分分析图 Fig.4 Principal component analysis diagram |

|
| A, in the negative ion mode; B, in the positive ion mode. The abscissa is the score of the sample in the first principal component; the ordinate is the score of the sample on the second principal component. 图 5 偏最小二乘法-判别分析图 Fig.5 Partial least squares-discriminant analysis diagram |
2.4.3 差异代谢产物
如表 2所示,HMH组和PQ组间的差异代谢产物代谢通路主要集中于柠檬酸循环、丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢、牛磺酸和亚牛磺酸代谢、微生物代谢、脂肪细胞脂解调控、嘌呤嘧啶代谢。
| Metabolites | VIP | P | Metabolic pathways | Trend |
| N-acetyl-L-aspartic acid | 1.770 | 0.049 8 | Alanine,aspartate and glutamate metabolism | ↑ |
| L-glutamic acid | 1.008 | 0.007 5 | Alanine,aspartate and glutamate metabolism;arginine biosynthesis;Histidine metabolism | ↑ |
| L-aspartic acid | 1.058 | 0.004 7 | Alanine,aspartate and glutamate metabolism;arginine biosynthesis; Histidine metabolism | ↑ |
| Mesaconic acid | 1.619 | 0.011 3 | Pyrimidine metabolism;C5-branched dibasic acid metabolism | ↑ |
| Adenosine 5’-monophosphate | 2.005 | 0.026 7 | Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes;pyrimidine metabolism | ↑ |
| Corticosterone | 1.249 | 0.024 1 | Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes;aldosterone synthesis and secretion | ↓ |
| Methylmalonic acid | 1.032 | 0.001 5 | Pyrimidine metabolism;valine,leucine and isoleucine degradation | ↑ |
| Cytidine | 1.535 | 0.036 8 | Pyrimidine metabolism | ↑ |
| Prostaglandin G2 | 1.500 | 0.003 3 | Platelet activation | ↓ |
| 4-pyridoxic acid | 1.914 | 0.036 1 | Vitamin B6 metabolism | ↓ |
| Citric acid | 1.300 | 0.022 2 | TCA cycle;alanine,aspartate and glutamate metabolism | ↓ |
| Xanthine | 1.682 | 0.006 2 | Biosynthesis of alkaloids derived from histidine and purine;purine metabolism | ↓ |
| Thiobenzamide S,S-dioxide | 2.106 | 0.001 7 | Microbial metabolism in diverse environments;aminobenzoate degradation | ↑ |
| Phosphonoacetic acid | 1.249 | 0.011 5 | Microbial metabolism in diverse environments;phosphonate and phosphinate metabolism | ↑ |
| Hypotaurine | 2.518 | 0.021 4 | Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | ↑ |
3 讨论
肺脏是PQ中毒主要的靶器官,经肺脏摄取PQ后发生氧化还原反应,干扰线粒体电子传递,产生大量氧自由基,诱发脂质过氧化损伤[9]。PQ进入体内后以原型形式经肾排泄,在肾脏浓度最高,导致肾脏功能受损,使PQ不能被正常排泄,在体内进一步蓄积,从而累及肝、心、肺等其他器官,导致多器官功能衰竭[11-12]。
肌酐是肌酸以恒定速率产生的降解产物,在肾功能受损时,肌酐大量蓄积后代谢产生HMH。HMH是一种抗氧化剂,能消除羟基自由基[1-2]。本研究发现,PQ中毒模型小鼠肺组织抗氧化应激指标MDA含量显著升高,而SOD活性显著下降。与PQ组相比,HMH组MDA含量显著降低,SOD活性显著升高,提示HMH对PQ中毒所致肺损伤有保护作用。
HO-1是一种应激蛋白和内源性保护因子,是细胞对抗氧化应激反应的重要组成部分,在抗氧化应激、抗炎等方面起着重要作用[13-14]。研究[13]发现,PQ中毒小鼠肺组织中HO-1蛋白表达升高。邱俏檬等[15]发现,血必净注射液治疗可提高硫化氢中毒大鼠肺组织HO-1蛋白活性,减轻肺损伤。本研究结果显示,HO-1在PQ中毒小鼠肺组织中表达增加,而HMH组HO-1水平较PQ组显著增高。因此,推测HMH通过激活HO-1蛋白表达发挥抗氧化应激作用。
天冬氨酸普遍存在于生物合成作用中,是生物体内赖氨酸、苏氨酸、异亮氨酸、蛋氨酸等氨基酸及嘌呤、嘧啶碱基的合成前体。研究[16]显示,氧化应激反应使N-乙酰天冬氨酸浓度降低。HMH组N-乙酰-L-天冬氨酸水平和谷氨酸含量较PQ组增高,猜测谷氨酸可能改善PQ中毒所致氧化损伤。与PQ组相比,HMH组嘧啶代谢相关产物增加,黄嘌呤含量降低,提示HMH能调节PQ导致的嘧啶嘌呤代谢紊乱;研究[17]显示,5’-磷酸腺苷诱导低温发挥抗炎功能,HMH组5’-磷酸腺苷水平升高,推测HMH能抑制炎症的发生发展。前列腺素是二十碳不饱和脂肪酸花生四烯酸经酶促代谢产生的一类脂质介质,HMH组的前列腺素G水平较PQ组下降,提示中毒模型小鼠肺组织炎症减轻。吡哆酸是维生素B6的代谢产物,维生素B6是抗氧化物质[18],HMH组吡哆酸低于PQ组,推测维生素B6与过氧化物发生反应,从而防护PQ造成的氧化损伤。亚牛磺酸在体内可与过氧化物反应生成牛磺酸,次牛磺酸是很好的抗氧化物质[19-20]。HMH组亚牛磺酸含量高于PQ组,猜测HMH能防护PQ引发的氧化自由基损伤。皮质甾酮参与细胞脂质氧化代谢和醛固酮合成与分泌,HMH组皮质甾酮含量下降,说明脂质过氧化水平减弱,醛固酮水平降低,这与研究[5]报道的HMH能够平缓血管平滑肌作用一致。硫代苯甲酰胺二硫化物是氨基苯甲酸的降解产物,与磷酸乙酸共同参与微生物代谢,故推测HMH组可能通过影响微生物代谢,从而对机体代谢产生影响,改善PQ导致的脂质过氧化反应。
总之,HMH能显著降低PQ中毒模型小鼠肺组织MDA水平,增加SOD活性及HO-1蛋白表达,纠正PQ导致的TCA循环、嘧啶嘌呤类物质代谢、氨基酸代谢紊乱和脂质过氧化损伤,减轻PQ所致炎症反应。因此,HMH可作为防护PQ中毒损伤的替代治疗药物。
| [1] |
IENAGA K, YOKOZAWA T. Creatinine and HMH (5-hydroxy-1-methylhydantoin, NZ-419) as intrinsic hydroxyl radical scavengers[J]. Drug Discov Ther, 2011, 5(4): 162-175. DOI:10.5582/ddt.2011.v5.4.162 |
| [2] |
HASEGAWA G, NAKANO K, IENAGA K. Serum accumulation of a creatinine oxidative metabolite (NZ-419:5-hydroxy-1-methylhydatoin) as an intrinsic antioxidant in diabetic patients with or without chronic kidney disease[J]. Clin Nephrol, 2011, 76(4): 284-289. DOI:10.5414/CN107025 |
| [3] |
IENAGA K, YOKOZAWA T. Treatment with NZ-419(5-hydroxy-1-methylimidazoline-2, 4-dione), a novel intrinsic antioxidant, against the progression of chronic kidney disease at stages 3 and 4 in rats[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2010, 33(5): 809-815. DOI:10.1248/bpb.33.809 |
| [4] |
IENAGA K, MIKAMI H, YOKOZAWA T. First indications demonstrating the preventive effects of NZ-419, a novel intrinsic antioxidant, on the initiation and/or progression of chronic renal failure in rats[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2009, 32(7): 1204-1208. DOI:10.1248/bpb.32.1204 |
| [5] |
IENAGA K, SOHN M, NAIKI M, et al. Creatinine metabolite, HMH (5-hydroxy-1-methylhydantoin; NZ-419), modulates bradykinin-induced changes in vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 2014, 34(3): 195-200. DOI:10.3109/10799893.2013.876039 |
| [6] |
HANTSON P, WEYNAND B, DOYLE I, et al. Pneumoproteins as markers of paraquat lung injury:a clinical case[J]. J Forensic Leg Med, 2008, 15(1): 48-52. DOI:10.1016/j.jcfm.2006.09.003 |
| [7] |
曹钰, 董玉龙, 姚尧, 等. 急性百草枯中毒所致急性肺损伤机制研究[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2005, 4(4): 303-305, 329. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-6205.2005.04.018 |
| [8] |
张朝辉, 廖海燕, 雷超. 百草枯中毒的发病机制及救治[J]. 中国工业医学杂志, 2018, 31(2): 96-98. DOI:10.13631/j.cnki.zggyyx.2018.02.005 |
| [9] |
高利娜, 袁慧雅, 曹志鹏, 等. 5-羟基-1-甲基海因对百草枯中毒小鼠肾损伤的防护作用研究[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2018, 30(12): 1184-1189. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.12.016 |
| [10] |
高利娜, 杨爽, 刘俊亭, 等. 5-羟基-1-甲基海因对百草枯所致大鼠肾毒性防护作用的实验研究[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2015, 27(4): 246-249. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.04.004 |
| [11] |
才权, 刘志. 急性百草枯中毒早期死亡相关因素分析[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2014, 26(6): 379-382. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.06.003 |
| [12] |
张随玉. 阿魏酸钠和思密达联合大黄对急性百草枯中毒患者器官的保护作用[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2012, 19(4): 238-240. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-9691.2012.04.015 |
| [13] |
刘刚, 宋冬梅, 江宇, 等. 血红素氧合酶-1在急性百草枯中毒小鼠肺组织中的表达及意义[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2015, 27(4): 280-284. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.04.011 |
| [14] |
SO H, KIM H, KIM Y, et al. Evidence that cisplatin-induced auditory damage is attenuated by downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines via Nrf2/HO-1[J]. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol, 2008, 9(3): 290-306. DOI:10.1007/s10162-008-0126-y |
| [15] |
邱俏檬, 葛赟, 孙未, 等. 血必净注射液对硫化氢急性中毒大鼠肺组织氧化应激的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2012, 19(3): 144-148. |
| [16] |
FEIN G, DI SCLAFANI V, TANABE J, et al. Hippocampal and cortical atrophy predict dementia in subcortical ischemic vascular disease[J]. Neurology, 2000, 55(11): 1626-1635. DOI:10.1212/wnl.55.11.1626 |
| [17] |
张爱华, 王云龙, 侯琳, 等. 5'-磷酸腺苷诱导低温治疗大鼠急性胰腺炎的效果[J]. 青岛大学医学院学报, 2014, 50(5): 408-410, 413. DOI:10.13361/j.qdyxy.201405011 |
| [18] |
RASCHKE M, BOYCHEVA S, CRÈVECOEUR M, et al. Enhanced levels of vitamin B (6) increase aerial organ size and positively affect stress tolerance in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant J, 2011, 66(3): 414-432. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04499.x |
| [19] |
GROVE RQ, KARPOWICZ SJ. Reaction of hypotaurine or taurine with superoxide produces the organic peroxysulfonic acid peroxytaurine[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2017, 108: 575-584. DOI:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.04.342 |
| [20] |
NISHIMURA T, HIGUCHI K, YOSHIDA Y, et al. Hypotaurine is a substrate of GABA transporter family members GAT2/Slc6a13 and TAUT/Slc6a6[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2018, 41(10): 1523-1529. DOI:10.1248/bpb.b18-00168 |
 2020, Vol. 49
2020, Vol. 49




