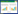文章信息
- 孙骏, 肖亮, 宋健博
- SUN Jun, XIAO Liang, SONG Jianbo
- 长链非编码RNA NEAT1对血管平滑肌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响及作用机制
- Effects of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 expression on proliferation and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells and mechanism
- 中国医科大学学报, 2020, 49(7): 601-605
- Journal of China Medical University, 2020, 49(7): 601-605
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2019-09-24
- 网络出版时间:2020-06-24 8:00
动脉粥样硬化是冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病、脑梗死和周围血管疾病的主要病因[1-2]。动脉粥样硬化的病理基础是脂质代谢紊乱,其特征是内膜和中膜的动脉病变[3]。血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cells,VSMCs)是动脉壁的重要组成部分,其功能变化可能参与动脉粥样硬化[4-5]。VSMCs的功能变化也发生在重要器官(心脏、脑和肾脏[6-7])血管中,可引起局部缺血和坏死(心肌梗死、脑梗死和肾梗死[8])。然而,目前VSMCs促成动脉粥样硬化的具体分子机制尚不完全清楚。
最近,已经充分确信了人类基因组表达的表观遗传调控,特别是长链非编码RNA(long-chain noncoding RNA,lncRNA)的功能[9]。lncRNA已确定与心血管疾病(动脉粥样硬化、心肌纤维化、脂质代谢和血管内皮异常等)有关[10]。在由氧化修饰的低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low-density lipoprotein,oxLDL)诱导的VSMCs中,尿路上皮癌相关1(urothelial carcinoma-associated 1,UCA1)lncRNA通过下调磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源蛋白(phosphatase and tensin homolog,PTEN)来上调表达并拮抗miR-26a,从而调节增殖细胞核抗原(proliferating cell nuclear antigen,PCNA)、α-SMA和SM22-α的表达[11]。在ox-LDL处理的人冠状动脉内皮细胞(human coronary artery endothelial cells,HCAECs)中,lncRNA MALAT1表达上调,敲除MALAT1可以通过结合miR -155/SOCS1轴促进ox-LDL处理的HCAECs的细胞因子释放和细胞凋亡[12]。本研究探讨lncRNA NEAT1在VSMCs增殖和凋亡中的作用及其信号传导机制。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料人主动脉VSMCs购自美国ATCC细胞库。TRIzol试剂盒购自宝生物工程有限公司。转染试剂LipofectamineTM3000购自美国Invitrogen公司,DEME培养基购自美国GE公司,RT-PCR试剂盒购自南京诺唯赞生物工程有限公司。PCR仪为ABI 7500,酶标仪为Thermo FC。β-actin及hnRNPA1抗体购自上海赛信通生物试剂有限公司。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 细胞培养与转染VSMCs用含10%胎牛血清、100 U/mL青霉素和100 mg/mL链霉素的DEME培养基于37 ℃、5%CO2培养,48 h消化传代。为了探究lncRNA NEAT1在动脉粥样硬化环境中的表达是否不同,对VSMCs给予ox-LDL梯度浓度处理,分别在细胞培养液中加入0、25、50、100、150 mg/L的ox-LDL后继续培养VSMCs 48 h。按照试剂说明书要求取处于对数生长期的VSMCs,待细胞生长密度约为70%时经LipofectamineTM3000进行转染,继续在培养箱内常规培养48 h后收集细胞用于后续实验。
1.2.2 实时定量PCR使用TRIzol试剂盒提取细胞总RNA,按照试剂盒说明书要求操作。逆转录反应为20 μL反应体系,反应条件25 ℃ 5 min,42 ℃ 30 min,85 ℃ 5 min,4 ℃保存。以18 S作为内参,实时PCR反应采用20 μL反应体系,反应条件为95 ℃ 10 min,95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 1 min,40个循环。2-△△Ct法分析数据,所有反应均设3个复孔,实验重复3次。NEAT1引物序列:F,5’-CAGTTAGTTTATCAGTTCTC CCATCCA-3’;R,5’-GTTGTTGTCGTCACCTTTCAAC TCT-3’。
1.2.3 CCK-8实验使用胰酶消化细胞,按照每孔3×103个细胞将细胞添加至96孔板,每组为5个复孔,于培养箱内继续常规培养,分别于1、2、3、4、5 d在每孔加入10 μL CCK-8溶液,置于培养箱继续培养2 h,使用酶标仪测量各孔的吸光度值。
1.2.4 细胞凋亡实验VSMCs加入处理因素48 h后进行实验。细胞用不含EDTA胰蛋白酶消化,1 500 g离心5 min后收集细胞,预冷的PBS洗涤2次,离心后收集细胞5×105,加入100 μL 1×结合缓冲液重悬细胞,加入5 μL Annexin V-FITC和5 μL PI染色液,轻轻混匀,室温避光孵育10 min,再加入400 μL 1×结合缓冲液,轻轻混匀。样品在1 h内流式细胞仪检测。
1.2.5 Western blotting检测VSMCs中hnRNPA1的表达培养或转染的细胞以RIPA缓冲液裂解,BCA法提取蛋白质定量,使用10%SDS-PAGE分离胶电泳分离蛋白质并转至PVDF膜,使用5%胎牛血清4 ℃封闭膜过夜。分别孵育hnRNPA1及β-actin一抗(1 : 1 000稀释)及二抗(1 : 5 000),最后用ECL底物试剂盒检测,实验重复3次。
1.3 统计学分析采用SPSS 17. 0统计软件进行分析,计量资料以x ±s表示,2组间比较采用t检验,3组比较先采用方差分析,然后两两比较采用LSD-t检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 lncRNA NEAT1对VSMCs增殖、凋亡的影响结果显示,使用0、25、50、100、150 mg/L ox-LDL处理后的VSMCs中NEAT1表达分别为1.09±0.08、1.38±0.07、3.13±0.07、5.11±0.10、5.42±0.11。与0、25 mg/L ox-LDL处理组比较,50、100、150 mg/L oxLDL处理组NEAT1表达明显增高,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。
VSMCs与ox-LDL(100 mg/L)一起培养0、6、12、24、48 h,NEAT1的表达分别为1.07±0.11、1.30±0.07、2.15±0.15、3.25±0.25、5.49±0.20。与一起培养0、6、12 h比较,24、48 h时NEAT1的表达增高显著(P < 0.05)。可见NEAT1的表达随着处理时间的延长而增加。
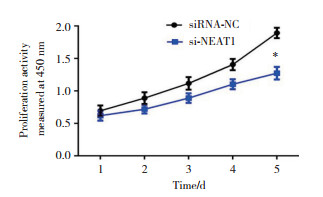
将靶向NEAT1的特殊寡核苷酸转染到VSMCs中以沉默NEAT1的表达。CCK-8增殖测定表明,与对照组(siRNA-NC组)比较,si-NEAT1组VSMCs增殖活性显著降低(P < 0.05)。表明NEAT1沉默抑制了VSMCs的增殖活性(图 1)。与对照组比较,转染siNEAT1后VSMCs表现诱导细胞早期凋亡(图 2)。
|
| *P < 0.05 vs siRNA-NC group. 图 1 NEAT1沉默对VSMCs增殖的影响 Fig.1 Effect of NEAT1 knockdown on the proliferation of VSMCs |
|
| A,NC group;B,si-NEAT1 group. 图 2 NEAT1沉默对VSMCs凋亡的影响 Fig.2 Effect of NEAT1 knockdown on the apoptosis of VSMCs |
2.2 miR-490-3p的表达
si-NEAT1转染细胞中miR-490-3p表达检测,结果显示,与si-NEAT1转染前(0.43±0.05)比较,siNEAT1转染后(1.01±0.07)miR-490-3p表达显著增高(P < 0.05)。然而NEAT1表达在miR-490-3p表达上调前后分别为0.98±0.06、0.97±0.04,差异无统计学意义(P > 0. 05),可见miR-490-3p表达上调并不影响NEAT1表达,因此推断miR-490-3p可能是NEAT1的抑制剂靶点。
2.3 starBase V3.0软件预测NEAT1互补结合的下游miRNA及基因结果显示,NEAT1可与miR-490-3p互补结合;miR-490-3p可与Hnrnp A1 mRNA互补结合,见图 3。

|
| 图 3 生物信息学软件预测NEAT1互补结合情况 Fig.3 Bioinformatics software predicts the sequences complementary to that of NEAT1 |
2.4 Western blotting检测VSMCs中hnRNPA1表达
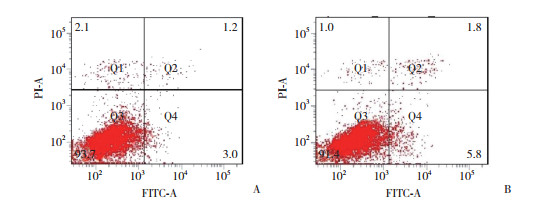
结果显示,与si-NC组(1.37±0.04)比较,si-NEAT1转染组(1.11±0.07)hnRNPA1表达显著降低(P < 0.05)。与NC组(1.89±0.07)比较,miR-490-3p过表达组(1.18±0.06)hnRNPA1表达显著降低(P < 0.05),见图 4。表明NEAT1/miR-490-3p/hnRNPA1信号通路在VSMCs的增殖和凋亡中具有重要作用。
|
| 1,si-NC group;2,si-NEAT1 group;3,NC group;4,miR-490-3p group. 图 4 si-NEAT1转染及miR-490-3p过表达时hnRNPA1的表达情况 Fig.4 Expression of hnRNPA1 during si-NEAT1 transfection and miR-490-3p overexpression |
3 讨论
已有研究[13]表明lncRNA与血管平滑肌细胞的增殖和侵袭有关。MANG等[14]报道lncRNA NEAT1可以通过调节hnRNPA2的表达促进肝癌细胞的发生发展,且该调控与NEAT1-U2AF65蛋白复合物有关。SUN等[15]研究发现,NEAT1通过与miRNA-19a- 3p结合来上调SMYD2,从而促进心脏肥大的发生和发展。ZOU等[16]报道NEAT1可以通过刺激miR-224- 5p促进黑素瘤细胞的增殖和侵袭,这表明NEAT1/ miR-224-5p轴可以作为黑素瘤标记物。然而lncRNA NEAT1在VSMCs中的具体作用机制尚不完全清楚。
本研究结果表明lncRNA NEAT1对VSMCs具有促进增殖作用,在经ox-LDL处理过的细胞中呈高表达,NEAT1沉默能够抑制VSMCs的增殖。lncRNA能够调控miRNA的表达和活性,LI等[17]发现lncRNA NEAT1通过海绵效应吸附miR-23c来促进小鼠肾小球系膜细胞的增殖、纤维化和上皮-间质转化,同时阻止小鼠肾小球系膜细胞凋亡,进而促进糖尿病性肾病的发生和发展,表明NEAT1可作为糖尿病性肾病治疗的有效标志物和潜在治疗靶点。WEI等[18]证明了lncRNA NEAT1通过海绵效应吸附miR-144- 3p来调节NF- κB信号传导途径,促进败血症诱导的心肌损伤进展,揭示了NEAT1对脓毒症和脓毒症所致心肌损伤的作用。lncRNA和miRNA在VSMCs中的研究目前鲜有报道,还需要大量实验予以证实。本研究证实了miR-490-3p为NEAT1的抑制靶标,下调NEAT1的表达能够增加miR-490-3p表达,但是miR-490-3p表达增高并不能影响NEAT1表达,因此认为miR-490-3p是NEAT1的直接靶标。
hnRNPA1属于保守的不均一性核糖核蛋白家族。研究[19]显示hnRNPA1主要有影响转录、mRNA剪切、核穿梭、miRNA生物合成4种功能。已有研究[20]表明hnRNPA1改变会影响转录后调控的不同RNA代谢过程,这种改变也参与癌症、神经降解性疾病和阿尔茨海默病。WEN等[21]发现lncRNA ANCR通过抑制hnRNPA1降解和海绵吸附miR-140-3p来上调hnRNPA1的表达,进而促进肝癌细胞转移,表明hnRNPA1可以促进肝癌细胞的增殖和迁移。NISHIKAWA等[22]研究表明hnRNPA1和hnRNPU调节TRA2B转录和外显子2的可变剪接并且在结肠癌细胞的异常增殖中起关键作用。本研究si-NEAT1转染VSMCs中hnRNPA1表达显著降低,同时在miR- 490-3p过表达的VSMCs中hnRNPA1表达显著降低。表明过表达lncRNA NEAT1通过使miR-490-3p/ hnRNPA1轴海绵化而促进VSMCs增殖。
综上所述,miR-490-3p是NEAT1的抑制靶标,lncRNA NEAT1通过激活miR-490-3p/ hnRNPA1轴促进VSMCs增殖、减少VSMCs早期凋亡。因此认为NEAT1有望成为动脉粥样硬化基因治疗的新靶标。
| [1] |
CHISTIAKOV DA, GRECHKO AV, MYASOEDOVA VA, et al. The role of monocytosis and neutrophilia in atherosclerosis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(3): 1366-1382. DOI:10.1111/jcmm.13462 |
| [2] |
GUO MQ, GUO GL, XIAO J, et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 stereoisomers differentially inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in diabetic atherosclerosis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2018, 22(6): 3202-3214. DOI:10.1111/jcmm.13601 |
| [3] |
CUI YM, LI CH, ZENG C, et al. Tongmai Yangxin pills antioxidative stress alleviates cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity:network pharmacology analysis and experimental evidence[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2018, 108: 1081-1089. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.095 |
| [4] |
LIU T, XU J, GUO JL, et al. YAP1 up-regulation inhibits apoptosis of aortic dissection vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2017, 21(20): 4632-4639. |
| [5] |
REN XS, TONG Y, LING L, et al. NLRP3 gene deletion attenuates angiotensin Ⅱ-induced phenotypic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells and vascular remodeling[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2017, 44(6): 2269-2280. DOI:10.1159/000486061 |
| [6] |
CUI YM, QI X, HUANG A, et al. Differential and predictive value of galectin-3 and soluble suppression of tumorigenicity-2(sST2)in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24: 5139-5146. DOI:10.12659/MSM.908840 |
| [7] |
LI J, CUI YM, HUANG A, et al. Additional diagnostic value of growth differentiation factor-15(GDF-15)to N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide(NT-proBNP) in patients with different stages of heart failure[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24: 4992-4999. DOI:10.12659/MSM.910671 |
| [8] |
ZHAO J, NISHIMURA Y, KIMURA A, et al. Chemokines protect vascular smooth muscle cells from cell death induced by cyclic mechanical stretch[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 16128. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-15867-8 |
| [9] |
HAN Z, SHI LY. Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 modulates methotrexate resistance in osteosarcoma via miR-200c/ABCB1 axis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 495(1): 947-953. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.121 |
| [10] |
ZENG YZ, REN K, ZHU X, et al. Long noncoding RNAs:advances in lipid metabolism[J]. Adv Clin Chem, 2018, 87: 1-36. DOI:10.1016/bs.acc.2018.07.001 |
| [11] |
TIAN SG, YUAN Y, LI Z, et al. LncRNA UCA1 sponges miR-26a to regulate the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Gene, 2018, 673: 159-166. DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.031 |
| [12] |
LI S, SUN Y, ZHONG L, et al. The suppression of ox-LDL-induced inflammatory cytokine release and apoptosis of HCAECs by long non-coding RNA-MALAT1 via regulating microRNA-155/SOCS1 pathway[J]. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2018, 28(11): 1175-1187. DOI:10.1016/j.numecd.2018.06.017 |
| [13] |
WU X, ZHENG X, CHENG J, et al. LncRNA TUG1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis by regulating miR-148b/IGF2 axis in oxLDL-stimulated VSMC and HUVEC[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 15: 243. DOI:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117287 |
| [14] |
MANG YY, LI L, RAN JH, et al. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion by regulating hnRNP A2 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2017, 10: 1003-1016. DOI:10.2147/OTT.S116319 |
| [15] |
SUN XL, LV JL, DOU L, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes cardiac hypertrophy through microRNA-19a-3p/SMYD2 axis[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(3): 1367-1377. DOI:10.26355/eurrev_202002_20194 |
| [16] |
ZOU JX, GE TW. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes tumor development and metastasis through targeting miR-224-5p in malignant melanoma[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(3): 1302-1308. DOI:10.26355/eurrev_202002_20187 |
| [17] |
LI N, JIA T, LI YR. LncRNA NEAT1 accelerates the occurrence and development of diabetic nephropathy by sponging miR-23c[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(3): 1325-1337. DOI:10.26355/eurrev_202002_20190 |
| [18] |
WEI JL, WU CJ, CHEN JJ, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes the progression of sepsis-induced myocardial cell injury by sponging miR-144-3p[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(2): 851-861. DOI:10.26355/eurrev_202001_20069 |
| [19] |
HE Y, SMITH R. Nuclear functions of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A/B[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2009, 66(7): 1239-1256. DOI:10.1007/s00018-008-8532-1 |
| [20] |
HAY DC, KEMP GD, DARGEMONT C, et al. Interaction between hnRNPA1 and I κ Bα is required for maximal activation of NF-κ B dependent transcription[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2001, 21(10): 3482-3490. DOI:10.1128/MCB.21.10.3482-3490.2001 |
| [21] |
WEN ZL, LIAN LY, DING H, et al. LncRNA ANCR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through upregulating hnRNPA1 expression[J]. RNA Biol, 2020, 17(3): 381-394. DOI:10.1080/15476286.2019.1708547 |
| [22] |
NISHIKAWA T, KUWANO Y, TAKAHARA Y, et al. HnRNPA1 interacts with G-quadruplex in the TRA2B promoter and stimulates its transcription in human colon cancer cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 10276. DOI:10.1038/s41598-019-46659-x |
 2020, Vol. 49
2020, Vol. 49