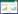文章信息
- 李岩, 张德巍, 杨大业
- LI Yan, ZHANG Dewei, YANG Daye
- 那可丁对人肺癌细胞A549生物学功能的影响
- Effect of Noscapine on the Biological Function of A549 Cells
- 中国医科大学学报, 2019, 48(1): 66-70
- Journal of China Medical University, 2019, 48(1): 66-70
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2017-11-09
- 网络出版时间:2019-01-02 09:24
肺癌是发病率和死亡率均高的恶性肿瘤,我国由于人口老龄化加剧、环境恶化以及人们不良生活习惯增加,肺癌发病率和死亡率呈明显上升趋势[1-2]。目前肺癌治疗仍然存在着治愈率低、复发转移率高等缺点,需要寻找可以延长患者生存期,同时减轻化疗药物不良反应的治疗方法。
那可丁是来自罂粟属植物鸦片中的一种异喹啉类生物碱,近几十年一直用作镇咳药,其代谢物归属、生物利用度和药物动力学都已得到了较深入的研究。近年来,那可丁及其衍生物的抗肿瘤作用得到了广泛而系统研究[3],它们具有抗肿瘤活性高、作用机制独特、不良反应小等特点。体外增殖实验[4-5]结果表明,不同肿瘤细胞株对那可丁的敏感性不同,IC50值为10~50 μmol/L,对于一些耐药肿瘤细胞也有明显的疗效。那可丁同样具有体内抗肿瘤活性,且对多种肿瘤细胞有效[6]。本研究以人肺癌细胞系A549作为研究对象,探讨那可丁对A549细胞生物学功能的影响,以期待寻找更好可以作为治疗肺癌的潜在化疗药物。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料人肺癌细胞系A549 (实验室冻存),DMEM培养基(美国Hyclone公司),胎牛血清(杭州四季青公司),那可丁(江苏豪森公司),四甲基偶氮唑蓝(北京中杉金桥公司),DMSO (美国Sigma公司),Hoechst 33258、台盼蓝(上海碧云天公司),Cyclin D1、bcl-2、MMP2和GAPDH抗体(美国Santa公司),实验所需二抗购于北京中杉金桥公司。
1.2 方法 1.2.1细胞培养:将A549细胞接种于含体积分数10%灭活胎牛血清的DMEM培养基中,置37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2培养箱中培养。
1.2.2MTT实验:将处于对数生长期的细胞消化传代,以1×104/mL浓度接种于96孔培养板中,终体积200 μL,贴壁后分别使用NaCl (对照组)及10 μmol/L与20 μmol/L那可丁分别处理细胞。处理后的细胞于0、12、24、36、48、60 h (3个副孔)分别加入5 mg/mL MTT溶液(10 μL),置37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2培养箱中培养4 h后,弃上清,每孔中加入200 μL DMSO,震荡10 min后在490 nm处记录吸光值。
1.2.3Hoechst 33258染色:将对数生长期的细胞制成1×106 /mL浓度的细胞悬液接种于6孔板中,贴壁培养24 h后,加入不同处理因素。药物作用24 h后,每孔加入100 μL Hoechst 33258孵育染色15 min,PBS洗净后,用荧光显微镜观察细胞凋亡情况。
1.2.4Transwell实验:对数生长期细胞以1×105/mL浓度接种于上室中,终体积200 μL,下室加入600 μL双无培养基,加入不同处理因素,各组均设3个副孔。24 h后取出小室,擦去上层细胞,PBS清洗后95%乙醇固定20 min,4%台盼蓝染色20 min。200倍显微镜下观察。
1.2.5Western blotting检测:不同浓度药物处理细胞24 h后,使用RIPA裂解液搜集并裂解细胞,提取蛋白,定量后取30 μg蛋白进行电泳、转膜(4 ℃,100 V,1 h)后,用5%脱脂奶粉室温封闭1 h。一抗4 ℃过夜后TBST清洗3次。二抗室温1 h后TBST清洗3次。
1.2.6实时PCR检测:trizol裂解细胞后通过氯仿抽提,异丙醇沉淀,乙醇洗涤后获取细胞RNA,反转录成cDNA,进行实时PCR反应。所用引物:Cyclin D1,正向5’-CCAACCTCCTCAACGACC-3’,反向5’-CACAGAGGGCAACGAAG-3’;BCL-2,正向5’-GGTGA ACTGGGGGAGGATTG-3’,反向5’-GGCAGGCATGT TGACTTCAC-3’;MMP2,正向5’-CGCATCTGGGGC TTTAAACAT-3’,反向5’-TCAGCACAAACAGGTTGC AG-3’;GAPDH,正向5’-GGCAAATTCAACGGCAC AGT-3’,反向5’-TAGGGCCTCTCTTGCTCAGT-3’。
1.3 统计学分析采用SPSS 17.0软件进行统计分析,组间比较采用非配对t检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 那可丁对A549细胞增殖的影响结果显示,那可丁对A549细胞作用0、12、24、36、48、60 h后可以显著抑制A549细胞增殖,与对照组比较差异有统计学意义(均P < 0.05),那可丁对细胞增殖抑制作用随着浓度增加而增加,10 μmol/L与20 μmol/L那可丁对A549细胞抑制率比较有统计学差异(P < 0.05)。见表 1。
| Group | Inhibitory rate of A549 cell proliferation | ||||
| 0 h | 12 h | 24 h | 36 h | 48 h | |
| Control | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.00±0.00 |
| 10 μmol/L nascapine | 24.71±2.191) | 32.98±1.091) | 41.82±2.381) | 53.72±1.821) | 59.98±3.461) |
| 20 μmol/L ascapine | 33.02±4.171),2) | 49.56±3.981),2) | 59.93±2.461),2) | 66.39±3.011),2) | 70.02±5.311),2) |
| 1) P < 0.05 vs control group;2) P < 0.05 vs 10 μmol/L nascapine group. | |||||
MTT实验发现那可丁可以显著抑制A549细胞增殖,本研究检测那可丁对调节细胞周期蛋白——Cyclin D1的作用,结果显示,对照组,那可丁10 μmol/L组、20 μmol/L组Cyclin D1 mRNA表达分别为1.34±0.04、0.55±0.17、0.36±0.03。不同浓度那可丁对Cyclin D1蛋白及mRNA均有一定程度抑制作用,并且随着药物浓度的升高抑制作用增强。见图 1。
|
| A,Western blotting;B,real-time PCR.1,control group;2,10 μmol/L noscapine group;3,20 μmol/L noscapine group.** P < 0.05 vs control group. 图 1 那可丁对A549细胞中Cyclin D1表达的影响 Fig.1 Cyclin D1 expression in A549 cells treated with different concentrations of noscapine |
2.2 那可丁对A549细胞凋亡的影响
通过Hoechst 33258染色检测那可丁对A549细胞凋亡的影响,结果显示,那可丁可以促进A549细胞凋亡,随着药物浓度的增加凋亡细胞明显增加。见图 2。

|
| A,control group;B,10 μmol/L noscapine group;C,20 μmol/L noscapine group. 图 2 不同浓度那可丁作用下A549细胞凋亡比较×200 Fig.2 Apoptosis of A549 cells treated with different concentrations of noscapine ×200 |
Bcl-2蛋白是调节细胞凋亡的重要蛋白,本研究检测那可丁对Bcl-2的调节作用,结果显示,对照组,那可丁10 μmol/L组、20 μmol/L组Bcl-2 mRNA表达分别为1.19±0.03、0.59±0.11、0.41±0.03。不同浓度那可丁对bcl-2 mRNA及蛋白表达均有一定程度的抑制作用,并且随着药物浓度升高抑制作用增强。见图 3。

|
| A,Western blotting;B,real-time PCR.1,control group;2,10 μmol/L noscapine group;3,20 μmol/L noscapine group.** P < 0.05 vs control group. 图 3 不同浓度那可丁作用下A549细胞中bcl-2表达比较 Fig.3 Bcl-2 expression in A549 cells treated with different concentrations of noscapine |
2.3 那可丁对A549细胞转移的影响
Transwell实验结果显示,对照组,那可丁10 μmol/L组、20 μmol/L组A549细胞转移分别为134.33±1.89、115.33±2.05、82.67±2.36。那可丁可以抑制A549细胞转移,并且随着药物浓度增加转移细胞数目减少;与对照组比较,那可丁10 μmol/L组、20 μmol/L组A549转移细胞数量差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图 4。

|
| A,transwell (×200);B,A549 cell count of migration.** P < 0.05 vs control group. 图 4 不同剂量那可丁作用下A549细胞转移比较 Fig.4 The migration of A549 cells treated with different concentrations of noscapine |
MMP2是调节细胞侵袭转移的关键性蛋白,检测那可丁对MMP2调节作用,结果发现,对照组,那可丁10 μmol/L组、20 μmol/L组A549细胞中MMP2 mRNA表达分别为1.01±0.27、0.52±0.11、0.39±0.06。不同浓度那可丁对MMP2蛋白及mRNA有一定程度抑制作用,随着药物浓度升高抑制作用增强,与对照组比较,那可丁10 μmol/L组、20 μmol/L组MMP2 mRNA表达差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图 5。
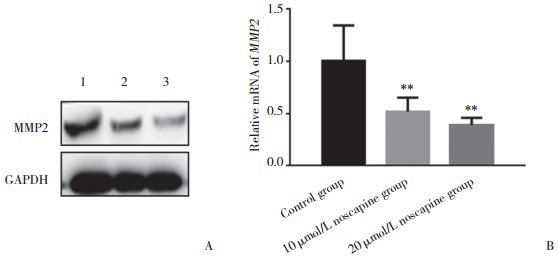
|
| A,Western blotting;B,real-time PCR.1,control group;2,10 μmol/L noscapine group;3,20 μmol/L noscapine group.** P < 0.05 vs control group. 图 5 不同浓度那可丁作用下A549细胞中MMP2表达比较 Fig.5 MMP2 expression in A549 cells treated with different concentrations of noscapine |
3 讨论
那可丁结构与秋水仙碱具有一定的相似性,在进行抗肿瘤活性筛选的过程中发现其具有一定的抗肿瘤活性,作用机制为微管蛋白抑制剂[7]。由前列腺癌研究教育基金会和Med Insight研究学院合作开展的研究[8]表明,前列腺癌动物模型中口服那可丁可以产生肿瘤抑制作用。第17届国际前列腺癌治疗进展大会上公布的一项研究[9]显示,那可丁有望成为治疗前列腺癌的有效药物。有研究[10-13]指出,那可丁通过作用于HIF-1α和EGFR等促进肠癌细胞凋亡,抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖和迁移功能。
本研究探讨了那可丁对A549细胞增殖的影响,发现那可丁对A549细胞增殖具有明显抑制作用,20 μmol/L那可丁作用于A549细胞24 h抑制率接近50%。深入研究发现那可丁可以通过抑制A549细胞中Cyclin D1表达来抑制A549细胞增殖。Cyclin D1是G1/S细胞周期相关因子,可以诱导细胞G1期向S期转化,抑制了Cyclin D1表达可以将细胞阻滞于G1期,从而抑制了肿瘤细胞增殖[14]。通过检测那可丁对A549细胞凋亡影响发现,那可丁可以促进A549细胞凋亡,这一作用可能是通过抑制bcl-2蛋白和mRNA表达来实现的。
已有研究[15]表明肺癌细胞一旦发生侵袭迁移,患者的生存期极短,因此,药物如果可以对肺癌细胞侵袭转移发挥抑制作用就能够很好抑制肺癌的进程。本研究通过Transwell实验发现那可丁以剂量依赖的方式抑制肺癌细胞A549的迁移能力。有研究[15]报道MMP2在调节细胞侵袭的功能中发挥重要作用。本研究结果表明那可丁以剂量依赖的方式影响MMP2的表达,与以往研究结果一致。
本研究认为,那可丁能够抑制A549细胞生长,其机制可能是通过抑制细胞周期蛋白Cyclin D1来抑制细胞周期的进程,同时抑制bcl-2促进细胞的凋亡。那可丁也可以通过抑制MMP2蛋白的表达来实现抑制细胞迁移的功能。本研究尚未对那可丁作用的具体信号通路途径进行深入探讨,而且缺乏体内实验的印证,将在后续实验中继续深入研究。那可丁可以通过调节多种蛋白的表达来实现抑制肺癌细胞A549生长和迁移的作用,由此推断那可丁可能成为治疗肺癌的潜在药物。
| [1] |
LEE JH, LEEM DG, CHUNG KS, et al. Panaxydol derived from Panax ginseng inhibits G1 cell cycle progression in non-small cell lung cancer via upregulation of intracellular Ca2+ levels[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2018, 41(11): 1701-1707. DOI:10.1248/bpb.b18-00447 |
| [2] |
OGATA T, KATSUI K, YOSHIO K, et al. Dose-volume parameters predict radiation pneumonitis after surgery with induction concurrent chemoradiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Acta Med Okayama, 2018, 72(5): 507-513. DOI:10.18926/AMO/56249 |
| [3] |
METHER RK, NAIK MR J, BASTIA B, et al. Comparative evaluation of anti-angiogenic effects of noscapine derivatives[J]. Bioinformation, 2018, 31(5): 236-240. DOI:10.6026/97320630014236 |
| [4] |
CRUIJSEN M, HOBO W, VAN DER VELDEN WJ, et al. Addition of 10-day noscapine to fludarabine/total body irradiation conditioning is feasible and induces tumor-associated antigen-specific T cell responses[J]. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant, 2016, 22(6): 1000-1008. DOI:10.1016/j.bbmt.2016.02.003 |
| [5] |
DODDAPANENI R, PATEL K, CHOWDHURY N, et al. Reversal of drug-resistance by noscapine chemo-sensitization in docetaxel resistant triple negative breast cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 15824. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-15531-1 |
| [6] |
TIAN X, LIU M, ZHU Q, et al. Down-regulation of liver-intestine cadherin enhances noscapine-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer cells[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2017, 17(9): 857-863. DOI:10.1080/14737140.2017.1344097 |
| [7] |
SONI N, JYOTI K, JAIN UK, et al. Noscapinoids bearing silver nanocrystals augmented drug delivery, cytotoxicity, apoptosis and cellular uptake in B16F1, mouse melanoma skin cancer cells[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 90: 906-913. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.042 |
| [8] |
GHALY PE, ABOU El-MAGD RM, CHURCHILL CD, et al. A new antiproliferative noscapine analogue:chemical synthesis and biological evaluation[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(26): 40518-40530. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.9642 |
| [9] |
SHEN W, LIANG B, YIN J, et al. Noscapine increases the sensitivity of drug-resistant ovarian cancer cell line SKOV3/DDP to cisplatin by regulating cell cycle and activating apoptotic pathways[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2015, 72(1): 203-213. DOI:10.1007/s12013-014-0438-y |
| [10] |
MAHADDALKAR T, NAIK PK, CHOUDHARY S, et al. Structural investigations into the binding mode of a novel noscapine analogue, 9-(4-vinylphenyl) noscapine, with tubulin by biochemical analyses and molecular dynamic simulations[J]. J Biomol Struct Dyn, 2017, 35(11): 2475-2484. DOI:10.1080/07391102.2016.1222969 |
| [11] |
QUISBERT-VALENZUELA EO, CALAF GM. Apoptotic effect of noscapine in breast cancer cell lines[J]. Int J Oncol, 2016, 48(6): 2666-2674. DOI:10.3892/ijo.2016.3476 |
| [12] |
DODDAPANENI R, PATEL K, CHOWDHURY N, et al. Noscapine chemosensitization enhances docetaxel anticancer activity and nanocarrier uptake in triple negative breast cancer[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2016, 346(1): 65-73. DOI:10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.05.006 |
| [13] |
XU G, NIU Z, DONG J, et al. Noscapine inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma growth through inducing apoptosis in vitro and in vivo[J]. Neoplasma, 2016, 63(5): 726-733. DOI:10.4149/neo_2016_509 |
| [14] |
WU DM, DENG SH, LIU T, et al. TGF-β-mediated exosomal lnc-MMP2-2 regulates migration and invasion of lung cancer cells to the vasculature by promoting MMP2 expression[J]. Cancer Med, 2018, 7(10): 5118-5129. DOI:10.1002/cam4.1758 |
| [15] |
CHEN Z, JI N, WANG Z, et al. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) promoted the invasion of lung cancer cells via an ARNT2/PP2A/STAT3/MMP2 pathway[J]. J Biomed Nanotechnol, 2018, 14(12): 2172-2184. DOI:10.1166/jbn.2018.2645 |
 2019, Vol. 48
2019, Vol. 48