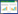文章信息
- 宫雪, 于柳, 祝兴旺, 刘嘉, 刘屹立, 王平
- GONG Xue, YU Liu, ZHU Xingwang, LIU Jia, LIU Yili, WANG Ping
- 抑制Rab11表达对人膀胱癌细胞增殖和侵袭的影响
- Effect of Low Rab11 Expression on the Proliferation and Invasion of Human Bladder Cancer Cells
- 中国医科大学学报, 2018, 47(3): 247-250, 259
- Journal of China Medical University, 2018, 47(3): 247-250, 259
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2017-07-20
- 网络出版时间:2018-03-02 17:38
膀胱癌是泌尿系统最常见的恶性肿瘤,常规行手术切除,但晚期患者手术疗效较差,放化疗等辅助治疗不敏感,患者生命受到严重威胁。因此,针对膀胱癌的靶向治疗研究具有极其重要的临床意义。Rab11是Rab小分子GTP酶家族的一个成员[1],参与再循环内体的形成,在有丝分裂纺锤体形成和定位的过程中发挥不可或缺的作用[2]。据文献[3-6]报道,Rab11与皮肤癌、乳腺癌、食管腺癌、结直肠癌等多种恶性肿瘤的发病进展有关。本课题组的前期实验通过免疫组织化学方法证实了Rab11在膀胱癌组织中过表达,并与膀胱癌细胞的侵袭深度显著相关。本研究在膀胱癌T24细胞系中转染Rab11 siRNA,抑制Rab11蛋白的表达,以探讨抑制Rab11表达对细胞增殖、细胞周期和侵袭的作用和机制,为晚期膀胱癌的靶向治疗提供依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 主要试剂及仪器人膀胱癌细胞系T24(美国ATCC公司);Rab11(美国Proteintech公司),cyclin D1、cyclin E、基质金属蛋白酶9(matrix metalloproteinase 9,MMP9)(美国Cell Signaling公司),β-actin(美国Santa Cruz公司);Rab11 ONTARGETplus siRNA,阴性对照NonTargeting siRNAa(美国Dharmacon公司);ECL试剂盒(美国Pierce公司);qRT-PCR试剂盒SYBR Green Master Mix Kit(美国Applied Biosystem公司)。发光仪器为DNR BioImaging System(以色列DNR公司),PCR仪为7500 Real-Time PCR System。
1.2 细胞培养与转染膀胱癌T24细胞系常规培养于含10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培养基,置于37℃、5% CO2饱和湿度的培养箱中,隔天换液。取对数生长期的T24细胞悬液接种于6孔板中(约1×106/孔)继续培养24 h,确保细胞密度>80%后进行转染。转染步骤及剂量参照说明书。将转染Rab11 siRNA的T24细胞作为实验组(Rab11 siRNA组),转染Control siRNA的T24细胞作为对照组(Control siRNA组)。
1.3 免疫印迹法转染48 h后,收集T24细胞,裂解提取总蛋白,用BCA法行目标蛋白定量,上样量为20 μg,电泳,转膜,孵育一抗Rab11(1:800)、cyclin D1、cyclin E、MMP9(1:1 000),β-actin(1:2 000),4 ℃过夜,二抗37 ℃孵育2 h,ECL发光。通过凝胶分析系统扫描目的条带和内参的灰度对比,严格按试剂盒说明书操作。
1.4 CCK8法取对数生长期的T24细胞,接种后转染,继续细胞培养。于检测细胞增殖率4 h前加入10 μL CCK8溶液处理细胞,通过酶标仪分析细胞增殖率变化,选用波长为490 nm。采用CCK8试剂盒,按照产品说明操作。
1.5 细胞周期检测将T24细胞接种后转染,继续培养48 h,收集细胞,用1%的多聚甲醛进行固定,用PBS缓冲液漂洗,用无RNA酶的碘化丙啶(5 mg/mL)对细胞进行染色。采用流式细胞仪,分析细胞内核DNA分布的规律,绘制直方图。
1.6 基质胶侵袭实验将Matrigel用培养液稀释,每孔20 µL Matrigel进行铺膜(24孔板)。转染48 h后,收集T24细胞,用培养液稀释制备细胞悬液(1×105/mL)。上室中每孔加入200 μL细胞悬液,下室中加入含20%胎牛血清的培养液800 μL,继续培养24 h。取出Transwell小室,PBS缓冲液冲洗,进行苏木精染色,室温干燥过夜。显微镜下对细胞进行计数,重复实验3次。
1.7 实时PCR按试剂盒步骤提取总RNA,测定浓度及纯度,使用7500 Real-Time PCR System将其逆转录为cDNA,PCR扩增过程中所用内参为β-actin。基因表达的相对量用ΔCt值代表,其中ΔCt =Ct基因-Ct内参,基因扩增倍数的估测方法采用2-ΔΔCt估测法。重复实验3次。
1.8 统计学分析统计学分析所用软件为SPSS 16,数据以x±s表示,应用t检验进行数据分析,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 免疫印迹法检测T24细胞系转染Rab11 siRNA的转染效率采用免疫印迹法检测转染效率,结果显示,Rab11 siRNA组与Control siRNA组相比,T24细胞系中Rab11表达量显著下调(图 1)。
|
| 1, control siRNA group; 2, Rab11 siRNA group. 图 1 免疫印迹法检测Rab11 siRNA的干扰效率 Fig.1 RNA interference efficiency of the Rab11 siRNA determined by performing Western blotting |
2.2 抑制Rab11表达能抑制膀胱癌细胞的增殖
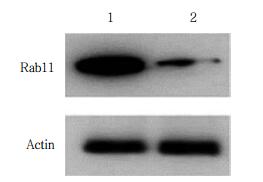
采用CCK8法分析抑制Rab11表达对细胞增殖的影响,结果表明,Rab11 siRNA组与Control siRNA组相比,第3天时膀胱癌细胞的增殖率明显降低(P < 0.05),见图 2。
|
| *P < 0.05 vs control siRNA group. 图 2 CCK8实验检测抑制Rab11表达对膀胱癌细胞增殖的影响 Fig.2 Effect of Rab11 inhibition on the proliferation of bladder cancer cells determined by performing the CCK8 assay |
2.3 抑制Rab11表达能抑制膀胱癌细胞周期进程
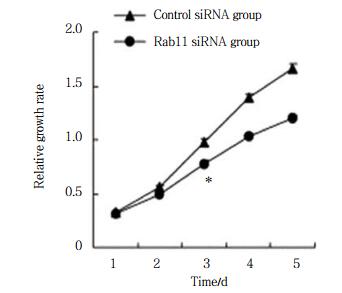
通过流式细胞术分析抑制Rab11表达对细胞周期进程的影响,结果表明,Rab11 siRNA组与Control siRNA组相比,G1期细胞数目明显上升,S期细胞数目明显下降(图 3)。
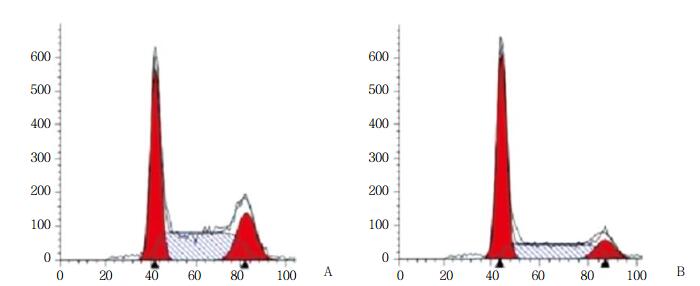
|
| A, control siRNA group; B, Rab11 siRNA group. 图 3 流式细胞术分析抑制Rab11表达对膀胱癌细胞周期进程的影响 Fig.3 Effect of Rab11 inhibition on cell cycle progression in bladder cancer cells determined by performing flow cytometry |
2.4 抑制Rab11表达能抑制膀胱癌细胞的侵袭能力
通过基质胶侵袭实验分析抑制Rab11表达对膀胱癌细胞侵袭能力的影响,结果表明,Rab11 siRNA组与Control siRNA组相比,穿过基质胶的细胞数目明显减少(分别为96±7和189±11,P < 0.05),见图 4。
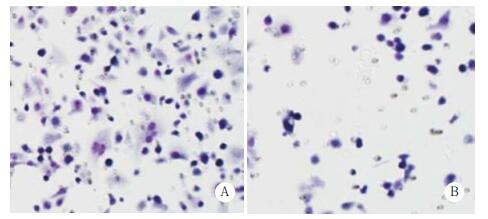
|
| A, control siRNA group; B, Rab11 siRNA group. 图 4 基质胶侵袭实验分析抑制Rab11表达对膀胱癌细胞侵袭能力的影响×200 Fig.4 Effect of Rab11 inhibition on the invasive ability of bladder cancer cells determined by performing the Matrigel invasion assay ×200 |
2.5 抑制Rab11表达显著下调细胞周期相关蛋白cyclin D1、cyclin E和侵袭相关蛋白MMP9的表达量
通过免疫印迹法和实时PCR技术分析抑制Rab11表达对T24细胞系中cyclin D1、cyclin E和MMP9表达情况的影响,结果表明,Rab11 siRNA组与Control siRNA组相比,细胞周期相关蛋白cyclin D1、cyclin E和侵袭相关蛋白MMP9的蛋白和mRNA的表达量显著降低(P < 0.05),见图 5。
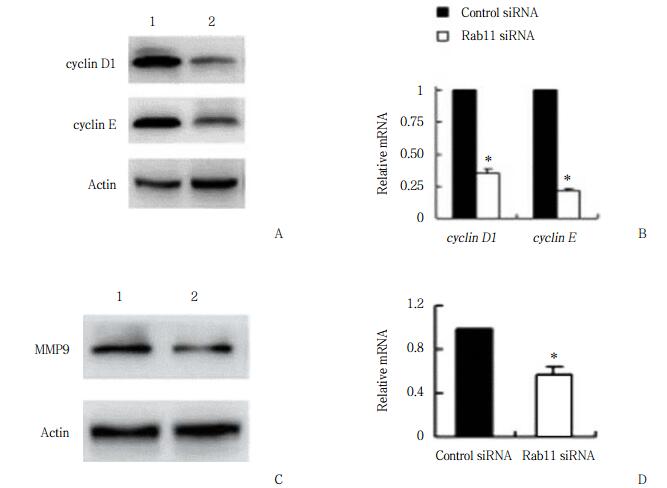
|
| A, expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E in T24 cells transfected with the Rab11 siRNA, as determined by performing Western blotting; B, expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E in T24 cells transfected with the Rab11 siRNA, as determined by performing RT-PCR; C, expression of MMP9 in T24 cells transfected with the Rab11 siRNA, as determined by performing Western blotting; D, expression of MMP9 in T24 cells transfected with the Rab11 siRNA, as determined by performing RT-PCR. 1, control siRNA group; 2, Rab11 siRNA group. * P < 0.05 vs control siRNA group. 图 5 免疫印迹法和实时PCR检测转染Rab11 siRNA的T24细胞系中cyclin D1、cyclin E和MMP9的表达情况 Fig.5 Expression of cyclin D1, cyclin E, and MMP9 in T24 cells transfected with the Rab11 siRNA determined by performing Western blotting and RT-PCR |
3 讨论
Rab11能够调控Rac活性的相对水平,并且在多细胞运动型结构形成过程中有利于单个细胞的形成。Rab11能调节再循环内体的形成、运输,并引导携带受体的膜泡锚定于质膜之上,从而实现了受体和脂质在细胞内的循环利用。近年文献[4-5]报道,Rab11与皮肤癌、乳腺癌等恶性肿瘤的发生进展相关。Rab11能够上调E-cadherin的表达,进而诱导结直肠癌细胞的转化[6]。以上研究表明,Rab11与恶性肿瘤的发生发展密切相关。本课题组前期实验已证实,Rab11在膀胱癌组织中过表达,并与肿瘤侵袭深度显著相关,表明Rab11在膀胱癌的发病机制中发挥重要作用。本研究在膀胱癌T24细胞系中转染Rab11 siRNA,分析抑制Rab11表达对癌细胞增殖、细胞周期进程和侵袭能力的影响,并探讨抑制Rab11表达对细胞周期相关因子cyclin D1、cyclin E和侵袭相关因子MMP9的作用。
本研究采用Rab11 siRNA转染T24细胞,下调T24细胞系中Rab11的表达量。结果表明,抑制Rab11表达后,细胞的增殖能力受到明显抑制。通过流式细胞术分析抑制Rab11表达对细胞周期进程的影响,结果表明细胞周期进程受到阻遏,G1期到S期的转化受到抑制。为进一步研究抑制Rab11表达对细胞周期进程的作用机制,检测了细胞周期相关蛋白的表达情况,结果发现抑制Rab11表达能够下调cyclin D1和cyclin E的表达量。cyclin D1和cyclin E蛋白在G1~S期的转化过程中发挥重要作用[7-8]。本研究结果表明,在T24细胞系中Rab11通过调控cyclin家族蛋白的表达,进而调控癌细胞的增殖和细胞周期进程。
基质胶侵袭实验结果表明,转染了Rab11 siRNA的T24细胞系其侵袭能力明显降低。MMP9在细胞中的主要作用是减少基底膜中胶原蛋白的含量,在膀胱癌细胞侵袭和转移的过程中至关重要[9-12]。深入研究受Rab11调控的与侵袭能力相关的蛋白质,发现MMP9可能是Rab11蛋白作用的一个潜在靶基因。本研究结果显示,抑制Rab11表达后MMP9的表达量也明显降低。因此,Rab11可能是通过调控侵袭相关因子MMP9的表达量进而调控膀胱癌细胞的侵袭和转移。
| [1] |
PASQUALATO S, SENIC-MATUGLIA F, RENAULT L, et al. The structural GDP/GTP cycle of Rab11 reveals a novel interface involved in the dynamics of recycling endosomes[J]. J Biol Chem, 2004, 279(12): 11480-11488. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M310558200 |
| [2] |
SEO M, NAM HJ, KIM SY, et al. Inhibitory heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins inhibit hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis by up-regulation of Bcl-2 via NF-kappaB in H1299 human lung cancer cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2009, 381(2): 153-158. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.01.188 |
| [3] |
DONG W, QIN G, SHEN R. Rab11-FIP2 promotes the metastasis of gastric cancer cells[J]. Int J Cancer, 2016, 138(7): 1680-1688. DOI:10.1002/ijc.29899 |
| [4] |
JING J, TARBUTTON E, WILSON G, et al. Rab11-FIP3 is a Rab11-binding protein that regulates breast cancer cell motility by modulating the actin cytoskeleton[J]. Eur J Cell Biol, 2009, 88(6): 325-341. DOI:10.1016/j.ejcb.2009.02.186 |
| [5] |
BOULAY PL, MITCHELL L, TURPIN J, et al. Rab11-FIP1C is a critical negative regulator in ErbB2-mediated mammary tumor progression[J]. Cancer Res, 2016, 76(9): 2662-2674. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2782 |
| [6] |
CHUNG YC, WEI WC, HUANG SH, et al. Rab11 regulates E-cadherin expression and induces cell transformation in colorectal carcinoma[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14: 587. DOI:10.1186/1471-2407-14-587 |
| [7] |
KNUDSEN KE, DIEHL JA, HAIMAN CA, et al. Cyclin D1:polymorphism, aberrant splicing and cancer risk[J]. Oncogene, 2006, 25(11): 1620-1628. DOI:10.1038/sj.onc.1209371 |
| [8] |
SANTO L, SIU K T, RAJE N. Targeting cyclin-dependent kinases and cell cycle progression in human cancers[J]. Semin Oncol, 2015, 42(6): 788-800. DOI:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2015.09.024 |
| [9] |
KUMAR B, KOUL S, PETERSEN J, et al. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-driven MAPKAPK2 regulates invasion of bladder cancer by modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity[J]. Cancer Res, 2010, 70(2): 832-841. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2918 |
| [10] |
JACOB A, PREKERIS R. The regulation of MMP targeting to invadopodia during cancer metastasis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2015, 3: 4. DOI:10.3389/fcell.2015.00004 |
| [11] |
GIALELI C, THEOCHARIS AD, KARAMANOS NK. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting[J]. FEBS J, 2011, 278(1): 16-27. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07919.x |
| [12] |
GONG Y, CHIPPADA-VENKATA UD, OH WK. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases and their natural inhibitors in prostate cancer progression[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2014, 6(3): 1298-1327. DOI:10.3390/cancers6031298 |
 2018, Vol. 47
2018, Vol. 47