四川盆地已初步建成长宁—威远国家级页岩气示范区,但30%以上的水平井在压裂过程中出现套管变形问题,套管变形不仅影响单井产量,还缩短井筒生命周期,严重制约着我国页岩气的高效开发。
针对造成页岩气开发套管变形的原因,许多学者开展了研究,提出了温度应力效应[1-3]、非对称压裂[4-9]、固井质量[10-15]和断层滑动[16-30]等原因。目前,大多数学者认识到水力压裂过程中的断层激活可能是导致套管变形的主控因素[17-29],这也得到了越来越多现场数据的验证。这些研究认识为现场提供了理论指导,但套管变形仍时有发生,还缺乏解决问题的具体措施,有待于进一步研究。
本文从套管变形的机理出发,分析套管变形的防控技术。首先,基于套管变形的地质和工程原因,建立了流体通道—断层激活模型,揭示了套管变形机理。其次,在该模型的基础上,从钻井、固井、压裂等方面提出了套管变形的防控策略,实现钻前预测、压前预防、压裂预警和压裂控制的一体化套管变形防控策略,为解决页岩气开发套管变形问题提供了依据。
1 套管变形机理四川盆地页岩气开发套管变形具有三大特征,其一,具有天然裂缝/断层相关性的套管变形点数量占套管变形总数的61.7%,这是地质特征[16, 31-32]。其二,套管变形均发生在水力压裂期间,井底施工压力均较大,这是工程特征[33]。其三,具有剪切特征的变形点数量占73%,这是套管变形形状特征[34]。因此,断层/天然裂缝是套管变形的地质原因,水力压裂是套管变形的工程原因。
基于套管变形的地质和工程原因,利用断层激活地质力学原理,建立流体通道—断层激活模型(图 1)。该模型包含几个矛盾运动过程:其一,水力压裂过程中,压裂液通过孔眼进入地层,在井底压力和地层闭合压力这两个相反的作用力的作用下,水力裂缝向地层深处不断扩展;其二,压裂液通过某条流体通道进入断层/天然裂缝,造成断层/天然裂缝内流体压力增加,滑动阻力减小,当滑动阻力小于断层/天然裂缝面的剪应力时,断层/天然裂缝发生滑动,同时伴随着能量释放,流体压力降低,滑动阻力增加,达到新的平衡状态;其三,断层/天然裂缝滑动过程中,对穿过断层/天然裂缝的套管施加剪切作用,引起套管变形。该模型将水力裂缝扩展、断层被激活、断层和套管相互作用这3个过程联系在一起,其中断层被激活的过程是该模型的核心。

|
图 1 流体通道—断层激活模型示意图 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of fluid channel-fault activation model |
流体通道—断层激活模型揭示了压裂时引起套管变形的发生过程和机理:压裂液沿着某条流体通道进入断层/天然裂缝,造成断层/天然裂缝内孔隙压力增加,当达到临界值时,激发断层/天然裂缝滑动,造成套管变形。流体通道可以是水力裂缝、井壁通道和层理裂缝[35-36],或者是由这几种通道组合形成的综合通道[37]。该模型为套管变形防控方法提供了理论依据。
2 套管变形风险预测技术依据断层激活地质力学原理,断层是否激活主要取决于地应力场的方向与大小、断层的方位、孔隙压力及摩擦系数等因素。通常获取这些参数存在一定的误差,在参数不确定的背景下,利用蒙特卡洛方法可以真实地模拟实际物理过程的优势,评估断层/天然裂缝滑动概率,以此表征其滑动风险,其分析流程如下:
(1)基于高分辨率地震资料,利用最大似然体属性方法,识别研究区内断层/天然裂缝分布特征;
(2)通过地质、钻井、测井等资料,获取研究区内基础的地应力场及孔隙压力数据;
(3)基于临界应力断层/天然裂缝假说原理,评估原始条件下研究区中断层/天然裂缝力学活动状态;
(4)基于压裂施工资料确定研究区孔隙压力变化规律;
(5)采用定量风险评估方法(QRA),确定研究区中断层/天然裂缝随地层孔隙压力变化的滑动概率。
断层/天然裂缝滑动风险是在考虑地层参数不确定性的基础上,以断层/天然裂缝滑动概率来表征的。当断层/天然裂缝滑动概率为50%时,表明该断层/天然裂缝处于即将滑动状态,但是在地层参数误差范围内,断层/天然裂缝滑动风险是应力状态中心值偏离临界破坏线的距离所决定的,所以以摩尔圆与临界破坏线交点为中心,将断层/天然裂缝滑动风险划分为3个等级:低风险(滑动概率小于30%)、中风险(滑动概率为30%~70%)、高风险(滑动概率大于70%),如图 2所示。

|
图 2 不同滑动风险断层/天然裂缝的应力状态 Fig. 2 Stress state of faults/natural fractures with various slip risks |
利用该方法,评估了宁201-H1井[38]、H19平台[39]的断层/天然裂缝滑动风险,评估结果和现场实际情况吻合较好。最近利用该方法对宁209井区进行了断层/天然裂缝滑动风险预测,结果如图 3所示。

|
图 3 宁209井区断层/天然裂缝滑动风险预测图 Fig. 3 Prediction of slip risks of faults/fractures in Ning 209 well block |
在断层/天然裂缝滑动过程中,会对穿过断层/天然裂缝的套管施加一个巨大的作用力和位移,2009—2016年现场采用了提高套管钢级和增加套管壁厚等措施,以抵抗这种外挤力。但现场实践表明,提高套管钢级和增加套管壁厚对减少套管变形的效果非常有限。为了分析影响套管变形的因素,从而寻找有效的预防方法,建立了断块滑动引起套管剪切变形的断块—水泥环—套管模型,实现了对断块滑动的数值模拟,并对套管钢级、套管壁厚和固井水泥弹性模量等参数的影响规律进行分析[40]。
计算结果表明,当提高套管钢级,屈服强度从655MPa上升至965MPa时,断层滑动30mm导致的套管变形量降低了1.31%;当套管壁厚从9.15mm上升至13.15mm时,断层滑动30mm导致的套管变形量降低了7.47%。这说明,提高套管钢级和壁厚对套管变形影响较小,这在理论上解释了这两种方法不能有效缓解套管变形的原因[40]。
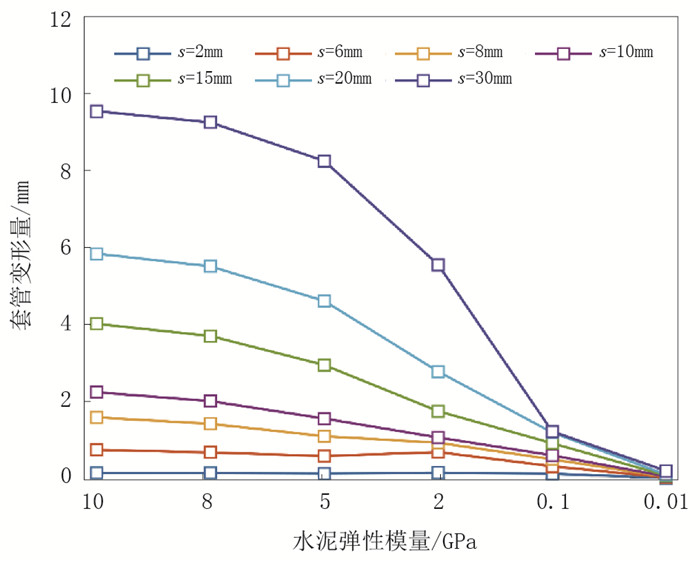
在断块滑动量s=30mm的情况下,当固井水泥弹性模量从10GPa降低到5GPa和2GPa时,套管变形量分别减小了13.56%、41.83%(图 4)。若采用超柔性固井材料(弹性模量为0.1GPa),甚至不固井的措施(弹性模量为0.01GPa),套管变形量可控制在2mm以内[40]。
|
图 4 水泥弹性模量对套管变形量的影响[40] Fig. 4 Influence of elastic modulus of cement sheath on casing deformation[40] |
基于上述实践和数值分析,为了预防套管变形,避免“硬碰硬”,应该采用“以柔克刚”的预防方法。基于该理念,提出了用“低弹模”水泥石,即水泥石的抗压强度在满足要求的情况下其弹性模量尽可能低的预防套管变形方法;在高风险井段下入膨胀橡胶组合套管等特殊工具,用于吸收套管变形,保护套管。最近,先后在威远区块高风险区域威204H38-4井、威204H18-5井和威204H40-3井开展了“高强度微珠固井”工艺现场试验,目前威204H38-4井已经顺利完成压裂,没有发生套管变形[41]。
4 套管变形预警技术断层/天然裂缝滑动过程伴随着能量释放,产生了微地震信号。对长宁H19平台实施微地震监测,提取了与套管变形点相关的微地震事件点,发现微地震在空间和时间上具有如下特征:(1)微地震信号与井筒不对称;(2)不同压裂段的微地震事件点大部分重叠,呈线性分布;(3)出现了较多的大矩震级事件;(4)时间上,大矩震级事件点出现在压裂中后期的频率较高;(5)微地震b值(b为震级和频度关系式中的比例系数)较小,接近于1。基于微地震信号特征和套管变形的剪切特征,这些微地震信号可以解释为激活的断层/天然裂缝,正是这些断层/天然裂缝的错动引起了套管发生剪切变形[42-43]。通过上面分析可以看出,套管变形时微地震特征很显著,可以将其作为套管变形发生的前兆信号,作为套管变形预警的手段。
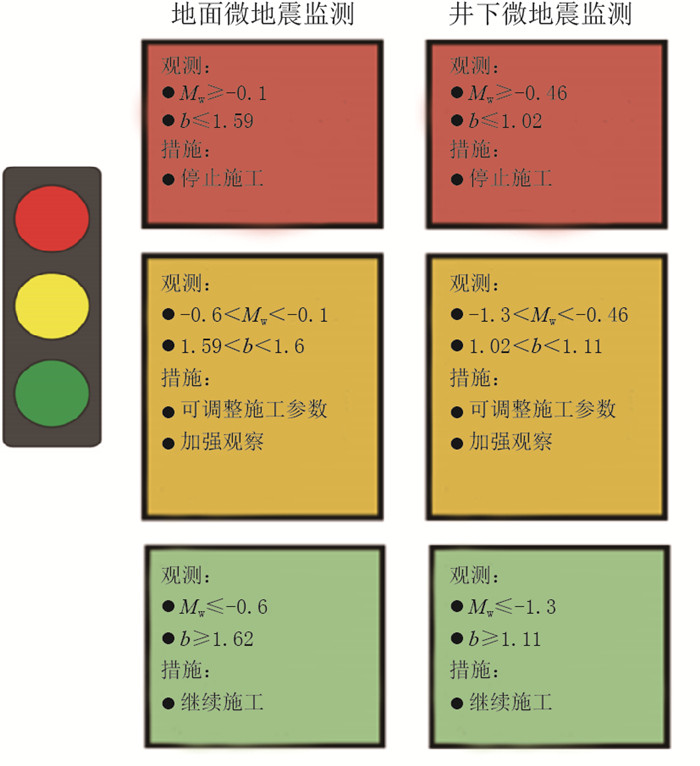
对长宁区块的微地震数据进行统计,可分成以下3级:高风险对应震级Mw≥-0.46,中等风险对应-1.3<Mw<-0.46,低风险对应Mw≤-1.3。同理b值也可分成3级:高风险对应b≤1.02,中等风险对应1.02<b<1.11,低风险对应b≥1.11。将高风险、中等风险和低风险分别对应“红、黄、绿”3个等级,建立分级预警标准(图 5)。当达到红色级别时,停止施工;当达到黄色级别时,调整施工参数,如降低排量、减小规模,同时继续观察,不升级为红色级别即可;当为绿色级别时,可继续施工不受影响。因此,通过实时监测微地震信号并处理分析,可实现套管变形预警。
|
图 5 基于微地震监测的套管变形“红黄绿灯”预警标准 Fig. 5 Early warning standard of "Red-Yellow-Green Light" for casing deformation based on microseismic monitoring |
压裂液通过孔眼进入地层,再通过某条流体通道进入断层/天然裂缝,流体通道不仅传递了压裂液,还传递了流体压力,地面施工压力改变了断层/天然裂缝面上的滑动阻力与剪应力之间的平衡,引起断层/天然裂缝滑动,造成套管变形。
基于上述原理,有两种控制套管变形的思路:第一种是优化压裂施工参数。为此,建立断层滑动的水力压裂数值模型,利用压裂数值模拟建立压裂施工参数与断层激活之间的定量联系。模拟分析的结果表明,降低排量和液量均能降低断层激活的长度,从而能在一定程度上控制断层滑动,进而控制套管变形。宁201井区套管变形比例为22%,而宁209井区采取了降排量和(或)降液量的措施后套管变形比例为13%[44]。
第二种方法是阻断流体通道。其原理如下,当水力裂缝沟通断层/天然裂缝后,通道内阻力减小,缝内净压力降低,井筒内的压裂液向其汇集,形成一条高速流动的流体通道;在压裂液中投放一定数量的暂堵球,暂堵球根据流速进行分配,倾向于流速大的孔眼,从而堵住与断层/天然裂缝沟通的孔眼,切断井筒和断层/天然裂缝的连接通道,从而控制住断层/天然裂缝的滑动(图 6)。因此,多簇射孔+暂堵孔眼可控制排量和液量分配,是一种有效的平衡套管变形和页岩气产量之间矛盾的手段。截至2020年底,威远区块28口井采用“裂缝暂堵+长段多簇”压裂工艺,只有4口井发生套管变形,套管变形比例从研究前54%降低到14.3%[41]。

|
图 6 多簇射孔+暂堵孔眼控制套管变形示意图 Fig. 6 Schematic diagram of multi-cluster perforation + temporary plugging for casing deformation controlling |
基于套管变形的地质、工程和形状特征,利用断层激活地质力学原理,建立了流体通道—断层激活模型,从而将水力裂缝扩展、断层/天然裂缝被激活、断层/天然裂缝和套管相互作用3个过程联系了起来。
流体通道—断层激活模型揭示了套管变形的发生过程和原因:压裂液沿着某条流体通道进入断层/天然裂缝,造成断层/天然裂缝内孔隙压力增加,当达到临界值时,激发断层/天然裂缝滑动,造成套管变形。
在流体通道—断层激活模型的基础上,分析断层滑动力学条件、断层滑动和套管相互作用规律、套管变形井微地震特征、优化压裂施工参数和多簇射孔+暂堵孔眼工艺,形成了钻前预测、压前预防、压裂预警和压裂控制一体化套管变形防控策略。
本文研究结果能对四川盆地页岩气开发套管变形问题的解决提供指导,也能为其他盆地套管变形问题的研究提供参考。
| [1] |
Sugden C, Johnson J, Chambers M, et al. Special considerations in the design optimization of the production casing in high-rate, multistage-fractured shale wells[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 2012, 27(4): 459-472. |
| [2] |
田中兰, 石林, 乔磊. 页岩气水平井井筒完整性问题及对策[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(9): 70-76. Tian Zhonglan, Shi Lin, Qiao Lei. Research of and countermeasure for wellbore integrity of shale gas horizontal well[J]. Nature Gas Industry, 2015, 35(9): 70-76. DOI:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.09.010 |
| [3] |
Yin F, Gao D. Prediction of sustained production casing pressure and casing design for shale gas horizontal wells[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 25: 159-165. DOI:10.1016/j.jngse.2015.04.038 |
| [4] |
Daneshy A A. Impact of off-balance fracturing on borehole stability and casing failure[C]. SPE Western Regional Meeting. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2005.
|
| [5] |
于浩, 练章华, 林铁军, 等. 页岩气体积压裂过程中套管失效机理研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2016, 12(10): 37-43. Yu Hao, Lian Zhanghua, Lin Tiejun, et al. Study on failure mechanism of casing in stimulated reservoir volume fracturing of shale gas[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2016, 12(10): 37-43. |
| [6] |
于浩, 练章华, 林铁军. 页岩气压裂过程套管失效机理有限元分析[J]. 石油机械, 2014, 42(8): 84-88. Yu Hao, Lian Zhanghua, Lin Tiejun. Finite element analysis of failure mechanism of casing during shale gas fracturing[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2014, 42(8): 84-88. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-4578.2014.08.020 |
| [7] |
于浩, 练章华, 徐晓玲, 等. 页岩气直井体积压裂过程套管失效的数值模拟[J]. 石油机械, 2015, 43(3): 73-77. Yu Hao, Lian Zhanghua, Xu Xiaoling, et al. Numerical simulation for casing failure during volumetric fracturing of shale gas vertical wells[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2015, 43(3): 73-77. |
| [8] |
Lian Z H, Yu H, Lin T J, et al. A study on casing deformation failure during multi-stage hydraulic fracturing for the stimulated reservoir volume of horizontal shale wells[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 23: 538-546. DOI:10.1016/j.jngse.2015.02.028 |
| [9] |
刘伟, 陶长洲, 万有余, 等. 致密油储层水平井体积压裂套管变形失效机理数值模拟研究[J]. 石油科学通报, 2017, 2(4): 466-477. Liu Wei, Tao Changzhou, Wan Youyu, et al. Numerical analysis of casing deformation during massive hydraulic fracturing of horizontal wells in a tight-oil reservoir[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2017, 2(4): 466-477. |
| [10] |
于浩, 练章华, 林铁军. 油田固井质量对套管损坏影响的数值仿真[J]. 计算机仿真, 2014, 31(9): 161-164. Yu Hao, Lian Zhanghua, Lin Tiejun. Numerical simulation of influence of cementing quality on casing failure for oil field[J]. Computer Simulation, 2014, 31(9): 161-164. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2014.09.035 |
| [11] |
蒋可, 李黔, 陈远林, 等. 页岩气水平井固井质量对套管损坏的影响[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(12): 77-82. Jiang Ke, Li Qian, Chen Yuanlin, et al. Influence of cementing quality on casing failures in horizontal shale gas wells[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(12): 77-82. DOI:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2015.12.012 |
| [12] |
范明涛, 柳贡慧, 李军, 等. 页岩气井温压耦合下固井质量对套管应力的影响[J]. 石油机械, 2016, 44(8): 1-5. Fan Mingtao, Liu Gonghui, Li Jun, et al. Effect of cementing quality on casing stress of shale gas well under heat-mechanical coupling[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2016, 44(8): 1-5. |
| [13] |
Liu K, Gao D, Wang Y, et al. Effect of local loads on shale gas well integrity during hydraulic fracturing process[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2017, 37: 291-302. DOI:10.1016/j.jngse.2016.11.053 |
| [14] |
刘奎, 高德利, 王宴滨, 等. 局部载荷对页岩气井套管变形的影响[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(11): 76-82. Liu Kui, Gao Deli, Wang Yanbin, et al. Effects of local load on shale gas well casing deformation[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(11): 76-82. DOI:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.11.010 |
| [15] |
刘奎, 王宴滨, 高德利, 等. 页岩气水平井压裂对井筒完整性的影响[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(3): 406-414. Liu Kui, Wang Yanbin, Gao Deli, et al. Effects of hydraulic fracturing on horizontal wellbore for shale gas[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(3): 406-414. |
| [16] |
陈朝伟, 石林, 项德贵. 长宁—威远页岩气示范区套管变形机理及对策[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(11): 70-75. Chen Zhaowei, Shi Lin, Xiang Degui. Mechanism of casing deformation in the Changning-Weiyuan national shale gas demonstration area and countermeasures[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(11): 70-75. DOI:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.11.009 |
| [17] |
Yin F, Han L, Yang S, et al. Casing deformation from fracture slip in hydraulic fracturing[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 166: 235-241. DOI:10.1016/j.petrol.2018.03.010 |
| [18] |
Qian B, Yin C, Li Y, et al. Diagnostics of casing deformation in multi-stage hydraulic fracturing stimulation in lower silurian marine shale play in southwestern China[C]. Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Society of Exploration Geophysicists, American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2015: 402-415.
|
| [19] |
Xi Y, Li J, Liu G, et al. Numerical investigation for different casing deformation reasons in Weiyuan-Changning shale gas field during multistage hydraulic fracturing[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 163: 691-702. DOI:10.1016/j.petrol.2017.11.020 |
| [20] |
Zhang F, Yin Z, Chen Z, et al. Fault reactivation and induced seismicity during multistage hydraulic fracturing: microseismic analysis and geomechanical modeling[J]. SPE Journal, 2019, 25(2): 692-711. |
| [21] |
Yan X, Jun L, Chunqing Z, et al. A new investigation on casing shear deformation during multistage fracturing in shale gas wells based on microseism data and calliper surveys[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 180: 1034-1045. DOI:10.1016/j.petrol.2019.05.079 |
| [22] |
Xi Y, Li J, Liu G, et al. Mechanisms and influence of casing shear deformation near the casing shoe, based on MFC surveys during multistage fracturing in shale gas wells in Canada[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(3): 372. DOI:10.3390/en12030372 |
| [23] |
Yin F, Xiao Y, Han L, et al. Quantifying the induced fracture slip and casing deformation in hydraulically fracturing shale gas wells[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 60: 103-111. DOI:10.1016/j.jngse.2018.10.005 |
| [24] |
Yin F, Deng Y, He Y, et al. Mechanical behavior of casing crossing slip formation in water flooding oilfields[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 167: 796-802. DOI:10.1016/j.petrol.2017.12.069 |
| [25] |
Li H, Deng J, Liu W, et al. Research on casing deformation failure mechanism during volume fracturing for tight oil reservoir of horizontal wells[C]. 51st US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium. American Rock Mechanics Association, 2017.
|
| [26] |
高利军, 柳占立, 乔磊, 等. 页岩气水力压裂中套损机理及其数值模拟研究[J]. 石油机械, 2017, 45(1): 75-80. Gao Lijun, Liu Zhanli, Qiao Lei, et al. Mechanism analysis and numerical simulation of casing failure in hydraulic fracturing of shale gas formation[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2017, 45(1): 75-80. |
| [27] |
高利军, 乔磊, 柳占立, 等. 页岩储层剪切套损的数值模拟及固井对策研究[J]. 石油机械, 2016, 44(10): 6-10, 16. Gao Lijun, Qiao Lei, Liu Zhanli, et al. Numerical modeling and cementing countermeasure analysis of casing shear damage in shale reservoir[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2016, 44(10): 6-10, 16. |
| [28] |
Guo X, Li J, Liu G, et al. Shale experiment and numerical investigation of casing deformation during volume fracturing[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2018, 11(22): 723. DOI:10.1007/s12517-018-4091-4 |
| [29] |
Guo X, Li J, Liu G, et al. Numerical simulation of casing deformation during volume fracturing of horizontal shale gas wells[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 172: 731-742. DOI:10.1016/j.petrol.2018.08.067 |
| [30] |
舒红林, 王利芝, 尹开贵, 等. 地质工程一体化实施过程中的页岩气藏地质建模[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(2): 84-95. Shu Honglin, Wang Lizhi, Yin Kaigui, et al. Geological modeling of shale gas reservoirs during the implementation process of geology-engineering integration[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(2): 84-95. |
| [31] |
周小金, 雍锐, 范宇, 等. 天然裂缝对页岩气水平井压裂的影响及工艺调整[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(6): 94-104. Zhou Xiaojin, Yong Rui, Fan Yu, et al. Influence of natural fractures on fracturing of horizontal shale gas wells and process adjustment[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(6): 94-104. |
| [32] |
陈朝伟, 曹虎, 周小金, 等. 四川盆地长宁区块页岩气井套管变形和裂缝带相关性[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2020, 23(4): 123-130. Chen Zhaowei, Cao Hu, Zhou Xiaojin, et al. Correlation between casing deformation and fracture zones in Changning shale gas block, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2020, 23(4): 123-130. |
| [33] |
陈朝伟, 曹虎, 石元会. 四川长宁区块地应力特征及裂缝带活化分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(增刊1): 86-95. Chen Zhaowei, Cao Hu, Shi Yuanhui. In-situ stress characteristics and fracture zone activation analysis of Changning shale gas in Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(S1): 86-95. |
| [34] |
陈朝伟, 房超, 朱勇, 等. 四川页岩气井套管变形特征及受力模式[J]. 石油机械, 2020, 48(2): 126-131. Chen Zhaowei, Fang Chao, Zhu Yong, et al. Deformation characteristics and stress modes of casing for shale gas wells in Sichuan[J]. China Petroleum Machinery, 2020, 48(2): 126-131. |
| [35] |
陈朝伟, 宋毅, 青春, 等. 四川长宁页岩气水平井压裂套管变形实例分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2019, 15(2): 513-524. Chen Zhaowei, Song Yi, Qing Chun, et al. A case study on casing deformation of horizontal well during hydraulic fracturing in Sichuan Changning[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2019, 15(2): 513-524. |
| [36] |
张华礼, 陈朝伟, 石林, 等. 流体通道形成机理及在四川页岩气套管变形分析中的应用[J]. 钻采工艺, 2018, 41(4): 8-11. Zhang Huali, Chen Zhaowei, Shi Lin, et al. Mechanism of how fluid passage formed and application in Sichuan shale gas casing deformation analysis[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2018, 41(4): 8-11. |
| [37] |
童亨茂, 张平, 张宏祥, 等. 页岩气水平井开发套管变形的地质力学机理及其防治对策[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(1): 189-197. Tong Hengmao, Zhang Ping, Zhang Hongxiang, et al. Geomechanical mechanisms and prevention countermeasures of casing deformation in shale gas horizontal wells[J]. 2021, 41(1): 189-197. |
| [38] |
Chen Zhaowei, Zhou Lang, Walsh F R, et al. Case study: casing deformation caused by hydraulic fracturing induced fault slip in the Sichuan Basin[C]. Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, 2018.
|
| [39] |
Chen Zhaowei, Fan Yu, Huang Rui, et al. Case study: fault slip induced by hydraulic fracturing and risk assessment of casing deformation in the Sichuan Basin[C]. SPE/AAPG/SEG Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, 2019.
|
| [40] |
蒋振源, 陈朝伟, 张平, 等. 断块滑动引起的套管变形及影响因素分析[J]. 石油管材与仪器, 2020, 6(4): 30-37. Jiang Zhenyuan, Chen Zhaowei, Zhang Ping, et al. Casing deformation and its influencing factors caused by block sliding[J]. Petroleum Tubular Goods & Instruments, 2020, 6(4): 30-37. |
| [41] |
张平, 何昀宾, 刘子平, 等. 页岩气水平井套管的剪压变形试验与套变预防实践[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(5): 84-91. Zhang Ping, He Yunbin, Liu Ziping, et al. Shear compression deformation test and deformation prevention practice of casing in shale gas horizontal wells[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(5): 84-91. |
| [42] |
Zeng Bo, Zhang Haozhe, Zhou Xiaojin, et al. Microseismic characteristics of shale gas wells with casing deformation in Sichuan Basin[C]. 55th US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, 2021.
|
| [43] |
陈朝伟, 王鹏飞, 项德贵. 基于震源机制关系的长宁—威远区块套管变形分析[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2017, 45(4): 110-114. Chen Zhaowei, Wang Pengfei, Xiang Degui. Analysis of casing deformation in the Changning-Weiyuan Block based on focal mechanism[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2017, 45(4): 110-114. |
| [44] |
陈朝伟, 黄锐, 曾波, 等. 四川盆地长宁页岩气区块套管变形井施工参数优化分析[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2021, 49(1): 93-100. Chen Zhaowei, Huang Rui, Zeng Bo, et al. Analysis and optimization of construction parameters for preventing casing deformation in the Changning shale gas block, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2021, 49(1): 93-100. |



