2. 中国石油新疆油田公司勘探开发研究院
2. Research Institute of Exploration & Development, PetroChina Xinjiang Oilfield Company
层序地层学理论的提出[1-3],极大地推动了大西洋两侧大陆边缘深水领域油气勘探[2]。20世纪80年代,国内地质学家将层序地层学引入中国[4-9],开始在层序地层格架内开展储层预测和油气富集规律研究工作[10-17],不仅促进了层序地层学发展,也极大地推动了国内油气勘探接连获得重大突破,如鄂尔多斯盆地延长组[18-21]、准噶尔盆地百口泉组—上乌尔禾组针对湖侵体系域(扇)三角洲前缘砂体进行钻井部署,先后发现亿吨级规模储量[22-26]。国外一些被动大陆边缘海相盆地油气勘探实践证实[27-28],低位体系域碎屑岩有利于油气富集[29]。在中国东部的小型断陷盆地内,低位体系域砂体发育,油气勘探也接连获得突破,表明低位体系域砂体具有优越的成藏条件[30-33]。但对中西部的大型坳陷湖盆来说,是否发育低位体系域砂体?砂体是否有利于形成岩性油气藏?这两个关键问题制约了油气勘探领域的提出和风险井部署。
准噶尔盆地腹部是岩性—地层油气藏勘探的重要领域[34]。但自石南31井突破之后,油气勘探近15年无重大发现,在目前北部凸起带勘探程度较高的情况下,南部的凹陷区是否发育有效砂体、砂体是否具备形成岩性圈闭的条件,这两个关键问题制约了油田有利区带优选和钻井部署。本文在充分梳理前人研究成果的基础上,综合运用地震解释、钻井及测井等资料,以准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷清水河组为例,建立大型坳陷湖盆层序地层格架,恢复古地貌格局,落实了两级坡折,明确了坡折之下低位体系域砂体较发育,并分析了低位体系域砂体的成藏条件,指出坡折之下的低位体系域砂体为下一步准噶尔盆地腹部岩性油藏最有利勘探领域。
1 地质概况准噶尔盆地位于新疆维吾尔自治区北部,夹持于北天山和阿尔泰山之间,平面形态呈北窄南宽的三角形,是一个三面被古生代缝合线包围的晚石炭世—第四纪发展起来的大型含油气叠合盆地[35]。盆地可划分为6个一级构造单元和44个二级构造单元,面积约为13×104km2。白垩系沉积期,盆地为一大型坳陷湖盆,沉降中心位于盆地南部的沙湾—阜康凹陷,区域构造呈现为南倾的单斜。研究区大致位于阜康凹陷中部(图 1),阜康凹陷为盆地最大的生烃凹陷,烃源岩条件极为有利[36]。白垩系清水河组自下而上可划分为两段,即清水河组一段(K1q1)和二段(K1q2)(图 1)。清水河组一段(K1q1)底部发育“底砂岩”,顶部发育一套厚度稳定的“高伽马”泥岩(图 1),构成良好的储盖组合,是目前准噶尔盆地岩性油藏勘探最主要目的层之一。
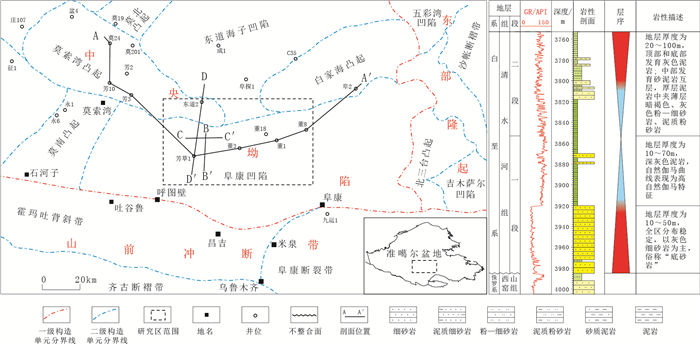
|
图 1 研究区构造位置图(左)和地层综合柱状图(右) Fig. 1 Structural location (left) and comprehensive stratigraphic column (right) in the study area |
层序地层学认为,低位体系域位于层序界面之上,当海平面下降至滨线坡折以下时,开始在坡折之下形成低位体系域复合砂体[6, 16]。因此,层序界面和坡折是低位体系域形成的必要条件。
通过研究区及周缘地区的95条二维地震测线和4800km2三维地震资料解释,对10口井进行井—震结合标定,建立了研究区等时层序地层格架。白垩系清水河组底部沉积一套粗碎屑“底砂岩”[37-38],“底砂岩”之上发育一套“高伽马”泥岩,随后湖平面缓慢下降,沉积一套细碎屑砂泥岩互层,在垂向上构成一个完整的低位体系域—湖侵体系域—高位体系域的三级层序[39-40]。其成因主要受燕山构造运动的影响,中—上侏罗统遭受大范围剥蚀,在白垩系与侏罗系之间形成区域性不整合面[37-38]。地震剖面显示,白垩系清水河组底部与侏罗系不整合接触,为典型层序界面,底界面SB1之上见上超及沟谷充填特征,界面之下见削截现象(图 2)。钻井资料揭示,底界面SB1为岩性突变面,界面之下为红褐色泥岩段,界面之上为河道滞留砂岩及含砾砂岩。测井曲线显示,底界面SB1为典型突变面,自然伽马曲线、自然电位曲线由低幅线性突变为中幅、高幅箱形或钟形,是地层叠加方式由加积到退积的转换面。受燕山期构造活动的影响,盆地周缘遭受广泛的风化剥蚀作用,物源供给充足,为低位体系域砂体的发育奠定了基础。

|
图 2 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷过莫24井—阜2井地震剖面(剖面位置见图 1) Fig. 2 Seismic profile cross Wells Mo 24-Fu 2 in Fukang Sag, Junggar Basin (section location is in Fig. 1) |
在建立等时层序地层格架的基础上,综合考虑研究区清水河组地层发育特征及实际资料的准确性,利用残余地层厚度法,恢复了研究区清水河组古地貌(图 3)。残余地层厚度法恢复古地貌的原理是地层未受剥蚀或剥蚀较少,且古水深变化较小的条件下,利用地层厚度变化反映沉积期古地貌样式,地层厚度由大到小反映了古地貌由低变高,即地层越厚,古地貌越低;地层越薄,古地貌越高[41]。古地貌图显示,白垩系清水河组沉积期,研究区古地貌格局北高南低,发育两级呈近东西向展布的坡折。坡折之下地层厚度较坡折之上明显增大,且在地震剖面上,上超特征较清晰(图 4)。多级坡折的发育为低位体系域砂体的发育创造了条件。在垂直坡折的南北方向,沟谷较发育,在剖面上呈“U”形或“V”形(图 5),为沉积物输送通道,来自北部物源的辫状河三角洲砂体经沟谷输导[41-42],进积至阜康凹陷多级坡折之下,为低位体系域砂体发育的物源基础。

|
图 3 阜康凹陷清水河组古地貌图 Fig. 3 Paleogeomorphic map of Qingshuihe Formation in Fukang Sag |
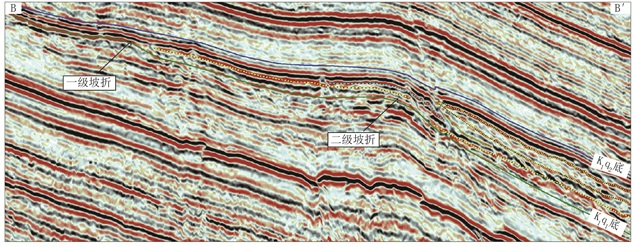
|
图 4 研究区南北向地震剖面(剖面位置见图 1) Fig. 4 NS direction seismic profile in the study area (section location is in Fig. 1) |

|
图 5 研究区东西向地震剖面(剖面位置见图 1) Fig. 5 WE direction seismic profile in the study area (section location is in Fig. 1) |
低位体系域砂体为层序地层学概念,为低位期扇三角洲、辫状河三角洲和滑塌扇砂体的总称,可进一步识别出盆底扇、斜坡扇和前积楔等微相[43-44]。研究区低位体系域砂体为经过长距离搬运的辫状河三角洲成因,岩心观察显示,低位体系域砂体以细砂岩和中砂岩为主,分选和磨圆均较好,成分成熟度高。垂向上单砂体厚度大于30m,下粗上细,测井曲线呈钟形,为正旋回沉积特征(图 6)。砂岩中槽状交错层理较发育,代表多期河道不断冲刷、切割和叠置的特征。显微镜下观察显示,低位体系域砂体岩性以中—细砂岩为主,孔隙类型主要为原生粒间孔(图 6),孔隙度平均为15.5%,渗透率平均为23.3mD,储层物性较好。在地震剖面上,低位体系域砂体沿坡折分布,表现为双向下超、较杂乱的反射特征,能量较弱—中等(图 4)。由于实测声波曲线无法有效区分砂岩、泥岩,因反演需要,将声波曲线作为低频曲线,对岩性比较敏感的自然伽马曲线作为高频曲线,在频率域合并成“特征曲线”,实现特征曲线重构。重构后得到的波阻抗,可以较好地区分砂岩、泥岩。在反演剖面上,低位体系域砂体具有高波阻抗的特征,前积特征明显(图 7)。

|
图 6 芳草1井沉积相综合柱状图 Fig. 6 Comprehensive sedimentary facies column of Well Fangcao 1 |
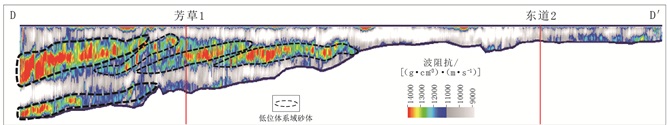
|
图 7 过芳草1井和东道2井反演剖面(剖面位置见图 1) Fig. 7 Inversion profile cross Wells Fangcao 1 and Dongdao 2 (section location is in Fig. 1) |
由于研究区钻井资料较少,勘探程度低,低位体系域砂体分布很难落实。利用“沟谷定方向、坡折+地震反射定扇体大小”的方法,对研究区低位体系域砂体的分布进行厘定。沟谷是沉积物输送通道,是沉积物输送至沉降中心的必经之路,因此,沟谷的分布可以确定低位体系域扇体的物源和输送方向;坡折之下的平台区是沉积物的卸载场所,利用地震反射相变特征可以确定扇体的规模和大小。研究结果表明:研究区发育两期低位体系域砂体,早期湖平面较低,湖岸线大致位于第一期坡折附近,坡折附近可以识别出4个沟谷体系,来自北部物源的辫状河三角洲前缘砂体,经沟谷体系输送至坡折之下发生卸载,形成第一期低位体系域砂体(图 8a);随着湖平面不断上升,湖岸线扩大至第二期坡折附近时,辫状河三角洲前缘砂体经过6个沟谷体系输送,在坡折之下卸载,形成第二期低位体系域砂体,坡折之上为“过路”沉积(图 8b)。两期低位体系域砂体面积可达1000 km2。至湖侵体系域,湖平面不断上升,辫状河三角洲向物源方向退积,沉积物很难到达坡折之下的湖盆沉降中心,在坡折之上发育辫状河三角洲前缘和滩坝砂体(图 8c)。
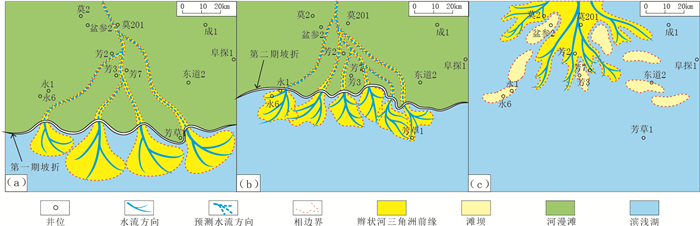
|
图 8 阜康凹陷清水河组沉积相图 Fig. 8 Sedimentary facies map of Qingshuihe Formation in Fukang Sag (a)第一期低位体系域;(b)第二期低位体系域;(c)湖侵体系域 |
坡折带的位置并非一成不变,而是受湖平面升降变化的影响,不断迁移,因为坡折的位置与浪基面的位置相当,浪基面的位置是动态的,坡折的位置也是来回不断迁移变化的。在低位体系域早期,第一期坡折的位置相当于早期的湖岸线,低位体系域砂体不断在坡折之下卸载,而在坡折之上“过路”沉积。随着湖平面逐渐上升,坡折的位置向湖岸方向迁移,第二期低位体系域砂体卸载至第二期坡折之下。这使得不同期次的低位体系域砂体在侧向上彼此分隔,互不连通,且低位体系域砂体侧向上通常与下伏侏罗系齐古组(J3q)泥岩直接接触,构成良好的侧向遮挡条件,因此岩性圈闭条件极为优越(图 9)。

|
图 9 阜康凹陷清水河组低位体系域沉积模式图 Fig. 9 Deposition pattern of lowstand system tract of Qingshuihe Formation in Fukang Sag |
阜康凹陷为准噶尔盆地最大的生烃凹陷,发育二叠系芦草沟组(P2l)和侏罗系八道湾组(J1b)两套烃源岩。其中芦草沟组发育半深湖—深湖环境下的黑色白云岩夹灰色泥岩,厚度为50~250m,有机质类型主体为Ⅱ1—Ⅱ2型,有机碳含量为0.65%~6.72%,平均为2.16%;生烃潜量S1+S2为0.36~26.28mg/g,平均为7.0mg/g,为一套中等—好的烃源岩。侏罗系八道湾组煤系烃源岩厚度大于450m,有机质类型以Ⅱ2型和Ⅲ型为主,有机碳含量大于2%,Ro为1.6%,已进入成熟—高成熟阶段,总体为一套优质烃源岩,有利于油气大规模生成。阜康凹陷周缘已发现的油气均为二叠系芦草沟组和侏罗系八道湾组两套优质烃源岩的混源[36]。另外,阜康凹陷周缘钻穿或钻揭清水河组的井油气显示活跃,且永6井已获工业油流,证实该领域勘探程度虽然较低,但勘探潜力大。
4.2 低位体系域砂体储层性质较好,盖层条件优越阜康凹陷芳草1井钻遇清水河组第二期低位体系域砂体,厚度较大,砂体横向延伸较长,储层岩性以中—细砂岩为主,孔隙类型包括原生粒间孔和次生溶蚀孔,在埋深接近6000m的条件下,储层平均孔隙度为15.5%,平均渗透率为23.3mD,表明研究区虽然埋深较大,凹陷内仍发育规模优质储层。储层之上为清水河组“高伽马”泥岩,厚度大于60m,为一套区域性盖层,在垂向上与低位体系域砂体构成良好的储盖组合。
4.3 印支期和燕山期两组断裂,构成“Y”形配置,沟通二叠系烃源岩2020年,阜康凹陷东斜坡上乌尔禾组油气风险勘探获重大突破[45],证实阜康凹陷周缘成藏条件优越,为继玛湖凹陷、沙湾凹陷和盆1井西凹陷之后,准噶尔盆地最主要的接替领域。凹陷周缘发育深浅层多期断裂,深层断裂沟通二叠系下乌尔禾组烃源岩,浅层断裂沟通白垩系清水河组砂体,深层断裂与浅层断裂在垂向上构成“Y”形组合[46],有利于二叠系油气进入斜坡区清水河组低位体系域砂岩储层中;在空间上构成“阶梯运移、毯式输导”的油气成藏模式(图 10),有利于油气最终聚集成藏。

|
图 10 阜康凹陷白垩系清水河组油气成藏模式图 Fig. 10 Hydrocarbon accumulation pattern of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in Fukang Sag |
(1)准噶尔盆地白垩系清水河组底界为三级层序界面,且阜康凹陷周缘发育两级坡折,为研究区低位体系域砂体的发育创造了条件。
(2)低位体系域砂体彼此分隔,且与湖侵期大面积分布的辫状河三角洲前缘砂体不连通,侧向遮挡条件较好,岩性圈闭条件优越。
(3)阜康凹陷北斜坡低位体系域砂体厚度大、面积广、物性好,盖层和侧向遮挡条件优越,且烃源岩和输导条件较好,为下一步最有利勘探领域。
| [1] |
Vail P R, Mitchum R M, Thompson S. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level (part3): relative changes of sea level from coastal onlap [C]//Payton C W. Seismic stratigraphy: applications to hydrocarbon exploration. AAPG Memoir, 1977, 26: 63-81.
|
| [2] |
Galloway W E. Genetic stratigraphic sequences in basin analysis (Ⅰ): architecture and genesis of flooding-surface bounded depositional units[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1989, 73: 125-142. |
| [3] |
Steven L, Lorraine Eglinton, Martin Schoell, et al. Vertical and lateral fluid flow related to a large growth fault, South Eugene island block 330 field, offshore Louisiana[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(2): 244-276. |
| [4] |
徐怀大. 层序地层学理论用于我国断陷盆地分析中的问题[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1991, 12(1): 52-57. Xu Huaida. Problems in analysis of faulted basins on sequence stratigraphic theory[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1991, 12(1): 52-57. |
| [5] |
魏魁生. 华北典型箕状断陷盆地层序地层学模式及其与油气赋存关系[J]. 地球科学, 1993, 18(2): 139-149. Wei Kuisheng. Sequence stratigraphic models and their relationship to oil and gas occurrence in typical faulted basins, northern China[J]. Earth Science, 1993, 18(2): 139-149. |
| [6] |
Catuneanu O. Principles of sequence stratigraphy [M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2006.
|
| [7] |
薛良清. 层序地层学研究现状、方法与前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1995, 22(5): 8-13. Xue Liangqing. Current status, methodology, and future directions of sequence stratigraphy study[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1995, 22(5): 8-13. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1995.05.005 |
| [8] |
张振生, 黎英, 王冰. 冀中坳陷陆相地层层序地层学的应用[J]. 石油学报, 1997, 18(2): 26-33. Zhang Zhensheng, Li Ying, Wang Bing. An application of sequence stratigraphy in continental deposit of Jizhong Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1997, 18(2): 26-33. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.1997.02.005 |
| [9] |
胡受权. 断陷湖盆陡坡带陆相层序地层的"沉积滨线坡折"问题探讨[J]. 古地理学报, 2000, 4(2): 20-29. Hu Shouquan. Study on depositional shoreline break for terrigenous sequence stratigraphy along the steep slope zone of fault-depressed lacustrine Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2000, 4(2): 20-29. |
| [10] |
李德江, 朱筱敏, 董艳蕾, 等. 辽东湾坳陷古近系沙河街组层序地层分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(6): 669-676. Li Dejiang, Zhu Xiaomin, Dong Yanlei, et al. Sequence stratigraphy and depositional system of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Liaodong Bay Depression[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2007, 34(6): 669-676. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2007.06.006 |
| [11] |
冯有良. 断陷盆地层序格架中岩性地层油气藏分布特征[J]. 石油学报, 2005, 26(4): 17-22. Feng Youliang. Distribution of stratigraphic and lithologic reservoirs in sequence framework of rift-subsidence Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005, 26(4): 17-22. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2005.04.004 |
| [12] |
王居峰, 邓宏文, 蔡希源. 准噶尔盆地中部侏罗系层序地层格架[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(1): 23-26. Wang Jufeng, Deng Hongwen, Cai Xiyuan. Jurassic sequence stratigraphic frames in the Middle Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(1): 23-26. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.01.006 |
| [13] |
李思田, 潘元林, 陆永潮, 等. 断陷湖盆隐蔽油藏预测及勘探的关键技术: 高精度地震探测基础上的层序地层学研究[J]. 地球科学, 2002, 27(5): 592-598. Li Sitian, Pan Yuanlin, Lu Yongchao, et al. Key technology of prospecting and exploration of subtle traps in lacustrine fault basins: sequence stratigraphic researches on the basis of high resolution seismic survey[J]. Earth Science, 2002, 27(5): 592-598. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.05.019 |
| [14] |
冯有良, 潘元林, 郑和荣. 东营凹陷中始新统上部—上始新统层序地层模式及其石油地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(3): 377-383. Feng Youliang, Pan Yuanlin, Zheng Herong. Sequence stratigraphic model and its petroleum geological significance of upper part of middle Eocene Series and upper Eocene Series in Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(3): 377-383. |
| [15] |
董清水, 刘招君, 方石, 等. 论陆相层序地层学四分方案的可行性[J]. 沉积学报, 2003, 21(2): 324-327. Dong Qingshui, Liu Zhaojun, Fang Shi, et al. On the feasibility of the four division scheme about continental sequence stratigraphica[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2003, 21(2): 324-327. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2003.02.021 |
| [16] |
刘招君, 董清水, 王嗣敏, 等. 陆相层序地层学导论与应用 [M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2002: 38-50. Liu Zhaojun, Dong Qingshui, Wang Simin, et al. Introduction to continental sequence stratigraphy & application [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2002: 38-50. |
| [17] |
刘招君, 胡菲, 孙平昌, 等. 再论陆相三级层序内四分方案及其在油气勘探中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(1): 1-12. Liu Zhaojun, Hu Fei, Sun Pingchang, et al. Re-discussion on the four division scheme about continental sequence stratigraphy and its application on oil and gas exploration[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2013, 43(1): 1-12. |
| [18] |
屈红军, 李文厚, 梅志超, 等. 论层序地层学与含油气系统在油气勘探中的联系: 以鄂尔多斯中生代盆地为例[J]. 地质论评, 2003, 49(5): 495-500. Qu Hongjun, Li Wenhou, Mei Zhichao, et al. Relationship between sequence stratigraphy and petroleum system in oil and gas exploration: an example in the Mesozoic Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2003, 49(5): 495-500. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.05.006 |
| [19] |
杨明慧, 刘池洋. 鄂尔多斯中生代陆相盆地层序地层格架及多种能源矿产聚集[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(4): 563-569. Yang Minghui, Liu Chiyang. Sequence stratigraphic framework and its control on accumulation of various energy resources in the Mesozoic continental basins in Ordos[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2006, 27(4): 563-569. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.04.019 |
| [20] |
陈洪德, 倪新锋. 陇东地区三叠系延长组沉积层序及充填响应特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2006, 27(2): 143-151. Chen Hongde, Ni Xinfeng. Depositional sequence and filling response characteristics of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Longdong area[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2006, 27(2): 143-151. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2006.02.002 |
| [21] |
付金华, 李士祥, 侯雨庭, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组7段Ⅱ类页岩油风险勘探突破及其意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(1): 78-92. Fu Jinhua, Li Shixiang, Hou Yuting, et al. Breakthrough of risk exploration for ClassⅡ shale oil in Chang 7 member of the Yanchang Formation and its significance in the Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(1): 78-92. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.008 |
| [22] |
宋涛, 黄福喜, 汪少勇, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷侏罗系油气藏特征及勘探潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(3): 341-350. Song Tao, Huang Fuxi, Wang Shaoyong, et al. Characteristics and exploration potential of Jurassic oil and gas reservoirs in Mahu Sag of the Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(3): 341-350. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.03.007 |
| [23] |
许琳, 常秋生, 冯玲丽, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油储层特征及控制因素[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5): 649-660. Xu Lin, Chang Qiusheng, Feng Lingli, et al. The reservoir characteristics and control factors of shale oil in Permian Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5): 649-660. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.011 |
| [24] |
匡立春, 唐勇, 雷德文, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷斜坡区三叠系百口泉组扇控大面积岩性油藏勘探实践[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(6): 14-23. Kuang Lichun, Tang Yong, Lei Dewen, et al. Exploration of fan controlled large area lithologic oil reservoirs of Triassic Baikouquan Formation in slope zone of Mahu Depression in Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(6): 14-23. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2014.06.002 |
| [25] |
支东明, 唐勇, 郑孟林, 等. 玛湖凹陷源上砾岩大油区形成分布与勘探实践[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(1): 1-8. Zhi Dongming, Tang Yong, Zheng Menglin, et al. Discovery, distribution and exploration practice of large oil provinces of above source conglomerate in Mahu Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(1): 1-8. |
| [26] |
雷德文, 瞿建华, 安志渊, 等. 玛湖凹陷百口泉组低渗砂砾岩油气藏成藏条件及富集规律[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2015, 36(6): 642-647. Lei Dewen, Qu Jianhua, An Zhiyuan, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and enrichment regularity of low permeability glutenite reservoirs of Baikouquan Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2015, 36(6): 642-647. |
| [27] |
Suseno P H, Zakaria, Mujahidin N, et al. Contribution of Lahat Formation as hydrocarbon source rock in south Palembang area, South Sumatra, Indonesia[C]. IPA92-13-03. Jakarta: Indonesia Petroleum Association, 1992: 325-337.
|
| [28] |
Rashid H, Sosrowidjojo I B, Wildiarto F X. Musi platform and Palembang high: a new look at the petroleum system [C]. IPA98-1-107. Jakarta: Indonesia Petroleum Association, 1998: 265-276.
|
| [29] |
Van Wagoner J C. Sequence stratigraphy and marine to nonmarine facies architecture of foreland basin strata, Book Cliffs, Utah, USA: reply[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82(8): 1607-1618. |
| [30] |
林畅松, 潘元林, 肖建新, 等. 构造坡折带—断陷盆地层序分析和油气预测的重要概念[J]. 地球科学, 2000, 25(3): 260-266. Lin Changsong, Pan Yuanlin, Xiao Jianxin, et al. Structural slope-break zong: key concept for stratigraphic sequence analysis and petroleum forecasting in fault subsidence basins[J]. Earth Science, 2000, 25(3): 260-266. |
| [31] |
王宁, 陈宝宁, 翟建飞. 岩性油气藏形成的成藏指数[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(6): 4-5. Wang Ning, Chen Baoning, Zhai Jianfei. Reservoir forming index for the lithological reservoir[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(6): 4-5. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2000.06.004 |
| [32] |
高瑞祺, 蔡希源. 松辽盆地油气田形成条件与分布规律 [M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997: 329. Gao Ruiqi, Cai Xiyuan. Formation conditions and distribution pattern of the oil-gas fields in Songliao Basin [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1997: 329. |
| [33] |
李阳, 蔡进功, 刘建民. 东营凹陷下第三系高分辨率层序地层研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(2): 210-216. Li Yang, Cai Jingong, Liu Jianmin. High resolution sequence stratigraphy of Paleogene in Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(2): 210-216. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2002.02.005 |
| [34] |
唐勇, 孔玉华, 盛建红, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部缓坡型岩性地层油气藏成藏控制因素分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(3): 567-572. Tang Yong, Kong Yuhua, Sheng Jianhong, et al. Controlling factors of reservoir formation in ramp type lithostratigraphic reservoir in hinterland of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(3): 567-572. |
| [35] |
何文军, 王绪龙, 邹阳, 等. 准噶尔盆地石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2): 75-84. He Wenjun, Wang Xulong, Zou Yang, et al. The geological conditions, resource potential and exploration direction of oil in Junggar Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(2): 75-84. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.02.008 |
| [36] |
郑金海, 向才富, 王绪龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷侏罗系烃源岩特征与页岩气勘探潜力分析[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(1): 217-226. Zheng Jinhai, Xiang Caifu, Wang Xulong, et al. Characteristics of the Jurassic source rocks and their shale gas exploration potential in the Fukang Sag of the Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(1): 217-226. |
| [37] |
方世虎, 宋岩, 贾承造, 等. 准噶尔盆地白垩系底砾岩与油气成藏的关系[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26(5): 13-16. Fang Shihu, Song Yan, Jia Chengzao, et al. Relationship between Cretaceous basal conglomerate and oil/gas reservoiring in the Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(5): 13-16. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2006.05.005 |
| [38] |
谷云飞, 马明福, 苏世龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地白垩系岩相古地理[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(4): 337-347. Gu Yunfei, Ma Mingfu, Su Shilong, et al. Lithofacies paleogeography of the Cretaceous in the Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2003, 25(4): 337-347. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2003.04.004 |
| [39] |
赵霞, 于兴河, 黄兴文, 等. 准噶尔盆地石南地区清水河组一段层序地层特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(5): 716-721. Zhao Xia, Yu Xinghe, Huang Xingwen, et al. Sequence stratigraphic characteristics of the first member of Qingshuihe Formation in Shinan area, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(5): 716-721. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.05.009 |
| [40] |
斯春松, 王海东, 唐勇, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部白垩系清水河组清一段高分辨率层序地层特征及岩性油气藏预测[J]. 东华理工学院学报(自然科学版), 2005, 28(4): 329-333. Si Chunsong, Wang Haidong, Tang Yong, et al. High-resolution sequence stratigraphic characteristic and lithological reservoir prediction of section 1 of Qingshuihe Formation in the central of Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science), 2005, 28(4): 329-333. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2005.04.006 |
| [41] |
厚刚福, 瞿建华, 朱峰, 等. 古地貌对沉积体系和沉积微相的控制作用分析: 以准噶尔盆地腹部白垩系清水河组为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2018, 47(5): 1137-1144. Hou Gangfu, Qu Jianhua, Zhu Feng, et al. Controlling effect of paleogeomorphology on sedimentary system and sedimentary microfacies: a case study of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in the hinterland of Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2018, 47(5): 1137-1144. |
| [42] |
阿布力米提, 邹志文, 鲍海娟, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部地区白垩系清水河组物源分析[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2012, 33(6): 690-693. Abulimiti, Zou Zhiwen, Bao Haijuan, et al. Provenance analysis of Qingshuihe Formation of Cretaceous in hinterland of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2012, 33(6): 690-693. |
| [43] |
隋风贵, 郭玉新, 王宝言, 等. 东营凹陷深陷期构造坡折带与低位扇序列[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(2): 63-67. Sui Fenggui, Guo Yuxin, Wang Baoyan, et al. Fault break-slope and low stand fan sequence in Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(2): 63-67. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.02.014 |
| [44] |
任建业, 张青林, 陆永潮. 东营凹陷弧形断裂坡折带系统及其对低位域砂体的控制[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(4): 628-635. Ren Jianye, Zhang Qinglin, Lu Yongchao. Arc-shaped fault break slope system and its control on low stand systems sandbodies in Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(4): 628-635. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.04.012 |
| [45] |
何海清, 支东明, 唐勇, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷康探1井重大突破及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(2): 1-11. He Haiqing, Zhi Dongming, Tang Yong, et al. A great discovery of Well Kangtan 1 in the Fukang Sag in the Junggar Basin and its significance[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(2): 1-11. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.02.001 |
| [46] |
孙靖, 宋永, 宋明星, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部低凸起带油气成藏研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(6): 1219-1229. Sun Jing, Song Yong, Song Mingxing, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation of low uplift belt in central Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2016, 45(6): 1219-1229. |




