扩展功能
文章信息
- 刘彪, 康迅, 刘琳, 赵秀娟, 符玉梅, 田国振, 康乐, 夏乾峰
- LIU Biao, KANG Xun, LIU Lin, ZHAO Xiu-juan, FU Yu-mei, TIAN Guo-zhen, KANG Le, XIA Qian-feng
- 海南省白纹伊蚊中肠感染沃尔巴克氏体种群结构调查研究
- An investigation of population structure in the Aedes albopictus midgut infected with Wolbachia in Hainan province, China
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32(3): 355-360
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2021, 32(3): 355-360
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2021.03.019
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2020-11-15
2 海南医学院热带转化医学教育部重点实验室, 海南 海口 571199;
3 中国科学院动物研究所, 农业虫害鼠害综合治理研究国家重点实验室, 北京 100101
2 Key Laboratory of Tropical Translalional Medicine of Ministry of Education and School of Tropical Medicine and Laboratory Medicine, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, Hainan 571199, China;
3 State Key Laboratory of Integrated Management of Pest Insects and Rodents, Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
沃尔巴克氏体(Wolbachia)属于变形菌门(Proteobacteria),变形菌纲α亚门(Alphaproteobacteria),立克次体目(Rickettsiales),立克次体科(Rickettsiaceae)的沃尔巴克氏体属(Wolbachia),最早由Hertig和Wolbach[1]在尖音库蚊(Culex pipiens pipiens)中发现,1936年被正式命名为Wolbachia pipientis[2],是一种母系遗传的革兰阴性胞内菌,常见于节肢动物[3],约28%的蚊种中发现感染该共生菌[4]。白纹伊蚊(Aedes albopictus)作为重要的医学媒介蚊虫[5-8],可传播登革病毒(Dengue virus)、基孔肯雅病毒(Chikungunya virus)等,体内普遍携带沃尔巴克氏体[9-10]。目前以沃尔巴克氏体诱导宿主间杂交的胞质不相容(cytoplasmic incompatibility,CI)为基础发展出的昆虫不育技术(incompatible insect technique,IIT),已被用于媒介生物防治实验[11-12],且该菌因对人和环境友好,在蚊虫和蚊媒传染病的防控方面受到广泛关注[12-13]。
海南省属于热带海洋气候,年平均气温24.2 ℃、平均降雨量1 684 mm,自然条件非常适宜各类病媒生物尤其是蚊类的生长和繁殖[14],在国际旅游岛的建立和“一带一路”政策的背景推进下,海南省的旅游、贸易等人员往来频繁,为登革热等蚊媒传染病提供了有利条件,出现了严重的疾病传播隐患,也为防控带来严峻挑战。本文应用HiSeq 4000系统对中肠微生物组16S rRNA基因的V3-V4高变区进行高通量测序[15],调查海南省白纹伊蚊中肠感染的沃尔巴克氏体种群结构以及进化史,旨在为将来应用沃尔巴克氏体感染蚊虫作为生物防控蚊虫和蚊媒传染病策略的实施提供理论基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料功夫小帅诱蚊灯(LTS-MO2,武汉吉星医疗科技有限公司)、Mighty Prep reagent for DNA试剂盒〔Cat#9182,宝生物工程(大连)有限公司〕、DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit抽提试剂盒(QIAGEN:69506,北京诺博莱德科技有限公司)、SCIENTZ-48高通量组织研磨仪(SCIENTZ-48,宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司)、基因扩增仪(Biometra Tone 96,德国耶拿分析仪器股份公司)、解剖镜(AE2000,麦克奥迪实业集团有限公司)、蚊笼、吸蚊器、75%乙醇溶液、镊子等。
1.2 白纹伊蚊标本采集鉴定及样本处理蚊种的采集地点根据文献报道[16],在2018年7-10月以海南岛东部、北部、南部、中部4个地理方位选取台地、平原、山地、滨海等典型地貌为采样地。每个采集地选取2~3个样点,采集时间为2~3 d。选取海南岛东部的陵水县,北部的海口和文昌市,南部的三亚市和乐东县,中部的屯昌及定安县和五指山市为采样区域。通过诱蚊灯法和人诱法捕捉成蚊[17-18],吸蚊器采集成蚊置于-20 ℃冰箱约5 min,待晕厥,通过形态学鉴定蚊种[19],选取雌性白纹伊蚊用无菌水冲洗3次,75%乙醇溶液消毒10 min,再用无菌水冲洗5次,0.8%盐水冲洗1次,去除乙醇溶液,在无菌水中解剖[20]。拔下蚊腿,每只蚊虫的腿分别放入装有95%乙醇溶液的96孔板孔内,做好标记,4 ℃保存,预备提取成蚊基因组。并对相应的单只成蚊解剖中肠,分别使用冻存管单只保存于-80 ℃,备用[21]。
1.3 成蚊DNA制备及PCR扩增将1.2步骤保存的单只蚊的蚊腿从95%乙醇溶液取出放入1.5 ml EP管中,取100 μl的Mighty Prep reagent for DNA添加到蚊腿被液体浸没,95 ℃水浴加热10 min,12 000 r/min离心2 min(13 201×g),取上清液作为PCR反应的模板。依据参考文献使用多细胞无脊椎动物细胞色素C氧化酶亚基Ⅰ(COⅠ)基因的通用引物[22],预期的PCR扩增条带片段大小约650 bp,正向引物LOC1490:5'-GGTCAACAAATCATAAAGATATTGG- 3',反向引物HCO2198:5'-TAAACTTCAGGGTGACCAAAAAATCA-3',PCR反应体系50 μl:Mix 25 μl,ddH2O 22.5 μl,R 0.75 μl,F 0.75 μl,DNA 1 μl。反应条件:初始变性94 ℃5 min,变性94 ℃1 min,退火45 ℃1 min,延伸72 ℃ 1 min,35个循环;终延伸72 ℃ 10 min,12 ℃保存。PCR产物在1%琼脂糖凝胶上电泳分离,确定PCR结果阳性,PCR产物送北京博云华康基因科技有限公司测序。COⅠ基因测序结果反馈后,使用COⅠ基因序列在美国国立生物技术信息中心(NCBI)对蚊种BLAST进行比对分子鉴定(http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi),并上传序列到NCBI获得GenBank登录号。
1.4 中肠微生物组DNA制备从-80 ℃取出1.2步骤保存的白纹伊蚊中肠样品,每个地点使用30只中肠进行实验,每10只蚊虫中肠合并为1组,重复3组。采用DNA提取试剂盒(QIAGEN:69506)提取合并蚊虫中肠的总微生物基因组DNA,-80 ℃保存,备用。
1.5 16S rRNA测定与生物信息分析应用HiSeq 4000系统对中肠微生物组16S rRNA基因的V3-V4高变区高通量测序[17],使用Greengene数据库比对。每个地点随机抽取1条沃尔巴克氏体序列作为代表,再次BLAST进行菌种鉴定,序列上传NCBI获得GenBank登录号,利用MEGA 7.0软件计算遗传距离。
1.6 统计学分析应用Excel 2019软件整理数据,使用SPSS 21.0软件分析数据,计数资料分析采用率或构成比之间的χ2检验,比较不同地区沃尔巴克氏体丰度的差异,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
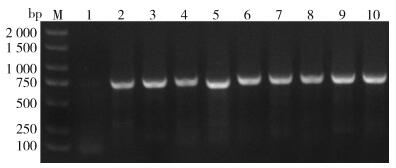
2 结果 2.1 蚊种鉴定结果蚊种的COⅠ基因PCR产物条带大小约为650 bp,其各地代表样品的电泳结果如图 1所示,产物送北京博云华康基因科技有限公司测序,NCBI序列比对鉴定,结合形态学鉴定可确定进入中肠微生物DNA高通量测序的蚊种均为雌性白纹伊蚊,各地区代表蚊种序列的GenBank登录号为:海口(MT890464)、屯昌(MT906353)、三亚(MT906351)、文昌(MT906350)、定安(MT890489)、陵水(MT906156)、乐东(MT890465)、五指山(MT906352)。依据蚊种鉴定结果合并中肠,10只/组、重复3组。
|
| 注:M表示DNA Marker;1阴性对照;2阳性对照;3~10表示海口、屯昌、三亚、文昌、定安、陵水、乐东、五指山8个县(市)白纹伊蚊的代表蚊种PCR扩增细胞色素C氧化酶亚基Ⅰ基因产物的电泳结果。 图 1 蚊虫样本细胞色素C氧化酶亚基Ⅰ基因的PCR扩增产物 Figure 1 PCR amplification products of the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene in mosquito samples |
| |
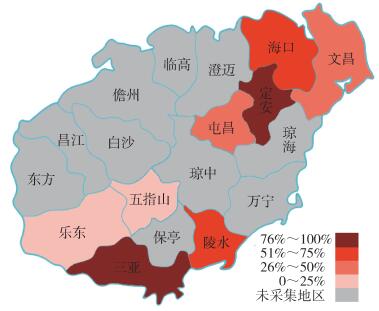
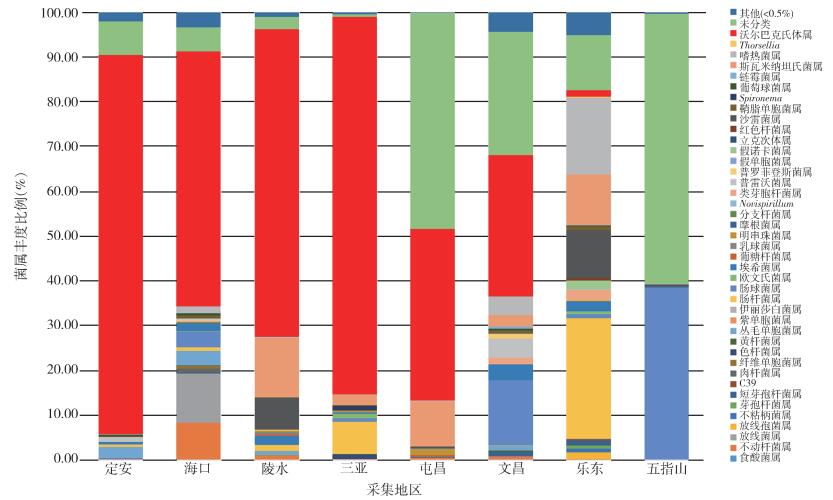
应用HiSeq 4000系统平台对16S rRNA V3-V4区高通量测序,3个组的数据通过质控分析处理后,合并分类至属,沃尔巴克氏体各地区丰度分布见图 2。沃尔巴克氏体的丰度占比以定安县最高(84.67%),其次为三亚、陵水、海口、屯昌和文昌市(县),分别占80.34%、68.77%、56.89%、38.28%和31.57%,丰度较低的为乐东县和五指山市,分别占1.50%和0.01%。而五指山市的肠球菌属占38.40%,乐东县的肠杆菌属占26.93%,为优势菌属,同时占比较高的还有乐东县的嗜热杆菌属(Thermus)、沙雷菌属(Serratia)和斯瓦米纳坦菌属(Swaminathania),分别占17.09%、10.79%和11.37%。且五指山市还有近60%的菌株未在检出的41个属种中,各菌属占比见图 3。应用χ2检验对沃尔巴克氏体的丰度在总体样品中分析,发现其含量差异有统计学意义(χ2=322.950,P < 0.001)。不同地区的沃尔巴克氏体占比两两χ2检验发现,定安与海口、乐东、屯昌、文昌、五指山、陵水县(市)(P < 0.05),海口与乐东、三亚、文昌、五指山市(县)(P < 0.05),乐东与陵水、三亚、屯昌、文昌市(县)(P < 0.05),陵水与屯昌、文昌、五指山、三亚市(县)(P < 0.05),三亚与屯昌、文昌、五指山市(P < 0.05),五指山与屯昌、文昌市(县)(P < 0.05),绝大部分差异有统计学意义,仅定安县与三亚市(P > 0.05),海口市与陵水县(P > 0.05),乐东县与五指山市(P > 0.05),屯昌县与文昌市(P > 0.05)差异无统计学意义。见表 1。
|
| 注:彩色区域为采集样品区域,颜色由浅到深代表沃尔巴克氏体丰度由低到高;灰色区域为未采集区域。 图 2 海南省不同地区白纹伊蚊沃尔巴克氏体丰度 Figure 2 Wolbachia abundance in Aedes albopictus in different areas of Hainan province |
| |
|
| 图 3 海南省不同地区白纹伊蚊中肠微生物丰度 Figure 3 Abundance of microorganisms in the midgut of Aedes albopictus in different areas of Hainan province |
| |
|
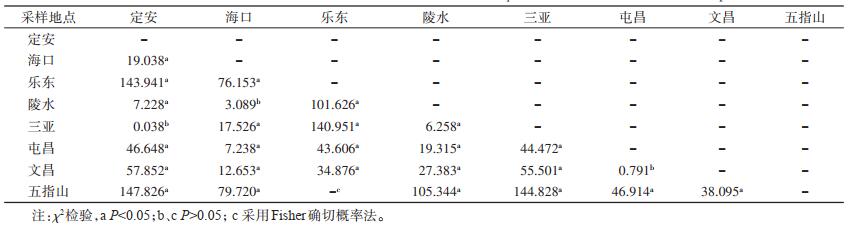
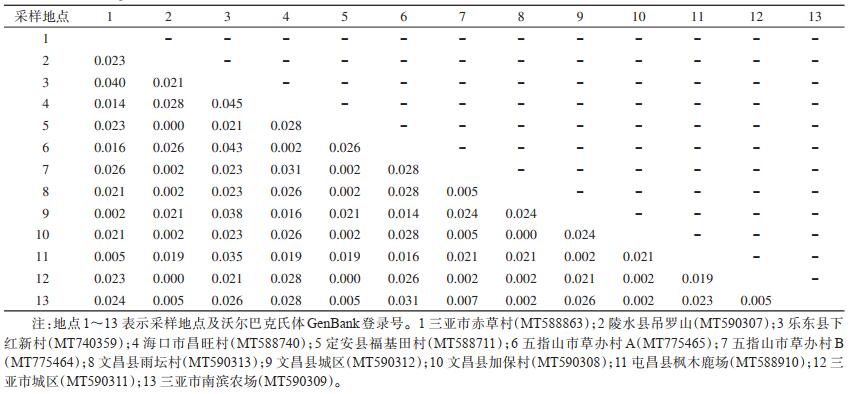
通过MEGA 7.0软件对各采样点抽取的序列分析可见,以乐东县下红新村与海口市昌旺村遗传距离最大(0.045),亲缘关系较远的还有乐东县下红新村与三亚市赤草村、五指山市草办村A、文昌县城区、屯昌县枫木鹿场,海口市昌旺村与五指山市草办村B,五指山市草办村A与屯昌县枫木鹿场,两两遗传距离均 > 0.030,而陵水县吊罗山与定安县福基田村、文昌县雨坛村与文昌县加保村的序列完全相同,具体遗传距离见表 2。
|
沃尔巴克氏体是一种母系遗传的革兰阴性菌,66.00%的节肢动物中有感染[3],目前基于CI为基础发展的IIT技术在白纹伊蚊种群控制研究中已经受到广泛关注[11],白纹伊蚊作为重要的医学媒介蚊虫,体内普遍携带沃尔巴克氏体[5-10]。故研究白纹伊蚊感染沃尔巴克氏体的丰度、种群结构,对IIT技术在防控蚊虫和蚊媒疾病的应用显得尤为重要,我们此次基于16S rRNA的V3-V4高变区对沃尔巴克氏体检测分析,发现沃尔巴克氏体作为白纹伊蚊肠道优势菌群的地区有定安(84.67%)、三亚(80.34%)、陵水(68.77%)、海口(56.89%)市(县),与王政艳等[23]报道相符,但也出现乐东县(1.50%)和五指山市(0.01%)感染率极低的情况,而五指山市肠球菌属(Enterococcus)为主要菌属(38.40%),乐东县肠杆菌属(Enterobacter)也达26.93%,这2种菌属在白纹伊蚊肠道的丰度明显高于其他地区。已有研究表明昆虫肠道微生物Asaia菌可以对沃尔巴克氏体产生共生竞争关系[24],虽然还未有在白纹伊蚊中的相关报道,但这说明昆虫肠道中存在细菌-细菌之间的某种互作关系,或是种群竞争,还有待进一步研究。还有研究表明白纹伊蚊对沃尔巴克氏体不同型别存在共生排斥[25],不同经纬度的特定环境可能与肠道细菌的差异有关,也不排除是影响其感染的因素之一。
在此次采集的样品中,不同区域的蚊虫肠道感染的菌群丰度比,运用χ2检验,提示各地区的沃尔巴克氏体在肠道菌群的丰度占比差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。研究表明,蚊种感染不同型别的沃尔巴克氏体,其丰度的差异,对IIT技术在蚊种总群防控的应用效果存在一定影响[26],具体的作用机制有待进一步探讨。
本研究使用的是16S rRNA的V3-V4高变区,在9个变异区中进化速度相对适中,能较好地满足属种的鉴定[27]。利用MEGA 7.0软件通过遗传距离分析可见,各地区沃尔巴克氏体碱基序列存在差异,乐东县下红新村与海口市昌旺村的遗传距离最远(0.045),这与经纬度位置相符。乐东县下红新村与三亚市赤草村、五指山市草办村A、文昌县城区、屯昌县枫木鹿场,海口市昌旺村与五指山市草办村B,五指山市草办村A与屯昌县枫木鹿场的亲缘关系较乐东县下红新村与海口市昌旺村稍近,而陵水县吊罗山与定安县福基田村、文昌县雨坛村与文昌县加保村基因序列完全相同,说明区域内菌株存在稳定的传代,而各地区间存在菌种的交流,这与武雅楠等[28]所报道的同地区相同蚊种存在感染不同类型的菌株相符。
综上所述,海南省的白纹伊蚊中肠内,大部分地区的沃尔巴克氏体作为优势菌种,但也出现乐东县和五指山市感染率极低的情况,或许这2个地区为基于CI为基础发展的IIT技术研究可提供便利。通过统计学分析发现,不同地区白纹伊蚊沃尔巴克氏体构成比在肠道微生物的构成差异有统计学意义,遗传距离显示不同地区存在菌株的交换,各地区菌株存在遗传多样性。应指出的是本研究采样未全域覆盖,以上研究结果并不排除在其他未覆盖地区存在不同或与现有结果不一致的情况,增加采样区域,研究结果能更具代表性。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
Hertig M, Wolbach SB. Studies on rickettsia-like micro-organisms in insects[J]. J Med Res, 1924, 44(3): 329-374. |
| [2] |
Hertig M. The rickettsia, Wolbachia pipientis (gen. et sp.n.) and associated inclusions of the mosquito, Culex pipiens[J]. Parasitology, 1936, 28(4): 453-486. DOI:10.1017/s0031182000022666 |
| [3] |
Werren JH, Baldo L, Clark ME. Wolbachia: master manipulators of invertebrate biology[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2008, 6(10): 741-751. DOI:10.1038/nrmicro1969 |
| [4] |
潘晓玲, 刘起勇, 奚志勇. 基于昆虫共生菌沃尔巴克氏体的蚊媒和蚊媒病控制研究进展[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2014, 25(1): 1-7. Pan XL, Liu QY, Xi ZY. Advance in developing Wolbachia as a mean to control mosquito and mosquito-borne diseases[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2014, 25(1): 1-7. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.4692.2014.01.001 |
| [5] |
Brady OJ, Golding N, Pigott DM, et al. Global temperature constraints on Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus persistence and competence for dengue virus transmission[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2014, 7(1): 338. DOI:10.1186/1756-3305-7-338 |
| [6] |
Lambrechts L, Scott TW, Gubler DJ. Consequences of the expanding global distribution of Aedes albopictus for dengue virus transmission[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2010, 4(5): e646. DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000646 |
| [7] |
Paupy C, Ollomo B, Kamgang B, et al. Comparative role of Aedes albopictus and Ae. aegypti in the emergence of dengue and chikungunya in central Africa[J]. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis, 2010, 10(3): 259-266. DOI:10.1089/vbz.2009.0005 |
| [8] |
Wu D, Wu J, Zhang QL, et al. Chikungunya outbreak in Guangdong province, China, 2010[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2012, 18(3): 493-495. DOI:10.3201/eid1803.110034 |
| [9] |
Moretti R, Calvitti M. Male mating performance and cytoplasmic incompatibility in a wPip Wolbachia trans-infected line of Aedes albopictus (Stegomyia albopicta)[J]. Med Vet Entomol, 2013, 27(4): 377-386. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2915.2012.01061.x |
| [10] |
宋社吾, 赵彤言, 董言德, 等. 我国蚊虫体内感染的Wolbachia的wsp基因序列测定与分析[J]. 昆虫学报, 2002, 45(5): 571-577. Song SW, Zhao TY, Dong YD, et al. Sequencing and sequence analysis of the wsp gene of Wolbachia in Chinese mosquitoes[J]. Acta Entomol Sin, 2002, 45(5): 571-577. DOI:10.16380/j.kcxb.2002.05.003 |
| [11] |
Zabalou S, Riegler M, Theodorakopoulou M, et al. Wolbachia-induced cytoplasmic incompatibility as a means for insect pest population control[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2004, 101(42): 15042-15045. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0403853101 |
| [12] |
Bourtzis K, Dobson SL, Xi ZY, et al. Harnessing mosquito-Wolbachia symbiosis for vector and disease control[J]. Acta Trop, 2014, 132 Suppl: S150-163. DOI:10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.11.004 |
| [13] |
郑小英, 刘起勇, 奚志勇. 基于沃尔巴克氏体的蚊媒和蚊媒病控制的生物安全性[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2014, 25(2): 93-96. Zheng XY, Liu QY, Xi ZY. The biosafety concerns of Wolbachia-mediated biological control of mosquitoes and mosquito-borne diseases[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2014, 25(2): 93-96. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.4692.2014.02.001 |
| [14] |
赵宣, 侯乃旭, 陈晨, 等. 海南省传播病毒蚊媒种类及蚊媒病毒流行情况分析[J]. 海南医学, 2017, 28(7): 1174-1179. Zhao X, Hou NX, Chen C, et al. Analysis of mosquito vector species and epidemic situation of mosquito-borne viruses in Hainan province[J]. Hainan Med J, 2017, 28(7): 1174-1179. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2017.07.052 |
| [15] |
Fadrosh DW, Ma B, Gajer P, et al. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform[J]. Microbiome, 2014, 2(1): 6. DOI:10.1186/2049-2618-2-6 |
| [16] |
Muturi EJ, Ramirez JL, Rooney AP, et al. Comparative analysis of gut microbiota of mosquito communities in central Illinois[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2017, 11(2): e0005377. DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0005377 |
| [17] |
周毅彬, 冷培恩, 朱江, 等. 人诱法和CO2诱捕法在白纹伊蚊监测中的比较研究[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2011, 17(3): 171-173. Zhou YB, Leng PE, Zhu J, et al. Comparison study on human-bait and CO2 trap in Aedes albopictus surveillance[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2011, 17(3): 171-173. DOI:10.19821/j.1671-2781.2011.03.003 |
| [18] |
郭玉红, 吴海霞, 刘小波, 等. 2018年全国媒介蚊虫监测报告[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30(2): 128-133. Guo YH, Wu HX, Liu XB, et al. National vectors surveillance report on mosquitoes in China, 2018[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30(2): 128-133. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2019.02.003 |
| [19] |
陆宝麟. 中国动物志. 昆虫纲. 第八卷. 双翅目: 蚊科(上卷)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 243-245. Lu BL. Zoology of China, insecta, volume 8. Diptera, mosquitoidae (vol. 1)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 243-245. |
| [20] |
Vavre F, Fleury F, Lepetit D, et al. Phylogenetic evidence for horizontal transmission of Wolbachia in host-parasitoid associations[J]. Mol Biol Evol, 1999, 16(12): 1711-1723. DOI:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026084 |
| [21] |
Zouache K, Raharimalala FN, Raquin V, et al. Bacterial diversity of field-caught mosquitoes, Aedes albopictus and Ae. aegypti, from different geographic regions of Madagascar[J]. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 2011, 75(3): 377-389. DOI:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.01012.x |
| [22] |
周东. 摇蚊(双翅目: 摇蚊科)成幼虫形态配对及对水质评价作用的研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2019. DOI: 10.27314/d.cnki.gsscu.2019.000419.ZhouD. Study on the assocation of adult and larval stage of chironomid (Diptera: Chironomidae) and its effect on water quality evaluation[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2019. DOI: 10.27314/d.cnki.gsscu.2019.000419. |
| [23] |
王政艳, 梁秋果, 杨茜, 等. 贵州白纹伊蚊感染沃尔巴克氏体以及WO噬菌体的初步调查[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2020, 15(1): 69-73, 77. Wang ZY, Liang QG, Yang Q, et al. A preliminary investigation of symbiotic bacteria (Wolbachia) and the WO phage infecting Aedes albopictus in Guizhou province[J]. J Parasit Biol, 2020, 15(1): 69-73, 77. DOI:10.13350/j.cjpb.200114 |
| [24] |
Baldini F, Segata N, Pompon J, et al. Evidence of natural Wolbachia infections in field populations of Anopheles gambiae[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5(1): 3985. DOI:10.1038/ncomms4985 |
| [25] |
Turelli M, Barton NH. Deploying dengue-suppressing Wolbachia: robust models predict slow but effective spatial spread in Aedes aegypti[J]. Theor Popul Biol, 2017, 115: 45-60. DOI:10.1016/j.tpb.2017.03.003 |
| [26] |
Haygood R, Turelli M. Evolution of incompatibility-inducing microbes in subdivided host populations[J]. Evolution, 2009, 63(2): 432-447. DOI:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00550.x |
| [27] |
刘明艳, 马嘉晗, 李瑜, 等. 16S rRNA基因高变区V4和V3-V4及测序深度对油藏细菌菌群分析的影响[J]. 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(2): 440-449. Liu MY, Ma JH, Li Y, et al. Influence of 16S rRNA gene V4 and V3-V4 sequencing and sequencing depth on unraveling bacterial communities inhabiting oil reservoirs[J]. Microbiol China, 2020, 47(2): 440-449. DOI:10.13344/j.microbiol.china.190251 |
| [28] |
武雅楠, 文赛, 梁秋果, 等. 贵阳市常见蚊虫共生菌沃尔巴克氏体的初步调查[J]. 贵州医科大学学报, 2017, 42(10): 1130-1133. Wu YN, Wen S, Liang QG, et al. The preliminary investigation on symbiotic bacteria (Wolbachia) of common mosquito in Guiyang[J]. J Guizhou Med Univ, 2017, 42(10): 1130-1133. DOI:10.19367/j.cnki.1000-2707.2017.10.004 |
 2021, Vol. 32
2021, Vol. 32


