扩展功能
文章信息
- 郭荣, 谢木西丁·艾麦提, 党辉, 马合木提, 排孜拉·海力力, 艾山吐尔·马坎, 拜合提牙·赛里木哈孜, 周志刚, 布仁明德, 黎唯, 崔燕
- GUO Rong, AIMAITI Xiemuxiding, DANG Hui, Mahemuti, HAILILI Paizila, MAKAN Aishantuer, SAILIMUHAZI Baihetiya, ZHOU Zhi-gang, Burenmingde, LI Wei, CUI Yan
- 中亚边境区域新疆天山南脉、帕米尔高原东部动物鼠疫疫情分析
- An epidemic analysis of the animal plague in southern Tianshan mountains in Xinjiang, China and eastern Pamir plateau of Central Asia's border areas
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31(1): 16-20
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2020, 31(1): 16-20
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2020.01.004
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2019-09-22
- 网络出版时间: 2019-12-30 09:37
2 克孜勒苏柯尔克孜自治州疾病预防控制中心, 新疆 克州 845000
2 Kizilsu Kirghiz Autonomous Prefecture Center for Disease Control and Prevention
塔吉克斯坦共和国和吉尔吉斯共和国是我国在中亚地区的重要邻国,中-塔、中-吉边境地区,是历史上“丝绸之路”的重要通道,有研究表明,古代的鼠疫、炭疽和麻风病就是沿着“丝绸之路”传播的[1-4]。在“一带一路”的建设和开发中,该边境地区将成为新疆维吾尔自治区(新疆)经济建设的重要区域。然而,该地区地形复杂,生境多样,为啮齿动物提供了多种栖息环境,拥有多种类型的鼠疫自然疫源地,对当地经济和公共卫生安全造成威胁。
克孜勒苏柯尔克孜自治州(克州)位于新疆西南部,地跨天山山脉西南部、帕米尔高原东部、昆仑山北坡和塔里木盆地西北缘。克州北部和西部分别与吉尔吉斯共和国、塔吉克斯坦共和国两国接壤,边境线长达1 195 km[5]。新疆共有5种类型鼠疫自然疫源地[6],克州有2种类型的鼠疫自然疫源地,即帕米尔高原-阿赖山红旱獭(Mamota caudata)鼠疫自然疫源地和南天山灰旱獭(M. baibacina)鼠疫自然疫源地,占地3.58万km2。由于两大疫源地所处的生境不同,各疫源地主要宿主、媒介优势种群也有所不同。本研究利用中国疾病预防控制信息系统中克州地区境内鼠疫网报数据,采用流行病学、统计学方法并结合地理地貌特征,对该地区2014-2018年鼠疫疫情进行了系统分析。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料旱獭脏器、旱獭血清、牧犬血清及蚤类均采自克州地区。免疫学检测试剂为中国疾病预防控制中心鼠疫布鲁氏菌病防治基地统一生产配发的鼠疫间接血凝试剂盒。
1.2 方法鼠疫耶尔森氏菌(鼠疫菌)分离、鼠疫菌F1抗体及媒介检测均按照《鼠疫诊断标准》WS 279-2008执行[7]。采用流行病学、统计学方法并结合克州地区地理地貌特征,分析近5年来该地区动物间鼠疫流行状况。
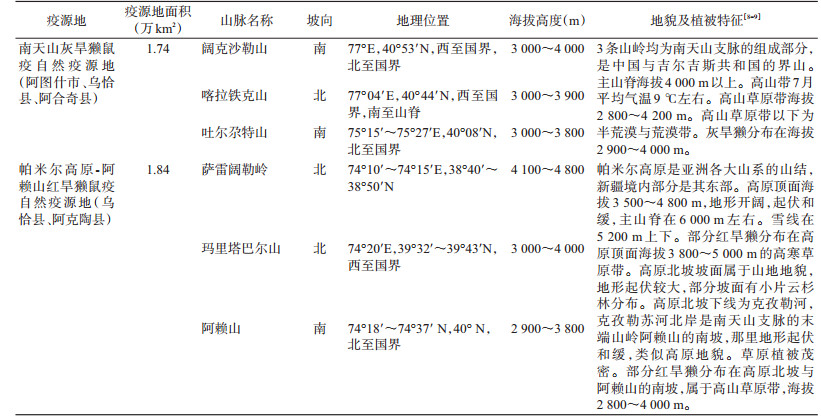
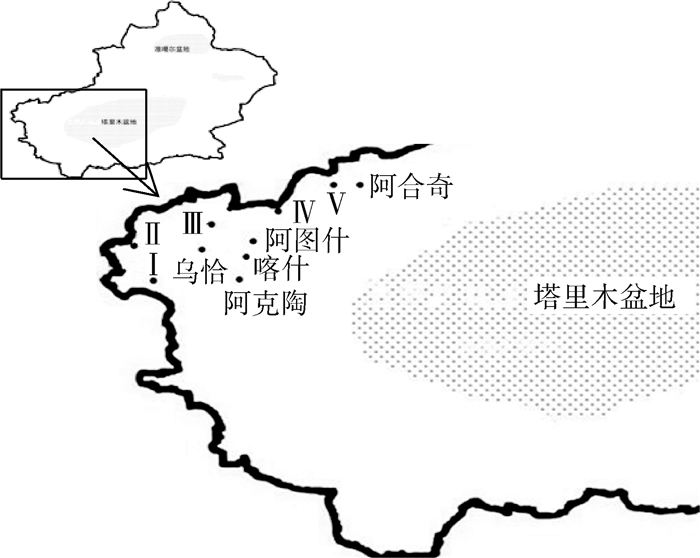
2 结果 2.1 疫源地空间分布克州地区有2种类型的鼠疫自然疫源地,设有5个鼠疫监测点,地理地貌特征见表 1,鼠疫疫源地及监测点的空间布局如图 1所示。
 |
|
| 注:Ⅰ.阿克陶县监测点木吉乡;Ⅱ.克州监测点吉根乡;Ⅲ.乌恰县监测点托云乡;Ⅳ.阿图什市监测点吐古买提乡;Ⅴ.阿合奇县监测点哈拉布拉克乡。 图 1 新疆克孜勒苏柯尔克孜自治州鼠疫自然疫源地空间分布示意图 Figure 1 Schematic diagram of spatial distribution of natural plague foci in Kizilsu Kirghiz autonomous prefecture, Xinjiang |
| |
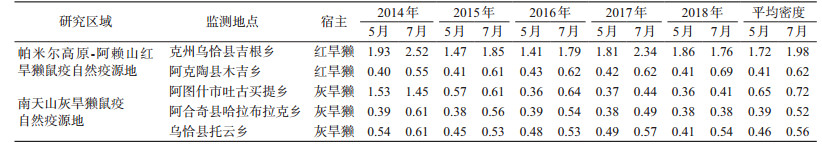
依据《新疆鼠疫监测工作实施方案》要求,于2014-2018年每年的5和7月采用路线法对克州地区鼠疫监测范围内的主要宿主动物密度进行调查,结果显示,除克州鼠防监测点、阿图什市鼠防监测点个别年份5月旱獭密度高于7月,其余年份5个监测点旱獭密度均是7月高于5月或与之持平。位于乌恰县境内的克州鼠疫监测点旱獭密度均高于其他监测点(表 2)。
 |
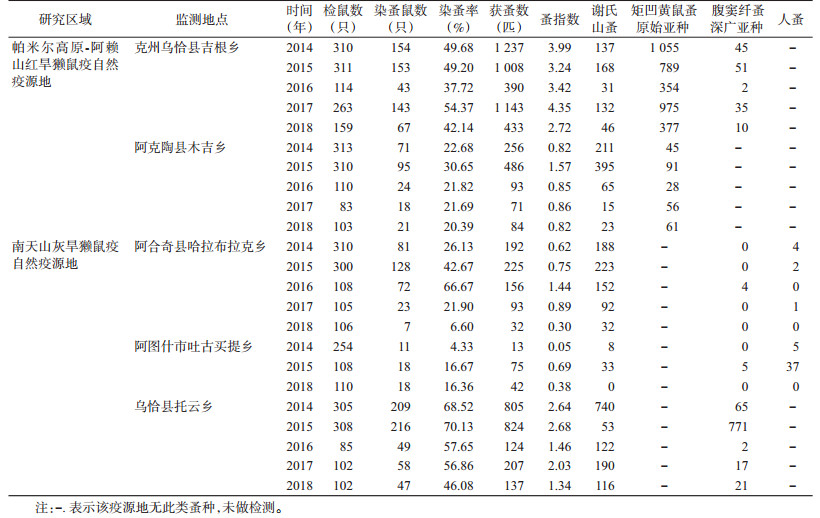
从2014-2018年的媒介监测结果看,帕米尔高原-阿赖山红旱獭鼠疫自然疫源地优势蚤种为矩凹黄鼠蚤原始亚种(Citellophilus lebedewi princeps)、谢氏山蚤(Oropsylla silantiewi)和腹窦纤蚤深广亚种(Rhadinopsylla li ventricosa);南天山灰旱獭鼠疫自然疫源地优势蚤种为谢氏山蚤和腹窦纤蚤深广亚种。监测数据显示,克州和乌恰县监测点历年的染蚤率、蚤指数均高于其他监测点。各监测点2014-2018年每年的染蚤率和蚤指数相对较平稳,见表 3。
 |
2014-2018年,克州监测点共采集犬血清194份,经间接血凝试验(IHA)检测鼠疫F1抗体,阳性血清26份,阳性率为13.40%;乌恰县共采集犬血清126份,阳性血清4份,阳性率为3.17%;阿图什市共采集犬血清134份,阳性血清3份,阳性率为2.24%;阿克陶和阿合奇分别采集犬血清128和180份,检测结果均为阴性,见表 4。
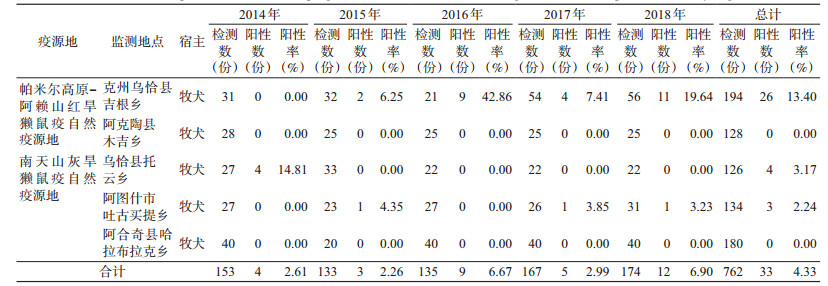 |
2014-2018年,克州5个鼠疫监测点共捕获旱獭4 962只,未分离出鼠疫菌;共发现病死旱獭36只,分离出3株鼠疫菌,检出率为8.33%。其中克州地区鼠疫监测点于2016-2017年连续2年从自毙病死旱獭体内分离出鼠疫菌,检出率为13.33%。阿图什市鼠疫监测点于2016年从自毙病死旱獭体内分离出1株鼠疫菌,检出率为10.00%,见表 5。
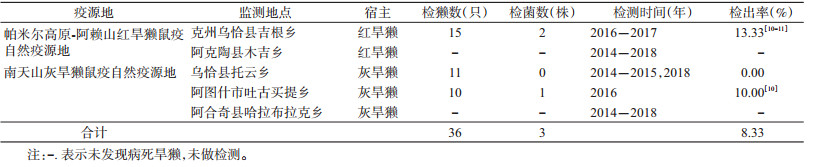 |
克州早在20世纪二三十年代就曾暴发过人间鼠疫,病死率高达99.19%[9]。克州西北部与吉尔吉斯共和国、塔吉克斯坦共和国接壤,境内拥有吐尔尕特和伊尔克什坦两大口岸,人口流动量大,经济贸易往来频繁,极大地增加了感染鼠疫的可能性和危险性。2017年6月,机场工作人员在由塔吉克斯坦共和国杜尚别飞抵乌鲁木齐国际机场的CZ6020次航班的飞机货舱内发现1只活鼠[12],虽然未在其体内检测出鼠疫菌,但提示存在输入性风险的可能。Kausrud等[13]使用回归模型对气候变化进行了预测,结果显示,鼠疫的流行可能在中亚地区变得更加频繁,输入鼠疫的风险也随之可能增加。尽管天山南脉和帕米尔高原鼠疫自然疫源地的动物间鼠疫流行态势趋于平缓,但鼠疫疫源地的宿主和媒介组成稳定,说明鼠疫疫源地的疫源性依然存在,局部范围内的动物间鼠疫流行仍会时有发生[14],鼠疫防制工作仍是防病工作的重中之重。1994年发生在印度的“苏拉特风暴”就给人们留下了惨痛教训[15]。
目前,用于鼠疫菌实验室检测方法较多[16-19],加之一些动物鼠疫流行强度预警模型的使用[20-21],为突发疫情能够及时准确地预判提供依据。未来需做好鼠疫防制工作的关口前移,积极主动开展动物间鼠疫监测,掌握动物间鼠疫的流行强度、分布规律等,为鼠疫流行的风险预测提供数据支持。
志谢 新疆维吾尔自治区疾病预防控制中心大数据培训班在数据的采集和应用中给予鼎力支持,特此志谢| [1] |
Cui YJ, Yu C, Yan YF, et al. Historical variations in mutation rate in an epidemic pathogen, Yersinia pestis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(2): 577-582. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1205750110 |
| [2] |
Morelli G, Song YJ, Mazzoni CJ, et al. Yersinia pestis genome sequencing identifies patterns of global phylogenetic diversity[J]. Nat Genet, 2010, 42(12): 1140-1143. DOI:10.1038/ng.705 |
| [3] |
杨瑞馥. 丝绸之路与传染病传播[J]. 中国基础科学, 2013, 15(6): 16-18. Yang RF. Silk road and spread of infectious diseases[J]. China Basic Sci, 2013, 15(6): 16-18. DOI:10.3969/J.ISSN.1009-2412.2013.06.003 |
| [4] |
张华荣, 文海燕, 彭彦卿, 等. "一带一路"与口岸公共卫生[J]. 中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2017, 40(1): 60-63. Zhang HR, Wen HY, Peng YQ, et al. "The belt and road" and public health at ports[J]. Chin J Front Health Quar, 2017, 40(1): 60-63. DOI:10.16408/J.1004-9770.2017.01.016 |
| [5] |
克孜勒苏柯尔克孜自治州人民网[EB/OL]. (2018-04-08)[2019-03-25]. http://www.xjkz.gov.cn/kzinto.htm. People's Network of Kizilsu Kirghiz Autonomous Prefecture[EB/OL]. (2018-04-08)[2019-03-25]. http://www.xjkz.gov.cn/kzinto.htm. |
| [6] |
曹汉礼, 张渝疆, 戴翔. 新疆鼠疫防治手册[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆科学技术出版社, 2007: 1-20. Cao HL, Zhang YJ, Dai X. Xinjiang plague control manual[M]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Science and Technology Press, 2007: 1-20. |
| [7] |
中华人民共和国卫生部卫生应急办公室, 中国疾病预防控制中心. 鼠疫防控应急手册[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2009: 340-343. Health Emergency Office of the People's Republic of China, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Emergency manual of plague prevention and control[M]. Beijing: Peking University Medical Press, 2009: 340-343. |
| [8] |
滕云峰, 张鸿猷, 谢杏初. 新疆鼠疫自然疫源地[J]. 地方病通报, 1994, 9(3): 35-41. Teng YF, Zhang HY, Xie XC. The natural foci of plague in Xinjiang, China[J]. Endem Dis Bull, 1994, 9(3): 35-41. |
| [9] |
张鸿猷, 腾云峰. 新疆鼠疫[M]. 乌鲁木齐: 地方病通报编辑部, 1994: 1-7. Zhang HY, Teng YF. Xinjiang plague[M]. Urumqi: Editorial Department of Endemic Disease Prevention, 1994: 1-7. |
| [10] |
张贵军, 段天一, 邵奎东, 等. 全国2016年鼠疫监测结果[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2017, 32(增刊): 1-7. Zhang GJ, Duan TY, Shao KD, et al. National plague surveillance results in 2016[J]. Chin J Endemiol, 2017, 32(Suppl 1): 1-17. |
| [11] |
雒涛, 李博, 布仁明德, 等. 新疆维吾尔自治区2017年鼠疫监测结果[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志, 2018, 33(增刊1): 58-61. Luo T, Li B, Burenmingde, et al. Plague surveillance results of the Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region in 2017[J]. Chin J Endemiol, 2018, 33(Suppl 1): 58-61. |
| [12] |
曹竹亭, 李江, 刘戈, 等. 新疆口岸首次从入境航空器内发现活鼠[J]. 中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2018, 41(1): 76. Cao ZT, Li J, Liu G, et al. Live rats discovered from inbound aircraft at Xinjiang port for the first time[J]. Chin J Front Health Quar, 2018, 41(1): 76. DOI:10.16408/J.1004-9770.2018.01.023 |
| [13] |
Kausrud KL, Viljugrein H, Frigessi A, et al. Climatically driven synchrony of gerbil populations allows large-scale plague outbreaks[J]. Proc Biol Sci, 2007, 274(1621): 1963-1969. DOI:10.1098/rspb.2007.0568 |
| [14] |
曹汉礼, 张渝疆. 2000-2009年新疆山地鼠疫自然疫源地动物鼠疫疫情形势分析[J]. 疾病预防控制通报, 2011, 26(1): 1-6. Cao HL, Zhang YJ. Analysis of epidemic situation of animal plague in mountainous plague natural foci in Xinjiang from 2000 to 2009[J]. Bull Dis Control Prev, 2011, 26(1): 1-6. |
| [15] |
俞东征. 苏拉特风暴过后[J]. 地方病通报, 1995, 10(2): 1-5. Yu DZ. After storm Surat[J]. Endem Dis Bull, 1995, 10(2): 1-5. |
| [16] |
王成祥, 梁坤, 王信惠, 等. 鼠疫检验新技术在乌鲁木齐县灰旱獭鼠疫疫源地中的应用[J]. 疾病预防控制通报, 2017, 32(2): 36-38, 50. Wang CX, Liang K, Wang XH, et al. Application of new plague inspection technology in plague focus of marmots in Urumqi county[J]. Bull Dis Control Prev, 2017, 32(2): 36-38, 50. DOI:10.13215/j.cnki.jbyfkztb.1609020 |
| [17] |
庄金秋, 梅建国, 王艳, 等. 反向间接血凝试验(RIHA)在动物疾病诊断中的应用进展[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2016, 33(6): 55-59. Zhuang JQ, Mei JG, Wang Y, et al. Progress on the application of reverse indirect hemagglutination test in the diagnosis of animal diseases[J]. China Anim Health Inspect, 2016, 33(6): 55-59. DOI:10.3969/J.ISSN.1005-944X.2016.06.017 |
| [18] |
杜春红, 王鹏, 常娅莉, 等. 鼠疫菌F1抗体/抗原酶联免疫诊断试剂盒的应用评价[J]. 微生物学免疫学进展, 2014, 42(4): 21-25. Du CH, Wang P, Chang YL, et al. Clinical evaluation of ELISA kit for antibody and antigen of Yersinia pestis F1[J]. Prog Microbiol Immunol, 2014, 42(4): 21-25. DOI:10.13309/j.cnki.pmi.2014.04.005 |
| [19] |
王蒴, 王信惠, 黎唯. 鼠疫免疫学检测技术的应用和研究进展[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30(2): 228-231. Wang S, Wang XH, Li W. Progress in the application and study of immunological detection technology for Yersinia pestis[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30(2): 228-231. DOI:10.11853/J.ISSN.1003.8280.2019.02.028 |
| [20] |
葛军旗, 李镜辉, 马永康, 等. 基于信息熵的动物鼠疫流行强度定量化初探[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2018, 29(5): 439-441. Ge JQ, Li JH, Ma YK, et al. The preliminary quantitative description of epidemic intensity in enzootic plague based on information entropy theory[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2018, 29(5): 439-441. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2018.05.004 |
| [21] |
米景川, 李仲来, 吕卫东, 等. 内蒙古北部荒漠草原沙鼠鼠疫流行强度的预报模型[J]. 中国地方病学杂志, 1997, 12(2): 109-112. Mi JC, Li ZL, Lyu WD, et al. Prediction model of epidemic intensity of gerbil plague in desert steppe of northern Inner Mongolia[J]. Chin J Control Endem Dis, 1997, 12(2): 109-112. |
 2020, Vol. 31
2020, Vol. 31


