扩展功能
文章信息
- 郑凌霄, 尹灿灿, 王逸枭, 李梦楠, 邵黄芳, 方惟希, 杨曼, 赵金红, 孙恩涛
- ZHENG Ling-xiao, YIN Can-can, WANG Yi-xiao, LI Meng-nan, SHAO Huang-fang, FANG Wei-xi, YANG Man, ZHAO Jin-hong, SUN En-tao
- 基于DNA条形码技术的粉螨种类鉴定研究
- Identification of acaroid mite species based on DNA barcoding
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30(2): 180-184
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2019, 30(2): 180-184
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2019.02.015
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2018-11-19
- 网络出版时间: 2019-3-1 09:11
2 皖南医学院寄生虫教研室, 安徽 芜湖 241002
2 Department of Medcine Parasitology, Wannan Medical College
粉螨隶属于蜱螨亚纲、真螨总目、粉螨亚目,是节肢动物中的一大类群,全球粉螨约有1 400种,其中在我国发现的有136种[1]。粉螨不仅会危害粮食、药材、干果等储藏物,还可携带黄曲霉、花斑曲霉等病原生物[2-3],严重影响社会经济和人类健康。此外,在我国各主要检疫口岸,粉螨也经常被截获。目前粉螨种类鉴定主要依据外部形态特征,但由于粉螨体型微小、形态相似,近缘物种较多,而且传统的形态学鉴定受到粉螨发育状态、肢体完整性、鉴定人员经验等因素的影响,对不同粉螨种类进行正确的鉴定特别困难[4]。因此,迫切需要能够对储藏物粉螨进行快速、准确鉴定的方法。随着分子生物学技术的迅猛发展,DNA分子鉴定已成为生物分类学中引人注目的新方向,成为物种鉴定的有利工具[5]。DNA条形码技术(DNA barcoding)是以线粒体细胞色素C氧化酶亚基Ⅰ(cytochrome C oxidase subunitⅠ,COⅠ)基因片段作为通用分子标记[6],利用标准基因片段序列的多态性对物种快速准确的鉴定。条形码序列分析不依赖形态特征,是传统物种形态鉴定方法的有力补充[7],广泛应用于粉螨种类的鉴定,Yang等[8]验证COⅠ和内转录间隔区(internal transcriptional spacer,ITS)序列可作为DNA条形码对粉螨种类进行鉴定。本研究在安徽省采集储藏物粉螨,在形态学鉴定的基础上,采用DNA条形码技术对粉螨种类进行快速准确鉴定。
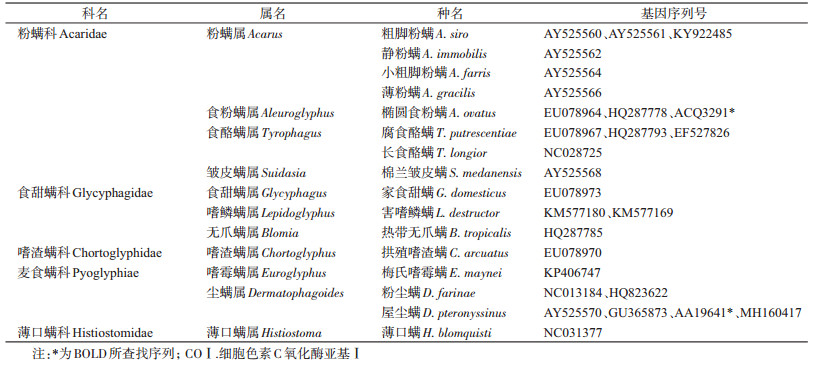
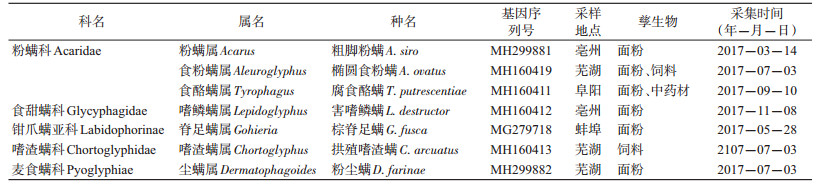
1 材料与方法 1.1 粉螨样本采集所获粉螨均采自于安徽省部分地区面粉、中药材、饲料等储藏物,见表 1。在光学显微镜下从粉螨样本中挑取单只雌螨,实验室中单个饲养。
 |
挑取一部分成螨制作成标本,在400倍镜下对标本进行形态特征观察,通过形态学特征进行粉螨种类鉴定[1],另一部分70%乙醇溶液固定,用于DNA的提取。
1.3 DNA的提取、扩增、克隆和测序参考Jia等[9]提取DNA方法,提取单个粉螨DNA。具体操作如下:①在含有单个雌螨的离心管中加入20 μl的STE缓冲液(10 mmol/L Tris-HCL,1 mmol/L EDTA,100 mmol/L NaCl,pH 8.0),冰上充分研磨;②在离心管内加入0.5 μl蛋白酶K(25 mg/ml),充分混匀;③将混匀的混合液于56 ℃水浴3 h,水浴完成后,95 ℃ 5 min,灭活蛋白酶K;④常温条件下,2 000×g离心1 min,取2 μl上清液作为PCR反应模板,其余DNA样本编号后,储存于-20℃冰箱中备用。扩增引物:COIF 5′-GTTTTGGGATATCTCTCATAC-3′;COIR 5′-GAGCAACAACATAATAAGTATC-3′[10]。扩增产物用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,通过琼脂糖凝胶DNA回收试剂盒(TIANGEN)纯化,纯化产物与pUCm-T载体[T载体PCR产物克隆试剂盒,生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司]连接形成克隆质粒,阳性克隆送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司测序。
1.4 序列分析通过DNA条形码专用数据库(BOLD)和美国国立生物技术信息中心(NCBI)的GenBank检索已知粉螨COⅠ基因序列,结合本研究所获得的序列,应用DNAStar和MEGA 6.0软件进行序列分析[11],以Kimura 2-parameter模型计算碱基差异度,以邻接法(Neighbor-Joining method,NJ)构建系统树。
2 结果 2.1 形态学鉴定结果依据形态学特征鉴定采集到的粉螨共4科7属7种,即粗脚粉螨(Acarus siro)、椭圆食粉螨(Aleuroglyphus ovatus)、腐食酪螨(Tyrophagus putrescentiae)、害嗜鳞螨(Lepidoglyphus destructor)、拱殖嗜渣螨(Chortoglyphus arcuatus)、棕脊足螨(Gohieria fusca)和粉尘螨(Dermatophagoides farinae),并将序列上传至GenBank(表 1)。
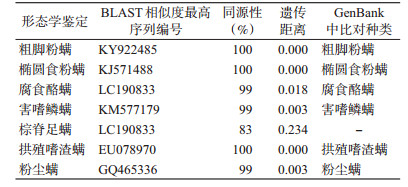
2.2 DNA条形码鉴定将本研究中所获得的序列经BLAST比对分析(表 2),其中6种粉螨均可鉴定到种,分子鉴定结果与形态学鉴定结果基本一致,且与NCBI数据库中最相似物种的遗传距离均<0.020。而棕脊足螨COⅠ序列在BOLD和GenBank中并未查到相应序列,仅BLAST到最为相近的物种序列,计算2条序列遗传距离为0.234,>0.02。
 |
共获得粉螨亚目7种粉螨的COⅠ序列,所有序列皆无碱基的缺失和插入,长度为377 bp,可编码125个氨基酸。并从数据库检索已知粉螨相应COⅠ序列共同分析(表 3)。17种粉螨平均碱基组成为A(19.97%)、T(43.20%)、G(22.71%)、C(14.12%),A+T(63.17%)远高于G+C(36.83%),由此可以看出COⅠ片段具有A+T含量偏向性。
粉螨COⅠ基因序列种间差异度的范围在4.6%~36.0%之间,种内差异度均<1%,种间差异均远大于种内差异。其中粗脚粉螨和害嗜鳞螨的种间差异度最高,为36.0%,而长食酪螨(T. longior)和腐食酪螨的种间差异度最低,为4.6%,粉螨科间差异远大于同一属内不同种的种间差异,同属粉螨的种间差异度均小于不同属粉螨之间的差异度(表 4)。
 |
计算粉螨COⅠ基因序列在不同科之间的遗传距离为0.200~0.289,种间遗传距离为0.058~0.323,种内遗传距离为0.000~0.015,结果显示种间遗传距离远大于种内遗传距离(表 4)。
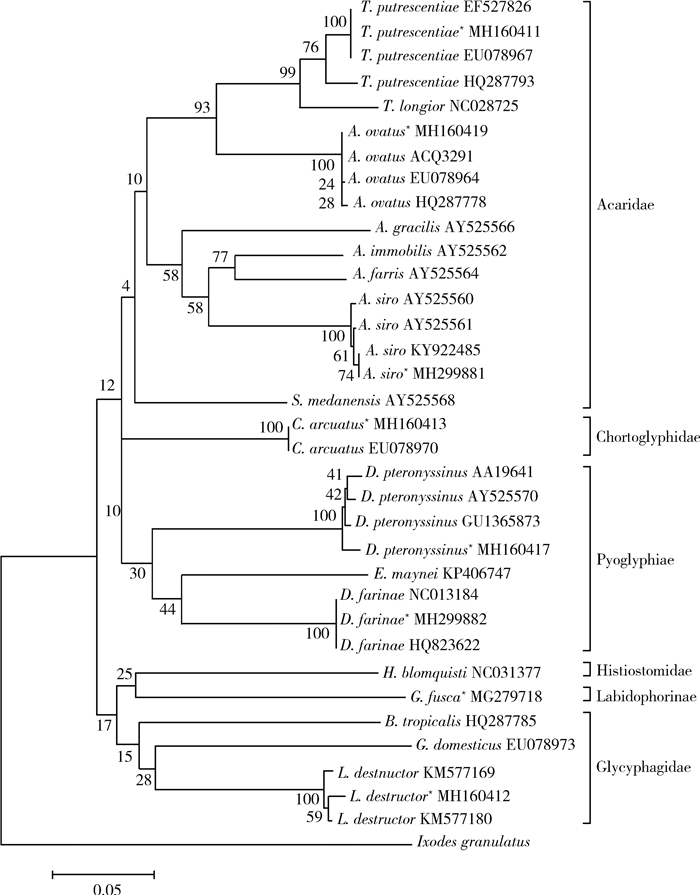
2.5 系统发育树分析基于COⅠ基因构建粉螨亚目NJ系统发育树。系统树结果见图 1,本次实验获得的COⅠ序列和数据库已知相同种类序列聚为一支,其聚类结果与形态学鉴定结果一致,相同物种的不同个体均聚在同一分支下,不存在不同物种个体交叉类聚。
|
| 注:*为本研究所获得的序列 图 1 基于DNA条形码构建的NJ系统进化树(Kimura 2-parameter模型) Figure 1 A neighbor-joining tree based on DNA barcodes (Kimura 2-parameter model) |
| |
传统形态学鉴定分类主要依据物种的表型特征,在物种鉴定的过程中可能会受到物种自身遗传因素或环境因素的影响,导致相同或相似物种鉴定错误[12],物种性别和发育阶段也会导致形态的不同,从而影响物种鉴定的准确性。DNA条形码技术不仅能避免个体形态特征的限制,同时由核苷酸序列组成的数据库能够提供较全面的生物学信息。本研究扩增的粉螨COⅠ基因片段作为DNA条形码可准确鉴别条形码数据库中已有粉螨种类,鉴定结果与形态学鉴定结果基本一致。同时,本研究所得的粉螨COⅠ序列种间遗传距离均>0.058,种内遗传距离<0.02;低于种内遗传距离0.02的界限[13]。
本研究获得的粉螨序列和数据库中检索已知同种粉螨COⅠ序列构建NJ系统发育树分析发现,通过NJ树也可区分不同粉螨种类,相同种类的粉螨序列在NJ树上聚为一支,种内序列多态性不影响分子鉴定的准确性[14]。通过种内、种间遗传距离和序列差异度分析,并结合BOLD和NCBI中已公开的部分粉螨COⅠ基因序列,证实DNA条形码技术可以用于粉螨种类的分子快速鉴定。同时,棕脊足螨COⅠ序列并未在数据库中查到,仅BLAST查到最为相近的物种序列,这与BOLD和GenBank数据库中无相应棕脊足螨COⅠ序列片段有关。因此,DNA条形码参考数据库的完整性直接影响到物种鉴定的准确率,需要广大研究者不断完善和补充DNA条形码数据库。
| [1] |
李朝品, 沈兆鹏. 中国粉螨概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 15.
|
| [2] |
Stalažs A, Moročko-Bičevska I. Species identification, host range and diversity of Cecidophyopsis mites (Acari:Trombidiformes) infesting Ribes in Latvia[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2016, 69(2): 129-153. DOI:10.1007/s10493-016-0024-7 |
| [3] |
Hubert J, Kopecky J, Sagova-Mareckova M, et al. Assessment of bacterial communities in thirteen species of laboratory-cultured domestic mites (Acari:Acaridida)[J]. J Econ Entomol, 2016, 109(4): 1887-1896. DOI:10.1093/jee/tow089 |
| [4] |
Vargas M, García-Varela M, Laclette JP, et al. Application of ITS-2 sequences as markers for identification and phylogenetic inference within the genus Geomylichus (Acari:Listrophoridae)[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2005, 35(3): 223-238. DOI:10.1007/s10493-004-2761-2 |
| [5] |
Zuo YJ, Chen ZJ, Kondo K, et al. DNA barcoding of Panax species[J]. Planta Med, 2011, 77(2): 182-187. DOI:10.1055/s-0030-1250166 |
| [6] |
Hebert PDN, Cywinska A, Ball SL, et al. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes[J]. Proc Biol Sci, 2003, 270(1512): 313-321. DOI:10.1098/rspb.2002.2218 |
| [7] |
Cruickshank RH. Molecular markers for the phylogenetics of mites and ticks[J]. Syst Appl Acarol, 2002, 7: 3-14. DOI:10.11158/saa.7.1.1 |
| [8] |
Yang B, Cai JL, Cheng XJ. Identification of astigmatid mites using ITS2 and COⅠregions[J]. Parasitol Res, 2011, 108(2): 497-503. DOI:10.1007/s00436-010-2153-y |
| [9] |
Jia FX, Yang MS, Yang WJ, et al. Influence of continuous high temperature conditions on Wolbachia infection frequency and the fitness of Liposcelis tricolor (Psocoptera:Liposcelididae)[J]. Environ Entomol, 2009, 38(5): 1365-1372. DOI:10.1603/022.038.0503 |
| [10] |
Webster LMI, Thomas RH, McCormack GP. Molecular systematics of Acarus siro s.lat., a complex of stored food pests[J]. Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2004, 32(3): 817-822. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2004.04.005 |
| [11] |
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, et al. MEGA:a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2008, 9(4): 299-306. DOI:10.1093/bib/bbn017 |
| [12] |
Yang BH, Li CP. The full-length mitochondrial rDNA sequence of Tyrophagus longior (Astigmata:Acaridae) and phylogeny of astigmatid mites based on mitochondrial rDNA sequence[J]. J Stored Prod Res, 2017, 71: 5-13. DOI:10.1016/j.jspr.2016.12.004 |
| [13] |
Hebert PDN, Stoeckle MY, Zemlak TS, et al. Identification of birds through DNA barcodes[J]. PLoS Biol, 2004, 2(10): e312. DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020312 |
| [14] |
Beroiz B, Couso-Ferrer F, Ortego F, et al. Mite species identification in the production of allergenic extracts for clinical use and in environmental samples by ribosomal DNA amplification[J]. Med Vet Entomol, 2014, 28(3): 287-296. DOI:10.1111/mve.12052 |
 2019, Vol. 30
2019, Vol. 30