扩展功能
文章信息
- 刘红, 梁国栋
- LIU Hong, LIANG Guo-dong
- 新发虫媒病毒:基因A型版纳病毒全基因组序列扩增引物
- The genotype A specific primers for amplifying and sequencing the whole genome of Banna virus
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2016, 27(6): 533-538
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2016, 27(6): 533-538
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2016.06.002
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2016-07-21
- 网络出版时间: 2019-06-09 13:42
2 中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所病毒性脑炎室, 传染病预防控制国家重点实验室, 北京 102206
2 Department of Viral Encephalitis, State Key Laboratory of Infectious Disease Prevention and Control, National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention
版纳病毒是呼肠孤病毒科新建立的Seadornavirus病毒性脑炎患者中分离[2], 此后相继在多种动物宿病毒属的模式病毒[1]。该病毒于1987年首次从我国主和蚊虫媒介中分离[3],广泛分布在我国和东南亚地区,2013年,版纳样病毒在匈牙利巴拉顿湖的淡水鲤鱼中分离[4]。版纳病毒宿主媒介丰富,地域分布广泛,表现出极强的环境适应力。作为一种新发病毒,版纳病毒相关研究相对滞后。国际上该病毒基因组序列少、遗传进化特征不清楚[5],有限的基因组序列信息成为制约版纳病毒相关研究的重要因素。因此,开展版纳病毒全基因组序列测定,了解不同生境、宿主、分离年代版纳病毒之间亲缘关系、分子差异、基因组结构特征及其分子生物学致病机制,对于科学地制定版纳病毒的防控策略具有重要意义。因此,针对不同片段设计工作效率高、特异性好的全基因组序列测定引物成为研究版纳病毒分子特征的重要技术环节。本研究报道了一整套版纳病毒型特异性全基因组序列测定引物,该套弓丨物在我国30余株版纳病毒全基因组序列测定中应用效果理想。
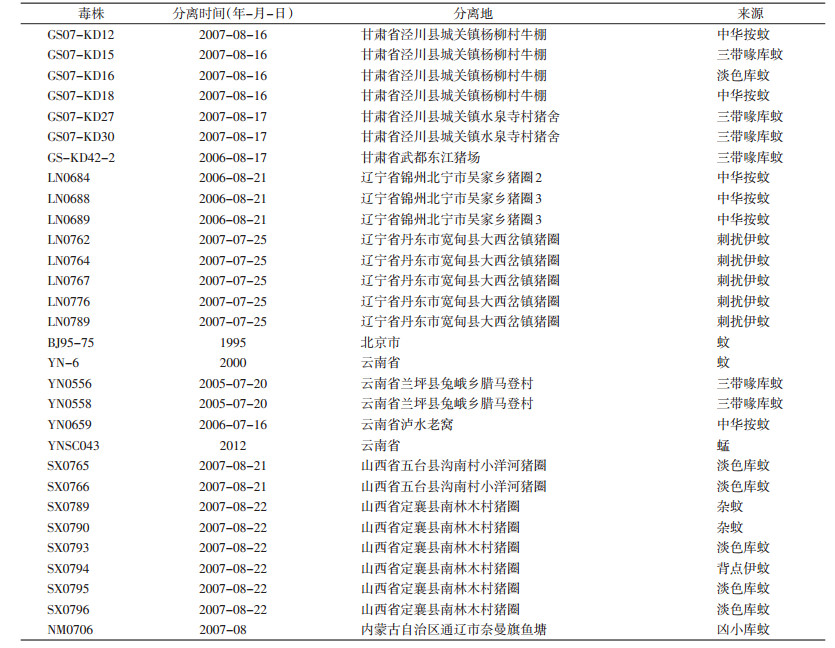
1 材料与方法 1.1 版纳病毒毒株以中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所病毒性脑炎室在我国采集并且分离的30株版纳病毒毒株作为测序毒株,毒株背景信息见表 1。
登录GenBank下载已有的版纳病毒12个节段基因序列,米用ClustalX 2.0软件进行序列比对,GenDoc软件和DNAStar软件开展版纳病毒12个节段核苷酸和氨基酸同源性分析,Mega软件开展版纳病毒基因分型分析。比对不同基因型别毒株,生成共有序列(concesus sequence)。
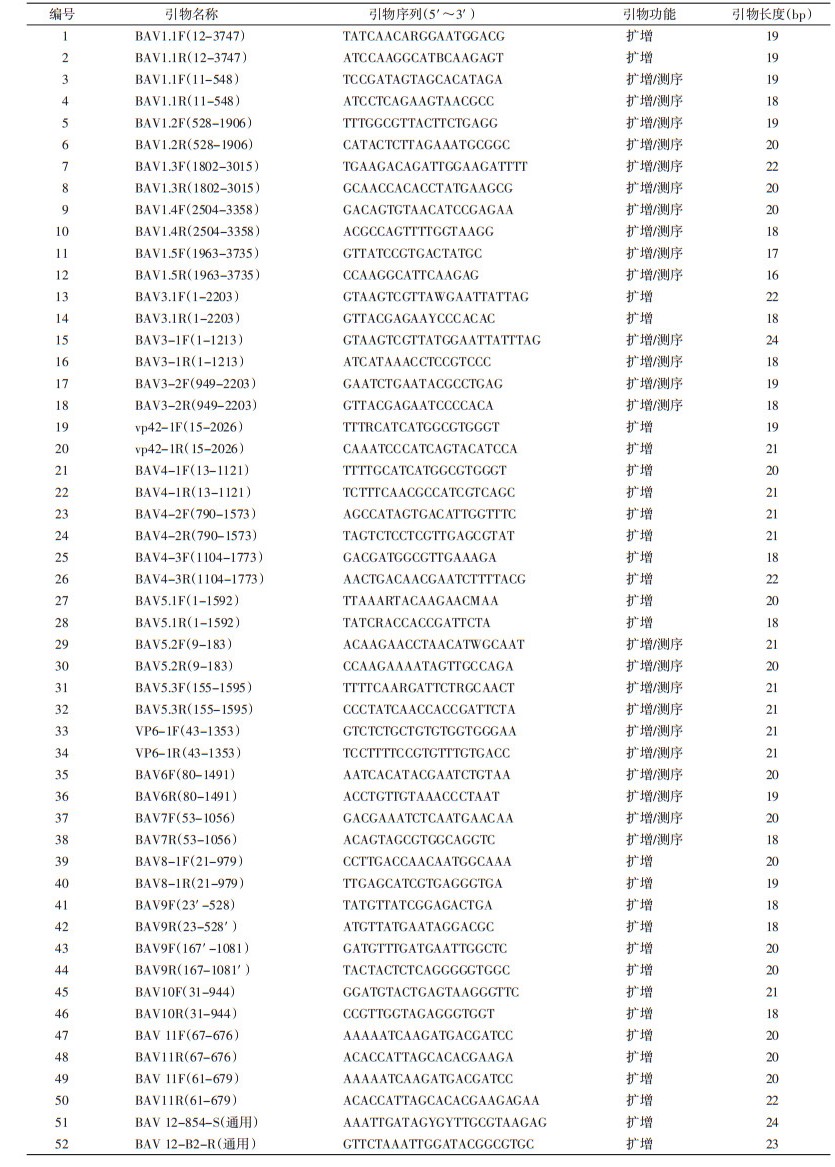
1.3 版纳病毒型别特异性引物设计使用Primer Premier v6.0软件(加拿大Premier公司)和Oligo 7.56软件(Molecular Biology Insight,Inc.美国)进行引物设计和评估。以不同基因型别版纳病毒参考株序列为模板,并结合节段同源性比对结果,分别设计型特异性基因A型和基因B型版纳病毒全基因组扩增引物。
1.4 RT-PCR、测序及序列分析 1.4.1 版纳病毒核酸提取及cDNA制备取140μl收获的病毒上清液,用RNA提取试剂盒(QIAGEN,德国),按照操作说明书进行,核酸洗脱体积为40μl,将提取的RNA置于99 ℃沸水2 min,以打开双链RNA,立即置于冰水浴中2 min,离心后取出32 1 RNA加入制备试剂盒(Ready-To-GoYou-Prime First-Strand Beads, 英国)提供的first strand反应管中,室温放置1min。加入1 μl随机引物pd (N)6(50ng/μl)或特异性引物(10mmol/L)至终体积为33μl。瞬离后放置于37 ℃水浴60min,完成cDNA制备。
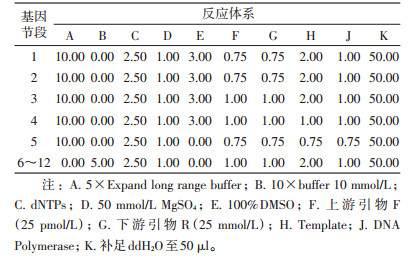
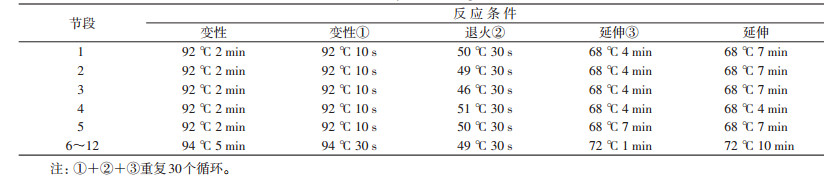
1.4.2 版纳病毒1~12节段PCR工作体系综合考虑模板特征性结构、扩增目的片段长度、引物退火温度等因素,采用梯度PCR的方式摸索出针对版纳病毒不同节段不同基因型别的最适反应条件。版纳病毒各节段PCR反应体系及反应条件见表 2、3。使用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳进行PCR产物检验,PCR产物经纯化后行序列测定,Sephaglas BandPre Kit(Amersham Pharmacia Biotech,美国)纯化PCR产物。纯化后的PCR产物进行序列测定。使用DNAStar软件包中SeqMan进行序列拼接、编辑和评分。
下载GenBank公布的版纳病毒基因组1~12节段,进行序列联配及核苷酸同源性分析,结果显示版纳病毒1~12节段核苷酸同源性在37.8%~84.8%之间。第12节段基因序列最为保守也是毒株序列信息最丰富的节段[6-7]。因此,本研究以第12节段基因序列开展病毒间亲缘关系的分析。版纳病毒第12节段系统进化树结果显示,中国版纳病毒毒株根据地理南北差异分为2个基因亚型:A1和A2亚型,见图 1。分别挑选2个基因型别的代表毒株作为引物设计参考序列。基因A1型的参考毒株为02VN078b(2010年,越南分离株[8]);基因A2型参考株为BAV_ch(1987年最初的版纳病毒分离株[9])。

|
| 图 1 版纳病毒基因分型 Figure 1 Phylogenetic analysis of BAV |
| |
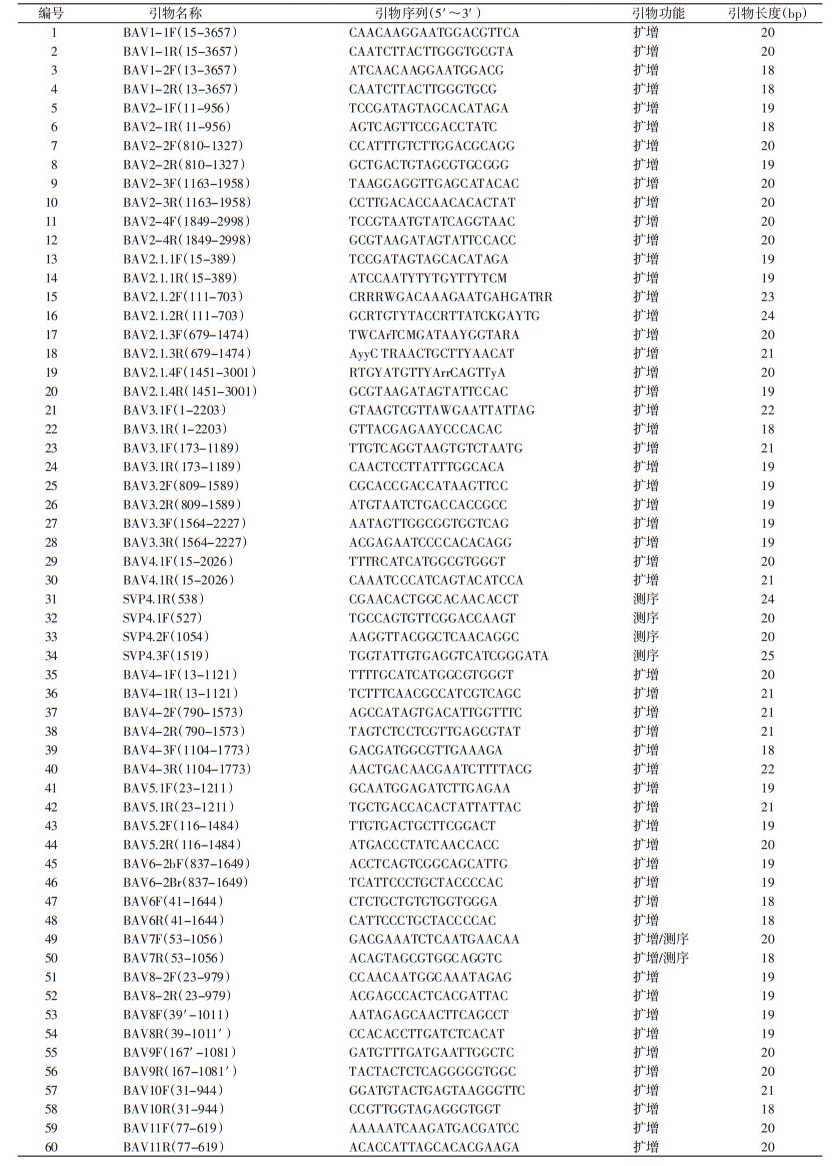
本研究设计了2套型别特异性版纳病毒全基因组扩增测定引物,可以完成基因A1型和A2型毒株1~12节段的序列扩增。版纳病毒A1型全基因组序列扩增测定引物见表 4,版纳病毒基因A2型全基因组序列扩增测定引物见表 5。
版纳病毒是一种新发的但一直未给予足够重视的虫媒病毒,与人类疾病有密切联系[10]。特别是近些年来其地理分布范围不断扩大,从最初的东南亚热带地区传播至东北亚地区,甚至在欧洲也报道了版纳病毒样病毒的分离[4]。其基因组全长约21 000 bp,由12条分节段的双链RNA组成,各基因节段长度从759 bp到3 747 bp大小不等[3]。每个节段含有一个开放读取码框(open reading frame,ORF)编码相应的蛋白质,版纳病毒各片段5′和3′ UTR区域序列保守并反向互补,极易形成稳定的锅柄状结构(panhandle),是病毒RNA聚合酶结合的重要部位[11],然而这种反向互补的区域对引物设计而言是极为不利的。本研究在进行引物设计时,采用引物3′末端序列高度保守严格和模板结合,而修改5′末端区段序列以消除颈环结构的策略。同时对修饰后的引物序列进行版纳全基因组同源性搜索,避免由于改变碱基引物修饰后造成错误的引物致使非特异扩增来克服这一技术难题。
以第二代DNA测序技术(next-generation sequencing,NGS)为代表的高通量测序技术的飞速发展,加快了基因组学研究的进程,使短时间完成一株病毒全基因组序列测定成为可能[12]。但版纳病毒为分节段的双链RNA病毒,极易发生基因漂移及片段间的重配变异,编码区基因序列结构中富含重复区域。版纳病毒基因组自身特点导致了采用NGS技术进行全基因组序列测定效率低且错误率高。因此,NGS并非大规模版纳病毒全基因组序列测定的优选方法。
本研究设计了两套基因亚型特异性版纳病毒全基因组序列扩增测定引物,并摸索出工作效率高结果稳定的RT-PCR工作系统,成功扩增了我国不同年代、不同宿主类型及分离地的30株版纳病毒全基因组序列。构建了高效、快速、稳定和便捷的版纳病毒全基因组序列测定平台。为开展版纳病毒的分子流行病学、分子生物学、致病机制等研究奠定了基础。
| [1] | Fauquet CM, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, et al. Virus taxonomy. Ⅷth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses[M]. San Diego: Elsevier Academic Press, 2005: 504-510. |
| [2] | 徐普庭, 王逸民, 左建民, 等. 从云南省无名热病人和脑炎病人分离到新环状病毒[J]. 病毒学报, 1990, 6(1): 27–33. |
| [3] | Liu H, Li MH, Zhai YG, et al. Banna virus, China, 1987-2007[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2010, 16(3) : 514–517 .DOI:10.3201/eid1408.080100. |
| [4] | Reuter G, Boros A, Delwart E, et al. Novel seadornavirus (family Reoviridae) related to Banna virus in Europe[J]. Arch Virol, 2013, 158(10) : 2163–2167 .DOI:10.1007/s00705-013-1712-9. |
| [5] | Liu H, Gao XY, Liang GD. Newly recognized mosquito-associated viruses in mainland China, in the last two decades[J]. Virol J, 2011: 68.DOI:10.1186/1743-422X-8-68. |
| [6] | Liu H, Gao XY, Fu SH, et al. Molecular evolution of emerging Banna virus[J]. Infect Genet Evol, 2016: 250–255 .DOI:10.1016/j.meegid.2016.08.034. |
| [7] | Attoui H, Billoir F, Cantaloube JF, et al. Strategies for the sequence determination of viral ds RNA genomes[J]. J Virol Methods, 2000, 89(1/2) : 147–158 . |
| [8] | Nabeshima T, Nga PT, Guillermo P, et al. Isolation and molecular characterization of Banna virus from mosquitoes, Vietnam[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2008, 14(8) : 1276–1279 .DOI:10.3201/eid1408.080100. |
| [9] | Attoui H, Jaafar FM, De Micco P, et al. Coltiviruses and seadornaviruses in North America, Europe, and Asia[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2005, 11(11) : 1673–1679 .DOI:10.3201/eid1111.050868. |
| [10] | 刘红, 梁国栋. 版纳病毒及其感染[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2010, 21(5): 502–504. |
| [11] | Jaafar FM, Attoui H, Mertens PP, et al. Identification and functional analysis of VP3, the guanylyltransferase of Banna virus (genus Seadornavirus, family Reoviridae)[J]. J Gen Virol, 2005, 86(Pt 4) : 1141–1146 . |
| [12] | Barzon L, Lavezzo E, Costanzi G, et al. Next-generation sequencing technologies in diagnostic virology[J]. J Clin Virol, 2013, 58(2) : 346–350 .DOI:10.1016/j.jcv.2013.03.003. |
 2016, Vol. 27
2016, Vol. 27