扩展功能
文章信息
- 张娟, 王婷婷, 普舒伟, 范芝宏, 毛梦菊, 蒋雪莹, 李文东, 周晓梅
- ZHANG Juan, WANG Ting-ting, PU Shu-wei, FAN Zhi-hong, MAO Meng-ju, JIANG Xue-ying, LI Wen-dong, ZHOU Xiao-mei
- 2023年云南省部分地区蚊虫种类及蚊媒病毒调查研究
- An investigation of mosquito species and mosquito-borne virus in some areas of Yunnan Province, China, 2023
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2024, 35(5): 616-620, 626
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2024, 35(5): 616-620, 626
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2024.05.018
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2024-04-02
2 红河州疾病预防控制中心, 云南 蒙自 661199;
3 玉溪市疾病预防控制中心, 云南 玉溪 653199;
4 开远市疾病预防控制中心, 云南 开远 661699
2 Honghe Prefecture Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Mengzi, Yunnan 661199, China;
3 Yuxi Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Yuxi, Yunnan 653199, China;
4 Kaiyuan Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Kaiyuan, Yunnan 661699, China
虫媒病毒是一种人畜共患传染病,主要以蚊虫、蜱、白蛉和蠓等为主要传播媒介,通过叮咬将病毒传播给人、畜引发自然疫源性疾病[1-2]。虫媒病毒在全球范围内广泛分布,随着地理扩张、全球贸易的增加以及城市建设和全球变暖等加快了虫媒病毒的传播和流行,成为全世界的公共卫生问题[3]。蚊虫是多种传染病的重要宿主和主要昆虫媒介,可传播包括流行性乙型脑炎(乙脑)、登革热、西尼罗病毒病,寨卡病毒病等在内的一系列疾病[4]。云南省因其特殊的地理位置和气候条件,成为虫媒病毒流行的重要地区之一[5]。以往对云南省虫媒病毒的研究主要集中在毗邻东南亚各国的边界及毗邻我国其他省(自治区)的地区[6],此次调查的红河哈尼族彝族自治州(红河州)开远市、玉溪市华宁县和元江哈尼族彝族傣族自治县(元江县)位于云南省东南部和中部地区,该地区进行虫媒研究较少。因此,2023年我们对这3个县(市)开展蚊媒病毒调查,以期进一步了解该地区蚊种及虫媒病毒分布特点,为虫媒病毒防控工作提供基本依据。
1 材料方法 1.1 标本采集2023年7-8月在红河州开远市中和营镇(王马村),玉溪市华宁县(八家村)、元江县各选择1个村开展蚊虫采集工作。利用紫外线诱蚊灯,于每天18∶00至次日8∶00在猪圈、羊圈和农户等生境诱捕蚊虫。将收集到的蚊虫于-20 ℃、冰箱冷冻30 min后,在冰排上对蚊虫进行分类鉴定。根据蚊虫采集的不同时间、地点以及种类,按照30支/管分装至冻存管中,编号登记后置于-80 ℃冰箱保存。
1.2 核酸提取及cDNA制备将蚊虫样本放入装有0.5 ml Hank's液的研磨管中,使用研磨器研碎,2 000 r/min离心15 min,离心半径为15 cm,取上清,按照QIAamp viral RNA minikit提取试剂盒(规格:50 T;货号52904;生产厂家:德国QIAGEN公司)说明书提取上清液病毒核酸,使用QuantiTect Reverse Transcription Kit试剂盒(规格:50 T;货号:205310;生产厂家:德国QIAGEN公司)制备cDNA。
1.3 实时荧光定量PCR检测采用实时荧光定量PCR法检测乙脑病毒、登革病毒、西尼罗病毒和基孔肯雅病毒。按照实时荧光定量PCR核酸检测试剂盒(规格:50 T;货号:YJC70108 N、YJC30101 N、YJC70109 N、YJC40104 N;生产厂家:江苏硕世生物科技公司)的说明书制备反应体系、设置反应程序。阳性判定值:循环阈值(Ct)≤37,曲线呈S型且有明显指数增长期。
1.4 PCR扩增对乙脑病毒检测阳性的样本使用TSINGKE TSE101金牌Mix(规格:5 ml;货号:TSE101;北京擎科生物有限公司)进行NS1基因的PCR扩增,反应条件为:98 ℃ 2 min;98 ℃ 10 s,55 ℃10 s,72 ℃ 10 s,40个循环;72 ℃ 1 min。NS1正向引物:TGGAAAGCATGGGGAAAAAG;NS1反向引物:GGTCTGATTTCCATTCCGTACC。PCR产物进行1%的琼脂糖凝胶电泳实验,观察有无扩增的目的条带,结果阳性者将PCR产物送擎科生物有限公司进行双向测序。
1.5 序列分析从美国国立生物技术信息中心(NCBI)中下载不同时间、地域、基因型的脑炎病毒基因序列,选择墨累谷脑炎病毒(Murray valley encephalitis virus)作为外群,对其进行基因亲缘关系树的构建及序列比对分析。利用BioEdit 7.0.9软件对测序产物进行序列拼接和多序列比对;利用MEGA 11.0软件以邻接法构建系统发育树,Bootstrap值设置为1 000;利用MegAlign 7.1软件进行核苷酸序列的同源性分析。
1.6 统计学分析利用Excel 2016软件完成原始数据的录入。蚊虫病原感染情况计算公式:

|
2023年7-8月在云南省3个地区共采集蚊虫9 060只,经形态学鉴定为4属5种,包括三带喙库蚊(Culex tritaeniorhynchus)、致倦库蚊(Cx. pipiens quinquefasciatus)、中华按蚊(Anopheles sinensis)、骚扰阿蚊(Armigeres subalbatus)和刺扰伊蚊(Aedes vexans)。其中三带喙库蚊数量最多,占捕获总数的54.30%(4 920/9 060),其次为中华按蚊,占比为33.77%(3 060/9 060),致倦库蚊、骚扰阿蚊和刺扰伊蚊占比较少,分别占该地捕获总数的5.96%(540/9 060)、2.98%(270/9 060)和2.98%(270/9 060)。3个采样点中,开远市和华宁县的优势蚊种为三带喙库蚊,分别占该地捕蚊总数的31.91%和84.40%,元江县的优势蚊种为中华按蚊,占该地捕蚊总数的73.68%。见表 1。
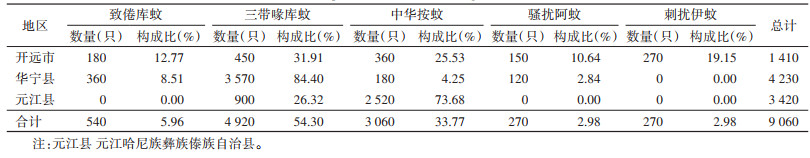
|
采集到的9 060只蚊虫标本共分装302管,使用实时荧光定量PCR法对302管蚊虫样本分别检测乙脑病毒、登革病毒、西尼罗病毒和基孔肯雅病毒的携带情况,检测结果显示,开远市检出3管阳性,华宁县检出7管阳性,元江县未检出阳性,见表 2。批阳性率为3.31%,其中9管为三带喙库蚊,1管为中华按蚊。三带喙库蚊和中华按蚊的乙脑病毒批阳性率分别为5.49%和0.98%,最小感染率分别为1.83%和0.33%。
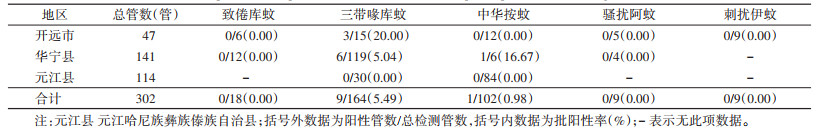
|
对开远市、华宁县检测出的10株乙脑病毒进行NS1基因扩增及测序,结果来自开远市的3株乙脑病毒(编号KY-1、KY-2、KY-3)和华宁县的5株乙脑病毒(编号HN-1、HN-2、HN-3、HN-4、HN-5)扩增成功,测序结果经比对为基因Ⅰ型乙脑病毒。
2.4 基于NS1基因的系统进化分析将本次测序得到的8株乙脑病毒与来源于GenBank中的22株不同基因型乙脑病毒及墨累谷脑炎病毒(NC_000943病毒株)构建NS1基因的系统进化树。系统进化分析显示,云南省新分离的8株乙脑病毒与中国近年分离的HM366552、KT229575、JF706274、HQ893545、KT957420病毒株和韩国分离的AY316157病毒株位于同一进化分支,均属于基因Ⅰ型,远离Ⅱ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ型乙脑病毒病毒株。见图 1。
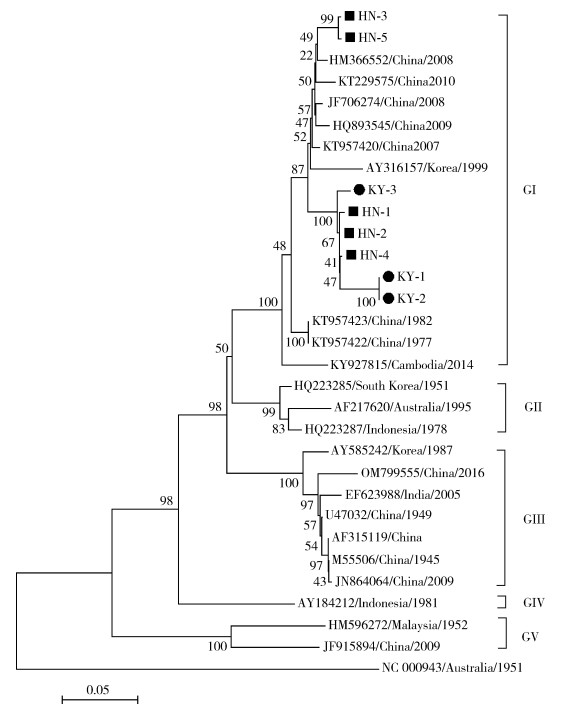
|
| 注:●本次检测到的红河州开远市的乙脑病毒序列;■本次检测到的玉溪市华宁县的乙脑病毒序列;NC 000943为墨累谷脑炎病毒序列。 图 1 流行性乙型脑炎病毒NS1基因系统进化树 Figure 1 Phylogenetic analysis of the NS1 gene of Japanese encephalitis virus |
| |
开远市和华宁县检测出的8株乙脑病毒NS1组间核苷酸同源性和氨基酸同源性分别为93.49%~100%和94.33%~100%,与来自GenBank的9株基因Ⅰ型乙脑病毒在核苷酸和氨基酸的同源性分别为90.83%~98.43%和91.15%~100%。
3 讨论云南省具有热带和亚热带气候特征,蚊虫资源丰富,是蚊媒传染病高发省份。自1975年以来已在云南省西部、西南部、南部、东南部、东北部和西北部6个地区的55个县开展蚊虫及蚊传虫媒病毒调查,而中部和东部地区开展工作相对较少[7]。本研究在云南省选取了3个标本采样点,分别为云南省东南部地区红河州开远市,中部地区玉溪市华宁县和元江县,进一步完善了云南省蚊虫及蚊传虫媒病毒的信息。
本次调查共采集到蚊虫4属5种共9 060只,以三带喙库蚊、中华按蚊数量最多,为该次云南省采集地的优势蚊种。本次采集到的蚊虫种类相对单一,由于不同蚊虫种类生活习性不同,伊蚊主要在白天活动,库蚊、阿蚊和按蚊大多在傍晚和夜间活动[8-9],而此次采集时间为18∶00到次日8∶00,采集地主要为猪圈、牛圈等牲畜棚,且紫外诱蚊灯法对库蚊的捕获率较高以及不同采集地生态环境的不同,本次蚊虫调查中未采集到白纹伊蚊(Ae. albopictus),三带喙库蚊为优势蚊种,各采集地的蚊虫种类构成均不均衡,伊蚊种类和数量明显低于库蚊和按蚊。
1952年云南省开始报告乙脑疫情,至今每年均有乙脑病例发生[10-12]。乙脑曾是云南省分布最广,发病最多,危害较大的一种虫媒病毒病[6]。已有研究表明,云南省有15种蚊虫可自然感染乙脑病毒,其中三带喙库蚊为最重要的传播媒介[13-15]。本研究对红河州开远市、玉溪市华宁县和元江县3个采集地的蚊虫进行多种蚊媒病毒分析,在三带喙库蚊和中华按蚊中首次检测出乙脑病毒,表明云南省蚊虫仍有乙脑传播风险。既往在红河州开远市、玉溪市华宁县和元江县有乙脑病例报告[16-17],但未见分离到乙脑病毒的报道,本次在3个县(市)进行蚊媒病毒调查从病原学上证实当地为乙脑流行区。调查发现,三带喙库蚊为开远市和华宁县的优势蚊种,具有分布广、种群数量大,乙脑病毒携带率高的特点,是当地乙脑的主要传播媒介。乙脑病毒分为5个基因型(G-Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ和Ⅴ)[18],云南省2005年以前主要为G-Ⅲ,2005-2009年主要为G-Ⅰ,2010年以来均为G-Ⅰ流行株[6]。本研究对2023年采自云南省3地的蚊虫进行乙脑核酸片段检测,并对阳性样本进行测序,NS1区的部分序列显示开远市、玉溪市的8个病毒样本均属于基因Ⅰ型。近年相继在云南省各地检测到基因Ⅰ型乙脑病毒[19-22],与本次结果一致,表明目前云南省的主要流行型为基因Ⅰ型,具有重要的流行病学意义。
云南省地处热带和亚热带交界地区,靠近缅甸、老挝、泰国,不仅具有适宜蚊虫孳生的环境、气候,还容易受到热带地区虫媒病毒的影响[23-25]。在虫媒监测工作中定期对蚊虫种群及携带的虫媒病毒进行调查,明确虫媒病毒基因型分布,具有重要意义[26-27]。本研究虽未检出多种病毒,但首次在红河州开远市和玉溪市华宁县分离到乙脑病毒,为了解该地虫媒病毒流行状况提供了新的数据资料,提示云南省仍是我国重要虫媒病毒病流行区,今后还需要对病媒生物蚊虫的种类、密度、病原体携带状况等开展深入的研究,以期为云南省的虫媒疾病防治工作奠定基础。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
夏菡, 袁志明. 70年来我国虫媒病毒发现分布与应对[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2023, 35(5): 427-436, 450. Xia H, Yuan ZM. Discovery and distribution of and response to arbovirus in China over the past seven decades[J]. Chin J Schistosomiasis Control, 2023, 35(5): 427-436, 450. DOI:10.16250/j.32.1374.2023152 |
| [2] |
康乐, 李毅, 程功, 等. 虫媒病毒感染传播及跨界免疫适应机制[J]. 中国科学基金, 2023, 37(6): 1011-1020. Kang L, Li Y, Cheng G, et al. Infection, transmission, and cross-kingdom immune adaption of arboviruses[J]. Bull Natl Nat Sci Found China, 2023, 37(6): 1011-1020. DOI:10.16262/j.cnki.1000-8217.2023.06.019 |
| [3] |
Weaver SC, Reisen WK. Present and future arboviral threats[J]. Antiviral Res, 2010, 85(2): 328-345. DOI:10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.10.008 |
| [4] |
Huang YJS, Higgs S, Vanlandingham DL. Emergence and re-emergence of mosquito-borne arboviruses[J]. Curr Opin Virol, 2019, 34: 104-109. DOI:10.1016/j.coviro.2019.01.001 |
| [5] |
Zhang HL, Zhang YZ, Yang WH, et al. Mosquitoes of western Yunnan province, China: Seasonal abundance, diversity, and arbovirus associations[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(10): e77017. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0077017 |
| [6] |
张海林. 云南省虫媒病毒与虫媒病毒病研究进展[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2022, 38(12): 1117-1129. Zhang HL. Research progress in arboviruses and arboviral diseases in Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2022, 38(12): 1117-1129. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2694.2022.00.165 |
| [7] |
查冰, 周红宁, 张海林, 等. 云南省蚊虫媒介与蚊传虫媒病毒研究现状[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2012, 23(5): 439-444. Zha B, Zhou HN, Zhang HL, et al. Investigation of mosquitoes and mosquito-borne arboviruses in Yunnan Province, China in 1975-2010[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2012, 23(5): 439-444. |
| [8] |
杨耀翔, 林祖锐, 娜安, 等. 中缅边境耿马县登革热媒介伊蚊重要生态习性及抗药性调查[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2023, 18(4): 447-450. Yang YX, Lin ZR, Na A, et al. Surveillances of the important ecological habits and insecticides resistance to dengue vector Aedes mosquito in Gengma County, China-Myanmar border[J]. Chin J Pathog Biol, 2023, 18(4): 447-450. DOI:10.13350/j.cjpb.230415 |
| [9] |
田华, 郭秀霞, 杨培培, 等. 山东省北湖地区蚊虫种类及生态习性调查[J]. 寄生虫病与感染性疾病, 2016, 14(3): 125-128. Tian H, Guo XX, Yang PP, et al. Species and ecological habits of mosquitoes in Beihu region of Shandong province[J]. Parasitoses Infect Dis, 2016, 14(3): 125-128. |
| [10] |
刘克娜, 马杨岭, 王钦, 等. 2010-2019年云南省流行性乙型脑炎流行特征分析[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2021, 22(1): 66-69. Liu KN, Ma YL, Wang Q, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of epidemic encephalitis B in Yunnan in 2010-2019[J]. China Prev Med, 2021, 22(1): 66-69. DOI:10.16506/j.1009-6639.2021.01.013 |
| [11] |
朱秋艳, 胡筱莛, 李琼芬, 等. 云南省2005-2015年流行性乙型脑炎流行病学特征分析[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2017, 23(1): 52-57. Zhu QY, Hu XT, Li QF, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of Japanese encephalitis in Yunnan Province, 2005-2015[J]. Chin J Vaccines Immun, 2017, 23(1): 52-57. DOI:10.19914/j.cjvi.2017.01.013 |
| [12] |
金安松, 钟莲梅. 2016-2022年云南省流行性乙型脑炎分子流行病学、实验室及影像学检查[J]. 中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2024, 47(1): 79-83. Jin AS, Zhong LM. Molecular epidemiology, laboratory and imaging of Japanese encephalitis in Yunnan Province from 2016 to 2022[J]. Chin J Front Health Quar, 2024, 47(1): 79-83. DOI:10.16408/j.1004-9770.2024.01.019 |
| [13] |
张海林, 自登云, 龚正达. 云南省乙型脑炎病毒宿主和媒介研究[J]. 中国预防兽医学报, 2000, 22(2): 81-83. Zhang HL, Zi DY, Gong ZD. Host and vector of Japanese encephalitis virus in Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chin J Prev Vet Med, 2000, 22(2): 81-83. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0589.2000.02.001 |
| [14] |
李佳, 周红宁. 云南省流行性乙型脑炎研究进展[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2008, 3(10): 784-787. Li J, Zhou HN. Advances of epidemic encephalitis B in Yunnan Province[J]. Chin J Pathog Biol, 2008, 3(10): 784-787. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5234.2008.10.021 |
| [15] |
邓淑珍, 张海林, 李金梅. 云南省蚊虫分布特点及自然感染乙型脑炎病毒的研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2009, 20(4): 344-348. Deng SZ, Zhang HL, Li JM. Distribution characteristics of mosquito and their natural infection with Japanese encephalitis virus in Yunnan Province[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2009, 20(4): 344-348. |
| [16] |
李秀华, 余庆福, 吴丽清, 等. 2001-2010年玉溪市乙型病毒性脑炎流行病学特征分析[J]. 预防医学情报杂志, 2012, 28(7): 567-569. Li XH, Yu QF, Wu LQ, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of Japanese encephalitis in Yuxi City from 2001 to 2010[J]. J Prev Med Inf, 2012, 28(7): 567-569. |
| [17] |
吕韬, 牟建春, 罗蟾卿. 2007-2011年云南省红河州流行性乙型脑炎流行特征分析[J]. 预防医学情报杂志, 2015, 31(4): 259-261. Lyu T, Mou JC, Luo CQ. Epidemiological characteristics of Japanese encephalitis in Honghe Prefecture, Yunnan, 2007-2011[J]. J Prev Med Inf, 2015, 31(4): 259-261. |
| [18] |
Roberts A, Gandhi S. Japanese encephalitis virus: A review on emerging diagnostic techniques[J]. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2020, 25(10): 1875-1893. DOI:10.2741/4882 |
| [19] |
凌珏, 李凯, 何于雯, 等. 云南省通海县蚊虫2株乙型脑炎病毒的分离鉴定[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2021, 16(5): 525-530. Ling J, Li K, He YW, et al. Isolation and identification of 2 strains of Japanese encephalitis virus from mosquitoes in Tonghai County, Yunnan Province[J]. Chin J Path Biol Parasit Biol, 2021, 16(5): 525-530. DOI:10.13350/j.cjpb.210506 |
| [20] |
张婧, 李加全, 冯云, 等. 云南省保山市蚊虫中检测到基因Ⅰ型流行性乙型脑炎病毒[J]. 疾病监测, 2018, 33(2): 150-154. Zhang J, Li JQ, Feng Y, et al. Identification of Japanese encephalitis virus genotype Ⅰ from mosquitoes in Baoshan, Yunnan[J]. Dis Surveill, 2018, 33(2): 150-154. DOI:10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2018.02.009 |
| [21] |
孙玉杰, 冯云, 章域震, 等. 云南新分离四株流行性乙型脑炎病毒全基因组序列特征研究[J]. 疾病监测, 2015, 30(8): 618-623. Sun YJ, Feng Y, Zhang YZ, et al. Molecular characteristics of full-length genomes of four strains of Japanese encephalitis virus newly isolated in Yunnan[J]. Dis Surveill, 2015, 30(8): 618-623. DOI:10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2015.08.004 |
| [22] |
冯云, 陈卫武, 杨卫红, 等. 云南省弥勒县2009年蚊媒病毒分离和鉴定[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2012, 23(5): 402-405. Feng Y, Chen WW, Yang WH, et al. Isolation and identification of mosquito-borne viruses in Mile County, Yunnan Province, China in 2009[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2012, 23(5): 402-405. |
| [23] |
谢吕, 林安琪, 王剑, 等. 云南省西南边境地区蚊虫及蚊媒病原体调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30(3): 264-267. Xie L, Lin AQ, Wang J, et al. An investigation of mosquitoes and mosquito-borne pathogens in the southwest border regions of Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30(3): 264-267. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2019.03.008 |
| [24] |
吴艳琴, 周友华, 周红宁, 等. 中越边境部分地区蚊虫种类及重要虫媒传染病带毒率调查[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2022, 17(2): 236-239. Wu YQ, Zhou YH, Zhou HN, et al. Investigation of mosquito species composition and their carrying virus rates of important mosquito borne diseases in the part of border areas of China-Vietnam[J]. Chin J Path Biol, 2022, 17(2): 236-239. DOI:10.13350/j.cjpb.220224 |
| [25] |
田杰, 郭晓芳, 周红宁, 等. 中缅边境地区不明原因发热病人蚊媒病毒性疾病分子流行病学调查[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2021, 16(5): 590-595, 613. Tian J, Guo XF, Zhou HN, et al. Molecular epidemiological survey of mosquito-borne viral diseases in patients with a fever of unknown origin at the border between China and Myanmar[J]. Chin J Path Biol, 2021, 16(5): 590-595, 613. DOI:10.13350/j.cjpb.210519 |
| [26] |
李雨晗, 张櫶文, 程功. 虫媒病毒与生物安全[J]. 生物学杂志, 2023, 40(6): 1-6. Li YH, Zhang XW, Cheng G. Arboviruses and biosafety[J]. J Biol, 2023, 40(6): 1-6. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2023.06.001 |
| [27] |
侯银续, 姚晨晨, 徐庆华, 等. 我国重要蚊媒病流行现状和疫苗研究进展[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2023, 29(4): 346-349. Hou YX, Yao CC, Xu QH, et al. Epidemic situation of important mosquito-borne diseases in China and the progress in vaccine research[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2023, 29(4): 346-349. DOI:10.19821/j.1671-2781.2023.04.015 |
 2024, Vol. 35
2024, Vol. 35


