扩展功能
文章信息
- 周秋明, 南春燕, 袁浩, 单文琪, 陶峰, 董昊炜, 彭恒, 马雅军
- ZHOU Qiu-ming, NAN Chun-yan, YUAN Hao, SHAN Wen-qi, TAO Feng, DONG Hao-wei, PENG Heng, MA Ya-jun
- 溴氰菊酯降解菌的筛选和鉴定研究
- Selection and identification of deltamethrin-degrading bacteria
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2024, 35(5): 517-522
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2024, 35(5): 517-522
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2024.05.002
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2023-10-24
拟除虫菊酯类化合物(pyrethroids,以下称菊酯类),是目前使用最为广泛的低毒杀虫剂,该类杀虫剂包括天然除虫菊素及其衍生物30余种,通过扰乱昆虫电压门控钠离子通道使之麻痹死亡[1]。溴氰菊酯(deltamethrin)是含有α-氰基的Ⅱ型拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂,具有高效杀虫活性,自1974年合成以来广泛应用于果蔬、谷物、茶叶等作物虫害防制,以及公共卫生领域防制蚊虫和蜚蠊等卫生害虫。由于菊酯类杀虫剂长期的暴露和积累,除了对藻类、鱼类、蜂类等有较高毒性,也会影响孕妇及儿童[2],对人体多个系统产生长期毒性[3]。自然环境中(土壤、水体)的菊酯类杀虫剂残留主要由微生物的活动去除[4-5],称为生物修复作用,微生物将杀虫剂作为其营养来源可分解矿化有机分子成为CO2和水,在短时间内有效降低杀虫剂残留的水平,使环境恢复健康状态[6]。
筛选可降解杀虫剂的微生物是生物修复作用研究的热点之一,其策略是从水体或土壤中培养、分离筛选出能够降解杀虫剂的菌种或菌群,再进一步测定其降解条件和降解效率。迄今,已筛选获得了多种可降解菊酯类杀虫剂的微生物[7],研究表明细菌[8]和真菌[9]均具有一定的降解潜能。本研究通过富集筛选、驯化分离得到稻田的溴氰菊酯降解菌,在鉴定菌种的基础上,进一步测定了降解菌群对溴氰菊酯、联苯菊酯和三氟氯氰菊酯的降解能力,以期将获得的降解菌群最终应用于原生地,以促进杀虫剂的快速分解。
1 材料与方法 1.1 水样分离降解菌的水样于2012年8月采自上海市嘉定区华亭镇稻田,现场分装入500 ml的无菌瓶中,带回实验室,4 ℃保存。
1.2 主要试剂溴氰菊酯原药(≥98%)、三氟氯氰菊酯原药(≥97%)和联苯菊酯原药(≥98%)(江苏扬州化工集团有限公司),牛肉膏提取物、琼脂(上海旭飞生物科技有限公司),胰蛋白胨、酵母提取物(Oxoid公司),2×Taq PCR Master Mix(北京艾德莱生物科技有限公司)。
1.3 培养基基础盐培养基(mineral salt medium,MSM)(选择性培养基,按需要添加菊酯类杀虫剂)和牛肉膏蛋白胨培养基[10],1×105 Pa灭菌15 min。固体培养基为上述培养基添加2%(质量体积比)琼脂粉,1×105 Pa灭菌20 min。
1.4 溴氰菊酯降解菌的驯化与富集降解菌的筛选驯化、富集纯化参照文献[11]进行。
1.4.1 筛选驯化取100 ml水样,5 000×g离心5 min,弃上清;无菌条件下向沉淀物中加入50 ml溴氰菊酯质量浓度为100 mg/L的MSM液体培养基,30 ℃,150 r/min条件下培养7 d。
接种上述培养液2.5 ml至溴氰菊酯浓度提高为300 mg/L的MSM液体培养基中,培养条件和时间同上;重复操作至溴氰菊酯质量浓度提高为500 mg/L,以培养7 d的培养液作为降解菌群种类鉴定的样本。
1.4.2 富集纯化在筛选驯化溴氰菊酯降解菌过程中,用接种环沾取少量培养液,以无菌水稀释后,涂布于相同浓度的MSM,30 ℃倒置培养,肉眼观察菌落生长情况和形态特征。
挑取单菌落的50%溶于10 μl ddH2O,以此为模板进行分子鉴定,其余50%接入MSM液体培养基富集扩大后,加入20%~50%的甘油,-80 ℃保存。
1.5 溴氰菊酯降解菌的种类鉴定 1.5.1 菌落16S rRNA序列分析单个菌落的16S rRNA基因扩增及PCR产物序列测定参照文献[12]进行。扩增16S rRNA基因全长的引物为27F(5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′)和1492R(5′-TACGGCTAC CTTGTTACGACTT-3′)。PCR反应体系:27F、1492R引物(10 mmol/L)各1 μl,2×Master Mix 12.5 μl,DNA模板2 μl,ddH2O补至25 μl。PCR反应条件:94 ℃ 1 min;95 ℃ 15 s,53 ℃ 15 s,72 ℃ 90 s,循环35次;72 ℃ 8 min。1%琼脂糖凝胶(含0.02‰ Goldview)电泳检测扩增产物,应用四色荧光标记的双脱氧末端终止法,用双向引物测序,所获序列提交至GenBank进行同源性比对分析,鉴定细菌种类。引物合成和序列测定由铂尚生物技术(上海)有限公司完成。
1.5.2 混合菌群Miseq宏基因组测序和分析取500 μl的降解菌培养液按照试剂盒操作步骤抽取基因组DNA,扩增细菌的16S rRNA V4区片段,正向引物为5′-AYTGGGYDTAAAGNG-3′,反向引物为5′-TACNVGGGTATC TAATCC-3′[12]。PCR产物通过3′-5′核酸外切酶及聚合酶的共同作用,修复带有突出末端的DNA片段,在3′端引入单碱基“A-”,与3′端“T-”的接头连接,利用PCR选择性富集有接头的DNA片段,同时扩增DNA文库,逐步稀释定量后上机测序,按照Illumina公司标准流程进行。获得的原始序列数据进行质量控制,双端拼接、过滤后,应用Qiime软件,在≥97%的相似度下,对获得的序列进行操作分类单元(operational taxonomic unit,OTU)聚类。通过比对亲缘关系的方法,注释每个OTU的分类学信息,在属和种水平分析细菌物种组成和丰度。MiSeq宏基因组测序由上海派森诺生物科技有限公司完成。
1.6 菌群降解效能的测定 1.6.1 培养液制备取降解菌菌群5 ml,接种到50 ml的牛肉膏蛋白胨培养液中,培养条件同上,间歇取样,测定600 nm处吸光值(A600),以OD600≈1时的菌液作为种子液。将种子液按5%的接种量分别接种到300 ml的溴氰菊酯、三氟氯氰菊酯和联苯菊酯质量浓度为50 mg/L的MSM培养基培养8 d,每组设置3次重复,未接种种子液的培养基为空白对照。培养至第2、3、4、6和8天时,从每组培养液中各取5 ml,混合后进行杀虫剂残留量测定,同时测A600。
1.6.2 杀虫剂残留测定参照《生活饮用水标准检验方法农药指标》(GB/T 5750.9-2006)[13],采用气相色谱-串联质谱(CC-MS/MS)测定杀虫剂残留,计算降解菌菌群对杀虫剂的降解率(ρ)。
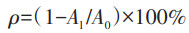
|
式中,Al为降解菌处理后杀虫剂残留浓度(mg/L),A0为对照组杀虫剂残留浓度(mg/L)。
1.6.3 降解菌群的生长情况观察降解菌群在降解3种菊酯类杀虫剂时的培养基混浊情况,并绘制生长曲线。
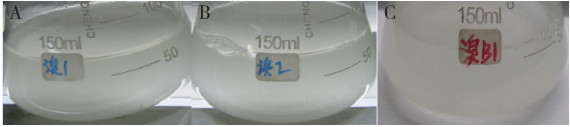
2 结果 2.1 溴氰菊酯降解菌的分离筛选本研究以溴氰菊酯为唯一碳源的MSM培养基进行降解菌的筛选,设置溴氰菊酯的浓度梯度为100、300和500 mg/L,振荡培养时,肉眼观察各浓度溴氰菊酯培养基中细菌的生长情况,出现浑浊的时间稍有差异,300 mg/L和500 mg/L出现浑浊时间为(4±1)d,100 mg/L出现浑浊时间为(5±1)d。见图 1。
|
| 注:A 100 mg/L,B 300 mg/L,C 500 mg/L。 图 1 溴氰菊酯降解菌在不同浓度溴氰菊酯基础盐培养基中的生长情况 Figure 1 The growth of deltamethrin-degrading bacteria in mineral salt medium containing deltamethrin at different concentrations |
| |
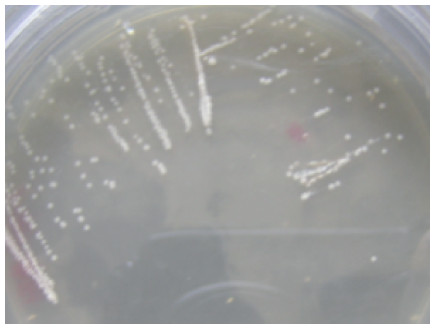
将分离的溴氰菊酯降解菌划线接种在MSM上,3 d后长出单菌落。肉眼观察显示绝大多数的菌落特征为:白色、圆形、湿润和扁平,表面光滑,边缘规则。见图 2。
|
| 图 2 溴氰菊酯降解菌在不同浓度溴氰菊酯基础盐固体培养基上的生长情况 Figure 2 The growth of deltamethrin-degrading bacteria in solid mineral salt medium containing deltaone thrin at different concetrations |
| |
挑取8个单菌落为模板PCR扩增16s rRNA全长,全长为1 500 bp左右,序列比对分析结果显示菌种为7种,除了2个菌落同为广温拟无枝酸菌(Amycolatopsis eurytherma)外,其他6个单菌落鉴定为鲍氏不动杆菌(Acinetobacter baumannii)、屈曲杆菌(Ancylobacter sp.)、红球菌(Rhodococcus gordoniae/R. pyridinivorans)、拟无枝酸菌(Am. eurytherma/Am. ethanolica/Am. thermoflava)、苍白杆菌(Ochrobactrum sp.)和黄色杆菌(Xanthobacter sp.)。
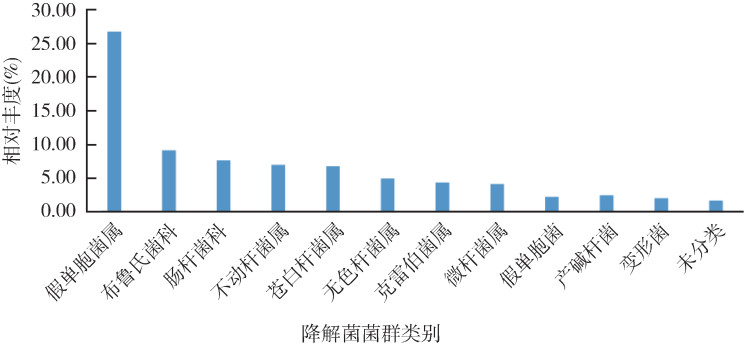
2.2.3 降解菌菌群鉴定对菌群样品的OTUs在属水平进行归类和整理。丰度 > 4%的细菌属分别为假单胞菌属(26.78%),不动杆菌属(7.00%),苍白杆菌属(6.82%),无色杆菌属(4.96%),克雷伯菌属(4.39%),微杆菌属(4.12%),有10.67%的细菌未注释。对科水平进行归类和整理,优势菌为布鲁氏菌科(9.15%)和肠杆菌科(7.68%)。丰度 > 1%的菌群菌种共12个。见图 3。
|
| 图 3 溴氰菊酯降解菌群的细菌及其相对丰度(> 1%) Figure 3 Bacterial genus and relative abundance (> 1%) in the deltamethrin-degrading bacterial flora |
| |
依据各时间段内测得的杀虫剂残留,计算菌群降解溴氰菊酯、联苯菊酯和三氟氯氰菊酯杀虫剂的降解率。3个实验组的杀虫剂浓度随着培养时间的延长,均存在一定程度的下降,降解率数据显示,联苯菊酯在第2天达60.44%,第8天时,降解率达76.75%;溴氰菊酯在第4天为61.51%,第8天为63.65%;三氟氯氰菊酯在前3 d降解缓慢,之后迅速上升,第6天达平台期,为74.10%。见表 1。
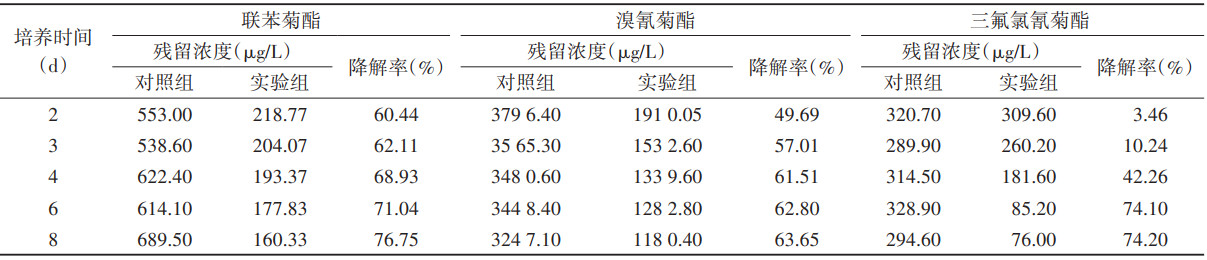
|
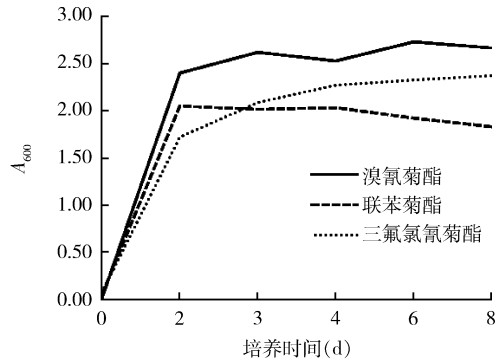
降解菌群在降解3种杀虫剂时的生长情况显示,从接种至第2天,菌群处于对数生长时期,之后三氟氯氰菊酯和溴氰菊酯实验组在第2~8天生长处于平台期,而降解联苯菊酯的实验组在第4天起即进入衰亡期,降解菌群的生长曲线符合微生物的生长规律。见图 4。
|
| 图 4 降解菌群降解3种菊酯类杀虫剂时的生长曲线 Figure 4 The growth curves of the flora degrading three pyrethroid insecticides |
| |
化学杀虫剂被广泛用于农作物害虫防制,稻田中杀虫剂的大量使用和残留,导致稻田水体中孳生的蚊虫暴露其中,在有些地区加剧和促进了其抗性水平[14]。生物修复作用可以消除环境中残留的杀虫剂,缓解和降低杀虫剂对蚊虫的选择压力。本研究通过富集筛选、驯化分离得到能降解溴氰菊酯的菌种,并测定了对溴氰菊酯、联苯菊酯和三氟氯氰菊酯的降解能力,获得的降解菌群为其最终应用至原生地—稻田,促进杀虫剂的快速降解提供了基础资料。
本研究分离筛选的可降解溴氰菊酯的优势细菌隶属于假单胞菌属、布鲁氏菌科、肠杆菌科、不动杆菌属、苍白杆菌属、无色杆菌属、拟无枝酸菌属、红球菌属和黄色杆菌属9个属(科),后3个属是单菌落鉴定的结果。目前已报告的对菊酯类杀虫剂具有降解效能的细菌很多,包括无色杆菌属[15]、芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)[16]、固氮弧菌(Azoarcus indigens)[17]、梭状芽孢杆菌属(Clostridium)[18]、鞘氨醇菌属(Sphingobium sp.)[19]、克雷伯菌属[20]、沙雷菌属(Serratia)[21]、酸单胞菌属(Acidomonas)[22]、假单胞菌属[23-24]、寡养单胞菌属(Stenotrophomonas)[25]和红球菌属[26]等,提示可降解菊酯类杀虫剂的细菌种类众多,本研究中溴氰菊酯降解菌筛选自水体,首次注释了黄色杆菌属、拟无枝酸菌属、不动杆菌属和苍白杆菌属,提示不同环境中筛选的降解菌有所不同。
拟除虫菊酯的衍生物较多,在自然环境中检测到的主要是Ⅱ型,残留量通常是作物 > 沉积物 > 土壤 > 水体,Ⅰ型主要在室内环境[27]。目前研究报告较多的是降解Ⅱ型菊酯类杀虫剂的效能,结果显示相同的细菌可降解多种菊酯类衍生物,如克雷伯菌可降解氯氰菊酯,假单胞菌属种类除了降解溴氰菊酯和联苯菊酯外,还可降解氯氰菊酯[24, 28]、β-氟氯氰菊酯[23]和甲氰菊酯[29];寡养单胞菌可降解联苯菊酯[23]、高效氯氰菊酯和氰戊菊酯[30]。本研究筛选的溴氰菊酯降解菌群对联苯菊酯、三氟氯氰菊酯均具有较强的降解效能,结合降解率和菌群的生长情况可见,菌群生长在对数期时,降解率均处于增长阶段;菌群生长在平台期和衰亡期时,降解率增长缓慢或不再增长。本研究分离鉴定的降解菌群中菌种150余种(类),各菌种的降解效能尚需纯化后进一步测定。此外,各菌种之间是协同或拮抗作用,也需深入探讨。
在实验室分离筛选环境中的降解菌,可为生物修复杀虫剂污染的环境提供优良的微生物资源。本研究中降解菌降解杀虫剂的实验是在30 ℃,150 r/min条件下进行的,因此有可能加速杀虫剂的降解,故降解菌在现场应用时,降解条件尚需优化,实际的降解效能也需要进一步确定[31-32]。
已证实孳生地水体中细菌是幼虫摄取的食物之一,但其肠道环境对细菌有一定的选择性,仅少数细菌才可定植,稻田水体中的菌群与蚊幼虫肠道共生菌更相似[33]。本研究分离筛选的降解菌,部分为蚊肠道共生菌,如不动杆菌属、红球菌属等,而有报告蚊虫可利用其肠道共生菌自身的降解和解毒作用降解杀虫剂,以增强蚊虫对杀虫剂抗性[34],因此,将降解菌应用于现场进行生物修复时,需要综合考量和平衡各种因素,避免在消除环境中残留的杀虫剂时,又带来了新的问题。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
Field LM, Emyr Davies TG, O'Reilly AO, et al. Voltage-gated sodium channels as targets for pyrethroid insecticides[J]. Eur Biophys J, 2017, 46(7): 675-679. DOI:10.1007/s00249-016-1195-1 |
| [2] |
Li HZ, Cheng F, Wei YL, et al. Global occurrence of pyrethroid insecticides in sediment and the associated toxicological effects on benthic invertebrates: An overview[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2017, 324: 258-271. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.056 |
| [3] |
张婉莉, 彭恒, 单文琪, 等. 驱避剂安全性研究进展[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2022, 33(4): 601-607. Zhang WL, Peng H, Shan WQ, et al. Research progress on safety of repellents[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2022, 33(4): 601-607. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2022.04.029 |
| [4] |
Cycoń M, Piotrowska-Seget Z. Pyrethroid-degrading microorganisms and their potential for the bioremediation of contaminated soils: A review[J]. Front Microbiol, 2016, 7: 1463. DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2016.01463 |
| [5] |
Williams IH, Brown MJ. Persistence of permethrin and WL 43775 in soil[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 1979, 27(1): 130-132. DOI:10.1021/jf60221a017 |
| [6] |
Huang YC, Xiao LJ, Li FY, et al. Microbial degradation of pesticide residues and an emphasis on the degradation of cypermethrin and 3-phenoxy benzoic acid: A review[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(9): 2313. DOI:10.3390/molecules23092313 |
| [7] |
王晓慧, 商文贤, 徐宏英, 等. 高效氯氟氰菊酯的微生物降解研究进展[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2020, 37(3): 7-14. Wang XH, Shang WX, Xu HY, et al. Research progress in microbial degradation of lambda-Cyhalothrin[J]. Chem Bioeng, 2020, 37(3): 7-14. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2020.03.002 |
| [8] |
Yang JJ, Feng YM, Zhan H, et al. Characterization of a pyrethroid-degrading Pseudomonas fulva strain P31 and biochemical degradation pathway of D-phenothrin[J]. Front Microbiol, 2018, 9: 1003. DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2018.01003 |
| [9] |
Deng WQ, Lin DR, Yao K, et al. Characterization of a novel β-cypermethrin-degrading Aspergillus niger YAT strain and the biochemical degradation pathway of β-cypermethrin[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2015, 99(19): 8187-8198. DOI:10.1007/s00253-015-6690-2 |
| [10] |
周德庆, 徐德强, 胡宝龙. 微生物学实验教程[M]. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2013: 87-90. Zhou DQ, Xu DQ, Hu BL. Experimental microbiology[M]. 3rd ed.. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2013: 87-90. |
| [11] |
胡琼, 唐洁, 雷丹, 等. 一株溴氰菊酯降解菌的分离鉴定及其降解条件优化[J]. 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(3): 699-709. Hu Q, Tang J, Lei D, et al. Isolation, identification and optimization of degradation conditions of a deltamethrin degrading strain[J]. Microbiol China, 2020, 47(3): 699-709. DOI:10.13344/j.microbiol.china.190633 |
| [12] |
Wang Y, Qian PY. Conservative fragments in bacterial 16S rRNA genes and primer design for 16S ribosomal DNA amplicons in metagenomic studies[J]. PLoS One, 2009, 4(10): e7401. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0007401 |
| [13] |
陈红平, 刘新, 汪庆华, 等. 气相色谱-串联质谱法测定茶叶中88种农药残留量[J]. 色谱, 2011, 29(5): 409-416. Chen HP, Liu X, Wang QH, et al. Determination of 88 pesticide residues in tea using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chin J Chromatogr, 2011, 29(5): 409-416. DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1123.2011.00409 |
| [14] |
Wang Y, Yu WQ, Shi H, et al. Historical survey of the kdr mutations in the populations of Anopheles sinensis in China in 1996-2014[J]. Malar J, 2015, 14: 120. DOI:10.1186/s12936-015-0644-0 |
| [15] |
Maloney SE, Maule A, Smith AR. Microbial transformation of the pyrethroid insecticides: Permethrin, deltamethrin, fastac, fenvalerate, and fluvalinate[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol, 1988, 54(11): 2874-2876. DOI:10.1128/aem.54.11.2874-2876.1988 |
| [16] |
Pankaj, Sharma A, Gangola S, et al. Novel pathway of cypermethrin biodegradation in a Bacillus sp. strain SG2 isolated from cypermethrin-contaminated agriculture field[J]. 3 Biotech, 2016, 6(1): 45. DOI:10.1007/s13205-016-0372-3 |
| [17] |
Ma Y, Chen LS, Qiu JG. Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin by a novel Azoarcus indigens strain HZ5[J]. J Environ Sci Health, Part B, 2013, 48(10): 851-859. DOI:10.1080/03601234.2013.795843 |
| [18] |
Zhang SB, Yin LB, Liu Y, et al. Cometabolic biotransformation of fenpropathrin by Clostridium species strain ZP3[J]. Biodegradation, 2011, 22(5): 869-875. DOI:10.1007/s10532-010-9444-y |
| [19] |
Guo P, Wang BZ, Hang BJ, et al. Pyrethroid-degrading Sphingobium sp. JZ-2 and the purification and characterization of a novel pyrethroid hydrolase[J]. Int Biodeter Biodegr, 2009, 63(8): 1107-1112. DOI:10.1016/j.ibiod.2009.09.008 |
| [20] |
梁卫驱, 刘玉焕, 李荷. 氯氰菊酯降解菌的分离鉴定及其降解特性研究[J]. 广东药学院学报, 2007, 23(2): 199-202, 204. Liang WQ, Liu YH, Li H. Isolation, identification and characterization of a cypermethrin-degrading strain J-2[J]. J Guangdong Coll Pharm, 2007, 23(2): 199-202, 204. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-8783.2007.02.033 |
| [21] |
Cycoń M, Żmijowska A, Piotrowska-Seget Z. Enhancement of deltamethrin degradation by soil bioaugmentation with two different strains of Serratia marcescens[J]. Int J Environ Sci Technol, 2014, 11(5): 1305-1316. DOI:10.1007/s13762-013-0322-0 |
| [22] |
Paingankar M, Jain M, Deobagkar D. Biodegradation of allethrin, a pyrethroid insecticide, by an Acidomonas sp.[J]. Biotechnol Lett, 2005, 27(23/24): 1909-1913. DOI:10.1007/s10529-005-3902-3 |
| [23] |
Saikia N, Das SK, Patel BKC, et al. Biodegradation of beta-cyfluthrin by Pseudomonas stutzeri strain S1[J]. Biodegradation, 2005, 16(6): 581-589. DOI:10.1007/s10532-005-0211-4 |
| [24] |
李青云, 顾宝群, 刘幽燕, 等. 氯氰菊酯降解菌GF31的分离鉴定及其降解特性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2009, 36(9): 1334-1339. Li QY, Gu BQ, Liu YY, et al. Isolation, identification and characteristics of a cypermethrin-degrading bacterium GF31[J]. Microbiology, 2009, 36(9): 1334-1339. |
| [25] |
Lee S, Gan JY, Kim JS, et al. Microbial transformation of pyrethroid insecticides in aqueous and sediment phases[J]. Environ Toxicol Chem, 2004, 23(1): 1-6. DOI:10.1897/03-114 |
| [26] |
许育新, 孙纪全, 李晓慧, 等. 两株菌对氯氰菊酯及其降解产物3-PBA的协同代谢研究[J]. 微生物学报, 2007, 47(5): 834-837. Xu YX, Sun JQ, Li XH, et al. Study on cooperating degradation of cypermethrin and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by two bacteria strains[J]. Acta Microbiol Sin, 2007, 47(5): 834-837. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-6209.2007.05.017 |
| [27] |
Tang WX, Wang D, Wang JQ, et al. Pyrethroid pesticide residues in the global environment: An overview[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 191: 990-1007. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.115 |
| [28] |
汤鸣强, 田盼, 尤民生. 氰戊菊酯降解菌FDB的分离鉴定及其生长特性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2010, 37(5): 682-688. Tang MQ, Tian P, You MS. Isolation, identification and growth characteristics of a fenvalerate degradation bacterium[J]. Microbiol China, 2010, 37(5): 682-688. DOI:10.13344/j.microbiol.china.2010.05.014 |
| [29] |
王兆守, 林淦, 尤民生, 等. 茶叶上拟除虫菊酯类农药降解菌的分离及其特性[J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(7): 1824-1827. Wang ZS, Lin G, You MS, et al. Isolation and character of synthetic pyrethroid insecticides-degrading bacteria from tea leaves[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2005, 25(7): 1824-1827. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.07.041 |
| [30] |
陈少华, 耿鹏, 胡美英, 等. 菌株Stenotrophomonas sp. ZS-S-01去除菜心中残留高效氯氰菊酯和氰戊菊酯农药的作用[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2011, 32(4): 47-52. Chen SH, Geng P, Hu MY, et al. Effects of Stenotrophomonas sp. strain ZS-S-01 on the degradation of β -cypermethrin and fenvalerate residue on flowering Chinese cabbage[J]. J South China Agric Univ, 2011, 32(4): 47-52. DOI:10.7671/j.issn.1001-411X.2011.04.011 |
| [31] |
韦  军, 刘幽燕, 张洪威, 等. 铜绿假单胞菌GF31降解土壤中氯氰菊酯的性能研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2011, 33(10): 55-58, 100. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2011.10.012. 军, 刘幽燕, 张洪威, 等. 铜绿假单胞菌GF31降解土壤中氯氰菊酯的性能研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2011, 33(10): 55-58, 100. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2011.10.012. Wei YJ, Liu YY, Zhang HW, et al. Biodegradation of cypermethrin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa GF31 in the soil environment[J]. Environ Pollut Control, 2011, 33(10): 55-58, 100. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2011.10.012.(in Chinese) |
| [32] |
丁海涛, 李顺鹏, 沈标, 等. 拟除虫菊酯类农药残留降解菌的筛选及其生理特性研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2003, 40(1): 123-129. Ding HT, Li SP, Shen B, et al. Isolation of pyrethroids degrading strain and its physiological characteristics[J]. Acta Pedol Sin, 2003, 40(1): 123-129. DOI:10.11766/trxb200012250117 |
| [33] |
董昊炜, 南春燕, 周秋明, 等. 基于16S rRNA高通量测序的现场中华按蚊及其孳生地水体菌群结构研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32(5): 533-540. Dong HW, Nan CY, Zhou QM, et al. Composition of microbiota in Anopheles sinensis and water in larvae breeding site: A study based on 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32(5): 533-540. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2021.05.005 |
| [34] |
Wang HY, Liu HM, Peng H, et al. A symbiotic gut bacterium enhances Aedes albopictus resistance to insecticide[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2022, 16(3): e0010208. |
 2024, Vol. 35
2024, Vol. 35


