扩展功能
文章信息
- 董学书, 施靖, 孙晓东, 郭小连
- DONG Xue-shu, SHI Jing, SUN Xiao-dong, GUO Xiao-lian
- 中国伊蚊属覆蚊亚属一新种(双翅目:蚊科)
- A new species of the subgenus Stegomyia in the genus Aedes in Yunnan Province, China (Diptera: Culicidae)
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2024, 35(4): 489-492
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2024, 35(4): 489-492
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2024.04.019
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2023-11-08
2 临沧市疾病预防控制中心传染病防治科, 云南 临沧 677000
2 Office for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Lincang Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Lincang, Yunnan 677000, China
伊蚊属(genus Aedes)覆蚊亚属(subgenus Stegomyia)包括至少132个蚊种,云南的覆蚊亚属蚊种包括至少16种。覆蚊亚属是一个重要的医学类群,该亚属中的埃及伊蚊(Aedes aegypti)和白纹伊蚊(Ae. albopictus)是登革病毒、黄热病毒、寨卡病毒和基孔肯雅病毒等的重要传播媒介[1-2],其他公认的黄热病毒媒介包括分布于非洲中部和西部地区的非洲伊蚊(Ae. africanus)和黄头伊蚊(Ae. luteocephalus),以及东非的凤梨伊蚊(Ae. bromeliae)。
白纹伊蚊在云南分布广泛,全省至少15个州(市)的71个县(市、区)的主城区有白纹伊蚊分布,而埃及伊蚊在2002年2月被首次发现于云南省瑞丽市后,目前已经在瑞丽市、芒市、勐腊县、勐海县、景洪市、盈江县、陇川县、泸水市、耿马傣族佤族自治县(耿马县)等地陆续被发现[3]。近年来,随着登革热暴发流行,云南省的重点县市持续不断地开展蚊虫监测,2017年2月在位于中缅边境的临沧市镇康县开展蚊虫监测过程中,在勐堆乡政府驻地周围(98°53′31″E,23°55′9″N)的一废弃轮胎中捕获一批伊蚊幼虫,通过单独饲养后,检视了6只3龄以上幼虫和4只成蚊,除幼虫样本因运输过程中保存方法不当导致无法制作成可供描述的标本外,其余4只成蚊均被收集制作成不同特征的针插和玻片标本(雄蚊1只、雌蚊3只、雄蚊尾器1片和雌蚊尾器1片),通过形态学观察,发现此标本为覆蚊亚属1新种——勐堆伊蚊[Aedes(Stegomyia)mengduiensis sp. nov],该新种与白纹伊蚊在形态学上具有相似性。全部标本均保存于云南省寄生虫病防治所蚊类标本馆。现将该新种成蚊记述如下。
1 形态描述成蚊为中型黑褐色蚊,翅长2.5~2.8 mm。
1.1 雌蚊(图 1A)
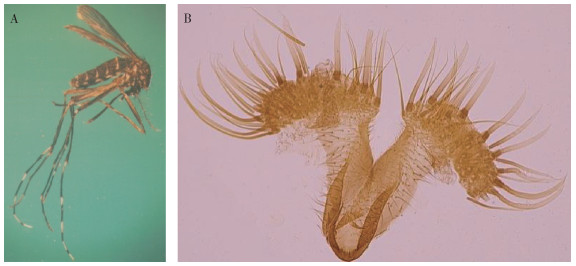
|
| 图 1 新种勐堆伊蚊雌蚊侧面观(A)和雄蚊小抱器(B) Figure 1 The lateral view of female adult (A) and male claspette (B) of Aedes (Stegomyia) mengduiensis sp. nov. |
| |
头 头顶中央具有发达的白斑,两侧密覆黑褐色宽鳞。唇基黑色光裸,触角梗节密覆银白宽鳞。触须长为喙长的1/5,末端背面具白鳞。喙全部黑褐色。
胸 前胸前背片和后背片密覆银色宽鳞,中胸盾片密覆黑褐色窄鳞,中央银白纵条在小盾前区中断,中侧纵条不明显,翅基前有窄白鳞,小盾片全部密覆银白宽鳞,后背片黑色光裸。翅:翅鳞密集呈黑褐色,前缘脉、亚前缘脉和纵脉1(V.1)为宽鳞,其余纵脉为窄鳞。平衡棒结节具黑鳞。足:前、中股节基段腹面淡色,背面全部黑色,后股节2/3腹面大部淡色,背面黑色。全部胫节为黑色。前、中跗节1~2有基白环或白斑,后跗节1~4有宽的基白环,节4的基白环占节4全长的3/4以上,节5全白色。
腹 腹节背板黑褐色,Ⅲ~Ⅵ背板的基白带不完整,与侧白斑分离。尾器:腹节Ⅷ背板前宽后窄,后缘平齐,后1/2有少量鳞毛和刚毛,腹节Ⅷ腹板后端宽于前端,后1/2中央深度内凹,凹部的两侧及后缘有密集的刺毛,并有稀疏分散的鳞片和刚毛。腹节Ⅸ背板前窄后宽,后端中央内凹呈弧形,凹部的两侧各有5~6根细毛。生殖后叶前宽后窄,后端中央凸起,其两侧各有1根长刚毛,前外侧各有1根短刚毛。上阴片不发达,短而较窄。尾须发达,亚基部外凸,端后缘刚毛稀少,且短而细。上阴唇和下阴唇窄带状。见图 2。
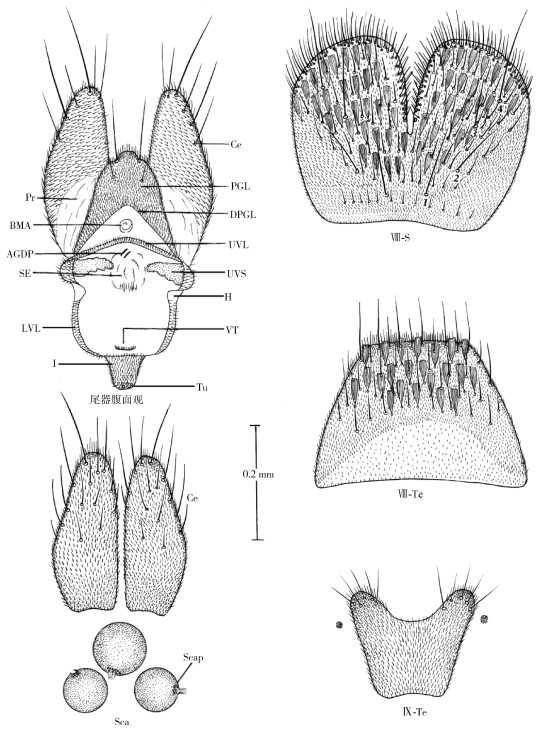
|
| 注:Ce尾须;PGL生殖后叶;Pr肛前膜;DPGL肛前膜附线;BMA基中内突;UVL上阴唇;AGDP附线管基;UVS上阴片;SE受精囊突起;H接点;LVL下阴唇;VT腹丛;I英岛片;Tu瘤突;Ⅷ-S腹节Ⅷ腹板;Ⅷ-Te腹节Ⅷ背板;Ⅸ-Te腹节Ⅸ背板;Sca受精囊;Scap受精囊孔。 图 2 勐堆伊蚊雌蚊尾器 Figure 2 Genitalia of female Aedes (Stegomyia) mengduiensis sp. nov. |
| |
尾器:腹节Ⅸ背板发达,前半部色淡,后半部色暗,中央后凸乳头状,两侧叶发达,各有4~5根细毛。抱肢基节粗壮,背外缘无鳞,但有密集的刚毛群。抱肢端节较短且粗壮,长为抱肢基节的2/3,末端明显膨大。小抱器形态特殊,端节膨大呈扇状,有7~8根叶状刺、5~6根弯刺和众多刚毛,柄部密覆细刺毛,见图 1B。肛侧片发达,末端钝圆。阳茎端部膨大,具端齿18~20个,并有4~5个侧齿。见图 3。
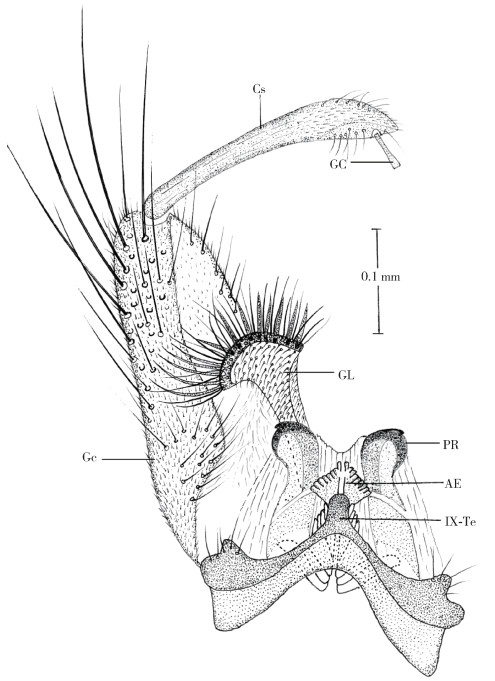
|
| 注:Gs抱肢端节;GC指爪;GL小抱器;Gc抱肢基节;PR肛侧片;AE阳茎;Ⅸ-Te腹节Ⅸ背板。 图 3 勐堆伊蚊雄蚊尾器 Figure 3 Genitalia of male Aedes (Stegomyia) mengduiensis sp. nov. |
| |
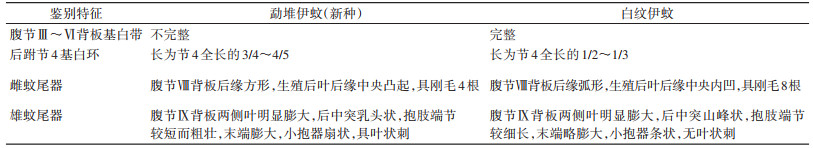
本新种与白纹伊蚊在形态学上近似,两者主要区别见表 1。
|
覆蚊亚属的蚊幼虫可孳生于天然和人工容器中。自然环境中,典型的孳生地是树洞,少数蚊种生长在岩石洞、螃蟹洞和各种植物的叶腋中[1]。在云南省居民区的调查中发现,白纹伊蚊主要孳生容器为废弃轮胎容器和水桶,埃及伊蚊具有明显的家栖性,2种蚊虫可混合孳生在同一个容器中[3-5],本次发现的勐堆伊蚊新种孳生于轮胎中,不排除该新种与白纹伊蚊混合孳生的可能,在新种幼虫形态与白纹伊蚊无明显区别的情况下,这无疑增加了准确识别和判断登革热等传播媒介种类和分布的难度。另外,由于勐堆伊蚊的种群数量和医学重要性尚不可知,更需要在实际工作中注意区分白纹伊蚊和勐堆伊蚊。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
Maquart PO, Fontenille D, Rahola N, et al. Checklist of the mosquito fauna (Diptera, Culicidae) of Cambodia[J]. Parasite, 2021, 28: 60. DOI:10.1051/parasite/2021056 |
| [2] |
董学书, 周红宁, 龚正达. 云南蚊类志(下卷)[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 2010: 92-113. Dong XS, Zhou HN, Gong ZD. The mosquito fauna of Yunnan, China (Vol. 2)[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science Press, 2010: 92-113. |
| [3] |
周克梅, 杨明东, 兰学梅, 等. 云南省129个县(市、区)主城区登革热媒介伊蚊分布调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32(2): 150-157. Zhou KM, Yang MD, Lan XM, et al. An investigation of the distribution of dengue vector Aedes in the main urban areas of 129 counties (cities, districts) of Yunnan Province, China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32(2): 150-157. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2021.02.006 |
| [4] |
Walker KR, Joy TK, Ellers-Kirk C, et al. Human and environmental factors affecting Aedes aegypti distribution in an arid urban environment[J]. J Am Mosq Control Assoc, 2011, 27(2): 135-141. DOI:10.2987/10-6078.1 |
| [5] |
王戈, 张恒端, 高剑, 等. 云南省边境地区埃及伊蚊和白纹伊蚊孳生特征调查[J]. 寄生虫与医学昆虫学报, 2021, 28(3): 159-164. Wang G, Zhang HD, Gao J, et al. Investigation on the breeding sites of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus in border areas of Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Parasitol Med Entomol Sin, 2021, 28(3): 159-164. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-0507.2021.03.005 |
 2024, Vol. 35
2024, Vol. 35


