扩展功能
文章信息
- 汪子豪, 常楠, 李晋宇, 李世豪, 郝馨凝, 胡伟超, 韦晓慧, 王晓旭, 刘起勇
- WANG Zi-hao, CHANG Nan, LI Jin-yu, LI Shi-hao, HAO Xin-ning, HU Wei-chao, WEI Xiao-hui, WANG Xiao-xu, LIU Qi-yong
- 内蒙古长爪沙鼠病原体监测研究
- Pathogen surveillance results of Meriones unguiculatus in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2024, 35(4): 422-428
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2024, 35(4): 422-428
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2024.04.007
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2024-01-18
2 传染病溯源预警与智能决策全国重点实验室, 中国疾病预防控制中心传染病预防控制所媒介生物控制室, 世界卫生组织媒介生物监测与管理合作中心, 北京 102206;
3 山东大学齐鲁医学院公共卫生学院, 山东, 济南 250012
2 Department of Vector Biology and Control, National Key Laboratory of Intelligent Tracking and Forecasting for Infectious Diseases, National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, WHO Collaborating Centre for Vector Surveillance and Management, Beijing 102206, China;
3 School of Public Health, Cheeloo College Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong 250012, China
鼠类是重要的疾病宿主,全球范围内约有90%的鼠种携带着超过200种病原微生物。其中,多达57种微生物对人类具有致病性,可引发31种病毒性疾病、14种细菌性疾病、5种立克次体病以及7种寄生虫病,对人类健康产生了潜在威胁[1]。近年来,我国出现了新发媒介生物传染病如发热伴血小板减少综合征(sever fever with thrombocytopenia syndrom,SFTS)等,并且肾综合征出血热(hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome,HFRS)多次暴发流行[2],鼠类作为大别班达病毒(Dabie bandavirus,DBV)和汉坦病毒(Hantavirus)的自然宿主[3-4],在疾病传播链中起着关键作用。研究显示[5-7],鼠源疾病的流行与气候密切相关。内蒙古自治区(内蒙古)属于温带大陆性气候,具有独特的季节变化:夏季温暖且降水丰沛,秋季则日夜温差大,冬季干燥且寒冷,这使得内蒙古成为众多鼠类的理想栖息地[8],特别是乌兰察布和鄂尔多斯高原,这些典型的荒漠草原区域以层状高平原地形和半荒漠景观著称[9],是长爪沙鼠(Meriones unguiculatus)鼠疫疫源地,近年来鼠疫在该地区偶发或散发[5]。目前,大多数研究主要集中在监测其携带鼠疫耶尔森菌(Yersinia pestis)上[10-11],但长爪沙鼠携带的其他病原体可能同样对公共卫生构成威胁。对长爪沙鼠进行多病原体的综合监测,不仅能建立起一种经济高效的早期预警系统,还能及时发现并应对新发或再发传染病,从而更有效地保护公众健康。
1 材料与方法 1.1 组织标本采集在内蒙古自治区选取呼伦贝尔市新巴虎右旗达赉苏木(116°58'48″E,49°7'12″N,代码N1)、锡林郭勒盟东乌珠穆沁旗(116°58'12″E,45°30'36″N,代码N2)、锡林浩特市朝克乌拉苏木(116°22'48″E,44°50'24″N,代码N3或W3)、白音锡勒牧场五连(116°47'24″E,44°4'48″N,代码N4)、太仆寺旗贡宝拉格苏木(115°10'12″E,41°42'36″N,代码N5);锡林郭勒盟苏尼特右旗(112°39'36″E,42°45'0″N,代码W1);锡林郭勒盟阿巴嘎旗(114°57'0″E,44°1'12″N,代码W2)、中东部西乌旗(118°26'24″E,44°42'0″N,代码W4)、通辽市科尔沁左中旗珠日河牧场(W5122°15'36″E,43°37'12″N,代码W5)等9个调查点,2021-2023年每年分别于5、7、9月进行动物的捕获及其组织标本的采集,其中W1至W5具有降水梯度。鼠类采集方法包括鼠夹法和鼠笼法。鼠夹法每样地布置300个鼠夹,每隔5 m布设一个,并保持布设2天2夜;鼠笼法每样地选择鼠类较为密集的样地或洞口,布设100个鼠笼,笼距为5 m。记录采获鼠位置坐标。捕获到的鼠根据外部特征参考《啮齿动物学(第二版)》进行形态学分类鉴定,并记录捕获方法、时间、地点、状态、性别、体质量等基本信息,取肝脏、脾脏等器官。采集到的标本保存于液氮中。野外标本采集时,遵循严格的标准和程序并且工作人员均经过生物安全防护培训。在野外,工作人员着白色防护服和防蚤袜,操作鼠夹时戴白色线手套,使用驱避剂保护身体暴露部位,采集过程中或结束后两人一组互相检查以确保无蚤或蜱附着;避免直接接触鼠体,并快速、安全地处理标本;对于死亡或出血的鼠标本,使用专用工具小心处理,确保安全。解剖过程中做好个人防护,防止被病原体感染或鼠体表寄生虫叮咬。
1.2 核酸提取和病原检测挑选长爪沙鼠样本,剪取米粒大小脾样本放入研磨管,加入200 µl磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)及少量研磨珠,在RZ-Gr96高通量研磨仪(北京国科融智生物技术有限公司)中选择程序进行研磨,参数设置为1 600 r/min,时间80 s,暂停30 s,循环3次。研磨好的样本吸取上清液采用病毒DNA/RNA提取试剂盒(西安天隆科技有限公司),使用TIANLONG NP968核酸提取仪(西安天隆科技有限公司)提取核酸。将提取完的核酸转移至离心管中,通过ND-1000分光光度计(美国Thermo NanoDrop)测定浓度并保存在-20 ℃冰箱。根据《全国病媒生物病原学监测方案(试行)》,针对法定传染病中的主要鼠源性疾病、引发新发和再发传染病的以及具有潜在人类健康威胁的鼠传病原体进行监测,包括巴尔通体(Bartonella)、DBV、致病性钩端螺旋体(致病性钩体,Leptospira interrogans)、土拉弗朗西斯菌(Francisella tularensis)、地方性斑疹伤寒立克次体[Rickettsia typhi,原莫氏立克次体(R. mooseri)]、恙虫病东方体(Orientia tsutsugamushi)、嗜吞噬细胞无形体(Anaplasma phagocytophilum)、汉坦病毒。采用上述方案中提供的引物及探针(均由北京擎科生物公司合成),其中6种细菌检测的反应体系配比为:10 μl Taq Pro HS Universal U⁺ Probe Master Mix,正、反向引物各0.4 μl,0.2 μl TaqMan Probe,3 μl DNA模板,6 μl ddH2O;DBV检测的反应体系配比为:10 μl One Step Q Probe Mix,1 μl One Step Q Probe Enzyme Mix,正、反向引物各1.2 μl,0.6 μl TaqMan Probe,3 μl RNA模板、3 μl ddH2O;汉坦病毒检测的反应体系配比为:10 μl One Step Q Probe Mix,1 μl One Step Q Probe Enzyme Mix,正、反向引物各0.8 μl,0.4 μl TaqMan Probe,3 μl RNA模板,4 μl ddH2O。使用Bio-Rad CFX96荧光定量PCR仪(美国伯乐)进行PCR扩增,同时设置阳性、阴性对照。DNA模板反应参数:95 ℃ 5 min;95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 45 s,40个循环。RNA模板反应参数:50 ℃ 30 min,95 ℃ 10 min;95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 45 s,40个循环。结果依据上述监测方案给定的循环阈值(Ct)参考值、扩增曲线的形状及阴性、阳性对照判定。
1.3 DNA序列分析将阳性率较高的巴尔通体DNA进行rpoB基因的常规PCR扩增,正向引物序列为5′-CGCATTATGGTCGTATTTGTCC-3′,反向引物序列为5′-GCACGATTYGCATCATCATTTTCC-3′,扩增产物送至北京德奥平生物公司进行测序。反应体系配比为:12.5 μl High-Fidelity Master Mix,正、反向引物各1 μl,2 μl DNA模板,8.5 μl ddH2O。测序得到的DNA序列通过MEGA 11.0软件进行多序列比对,bootstrap设为1 000次,通过邻接法构建系统进化树。
1.4 统计学分析使用Excel 2021与SPSS 26.0软件进行数据的整理与分析。使用χ2检验比较长爪沙鼠携带的巴尔通体与DBV阳性率在季节与地点间的差异。采用趋势χ2检验分析巴尔通体、DBV阳性率与季节和地点间线性相关关系。P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 病原体检测情况在N1、N2、N3/W3(N3、W3为同一采样点)、W1、W2、W4、W5捕获到长爪沙鼠。共检测长爪沙鼠样本320份,其中巴尔通体阳性128份,阳性率为40.00%,DBV阳性22份,阳性率为6.88%,土拉弗朗西斯菌阳性2份,钩体阳性9份,立克次体阳性2份,嗜吞噬细胞阳性1份,恙虫病东方体阳性1份,汉坦病毒阳性1份。见表 1。
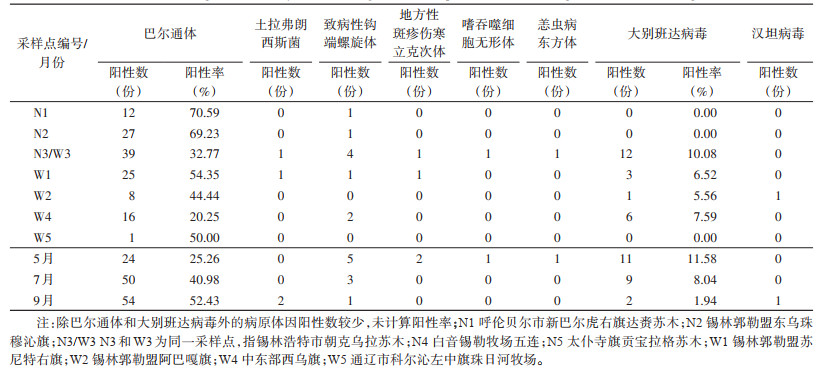
|
通过基于局部比对算法的搜索工具(BLAST)进行序列分别比对,结果显示内蒙古长爪沙鼠感染的巴尔通体序列分别与B. pachyuromydis、克氏巴尔通体(B. clarridgeiae)、罗莎利马巴尔通体(B. rochalimae)、道志巴尔通体(B. doshiae)、格拉汉姆巴尔通体(B. grahamii)、克拉斯诺夫巴尔通体(B. krasnovii)同源性最高,其中同源性最高的为100%,见表 2。系统进化树显示,本次检测的巴尔通体基因序列未形成明显的聚集群体,各采样点巴尔通体的基因序列特征表现出较大的相似性。见图 1。
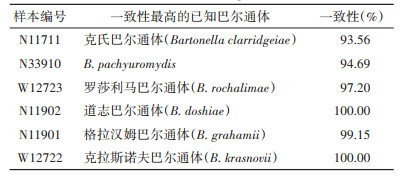
|
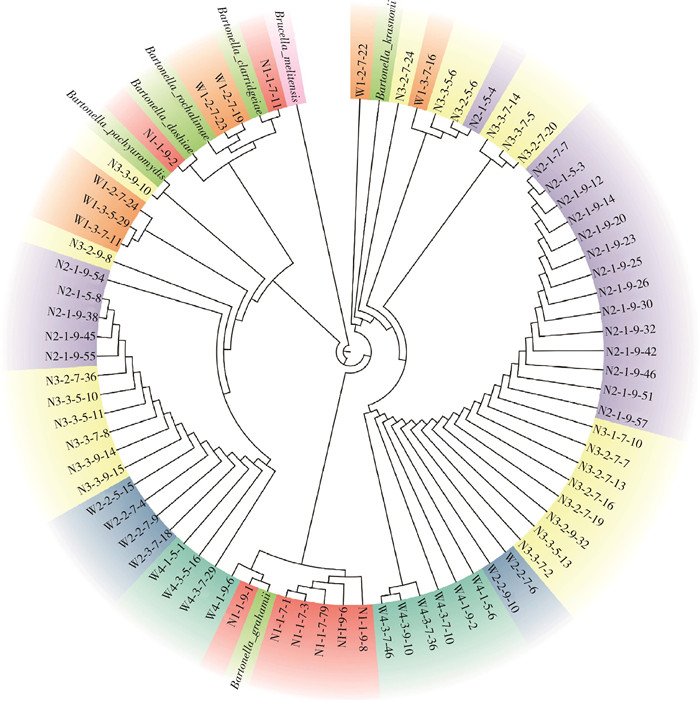
|
| 图 1 内蒙古自治区采获长爪沙鼠携带巴尔通体rpoB基因序列构建的系统进化树 Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree for the rpoB gene sequence of Bartonella carried by Meriones unguiculatus captured in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region |
| |
从采样的季节来看,5(春季)、7(夏季)和9月(秋季)巴尔通体阳性率分别为25.26%(24/95)、40.98%(50/122)和52.43%(54/103)(表 1),差异有统计学意义(χ2=15.274,P < 0.001),经过趋势χ2检验,季节因素和巴尔通体阳性率之间存在线性关系,即随着季节的推移,巴尔通体阳性率增加(χ趋势2=15.082,P < 0.001);5和7月、5和9月巴尔通体阳性率差异均有统计学意义,见表 3。5、7和9月DBV阳性率分别为11.58%、8.04%和1.94%(表 1),差异有统计学意义(χ2=7.247,P=0.025),经过趋势χ2检验,季节因素和DBV阳性率之间存在线性关系,即随着季节的推移,DBV阳性率降低(χ趋势2=7.179,P=0.007);5和9月的DBV阳性率差异有统计学意义(χ2=7.482,P < 0.006),见表 3。除巴尔通体及DBV外,其他病原体阳性率在季节之间的差异均无统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。
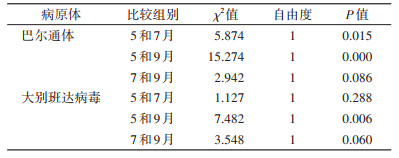
|
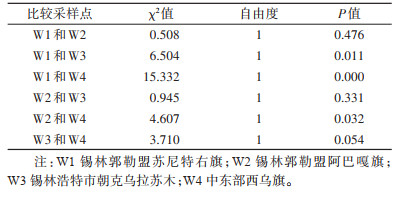
N1、N2、N3采样点长爪沙鼠的巴尔通体阳性率分别为70.59%(12/17)、69.23%(27/39)和32.77%(39/119)(表 1)。从以东西降水梯度划分的采样点(W1的年平均降水量为175.5 mm、W2为201.1 mm、W3为201.6 mm、W4为297.8 mm)(数据来源于国家地球系统科学数据中心,为2003年至2022年降水量平均值)来看,巴尔通体阳性率分别为54.35%(25/46)、44.44%(8/18)、32.77%(39/119)、20.25%(16/79)(表 1),W1~W4各样点间阳性率差异有统计学意义(χ2=16.172,P=0.001),经趋势χ2检验,不同采样点巴尔通体阳性率间存在线性关系,自西向东(从W1到W4),巴尔通体阳性率下降(χ趋势2=16.067,P < 0.001),其中W1和W3、W1和W4、W2和W4间阳性率差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05),见表 4。除巴尔通体外,其他病原体在各样点间的差异均无统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。
|
本研究共检测了内蒙古长爪沙鼠体内的8种病原体,发现巴尔通体的检出率最高,达40.00%。研究显示,在携带巴尔通体属的小型哺乳类动物中,啮齿类动物的检出率和巴尔通体种类数量均为最高[12]。张琳娜[13]对比黑龙江、福建、浙江、云南、台湾、海南省和内蒙古等地区的鼠传巴尔通体阳性率时发现,内蒙古地区啮齿动物中巴尔通体平均阳性率明显高于其他地区,高达56.40%[13],提示内蒙古地区的啮齿动物在携带、传播巴尔通体方面可能存在较高的风险,这可能与环境或其他因素有关。
本研究的分析表明,长爪沙鼠巴尔通体的阳性率随季节变化而变化,秋季阳性率最高,其次是夏季和春季。一些全球范围内的研究也显示啮齿动物中巴尔通体的阳性率秋季达到高峰[14-17]。然而,内蒙古乌拉特口岸地区的一项研究显示,春季的巴尔通体感染率高于夏季,与本文研究结果相反[18],推测可能是由于不同鼠种及巴尔通体分型的差异导致其生态特性在不同季节存在差异,例如一项研究中发现,伯特尔巴尔通体(B. birtlesii)、格拉汉姆巴尔通体、泰勒巴尔通体(B. taylorii)在秋季的发病率较高,而道志巴尔通体在春季的发病率较高[19]。此外,季节变化对不同鼠种也有影响,鼠种种群密度的变化可能影响巴尔通体的阳性率。如Čepelka等[20]在欧洲的研究表明,冬季温度越低,对Apodemus flavicollis种群的影响越大,而对Myodes glareolus的影响不明显。另外,与大多数啮齿类动物不同,达乌尔黄鼠(Spermophilus dauricus)在冬季会进行冬眠,这期间较少的种群间交流可能导致病原体阳性率呈现较低水平。本研究序列分析显示采样点长爪沙鼠携带的巴尔通体序列与克氏巴尔通体等6种巴尔通体高度相似,提示内蒙古地区长爪沙鼠存在多种巴尔通体感染,其中克氏巴尔通体、罗莎利马巴尔通体、格拉汉姆巴尔通体已确定对人类致病[13, 21],而感染巴尔通体可能会引发卡瑞恩病、猫抓病、杆菌性血管瘤、战壕热、心内膜炎、视网膜炎、菌血症、淋巴结病等[22-25],因此应对巴尔通体病的传播进行早期预警。同时,本研究也发现,巴尔通体阳性率在不同经度的采样点上存在差异。从生境上来看,内蒙古自西向东出现了由荒漠和荒漠草原到典型草原和草甸草原的过度[26],长爪沙鼠又喜栖于植被稀疏和低矮的干燥沙质土壤环境[10-11],巴尔通体在不同经度采样点上的阳性率差异,可能是由于荒漠地区长爪沙鼠种群数量较多,导致感染巴尔通体的概率增高所致。
有研究在内蒙古鼠源疾病的媒介蜱体内也检出DBV[27-28]。在本研究中,DBV的检出率为6.88%,同时,这一携带率随着采样季节的推移呈现下降趋势。这与目前关于SFTS作为季节性疾病的研究结果相符合,5月为发病高峰,6月后逐步减少[29]。此外,我们在检测其他6种病原体时发现它们的存在相对较少。靳木子等[18]在内蒙古乌拉特口岸地区对鼠类携带的病原体进行的调查显示,当地捕获的鼠类中未发现立克次体、土拉弗朗西斯菌、钩体和汉坦病毒,但巴尔通体的阳性率高达38.64%。此外,该团队在内蒙古各口岸地区的研究也未在长爪沙鼠中检测到汉坦病毒[30]。陈宇飞等[31]对内蒙古西部口岸地区的调查也发现长爪沙鼠中钩体和汉坦病毒的检出率为零。这些研究结果与我们的发现一致,提示内蒙古地区巴尔通体高度流行,而其他病原体相对散发。然而,一项在甘肃省进行的关于土拉弗朗西斯菌的研究发现长爪沙鼠中该菌的检出率最高[32],这与本研究发现不同,可能是由于病原体分布存在地区差异。本研究认为通过内蒙古地区长爪沙鼠传播土拉弗朗西斯菌、致病性钩体、地方性斑疹伤寒立克次体、嗜吞噬细胞无形体、恙虫病东方体、DBV和汉坦病毒的风险相对较低,尽管如此,仍需对其进行实时监测和追踪,以防止潜在的疾病暴发。
本项研究所使用的荧光定量PCR作为一种相对定量技术,其准确度和稳定性可能会受到PCR的抑制物、标准品质量以及标准曲线的偏差等因素的影响[33]。因此,本研究通过基因测序对阳性率较高的巴尔通体进行了更深入的验证并确定病原体种类,进一步提高研究的精度和可靠性。但对于DBV,本研究并未扩增出有效片段,猜测可能有以下原因:(1)样本保存时间较长,RNA可能发生了降解[34],今后在样本保存时应注意将RNA反转录成cDNA再进行保存。(2)引物存在特异性问题[35],或形成了二聚体[36],影响了扩增效率。(3)循环参数并非最佳,退火温度以及时间不合适,导致未扩增出目标条带[37]。总之,通过对长爪沙鼠进行多病原的综合监测,不仅能够为鼠源性疾病的有效防控提供坚实的科学依据,而且有助于从源头上做好公共卫生防范措施,提前做好应对传染病风险的充分准备。
利益冲突无
| [1] |
Li JM, Li LM, Shi JF, et al. Prevalence of Leptospira in murine in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Vet Sci, 2022, 9: 944282. DOI:10.3389/fvets.2022.944282 |
| [2] |
刘起勇. 2005-2020年我国媒介生物传染病报告病例: 流行趋势、防控挑战及应对策略[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2022, 33(1): 1-7. Liu QY. Reported cases of vector-borne diseases in China, 2005-2020: Epidemic trend, challenges in prevention and control, and related coping strategies[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2022, 33(1): 1-7. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2022.01.001 |
| [3] |
Gu XL, Su WQ, Zhou CM, et al. SFTSV infection in rodents and their ectoparasitic chiggers[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2022, 16(8): e0010698. DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0010698 |
| [4] |
Wang W, Wang MR, Lin XD, et al. Ongoing spillover of Hantaan and Gou hantaviruses from rodents is associated with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in China[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2013, 7(10): e2484. DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002484 |
| [5] |
刘起勇. 新时代媒介生物传染病形势及防控对策[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30(1): 1-6, 11. Liu QY. Epidemic profile of vector-borne diseases and vector control strategies in the new era[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30(1): 1-6, 11. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2019.01.001 |
| [6] |
Rupasinghe R, Chomel BB, Martínez-López B. Climate change and zoonoses: A review of the current status, knowledge gaps, and future trends[J]. Acta Trop, 2022, 226: 106225. DOI:10.1016/j.actatropica.2021.106225 |
| [7] |
Beermann S, Dobler G, Faber M, et al. Impact of climate change on vector- and rodent-borne infectious diseases[J]. J Health Monit, 2023, 8 Suppl 3: S33-61. DOI:10.25646/11401 |
| [8] |
司晓艳, 白国辉, 宋利桃, 等. 内蒙古自治区人居环境2017-2019年鼠类监测数据分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32(5): 586-589. Si XY, Bai GH, Song LT, et al. An analysis of rodent surveillance data in human settlements of Inner Mongolia, China, in 2017-2019[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32(5): 586-589. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2021.05.015 |
| [9] |
郝静云, 朱明达, 于占海. 内蒙古边境地区鼠疫自然疫源地景观特征的研究[J]. 口岸卫生控制, 2010, 15(6): 49-50. Hao JY, Zhu MD, Yu ZH. Research on landscape features of plague natural foci at Inner Mongolia border area[J]. Port Health Control, 2010, 15(6): 49-50. |
| [10] |
李建云, 张忠兵, 范蒙光, 等. 内蒙古2004年至2013年长爪沙鼠鼠疫疫源地鼠疫监测结果分析[J]. 内蒙古医学杂志, 2014, 46(9): 1082-1085. Li JY, Zhang ZB, Fan MG, et al. Analysis of plague surveillance results in the plague foci of Meriones unguiculatus in Inner Mongolia from 2004 to 2013[J]. Inner Mongolia Med J, 2014, 46(9): 1082-1085. DOI:10.16096/j.cnki.nmgyxzz.2014.09.080 |
| [11] |
胡艳红, 王姝懿, 李建云, 等. 内蒙古自治区2020年鼠疫监测调查与分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2022, 33(3): 418-425. Hu YH, Wang SY, Li JY, et al. Analysis of plague surveillance in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China, 2020[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2022, 33(3): 418-425. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2022.03.020 |
| [12] |
Krügel M, Król N, Kempf VAJ, et al. Emerging rodent-associated Bartonella: A threat for human health?[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2022, 15(1): 113. DOI:10.1186/S13071-022-05162-5 |
| [13] |
张琳娜, 孟建宇. 内蒙古野生动物资源概况[J]. 北方经济, 2002(S1): 352-352. Zhang LN, Meng JY. Overview of wildlife resource in Inner Mongolia[J]. North Econ, 2002(S1): 352-352. |
| [14] |
Jardine C, Waldner C, Wobeser G, et al. Demographic features of Bartonella infections in Richardson's ground squirrels (Spermophilus richardsonii)[J]. J Wildl Dis, 2006, 42(4): 739-749. DOI:10.7589/0090-3558-42.4.739 |
| [15] |
Bai Y, Kosoy MY, Ray C, et al. Temporal and spatial patterns of Bartonella infection in black-tailed prairie dogs (Cynomys ludovicianus)[J]. Microb Ecol, 2008, 56(2): 373-382. DOI:10.1007/s00248-007-9355-6 |
| [16] |
Paziewska A, Harris PD, Zwolińska L, et al. Differences in the ecology of Bartonella infections of Apodemus flavicollis and Myodes glareolus in a boreal forest[J]. Parasitology, 2012, 139(7): 881-893. DOI:10.1017/S0031182012000170 |
| [17] |
Gutiérrez R, Krasnov B, Morick D, et al. Bartonella infection in rodents and their flea ectoparasites: An overview[J]. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis, 2015, 15(1): 27-39. DOI:10.1089/vbz.2014.1606 |
| [18] |
靳木子, 郝广福, 王静, 等. 内蒙古乌拉特口岸地区2015年鼠类携带病原体情况调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2018, 29(3): 296-297. Jin MZ, Hao GF, Wang J, et al. Investigation on natural infection of rodent-borne pathogens in rodent populations in Urad port area, Inner Mongolia, China in 2015[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2018, 29(3): 296-297. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2018.03.020 |
| [19] |
Telfer S, Clough HE, Birtles RJ, et al. Ecological differences and coexistence in a guild of microparasites: Bartonella in wild rodents[J]. Ecology, 2007, 88(7): 1841-1849. DOI:10.1890/06-1004.1 |
| [20] |
Čepelka L, Šipoš J, Suchomel J, et al. Can we detect response differences among dominant rodent species to climate and acorn crop in a Central European forest environment?[J]. Eur J Forest Res, 2020, 139(4): 539-548. DOI:10.1007/s10342-020-01267-7 |
| [21] |
孙继民, 鲁亮, 刘起勇, 等. 浙江省蜱中巴尔通体感染的分子流行病学调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2010, 21(3): 232-234. Sun JM, Lu L, Liu QY, et al. Molecular epidemiological investigation of Bartonella infection in ticks in Zhejiang Province[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2010, 21(3): 232-234. |
| [22] |
Chomel BB, Kasten RW. Bartonellosis, an increasingly recognized zoonosis[J]. J Appl Microbiol, 2010, 109(3): 743-750. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2010.04679.x |
| [23] |
Kosoy M, Hayman DTS, Chan KS. Bartonella bacteria in nature: Where does population variability end and a species start?[J]. Infect Genet Evol, 2012, 12(5): 894-904. DOI:10.1016/j.meegid.2012.03.005 |
| [24] |
刘云彦, 栗冬梅, 刘起勇, 等. 巴尔通体感染性心内膜炎的研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 2015, 42(1): 192-199. Liu YY, Li DM, Liu QY, et al. Research progress on Bartonella endocarditis: A review of the literatures[J]. Microbiol China, 2015, 42(1): 192-199. DOI:10.13344/j.microbiol.china.140375 |
| [25] |
栗冬梅, 张建中, 刘起勇. 中国巴尔通体与相关疾病的研究进展[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2008, 24(8): 762-765, 770. Li DM, Zhang JZ, Liu QY. Progress of research on Bartonella and related diseases in China[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2008, 24(8): 762-765, 770. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2694.2008.08.019 |
| [26] |
Eads DA, Hoogland JL. Factors that affect parasitism of black-tailed prairie dogs by fleas[J]. Ecosphere, 2016, 7(7): e01372. DOI:10.1002/ecs2.1372 |
| [27] |
李伊娜, 陈宇飞, 云托娅, 等. 内蒙古自治区中西部口岸地区2020年蜱类优势种及其病原携带情况的调查研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2022, 33(2): 216-220. Li YN, Chen YF, Yun TY, et al. Dominant species of ticks and tick-borne pathogens in the central and western ports areas of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China, 2020[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2022, 33(2): 216-220. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2022.02.009 |
| [28] |
Hu YY, Zhuang L, Liu K, et al. Role of three tick species in the maintenance and transmission of Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2020, 14(6): e0008368. DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0008368 |
| [29] |
Ding F, Zhang WY, Wang LY, et al. Epidemiologic features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011-2012[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2013, 56(11): 1682-1683. DOI:10.1093/cid/cit100 |
| [30] |
靳木子, 云华, 陈宇飞, 等. 2014-2015年内蒙古口岸地区鼠类及其携带病原体调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2017, 28(4): 347-349. Jin MZ, Yun H, Chen YF, et al. Investigation and analysis of rodent-borne pathogens in Inner Mongolia port areas of China from 2014 to 2015[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2017, 28(4): 347-349. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2017.04.010 |
| [31] |
陈宇飞, 靳木子, 白潇. 内蒙古西部口岸地区鼠类及其携带病原体调查[J]. 中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2023, 46(6): 536-538. Chen YF, Jin MZ, Bai X. Investigation on rodents and their pathogens in western port area of Inner Mongolia[J]. Chin J Front Health Quar, 2023, 46(6): 536-538. DOI:10.16408/j.1004-9770.2023.06.007 |
| [32] |
Zhang F, Wang XH, Yu GW, et al. Detection and genotyping of Francisella tularensis in animal hosts and vectors from six different natural landscape areas, Gansu Province, China[J]. Comput Math Methods Med, 2021, 2021: 6820864. DOI:10.1155/2021/6820864 |
| [33] |
Bounaadja L, Albert D, Chénais B, et al. Real-time PCR for identification of Brucella spp. : A comparative study of IS711, bcsp31 and per target genes[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2009, 137(1/2): 156-164. DOI:10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.12.023 |
| [34] |
孙冰, 郭晓红, 江泽飞, 等. 乳腺癌冰冻和石蜡包埋样本的RNA以及基因表达情况的比较研究[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2010, 15(7): 588-592. Sun B, Guo XH, Jiang ZF, et al. Analysis of RNA and gene expression from frozen and paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissues[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2010, 15(7): 588-592. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-0460.2010.07.003 |
| [35] |
申志勇, 屈武斌, 李稚锋, 等. PCR引物特异性核查系统(PSC)的构建与应用[J]. 生物信息学, 2010, 8(2): 134-138, 141. Shen ZY, Qu WB, Li ZF, et al. PSC: A system for PCR primer specificity checking and application[J]. Chin J Bioinf, 2010, 8(2): 134-138, 141. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-5565.2010.02.009 |
| [36] |
白雪芹, 杨瑞瑞, 曾幼玲. 不同引物对和退火温度对盐生植物盐穗木内参基因β-actin扩增效率的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(2): 352-360. Bai XQ, Yang RR, Zeng YL. Effects of different primers and annealing temperatures on the amplification efficiency of real-time PCR reference gene β-actin in the halophyte Halostachys caspica[J]. Xinjiang Agric Sci, 2017, 54(2): 352-360. DOI:10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2017.02.019 |
| [37] |
黄银花, 胡晓湘, 徐慰倬, 等. 影响多重PCR扩增效果的因素[J]. 遗传, 2003, 25(1): 65-68. Huang YH, Hu XX, Xu WZ, et al. The factors affecting the efficiency of mutiplex PCR[J]. Hereditas, 2003, 25(1): 65-68. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-9772.2003.01.015 |
 2024, Vol. 35
2024, Vol. 35


