扩展功能
文章信息
- 雷雯, 赵鑫, 刘建华, 张皓, 笪琴, 朱文祥, 吴娟娟, 田雨, 鲁芳芳, 李芳芳
- LEI Wen, ZHAO Xin, LIU Jian-hua, ZHANG Hao, DA Qin, ZHU Wen-xiang, WU Juan-juan, TIAN Yu, LU Fang-fang, LI Fang-fang
- 鄂西地区某县一起发热伴血小板减少综合征聚集性疫情调查
- An investigation of a cluster epidemic of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in a county in western Hubei Province, China
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2024, 35(1): 100-103
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2024, 35(1): 100-103
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2024.01.018
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2023-09-05
2 湖北省疾病预防控制中心, 湖北 武汉 430000;
3 宜昌市夷陵区疾病预防控制中心, 湖北 宜昌 443100
2 Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Wuhan, Hubei 430000, China;
3 Yiling District Center for Disease Control and Prevention of Yichang, Yichang, Hubei 443100, China
发热伴血小板减少综合征(SFTS)是由一种由大别班达病毒(Dabie bandavirus,DBV)引起的急性传染病,2006年开始在我国中东部农村地区出现,其临床表现以发热伴血小板减少为主,同时可出现高热、头痛、全身不适、呕吐和多脏器功能损害等症状。主要分布在山区和丘陵地带的农村,病例高度散发,但在地域分布上呈现相对集中趋势,以山东、河南、辽宁、安徽、湖北、江苏和浙江7个省份为主[1-3]。传播途径多为蜱虫叮咬,此外,接触急性期患者的血液和体液也可能被感染[4-6]。SFTS平均报告病死率为10%,有些地区可高达30%,目前临床上尚无有效药物治疗及疫苗预防[7-8],且报告发病率不断升高,区域不断扩大[3]。2022年8月6日,Y市疾病预防控制中心(疾控中心)接到某县报告1例X村SFTS死亡病例的2名家属出现高热、呕吐、腹泻、四肢无力等症状。现将流行病调查结果报告如下。
1 材料与方法 1.1 研究对象鄂西地区某县X村本起聚集性疫情相关病例及密切接触者。
1.2 病例定义疑似病例:2022年7月1日-8月23日,X村中具备相关流行病学史且出现发热或皮肤黏膜有出血点/便血/呕吐带血等症状者。确诊病例:疑似病例中,经实验室检测为新布尼亚病毒(大别班达病毒既往用名)核酸阳性的人员。密切接触者:未采取保护措施参加病例护理及丧事处理人员。
1.3 研究方法 1.3.1 调查内容在取得病例及其家属同意的情况下,按照SFTS流行病学个案调查表对病例的基本情况,家庭及居住环境,暴露史及活动史,发病情况及临床就诊过程,实验室检查及转归情况和密切接触者与病例的具体接触方式等进行调查。并采集病例急性期及其密接者血液标本,开展病原检测。
1.3.2 调查对象搜索对疫点及周围开展主动病例搜索,对村委会相关负责人、病例家属和邻居、村医等相关人员进行走访调查,通过查看医院就诊情况、查询中国疾病预防控制信息系统等方式搜集调查对象,从而获取病例的发病时间、就诊经过、临床症状表现等病例信息。
1.3.3 标本检测方法依据《发热伴血小板减少综合征实验室检测方案》要求,由Y市疾控中心对病例及密切接触者的血液标本采用实时荧光定量PCR方法进行检测。
1.4 统计学分析运用描述流行病学方法,分析此次疫情的分布特征,用SPSS 28.0软件分析数据。应用Fisher确切概率法比较首发病例密切接触者不同暴露方式罹患率的差异。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 疫情概况本起疫情为一起聚集性疫情,共搜集到5例SFTS确诊病例。患者既往常年在家务农,健康状况良好,均无外出旅居史。男性2例,女性3例,年龄为54~86岁,中位数为64岁。死亡1例,治愈出院4例。
2.2 发病主要特征5例病例均出现发热、白细胞及血小板降低、心肌酶谱异常,其中有4例病例出现转氨酶升高,2例病例出现呕血,1例病例出现头痛症状。首发病例出现合并凝血功能障碍、多脏器损伤衰竭和全血细胞减少的临床表现。
2.3 流行病学调查 2.3.1 事发地概况X村共有5个村民小组,全村共2 000余人,其中X村3组约440人。X村离城区不足6 km,属丘陵地貌,村域面积10.48 km2,村绿化覆盖率达85%以上,村民主导产业为柑橘、蔬菜、养殖和水库渔业。
2.3.2 首发病例基本情况首发病例,女,62岁,为X村3组村民,近期在家务农,同时在周边某厂绿化带从事绿植养护工作。其住所周围被农田半环绕,家中常住人口为6人,卫生条件尚可。在村内有4块分片的柑橘园。农田有耕种蔬菜、玉米等。家中圈养猪和鸡,周围农户有散养猫、犬。
2022年7月初首发病例在柑橘树园及田间进行打农药、割草等务农活动,活动期间未采取任何防护措施。7月16日开始出现头晕、乏力等不适,自认为中暑,未就医。7月20日,患者在柑橘园打农药时症状加重,遂前往县人民医院就诊,查血常规及农药中毒等相关检测项目未见异常,对症处理后回家观察。7月22日因出现呕吐,且呕吐物中伴血,即再次前往县医院就诊开始入院治疗,当晚因病情无好转,转入市三甲医院血液科。7月23日转入重症监护室治疗,诊断为疑似SFTS。7月25日因治疗无效,患者家属放弃治疗出院。7月25日09:00患者由救护车送回家中,在家中由医护人员拔出身体多处插管后死亡。死者遗体由家属和邻居整理后,在家中冰棺放置3 d,后于7月28日送区殡仪馆火化。
2.3.3 续发病例流行病学调查4名续发病例均为7月25日参加首发病例丧葬事宜的亲友,在未采取任何防护措施的情况下用纸巾为首发病例堵住气管插管和体内多处插管出血创口,擦拭身上血液,事后仅短暂清水冲洗,未进行手消毒。4名续发病例在接触死者遗体及血液后,分别在第5、5、9、13天发病,自述无蜱虫叮咬,诊疗期间也未发现蜱虫叮咬痕迹,发病情况及就诊时间见图 1。
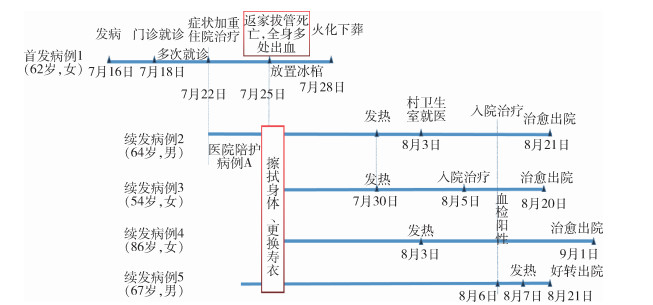
|
| 图 1 发热伴血小板减少综合征病例发病及就诊时间分布 Figure 1 Timeline of disease onset and medical treatment of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome cases |
| |
经排查,首发病例从住院到遗体火化期间的密切接触者有31名,续发病例密切接触者5名,共计36名密切接触者,均为本市居民,近期无外出旅居史。36名密切接触者男女性别比为0.88∶1,年龄为6~88岁,中位数为55.5岁。采集36名密切接触者血液样本,经市疾控中心实验室检测,4人新型布尼亚病毒核酸阳性,其他32人均为阴性且在14 d的观察期内未出现异常症状。为首发病例擦拭身体(接触到血液)的7名密切接触者中有4人发病。其余29名未接触病例血液的密切接触者均未发病。密切接触者与病例不同暴露方式的罹患率差异有统计学意义(P=0.003)。
3 讨论SFTS疫情在我国呈现逐年扩大的趋势,病例发生的时间多在每年4-10月,5-7月是发病高峰期,中老年农民高发[9-12]。通过查询中国疾病预防控制信息系统,该村所处县近5年共报告13例SFTS病例(该村1组既往报告1例SFTS病例),发病时间集中在5月(6例)、7月(4例)和8月(3例),既往均无死亡病例,其疫情特征与全省其他地区基本一致[12-13]。X村属丘陵地貌,村绿化覆盖率高,村民以种植和养殖业为生,该地貌环境及劳作方式SFTS感染发病风险高[14-16]。本起疫情为一起SFTS聚集性疫情,结合该村的地理环境、发病时间、持续无防护的田间作业史等因素判断首发病例可能在田间劳作期间经蜱叮咬感染。续发病例未采取防护措施接触死者血液及血性分泌物后均在最长潜伏期14 d内发病,且无蜱叮咬史,判断通过接触血液及血性分泌物导致感染的可能性大,既往也有文献报道接触急性期病例血液及分泌物被感染的病例[17-21]。
SFTS病例数逐年上升,但农民及医护人员对其未能引起足够的重视,对其防护和诊断认知不足,在发病初期易被中暑、农药中毒等疾病误导诊断,延误最佳治疗时机。鉴于目前SFTS无特效药,只能对症治疗的现状,早发现、早诊断、早治疗可以有效降低疾病病死率[7],因此开展医务人员SFTS培训,尽早识别病例,及时救治,可以有效提高患者生存概率。死亡病例的规范处理也需要得到相关部门的高度关注,把好防控的重要关口。多途径多渠道普及SFTS知识是目前控制该疾病传播的重点及有效措施[16]。医疗机构要叮嘱家属在护理患者或接触患者遗体时佩戴口罩、手套等,做好个人防护,告诫家属避免直接接触感染者血液或分泌物,并且要注重手消毒;相关部门需将经济且易于实施的防护措施宣传到每村每户,提醒农户田间作业期间穿长衣长裤,扎紧裤脚、袖口和领口,做好蜱叮咬预防。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel Bunyavirus in China[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011, 364(16): 1523-1532. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1010095 |
| [2] |
Miao D, Liu MJ, Wang YX, et al. Epidemiology and ecology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2010-2018[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2021, 73(11): e3851-e3858. DOI:10.1093/cid/ciaa1561 |
| [3] |
李佳宸, 王玉娜, 赵静, 等. 发热伴血小板减少综合征流行病学研究进展[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2021, 42(12): 2226-2233. Li JC, Wang YN, Zhao J, et al. A review on the epidemiology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2021, 42(12): 2226-2233. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20210529-00439 |
| [4] |
Fang XY, Hu JL, Peng ZH, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome Bunyavirus human-to-human transmission[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2021, 15(4): e0009037. DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0009037 |
| [5] |
王建跃, 邬辉, 仝振东, 等. 发热伴血小板减少综合征流行病学研究进展[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2016, 37(2): 294-298. Wang JY, Wu H, Tong ZD, et al. A review on the epidemiologic features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2016, 37(2): 294-298. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.02.029 |
| [6] |
中华人民共和国卫生部. 发热伴血小板减少综合征防治指南(2010版)[J]. 中华临床感染病杂志, 2011, 4(4): 193-194. Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. Guideline for prevention and treatment of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (2010 vesrion)[J]. Chin J Clin Infect Dis, 2011, 4(4): 193-194. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-2397.2011.04.001 |
| [7] |
中华医学会感染病学分会. 发热伴血小板减少综合征诊疗共识[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2022, 40(12): 711-721. Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2022, 40(12): 711-721. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn311365-20221017-00425 |
| [8] |
He ZQ, Wang BH, Li Y, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A systematic review and Meta-analysis of epidemiology, clinical signs, routine laboratory diagnosis, risk factors, and outcomes[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2020, 20(1): 575. DOI:10.1186/s12879-020-05303-0 |
| [9] |
Zhang DW, Sun CK, Yu HY, et al. Environmental risk factors and geographic distribution of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Jiangsu province, China[J]. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis, 2019, 19(10): 758-766. DOI:10.1089/vbz.2018.2425 |
| [10] |
Sun JM, Lu L, Wu HX, et al. The changing epidemiological characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011-2016[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 9236. DOI:10.1038/s41598-017-08042-6 |
| [11] |
陈秋兰, 朱曼桐, 陈宁, 等. 2011-2021年全国发热伴血小板减少综合征流行特征分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2022, 43(6): 852-859. Chen QL, Zhu MT, Chen N, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011-2021[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2022, 43(6): 852-859. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20220325-00228 |
| [12] |
张乾通, 孙继民, 凌锋, 等. 浙江省2021年发热伴血小板减少综合征报告病例及蜱媒监测结果分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2022, 33(4): 485-488. Zhang QT, Sun JM, Ling F, et al. Analysis of reported cases of fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and tick vectors surveillance results in Zhejiang province of China in 2021[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2022, 33(4): 485-488. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2022.04.008 |
| [13] |
熊进峰, 占建波, 谭梁飞, 等. 黄冈市蜱及宿主动物携带发热伴血小板减少综合征病毒情况调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2016, 27(5): 504-505. Xiong JF, Zhan JB, Tan LF, et al. Survey on ticks and host animals of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in Huanggang, Hubei province[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2016, 27(5): 504-505. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2016.05.023 |
| [14] |
崔荣敏, 于丹梅, 苗长青, 等. 丹东市2010-2015年发热伴血小板减少综合征流行特征分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2017, 28(1): 60-63. Cui RM, Yu DM, Miao CQ, et al. Analysis of the epidemic characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Dandong city of Liaoning province, 2010-2015[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2017, 28(1): 60-63. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2017.01.016 |
| [15] |
Huang XX, Li JD, Li AQ, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome from 2010 to 2019 in Mainland China[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18(6): 3092. DOI:10.3390/ijerph18063092 |
| [16] |
姜晓林, 陈德颖, 吕涛, 等. 山东省威海市文登区3例发热伴血小板减少综合征死亡病例危险因素调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30(6): 603-606. Jiang XL, Chen DY, Lyu T, et al. An investigation of risk factors for death in three patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Wendeng district, Weihai, Shandong province, China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30(6): 603-606. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2019.06.002 |
| [17] |
王娟, 蔡亮, 杨浩, 等. 一起家庭聚集性发热伴血小板减少综合征疫情的流行病学及病原学分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2021, 36(7): 729-733. Wang J, Cai L, Yang H, et al. Epidemiological investigation and etiological analysis on a cluster of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in a family[J]. Dis Surveill, 2021, 36(7): 729-733. DOI:10.3784/jbjc.202011100380 |
| [18] |
Du YH, Cheng NN, Li Y, et al. Seroprevalance of antibodies specific for Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus and the discovery of asymptomatic infections in Henan province, China[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2019, 13(11): e0007242. DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0007242 |
| [19] |
Huang XY, He ZQ, Wang BH, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: A systematic review and Meta-analysis of transmission mode[J]. Epidemiol Infect, 2020, 148: e239. DOI:10.1017/S0950268820002290 |
| [20] |
尤爱国, 李懿, 李东晓, 等. 河南省2017-2020年发热伴血小板减少综合征监测分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2021, 42(11): 2024-2029. You AG, Li Y, Li DX, et al. Surveillance for sever fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Henan province, 2017-2020[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2021, 42(11): 2024-2029. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20210426-00345 |
| [21] |
顾时平, 吴雪, 周斌, 等. 浙江省一起发热伴血小板减少综合征聚集性疫情调查[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2015, 36(4): 364-367. Gu SP, Wu X, Zhou B, et al. Epidemiological investigation on an outbreak of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in northwest Zhejiang province[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2015, 36(4): 364-367. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2015.04.015 |
 2024, Vol. 35
2024, Vol. 35


