扩展功能
文章信息
- 李德, 殷启凯, 侯泽英, 王瑞晨, 张维嘉, 付士红, 何英, 聂凯, 梁国栋, 许松涛, 李樊, 李兴洲, 王环宇
- LI De, YIN Qi-kai, HOU Ze-ying, WANG Rui-chen, ZHANG Wei-jia, FU Shi-hong, HE Ying, NIE Kai, LIANG Guo-dong, XU Song-tao, LI Fan, LI Xing-zhou, WANG Huan-yu
- 阿龙山病毒及松岭病毒多重实时荧光定量RT-PCR快速检测方法的建立
- Establishment of multiplex real-time fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR for rapid detection of Alongshan virus and Songling virus
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2024, 35(1): 74-78
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2024, 35(1): 74-78
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2024.01.013
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2023-08-31
2 传染病溯源预警与智能决策全国重点实验室, 中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所, 北京 102206
2 National Key Laboratory of Intelligent Tracking and Forecasting for Infectious Diseases, National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 102206, China
蜱是仅次于蚊虫的第二大病原传播媒介生物,在我国分布广泛。蜱媒病毒(Tick-borne viruses,TBV)分布在2个目,9个科,12个属,约160余种[1]。重要的蜱媒病毒包括蜱传脑炎病毒(Tick-borne encephalitis virus,TBEV)、大别班达病毒[(Dabie bandavirus,DBV,又称发热伴血小板减少综合征病毒,Severe fever with thrombocypenia syndrome virus,SFTSV)]、克里米亚-刚果出血热病毒(Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus,CCHFV)等[2]。近年,我国东北地区陆续发现了多种新发蜱媒病毒,包括2019年从内蒙古自治区阿龙山镇被蜱叮咬患者的血样中分离鉴定到的阿龙山病毒(Alongshan virus,ALSV),其属于黄病毒科(Flaviviridae)荆门病毒组(Jingmenvirus)[3-4];2021年从黑龙江省松岭区有蜱叮咬史农民的血清中分离鉴定到松岭病毒(Songling virus,SGLV),其属于布尼亚病毒目(Bunyavirales)内罗病毒科(Nairoviridae)正内罗病毒属(Orthonairovirus)[5]。目前,国内尚无同时针对2种病毒核酸的高效、快速的检测方法,本研究旨在建立针对ALSV和SGLV 2种病毒的多重实时荧光定量反转录聚合酶链式反应(multiplex real-ime fluorescent quantitative reverse transcription PCR,multiplex real-ime fluorescent qRT-PCR)(以下称多重实时qRT-PCR)检测方法。
1 材料与方法 1.1 引物和探针的设计与合成从美国国立生物技术信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information,NCBI)分别获取ALSV和SGLV全基因序列信息,在ALSV NS 3基因和SGLV S基因的保守区域设计正向和反向引物,在正、反向引物之间设计可特异性结合目的基因的探针,在探针的5'端和3'端分别标记六氯荧光素(hexachlorofluorescein,HEX)、羧基荧光素(carboxyfluorescein,FAM)荧光基团和小沟结合物(minor groove binder,MGB)、黑洞猝灭剂1(black hole quencher 1,BHQ1)淬灭基团(表 1)。引物和探针由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成,引物和探针稀释混匀至10 μmol/L的工作浓度,-20 ℃保存备用。

|
对2019年黑龙江省采集的300只游离蜱样本按采集时间,采集地点,蜱种类、性别和数量分为30组,10只混为1组。进行机械研磨后,吸取研磨液上清进行后续实验。使用病毒核酸提取或纯化试剂盒(CqEx-RNA/DNA,规格:64T/盒、16T/板×4板;货号:T332;生产厂家:中国西安天隆科技有限公司)从研磨液上清中提取全部病毒核酸。
1.3 多重实时qRT-PCR反应体系使用荧光定量试剂盒(AgPath-IDTM One-stepRT-PCR Kit,规格:1000 reactions;货号:4387391;生产厂家:美国Thermo Fisher Scientific)体系进行多重实时qRT-PCR反应。该体系包括:RT-PCR buffer(2×)12.5 μl,RT-PCR Mix Enzyme(25×)1 μl,正、反向引物(10 μmol/L)各0.5 μl,探针(10 μmol/L)0.25 μl,核酸模板1 μl,DEPC水将体积补充至25 μl。置于CFX96全自动荧光定量PCR仪(美国BIO-RED公司)进行反应,反应程序:45 ℃ 10 min,95 ℃ 5 min,95 ℃ 15 s和60 ℃ 30 s(采集荧光信号)共45个循环。
1.4 阳性质控品的制备ALSV NS 3基因重组质粒和SGLV S基因重组质粒由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成。将重组质粒进行梯度稀释,获得1×101~1×107拷贝/μl的阳性质控品。
1.5 多重实时qRT-PCR方法 1.5.1 特异性试验使用该反应体系对本实验室保藏的与ALSV同属黄病毒科的流行性乙型脑炎病毒(Japanese encephalitis virus,JEV)、西尼罗病毒(West Nile virus,WNV)、TBEV,与SGLV同属布尼亚病毒目的山西蜱病毒2(Shanxi tick virus 2,SXTV)、DBV、Antu病毒(Antu virus,ATV)阳性核酸进行检测,评价该方法的特异性。设置ALSV和SGLV的阳性质控品为阳性对照,ALSV和SGLV阴性的蜱标本研磨取上清核酸提取物作为阴性对照,ddH2O为空白对照。
1.5.2 灵敏度试验通过多重实时qRT-PCR检测方法对终浓度为1×101~1×107拷贝/μl的7个稀释浓度的ALSV NS 3和SGLV S基因阳性质控品进行检测,得到相应循环阈值(Ct),评价该检测体系的灵敏度。空白对照同上。根据不同浓度样品拷贝数和Ct值的对应关系绘制出定量检测结果的标准曲线。Ct<36为阳性。
1.5.3 重复性试验将浓度为1×101~1×103拷贝/μl的ALSV和SGLV阳性质控品平行重复检测3次,根据检测Ct值计算其平均值、标准差及其变异系数,用以评价该反应体系的稳定性。空白对照同上。
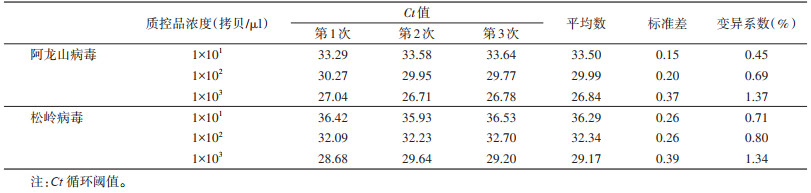
2 结果 2.1 多重实时qRT-PCR方法的特异性用建立的多重实时qRT-PCR检测方法同时对多种虫媒病毒核酸进行检测,其中仅ALSV和SGLV阳性核酸有明显的扩增信号,JEV、WNV、TBEV、SXTV、DBV、ATV、阴性对照和空白对照无扩增信号。见图 1。
|
| 图 1 多重实时荧光定量反转录PCR方法对阿龙山病毒与松岭病毒的特异性检测 Figure 1 Specificity of the multiplex real-time qRT-PCR for detection of Alongshan virus and Songling virus |
| |
利用建立的多重实时qRT-PCR检测方法同时检测7个浓度(1×101~1×107拷贝/μl)的ALSV和SGLV阳性质控品,最低检测限为1×101拷贝/μl。空白对照无Ct值。ALSV和SGLV的标准曲线方程分别为Y=-3.31lg(X)+ 36.39,R2=0.999(图 2A)、Y=-3.46lg(X)+39.45,R2=0.990(图 2B)。

|
| 注:A阿龙山病毒阳性质控品的标准曲线;B松岭病毒阳性质控品的标准曲线。 图 2 多重实时荧光定量反转录PCR检测阿龙山病毒和松岭病毒基因拷贝数的标准曲线 Figure 2 Standard curves of the gene copy number of Alongshan virus and Songling virus detected by the multiplex real-time qRT-PCR |
| |
取3个浓度(1×101~1×103拷贝/μl)的ALSV和SGLV阳性质控品为模板,每个浓度平行重复检测3次,变异系数为0.45%~1.37%(表 2)。空白对照无Ct值。
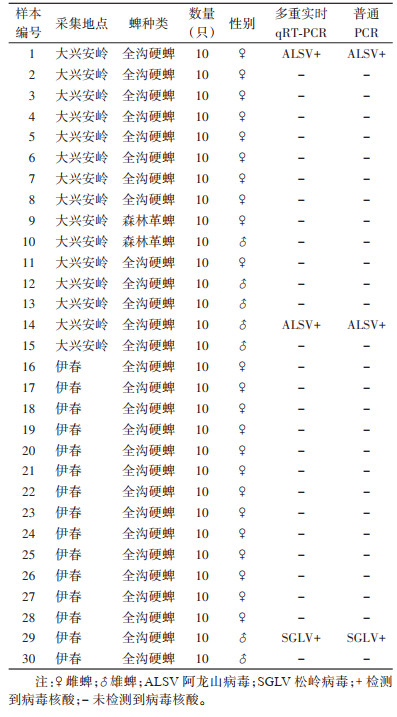
应用建立的多重实时qRT-PCR检测方法对2019年黑龙江省采集的30组蜱样本进行ALSV和SGLV 2种病毒的核酸检测。结果显示,1号和14号样本ALSV核酸阳性,Ct值为22和16;29号样本SGLV核酸阳性,Ct值为25。经普通PCR法验证,2种检测方法的结果一致性为100%。见表 3。
|
近年来,研究人员在东北亚地区发现了多种新蜱媒病毒,包括在日本蜱类中发现的Muko病毒(Muko virus,MUV)[6]、Kabuto Mountain病毒(Kabuto Mountain virus,KAMV)[7]、Oz病毒(Oz virus,OZV)[8]、Tarumizu tick病毒(Tarumizu tick virus,TarTV)[9]、Yezo病毒(Yezo virus,YZV)[10]和Mukawa病毒(Mukawa virus,MKWV)[11],及在我国东北地区发现的ATV[12]、ALSV[13]和SGLV[5]等。最新研究结果显示在俄罗斯采集的全沟硬蜱(Ixodes persulcatus)[14-15]、芬兰[16]和瑞士[17]采集的蓖麻硬蜱(I. ricinus)以及韩国采集的长角血蜱(Haemaphysalis longicornis)中检测到ALSV核酸[18],在我国新疆维吾尔自治区大沙鼠(Rhombomys opimus)中检测到SGLV核酸[19]。此外,在我国内蒙古自治区呼伦贝尔市的家畜[20]和德国的家畜及野生动物血清中检测到ALSV特异性抗体[21]。目前,关于ALSV和SGLV的流行地区、动物和媒介宿主范围等尚不明确。因此建立灵敏快速的核酸检测方法对于开展病原监测十分必要。
多重实时qRT-PCR法较其他检测方法具有成本低、耗时较短、单次检测量大、灵敏度高、特异性好、线性范围宽且操作简单、快速、防污染、可实现对产物进行定量等特点。近年来,在国内外针对虫媒病毒的实时qRT-PCR检测方法已大量建立及应用,包括马达里亚加病毒(Madariaga virus,MADV)[22]、Koutango病毒(Koutango virus,KOUTV)[23]、Flanders病毒(Flanders virus,FLAV)[24]、WNV[25]、基孔肯雅病毒(Chikungunya virus,CHIKV)[26]等。本研究针对ALSV NS 3和SGLV S段保守区域设计引物和探针。建立的多重实时qRT-PCR检测方法与其他多种蜱媒病毒无交叉反应,表明该方法特异性良好。同时,该检测体系具有较好的灵敏度和重复性,检测下限可达1×101拷贝/μl。重复性试验中Ct值变异系数均<2.00%。使用该方法检测2019年黑龙江省采集的30组蜱样本,发现2组ALSV阳性、1组SGLV阳性,与普通PCR检测结果一致性达到100%。
本研究建立了针对ALSV和SGLV的多重实时qRT-PCR检测方法。该方法可同时检测ALSV和SGLV,灵敏度高、特异性好、重复性强,可应用于疾病控制现场和临床等多个场景,实现对2种病毒的快速检测。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
逯军, 潘翔. 蜱媒病毒: 人畜动物的重要致病病原体[J]. 中国热带医学, 2020, 20(4): 309-319. Lu J, Pan X. Tick-borne viruses: The important pathogens of human beings and livestocks[J]. China Trop Med, 2020, 20(4): 309-319. DOI:10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2020.04.04 |
| [2] |
赵俊伟, 王环宇, 王英. 中国蜱传病原体分布研究概况[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2012, 23(5): 445-448. Zhao JW, Wang HY, Wang Y. Regional distribution profiles of tick-borne pathogens in China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2012, 23(5): 445-448. |
| [3] |
Zhang X, Wang NN, Wang ZD, et al. The discovery of segmented Flaviviruses: Implications for viral emergence[J]. Curr Opin Virol, 2020, 40: 11-18. DOI:10.1016/j.coviro.2020.02.001 |
| [4] |
Wang ZD, Wang B, Wei F, et al. A new segmented virus associated with human febrile illness in China[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380(22): 2116-2125. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1805068 |
| [5] |
Ma J, Lv XL, Zhang X, et al. Identification of a new Orthonairovirus associated with human febrile illness in China[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(3): 434-439. DOI:10.1038/s41591-020-01228-y |
| [6] |
Ejiri H, Lim CK, Isawa H, et al. Genetic and biological characterization of Muko virus, a new distinct member of the species Great Island virus (genus Orbivirus, family Reoviridae), isolated from ixodid ticks in Japan[J]. Arch Virol, 2015, 160(12): 2965-2977. DOI:10.1007/s00705-015-2588-7 |
| [7] |
Ejiri H, Lim CK, Isawa H, et al. Isolation and characterization of Kabuto Mountain virus, a new tick-borne Phlebovirus from Haemaphysalis flava ticks in Japan[J]. Virus Res, 2018, 244: 252-261. DOI:10.1016/j.virusres.2017.11.030 |
| [8] |
Ejiri H, Lim CK, Isawa H, et al. Characterization of a novel Thogotovirus isolated from Amblyomma testudinarium ticks in Ehime, Japan: A significant phylogenetic relationship to Bourbon virus[J]. Virus Res, 2018, 249: 57-65. DOI:10.1016/j.virusres.2018.03.004 |
| [9] |
Fujita R, Ejiri H, Lim CK, et al. Isolation and characterization of Tarumizu tick virus: A new Coltivirus from Haemaphysalis flava ticks in Japan[J]. Virus Res, 2017, 242: 131-140. DOI:10.1016/j.virusres.2017.09.017 |
| [10] |
Matsuno K. Yezo virus and emerging Orthonairovirus diseases[J]. Uirusu, 2021, 71(2): 117-124. DOI:10.2222/jsv.71.117 |
| [11] |
Matsuno K, Kajihara M, Nakao R, et al. The unique phylogenetic position of a novel tick-borne Phlebovirus ensures an ixodid origin of the genus Phlebovirus[J]. mSphere, 2018, 3(3). DOI:10.1128/mSphere.00239-18 |
| [12] |
Li F, Li JX, Song JD, et al. Novel Orthonairovirus isolated from ticks near China-North Korea border[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2023, 29(6): 1254-1257. DOI:10.3201/eid2906.230056 |
| [13] |
Liu ZY, Li L, Xu WB, et al. Extensive diversity of RNA viruses in ticks revealed by metagenomics in northeastern China[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2022, 16(12): e0011017. DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0011017 |
| [14] |
Kholodilov IS, Belova OA, Ivannikova AY, et al. Distribution and characterisation of tick-borne Flavi-, Flavi-like, and Phenuiviruses in the Chelyabinsk region of Russia[J]. Viruses, 2022, 14(12): 2699. DOI:10.3390/v14122699 |
| [15] |
Kholodilov IS, Litov AG, Klimentov AS, et al. Isolation and characterisation of Alongshan virus in Russia[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(4): 362. DOI:10.3390/v12040362 |
| [16] |
Kuivanen S, Levanov L, Kareinen L, et al. Detection of novel tick-borne pathogen, Alongshan virus, in Ixodes ricinus ticks, south-eastern Finland, 2019[J]. Euro Surveill, 2019, 24(27): 1900394. DOI:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.27.1900394 |
| [17] |
Stegmüller S, Fraefel C, Kubacki J. Genome sequence of Alongshan virus from Ixodes ricinus ticks collected in Switzerland[J]. Microbiol Resour Announc, 2023, 12(3): e128722. DOI:10.1128/mra.01287-22 |
| [18] |
Lee MR, Kim JC, Park SE, et al. Detection of viral genes in Metarhizium anisopliae JEF-290-infected longhorned tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis using transcriptome analysis[J]. J Invertebr Pathol, 2023, 198: 107926. DOI:10.1016/j.jip.2023.107926 |
| [19] |
Ji N, Wang N, Liu G, et al. Tacheng tick virus 1 and Songling virus infection in great gerbils (Rhombomys opimus) in Northwestern China[J]. J Wildl Dis, 2023, 59(1): 138-142. DOI:10.7589/JWD-D-21-00137 |
| [20] |
Wang ZD, Wang W, Wang NN, et al. Prevalence of the emerging novel Alongshan virus infection in sheep and cattle in Inner Mongolia, northeastern China[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2019, 12(1): 450. DOI:10.1186/s13071-019-3707-1 |
| [21] |
Ebert CL, Söder L, Kubinski M, et al. Detection and characterization of Alongshan virus in ticks and tick saliva from lower Saxony, Germany with serological evidence for viral transmission to game and domestic animals[J]. Microorganisms, 2023, 11(3): 543. DOI:10.3390/microorganisms11030543 |
| [22] |
殷启凯, 刘文婧, 王国玮, 等. 马达里亚加病毒TaqMan RT-PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2022, 38(5): 428-432. Yin QK, Liu WJ, Wang GW, et al. Establishment of a TaqMan RT-PCR assay for the detection of Madariaga virus[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2022, 38(5): 428-432. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2694.2022.00.057 |
| [23] |
殷启凯, 陈晓菁, 付士红, 等. Koutango病毒TaqMan反转录聚合酶链式反应方法的建立[J]. 疾病监测, 2020, 35(3): 197-201. Yin QK, Chen XJ, Fu SH, et al. Establishment of TaqMan RT-PCR for detection of Koutango virus[J]. Dis Surveill, 2020, 35(3): 197-201. DOI:10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2020.03.005 |
| [24] |
李浩, 赫晓霞, 曹玉玺, 等. Flanders病毒TaqMan RT-PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2015, 31(3): 212-215. Li H, He XX, Cao YX, et al. Establishment of TaqMan RT-PCR assay for Flanders virus[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2015, 31(3): 212-215. DOI:10.3969/cjz.j.issn.1002-2694.2015.03.005 |
| [25] |
Fall G, Faye M, Weidmann M, et al. Real-time RT-PCR assays for detection and genotyping of West Nile virus lineages circulating in Africa[J]. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis, 2016, 16(12): 781-789. DOI:10.1089/vbz.2016.1967 |
| [26] |
Andrew A, Citartan M, Wong KA, et al. Analytical and clinical evaluation of a TaqMan real-time PCR assay for the detection of Chikungunya virus[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2023, 11(4): e8823. DOI:10.1128/spectrum.00088-23 |
 2024, Vol. 35
2024, Vol. 35