扩展功能
文章信息
- 王彬, 李贵昌, 董利, 母群征, 赵宁, 宋秀平, 鲁亮, 栗冬梅, 李兴洲, 刘起勇
- WANG Bin, LI Gui-chang, DONG Li, MU Qun-zheng, ZHAO Ning, SONG Xiu-ping, LU Liang, LI Dong-mei, LI Xing-zhou, LIU Qi-yong
- 内蒙古地区鼠类体表革螨携带立克次体研究
- Rickettsia carried by gamasid mites on the body surface of rodents in Inner Mongolia, China
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2023, 34(2): 244-249
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2023, 34(2): 244-249
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2023.02.017
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2022-10-18
2 中国疾病预防控制中心传染病预防控制所媒介生物控制室, 传染病预防控制国家重点实验室, 北京 102206;
3 山东大学齐鲁医学院公共卫生学院, 山东 济南 250012
2 State Key Laboratory of Infectious Disease Prevention and Control, Department of Vector Biology and Control, National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 102206, China;
3 Public Health School, Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Ji'nan, Shandong 250012, China
革螨通常是指中气门目(Mesostigmata)革螨股(Gamasina)中的螨类。鼠类体表寄生性革螨可携带多种病原体,包括原虫、病毒和细菌[1-2]。立克次体属(Rickettsia)是一类专性真核细胞内寄生的革兰阴性微小杆菌,其中部分种类可感染人类,引起多种急性发热性疾病,统称为立克次体病。全世界目前已发现20余种对人类致病的立克次体[3-4],我国已报道10余种,并且在我国分布十分广泛[5]。人被携带立克次体的吸血节肢动物叮咬或接触其粪便而发病,常见的立克次体媒介包括虱、蚤、蜱,尚缺乏革螨携带和传播立克次体方面的研究[2]。本课题组用分子生物学技术,检测了2021年在内蒙古自治区(内蒙古)部分地区鼠体采集的革螨中立克次体特异性核酸片段,了解革螨感染立克次体情况,期望为我国立克次体病和革螨危害的防控提供参考依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 标本来源革螨标本来源于本课题组2021年在内蒙古地区捕获的鼠类体表,放入装有75%乙醇溶液冻存管中,1鼠1管,-80 ℃冰箱保存。采集地点包括呼伦贝尔市新巴尔虎右旗(N1)、锡林郭勒盟东乌珠穆沁旗(N2)、锡林浩特市朝克乌拉苏木(N3)和白音锡勒牧场(N4)、太仆寺旗(N5)、阿巴嘎旗(W2)、西乌珠穆沁旗(W4)、通辽市科尔沁左翼中旗和扎鲁特旗(W5)。根据参考资料和革螨形态特征鉴定革螨种类[6-7]。
1.2 螨基因组DNA提取和立克次体检测将革螨标本从乙醇溶液中取出,在75%乙醇溶液中涮洗1次,置于一次性培养皿中,使用酒精灯灼烧过的昆虫解剖针刺穿螨躯体后部,然后转移至QIAGEN公司的QIAamp DNA Mini Kit试剂盒的组织裂解液中,按说明书提取基因组DNA,洗脱缓冲液(AE)加入量为50 μl。
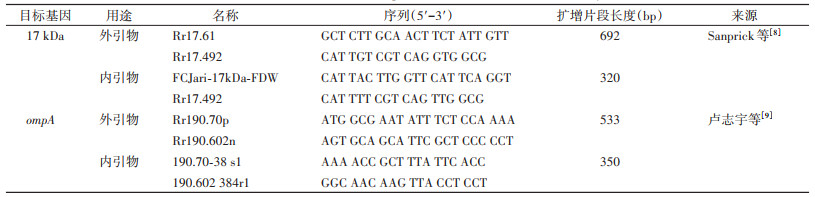
根据文献[8]合成立克次体17 kDa蛋白基因特异性引物,用巢氏PCR扩增立克次体属特异性核酸片段,PCR引物见表 1。宝日医(TaKaRa)生物(北京)有限公司EX Taq™ Version 2.0试剂,反应体系为25 μl模板体系:加入2 μl模板DNA进行第1次PCR扩增,取1 μl第1轮扩增产物进行第2轮PCR扩增,在1.0%琼脂糖凝胶上电泳,阳性产物送于北京奥科生物技术有限公司进行测序。PCR扩增条件:95 ℃预变性3 min;94 ℃ 30 s,55 ℃退火40 s,68 ℃延伸1 min,循环40次;最后在68 ℃延伸7 min。测序证实立克次体阳性的标本再用外膜蛋白A(outer membrane protein A,ompA)基因引物进行巢式PCR扩增,反应体系及反应条件同上。
根据文献在美国国立生物技术信息中心(NCBI)中下载36个立克次体17 kDa基因参考序列[10-13]和8个ompA基因参考序列[14]。将阳性序列与NCBI中下载的立克次体17 kDa基因放在一起,用MEGA 11软件进行序列编辑、Clustal W法序列比对,用最大似然法(ML)构建系统发育树。用SPSS 24.0软件计算立克次体阳性率,用χ2检验分析其阳性率差异,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
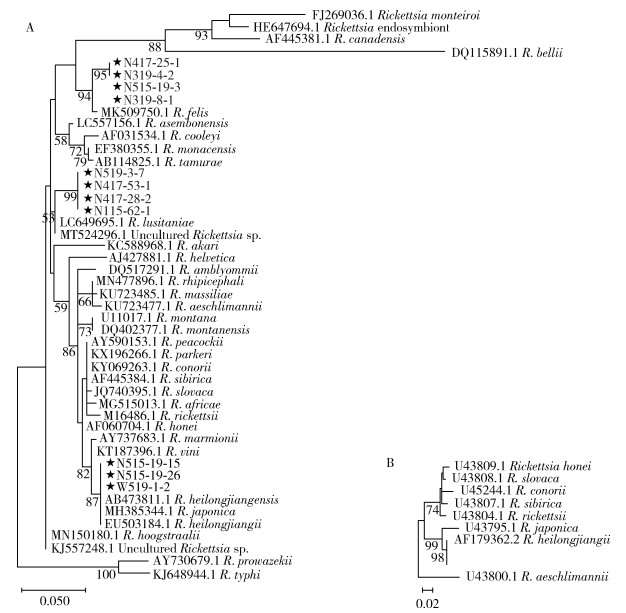
2 结果 2.1 革螨携带立克次体种类本研究用17 kDa基因引物扩增并测序,获得11条核酸片段。用320 bp阳性序列与参考序列构建ML系统发育树(图 1)。其中3个序列(W519-1-2、N515-19-26、N515-19-15)与日本立克次体(R. japonica)和黑龙江立克次体(R. heilongjiangensis)具有较高的同源性(99.40%~100%);4个序列与猫立克次体(R. felis)聚为一个分支,其中N319-8-1、N515-19-3为一组,与猫立克次体同源性在99.70%~99.71%;N417-25-1、N319-4-2为另一组,与猫立克次体同源性在98.50%~98.80%,2组内同源性为100%,组间同源性为99.05%;4个序列(N115-62-1、N417-28-2、N417-53-1、N519-3-7)单独聚成一支,同源性最近为R. lusitaniae。经BLAST比对其与R. lusitaniae同源性为97.79%~97.87%。
|
| 注:★为本研究获得序列;A. 基于17 kDa基因的系统发育树;B. 基于ompA基因的系统发育树。 图 1 立克次体基因序列最大似然法(ML)系统发育树 Figure 1 ML phylogenetic tree of Rickettsia gene sequence |
| |
对17 kDa阳性样本进行ompA基因巢式PCR扩增,成功获得2个277 bp阳性序列(N515-19-26和W519-1-2),与参考序列构建ML系统发育树,阳性序列与黑龙江立克次体聚为一支,经NCBI比对与黑龙江立克次体(AF179362.2)序列同源性为100%,与日本立克次体(U43795.1)同源性为95.85%,结合17 kDa的比对结果,初步确定W519-1-2、N515-19-26和N515-19-15为黑龙江立克次体。
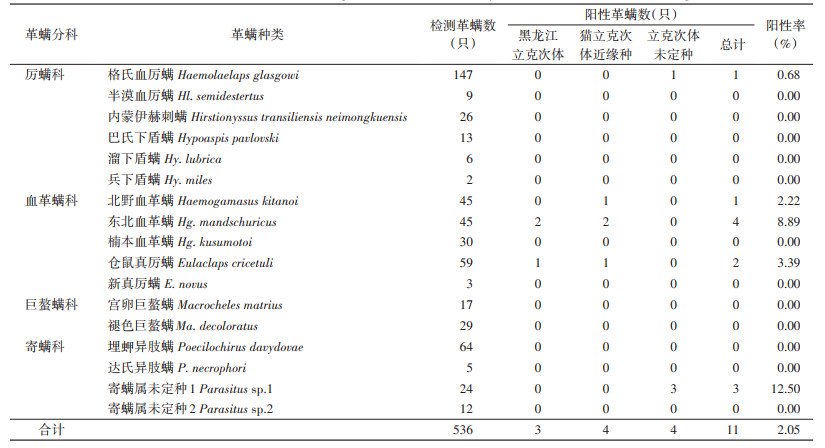
2.2 革螨与立克次体的关系共检测了4科8属17种536只革螨,在其中5种共11只革螨中检测到立克次体阳性,总阳性率为2.05%,其中阳性率最高的是寄螨属未定种1,阳性率为12.50%(3/24),其次是东北血革螨为8.89%(4/45),仓鼠真厉螨为3.39%(2/59),北野血革螨为2.22%(1/45),格氏血厉螨为0.68%(1/147)(表 2)。运用Fisher确切概率法对不同革螨立克次体阳性率进行检验,差异有统计学意义(P=0.005)。
|
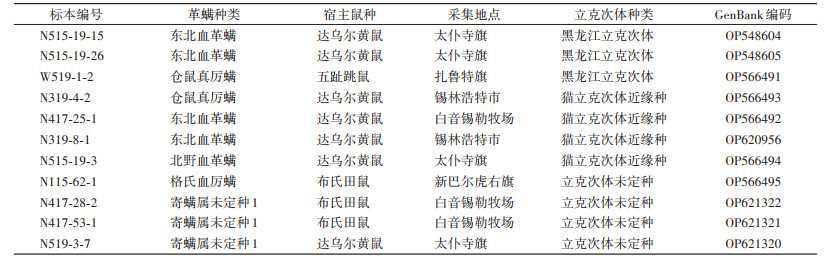
黑龙江立克次体阳性的革螨包括东北血革螨和仓鼠真厉螨,宿主是达乌尔黄鼠(Spermophilus dauricus)和五趾跳鼠(Allactaga sibirica),分布在锡林郭勒盟太仆寺旗和通辽市扎鲁特旗。猫立克次体近缘种阳性的革螨包括东北血革螨、北野血革螨和仓鼠真厉螨,其宿主均为达乌尔黄鼠,分布在锡林郭勒盟锡林浩特市、白音锡勒牧场和太仆寺旗。立克次体未定种阳性革螨包括格氏血厉螨和1种寄螨属种类的第二若螨,其宿主为布氏田鼠(Lasiopodomys brandtii)和达乌尔黄鼠,分布在白音锡勒牧场、新巴尔虎右旗和太仆寺旗。见表 3。
|
立克次体属微生物为节肢动物体内共生菌,已命名45种[15],我国发现10余种[16-19]。根据进化关系立克次体属可分为祖先群、斑疹伤寒群、斑点热群和过渡群,除祖先群中个别种类以外都以节肢动物为宿主[20]。世界上目前已发现20余种对人类致病的立克次体[3-4]。立克次体由虱、蚤、蜱、革螨等吸血节肢动物叮咬而传播给人或动物,其中斑点热群立克次体种类最多,此群均以蜱为其宿主和传播媒介。螨立克次体(R. acari)属于过渡群,是已知唯一以螨为传播媒介的立克次体,其传播媒介是血红异皮螨(Allodermanyssus sanguineus),属于皮刺螨总科(Dermanyssoidea)皮刺螨科(Dermanyssidae)。在西方盲走螨(Metaseiulus occidentalis)[革螨股植绥螨科(Phytoseiidae)]中曾检出立克次体,该螨是一种捕食螨[21]。Moro等[2]综述既往皮刺螨总科革螨携带和传播病原体的研究,在以哺乳动物为主要宿主的皮刺螨科、巨刺螨科(Macronyssidae)和厉螨科(Laelapidae)中的部分种类中曾检出多种人兽共患传染病病原体,但立克次体属只有4例报道,除上述螨立克次体,还有普氏立克次体(R. prowazeki)、未鉴定种类立克次体和斑点热群立克次体。Reeves等[22]应用PCR技术检测埃及的褐家鼠(Rattus norvegicus)和黑家鼠(R. rattus)体表的柏氏禽刺螨(Ornithonyssus bacoti)中立克次体的17 kDa基因,其阳性率达6.70%,其中1株与澳大利亚立克次体(R. australis)序列同源性为99.00%,另外5株与蚤中检测出的序列完全相同。在我国台湾省的褐家鼠体表革螨中曾检出猫立克次体[23]。但我国革螨种类多,分布广,其中仅皮刺螨总科革螨就已记录356种[24],其中多数以鼠类为寄生宿主,在人居环境中游离的革螨可以叮咬人,已经证实格氏血厉螨可传播肾综合征出血热(HFRS)病毒[25]。
本研究首次在5种革螨中发现3种立克次体,包括黑龙江立克次体、猫立克次体近缘种以及1种未知立克次体。黑龙江立克次体属于斑点热群立克次体,1982年首次在我国黑龙江省绥芬河市采集的嗜群血蜱(Haemaphysalis concinna)和森林革蜱(Dermacentor silvarum)中发现,已证实其对人具有致病性,世界卫生组织将其命名为远东斑点热(又称黑龙江蜱传斑点热)。黑龙江立克次体已证实由蜱传播,在我国东北、华北、华东和华南地区以及俄罗斯远东地区、日本、泰国的鼠类和多种蜱均曾有阳性报道,但未见其他节肢动物携带该种立克次体的报道[14, 16, 26-32]。本研究从内蒙古锡林郭勒、通辽市的东北血革螨(达乌尔黄鼠)和仓鼠真厉螨(五趾跳鼠)中检出黑龙江立克次体。2种革螨广泛分布于东北、华北、西北和西南地区,其在立克次体传播中的作用需要进一步研究。
猫立克次体属于过渡群立克次体,可引起人类疾病,近几年在我国有不止1例人感染猫立克次体并致病的报道[33-34]。猫立克次体主要宿主和传播媒介是猫栉首蚤(Ctenocephalides felis),与该蚤一样呈世界性分布,但是在其他蚤以及蜱、螨、木虱中也曾检出,具有多种宿主。我国台湾省在褐家鼠体表革螨中检出过该菌,其17 kDa同源性为100%。本研究发现有4株立克次体17 kDa序列可分为2组,与猫立克次体同源性分别为99.70%~99.71%和98.50%~98.80%,2组之间同源性为99.05%。前者为猫立克次体可能性较大,而后者可能是猫立克次体的近缘种,由于缺少其他证据,暂认为4株均是猫立克次体近缘种。
近年来用分子生物学检测方法已发现多种未知的立克次体,说明作为节肢动物体内共生菌种的立克次体远不止现有的已知种类。本研究发现1种17 kDa序列与R. lusitaniae同源性达97.93%。R. lusitaniae属于斑点热群立克次体,在美洲、欧洲、非洲和中国软蜱(或软蜱宿主鸽子)中检出[35]。本种在布氏田鼠和达乌尔黄鼠体表的格氏血厉螨和1种寄螨属种类的第二若虫中检出,该寄螨与鼠类的关系尚不了解。格氏血厉螨宿主广泛,包括多种家鼠,全国均有分布,是HFRS病毒的传播媒介,如果证实其携带的立克次体可对人致病,其危害应引起重视[6, 25]。
我国内蒙古东部地区与俄罗斯、蒙古国接壤,东邻东北3省、南接华北,已在该地区蜱中发现塔拉塞维奇立克次体(Candidatus R. tarasevichiae)、内蒙古立克次体(R. mongolitimonae)、劳氏立克次体(R. raoultii)和黑龙江立克次体[13, 26-27]。本研究在此区域采集的鼠体革螨中除了发现黑龙江立克次体外,还检测到猫立克次体近缘种和1种未知的立克次体,采集区域包括锡林郭勒盟、呼伦贝尔和通辽市,说明上述区域内革螨也可自然携带多种立克次体。然而目前对革螨体内的立克次体只限于核酸检测,且局限于个别基因的扩增比对,部分已获得序列尚不能确定种类。因此需对革螨中立克次体开展多基因扩增测序,或通过立克次体分离培养和基因组测序来确定种类,以便对革螨在立克次体保存、传播中的作用以及可能对人类和其他动物的危害开展深入研究。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
张云, 朱进, 邓小昭, 等. 革螨、恙螨传播肾综合征出血热病毒的实验研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2001, 22(5): 352-354. Zhang Y, Zhu J, Deng XZ, et al. Experimental study on the roles of gasmid mite and chigger mite in the transmission of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome virus[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2001, 22(5): 352-354. DOI:10.3760/j.issn:0254-6450.2001.05.013 |
| [2] |
Moro CV, Chauve C, Zenner L. Vectorial role of some dermanyssoid mites (Acari, Mesostigmata, Dermanyssoidea)[J]. Parasite, 2005, 12(2): 99-109. DOI:10.1051/parasite/2005122099 |
| [3] |
Blanton LS. The rickettsioses: A practical update[J]. Infect Dis Clin North Am, 2019, 33(1): 213-229. DOI:10.1016/j.idc.2018.10.010 |
| [4] |
Fang R, Blanton LS, Walker DH. Rickettsiae as emerging infectious agents[J]. Clin Lab Med, 2017, 37(2): 383-400. DOI:10.1016/j.cll.2017.01.009 |
| [5] |
张丽娟. 中国立克次体病监测及防治现状与展望[J]. 疾病监测, 2007, 22(9): 577-579. Zhang LJ. Prospect and status of rickettsioses surveillance in China[J]. Dis Surveill, 2007, 22(9): 577-579. DOI:10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2007.09.001 |
| [6] |
邓国潘. 中国经济昆虫志. 第四十册. 蜱螨亚纲: 皮刺螨总科[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993: 26-300. Deng GP. Economic insect fauna of China, Fasc. 40, Acari: Dermanyssoideae[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993: 26-300. |
| [7] |
殷绥公, 贝纳新, 陈万鹏. 中国东北土壤革螨[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2013: 121-224. Yin SG, Bei NX, Chen WP. Gamasid mites in soil of northeast China[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2013: 121-224. |
| [8] |
Sanprick A, Yooyen T, Rodkvamtook W. Survey of Rickettsia spp. and Orientia tsutsugamushi pathogens found in animal vectors (Ticks, Fleas, Chiggers) in Bangkaew district, Phatthalung province, Thailand[J]. Korean J Parasitol, 2019, 57(2): 167-173. DOI:10.3347/kjp.2019.57.2.167 |
| [9] |
卢志宇, 付梦姣, 熊进峰, 等. 湖北省东北部地区蜱携立克次体的调查[J]. 军事医学, 2021, 45(4): 262-266. Lu ZY, Fu MJ, Xiong JF, et al. Investigation of rickettsiae in ticks from the northeast of Hubei province[J]. Mil Med Sci, 2021, 45(4): 262-266. DOI:10.7644/j.issn.1674-9960.2021.04.005 |
| [10] |
Díaz-Sánchez AA, Corona-González B, Meli ML, et al. Molecular diagnosis, prevalence and importance of zoonotic vector-borne pathogens in Cuban shelter dogs-A preliminary study[J]. Pathogens, 2020, 9(11): 901. DOI:10.3390/pathogens9110901 |
| [11] |
Chitanga S, Chambaro HM, Moonga LC, et al. Rickettsia lusitaniae in Ornithodoros porcinus ticks, Zambia[J]. Pathogens, 2021, 10(10): 1306. DOI:10.3390/pathogens10101306 |
| [12] |
Han SW, Chae JB, Jo YS, et al. First detection of Borrelia and Rickettsia species from Ornithodoros ticks in the Republic of Korea[J]. Ticks Tick Borne Dis, 2021, 12(4): 101689. DOI:10.1016/j.ttbdis.2021.101689 |
| [13] |
Fujita H, Takada N, Chaithong U. Preliminary report on rickettsial strains of spotted fever group isolated from ticks of China, Nepal and Thailand[J]. Annu Rep Ohara Gen Hosp, 2002, 44: 15-18. |
| [14] |
Fournier PE, Dumler JS, Greub G, et al. Gene sequence-based criteria for identification of new Rickettsia isolates and description of R. heilongjiangensis sp. nov.[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2003, 41(12): 5456-5465. DOI:10.1128/JCM.41.12.5456-5465.2003 |
| [15] |
张婧, 张毅波, 薛延韬, 等. 昆虫次生内共生菌Rickettsia研究进展[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2017, 39(2): 431-443. Zhang J, Zhang YB, Xue YT, et al. Research advances on a secondary endosymbiont Rickettsia in insect[J]. J Environ Entomol, 2017, 39(2): 431-443. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-0858.2017.02.24 |
| [16] |
张丽娟, 付秀萍, 范明远. 我国立克次体研究与立克次体病的流行现状[J]. 热带病与寄生虫学, 2005, 3(1): 37-42. Zhang LJ, Fu XP, Fan MY. Research on rickettsiae and rickettsial disease and epidemic situation in China[J]. J Trop Dis Parasitol, 2005, 3(1): 37-42. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2302.2005.01.016 |
| [17] |
Zhang LJ, Han J, Xu JG, et al. Identification of a new serotype of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis in wild rats from Guangdong province, China[J]. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2009, 15(2): 338-339. DOI:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02266.x |
| [18] |
Wang Q, Pan YS, Jiang BG, et al. Prevalence of multiple tick-borne pathogens in various tick vectors in Northeastern China[J]. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis, 2021, 21(3): 162-171. DOI:10.1089/vbz.2020.2712 |
| [19] |
Sun JM, Lin JF, Gong ZY, et al. Detection of spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks from Zhejiang province, China[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2015, 65(3): 403-411. DOI:10.1007/s10493-015-9880-9 |
| [20] |
Gillespie JJ, Williams K, Shukla M, et al. Rickettsia phylogenomics: Unwinding the intricacies of obligate intracellular life[J]. PLoS One, 2008, 3(4): e2018. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0002018 |
| [21] |
Van Der Geest LP, Elliot SL, Breeuwer JAJ, et al. Diseases of mites[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2000, 24(7): 497-560. DOI:10.1023/a:1026518418163 |
| [22] |
Reeves WK, Loftis AD, Szumlas DE, et al. Rickettsial pathogens in the tropical rat mite Ornithonyssus bacoti (Acari: Macronyssidae) from Egyptian rats (Rattus spp.)[J]. Exp Appl Acarol, 2007, 41(1/2): 101-107. DOI:10.1007/s10493-006-9040-3 |
| [23] |
Tsui PY, Tsai KH, Weng MH, et al. Molecular detection and characterization of spotted fever group rickettsiae in Taiwan[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2007, 77(5): 883-890. DOI:10.4269/ajtmh.2007.77.883 |
| [24] |
任天广, 郭宪国. 中国皮刺螨总科区系研究报告[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2009, 4(2): 99-104. Ren TG, Guo XG. Preliminary study on Dermanyssoidea fauna in China[J]. J Pathog Biol, 2009, 4(2): 99-104. DOI:10.13350/j.cjpb.2009.02.011 |
| [25] |
Yu XJ, Tesh RB. The role of mites in the transmission and maintenance of Hantaan virus (Hantavirus: Bunyaviridae)[J]. J Infect Dis, 2014, 210(11): 1693-1699. DOI:10.1093/infdis/jiu336 |
| [26] |
吴益民, 杨国平, 王洪军. 对黑龙江立克次体和远东蜱传斑点热调查研究的思考[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2008, 24(11): 1083-1084. Wu YM, Yang GP, Wang HJ. Reflections on the investigation and research of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis and tick-borne spotted fever in the Far East[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2008, 24(11): 1083-1084. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2694.2008.11.025 |
| [27] |
Mediannikov OY, Sidelnikov Y, Ivanov L, et al. Acute tick-borne rickettsiosis caused by Rickettsia heilongjiangensis in the Russian Far East[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2004, 10(5): 810-817. DOI:10.3201/eid1005.030437 |
| [28] |
Kasama K, Fujita H, Yamamoto S, et al. Genomic features of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis revealed by intraspecies comparison and detailed comparison with R. japonica[J]. Front Microbiol, 2019, 10: 2787. DOI:10.3389/fmicb.2019.02787 |
| [29] |
Takajo I, Kurosawa M, Sakata A, et al. Human Rickettsia heilongjiangensis infection, Japan[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2010, 16(8): 1306-1308. DOI:10.3201/eid1608.100049 |
| [30] |
Granitov V, Shpynov S, Beshlebova O, et al. New evidence on tick-borne rickettsioses in the Altai region of Russia using primary lesions, serum and blood clots of molecular and serological study[J]. Microbes Infect, 2015, 17(11/12): 862-865. DOI:10.1016/j.micinf.2015.08.011 |
| [31] |
崔云虹, 刘丹, 乌兰图雅, 等. 2016-2019年内蒙古大兴安岭林区立克次体关联细菌群监测[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(15): 2850-2856. Cui YH, Liu D, Wulan TY, et al. Tick surveillance for Rickettsia-associated bacterial communitie in the Greater Xing'an Mountains, Inner Mongolia, 2016-2019[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(15): 2850-2856. |
| [32] |
周磊, 汤芳, 栾进, 等. 内蒙古奇乾地区蜱携带斑点热立克次体的调查[J]. 中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2017, 40(2): 96-99. Zhou L, Tang F, Luan J, et al. Investigation on spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks collected from Qiqian areas of Inner Mongolia[J]. Chin J Front Health Quar, 2017, 40(2): 96-99. DOI:10.16408/j.1004-9770.2017.02.006 |
| [33] |
杨晓珊, 黎海滨, 严志东, 等. 猫立克次体合并鲍曼不动杆菌感染一例报告及用药分析[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志, 2021, 19(11): 84-86. Yang XS, Li HB, Yan ZD, et al. Rickettsia felis complicated with Acinetobacter baumannii infection: A case report and drug use analysis[J]. Clin Med J, 2021, 19(11): 84-86. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2021.11.018 |
| [34] |
张丽丽, 张俊湖, 胡铭, 等. 感染猫立克次体导致重症脑炎1例报告[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2021, 33(4): 491-493. Zhang LL, Zhang JH, Hu M, et al. Severe encephalitis caused by infection of Rickettsia felis: A case report[J]. Chin Crit Care Med, 2021, 33(4): 491-493. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201110-00709 |
| [35] |
Milhano N, Palma M, Marcili A, et al. Rickettsia lusitaniae sp. nov. isolated from the soft tick Ornithodoros erraticus (Acarina: Argasidae)[J]. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis, 2014, 37(3): 189-193. DOI:10.1016/j.cimid.2014.01.006 |
 2023, Vol. 34
2023, Vol. 34