扩展功能
文章信息
- 李超, 杨海波, 梁莹, 王国政, 李阳, 王彬, 李泓运, 王君, 刘起勇
- LI Chao, YANG Hai-bo, LIANG Ying, WANG Guo-zheng, LI Yang, WANG Bin, LI Hong-yun, WANG Jun, LIU Qi-yong
- 须喙按蚊入侵中国对未来气候变化的响应及风险评估
- Risk assessment of Anopheles barbirostris invasion responding to future climate change in China
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2023, 34(2): 145-153
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2023, 34(2): 145-153
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2023.02.003
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2023-02-03
2 中国疾病预防控制中心传染病预防控制所媒介生物控制室, 传染病预防控制国家重点实验室, 北京 102206
2 State Key Laboratory of Infectious Diseases Prevention and Control, Department of Vector Biology and Control, National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 102206, China
全球气候变化已经对自然生态系统造成了严重影响[1],根据联合国政府间气候变化专门委员会第五次评估报告(IPCC AR5),1901-2012年,全球陆地和海洋温度上升了0.89 ℃。气候变化不仅使全球地理环境发生变化,而且破坏了生物多样性,甚至严重威胁到人群的生命健康[2]。在气候变化对传染病的影响中,以媒介生物传染病最为敏感,一方面由于媒介生物的时空分布易受气候因素的影响,温度即使是微小的上升也会引发媒介生物数量和分布的巨大变化;另一方面病原体在媒介生物体内的繁殖与扩增也受到气候因素的影响[3-4]。
疟疾是由疟原虫所致的虫媒传染病,引起疟疾的疟原虫有恶性疟、间日疟、三日疟和卵形疟4种[5-6]。研究证明,疟原虫主要通过按蚊叮咬传播,此外也可以通过输血和分娩等途径传播[7-8]。在全世界472个正式确认的按蚊物种中[9],约有41个被认定为重要的疟疾病媒[10-11],其中就有须喙按蚊(Anopheles barbirostris)。须喙按蚊主要分布在印度尼西亚的爪哇岛一带,雌蚊主吸畜血,兼吸人血。在印度尼西亚部分地区,须喙按蚊是淋巴丝虫病的传播媒介之一;在印度西孟加拉邦地区,须喙按蚊有日本乙型脑炎病毒的自然感染记录[12-14]。根据《2020年世界疟疾报告》,东南亚区域有9个疟疾流行国家,约占全球疟疾病例疾病负担的3%。在未来气候变化的影响下,物种的潜在适生区范围将发生迁移[15],这与生物入侵直接相关,并可能在入侵地区扩大入侵物种带来的负面影响[16]。中国幅员辽阔,地理环境复杂,加之贸易往来日益密切,大大增加了外来物种入侵、定殖和扩散的风险。一旦病媒生物入侵到新的生态环境或者没有防范措施的领域,将会增加入侵地人民群众的疾病风险。因此,对须喙按蚊入侵中国进行风险评估具有非常重要的现实意义。
本研究运用最大熵模型(MaxEnt)预测须喙按蚊在近期和未来气候条件下的潜在适生区。MaxEnt模型是一种以最大熵理论为基础的物种分布预测模型,将物种的当前分布点数据和预测所需的环境变量数据导入模型中,经过运算可模拟出目标物种的可能分布情况[17]。在众多物种分布预测模型中,MaxEnt模型表现出了较强的预测能力[18],尤其是在物种分布点数据较少的情况下往往优于同类型的其他预测模型[19-24]。此外,我们还构建了病媒生物风险评估指标体系,从入侵物种的进入风险、定殖扩散风险和危害后果3个方面综合分析,对须喙按蚊入侵中国进行风险评估,结果可为相关部门制定有效的监测措施及合理的防控手段提供依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料 1.1.1 物种分布数据须喙按蚊的分布数据主要来自全球生物多样性信息网络数据库[GBIF.org(5 March 2021)GBIF Occurrence Downloadhttps://doi.org/10.15468/dl.x6bkvr]以及中国知网、Web of Science、PubMed、Medline等网络数据库公开发表的相关论文。从GBIF数据库及相关论文中获得须喙按蚊的记录数据为157条。将整理的数据按照物种名、经度和纬度的顺序储存为CSV格式,以便maxent 3.4.4软件(http://biodiversityinformatics.amnh.org/open_source/maxent)能够识别,并使用ENMtools工具包将同一栅格内的冗余数据删除,以避免数据偏倚的发生[25]。
1.1.2 环境数据环境数据通过WorldClim(http://www.worldclim.org/)气象网站下载获得,包括生物气候变量、月最高温、月最低温、月降雨量以及海拔的气候数据,空间分辨率均为5 arc min。选择中国(北京)气候中心中等分辨率气候系统(BCC-CSM2-MR)全球气候模式下的近期(1970-2000年)气候情景和未来4个时间段(2021-2040、2041-2060、2061- 2080和2081-2100年)的4个社会共享经济路径(SSP)(SSP126、SSP245、SSP370和SSP585)下的环境数据导入模型。将下载的数据通过ArcGIS 10.6软件(http://www.esri.com/software/arcgis)(Esri,Redlands,California,USA)转换为maxent软件能够识别的ASC格式。为避免环境数据过度拟合的问题,采用皮尔森相关性分析,通过R 4.0.3软件(http://www.r-project.org/)探讨各环境因素之间的相关性,相关系数绝对值> 0.8的变量被视为高度相关,保留对模型预测贡献度较高的变量。
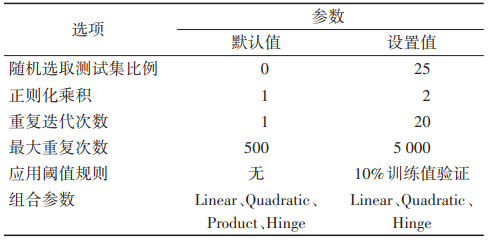
1.1.3 基础地图数据于国家基础地理信息系统(http://www.ngcc.cn/ngcc/)下载获得1∶400万的中国国界和省界以及县界行政区划图;于Natural Earth(https://www.naturalearthdata.com/downloads/)下载获得1∶1 000万的世界矢量地图。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 须喙按蚊的适生区预测运用MaxEnt模型对须喙按蚊在近期和未来气候情景下的潜在适生区进行预测。使用R语言ENMeval数据包对模型参数设置进行优化。ENMeval通过测试赤池信息量准则(Akaike information criterion,AIC)衡量统计模型拟合的优良性,优先选取AIC值较小时对应的参数进行模型模拟。通过测试,本研究中模型选取的参数组合为线性(linear,L)、二次型(quadratic,Q)和乘积型(hinge,H),正则化乘积(regularization multiplier,RM)值为2。将筛选得到的物种分布点和环境变量导入模型,参数中的重复迭代次数设置为20,最大重复次数设置为5 000,输出方式选择Cloglog,文件输出类型为“.asc”,选取25%的分布点作为测试集(表 1),以削减取样范围带来的误差。模型运行后,预测结果以ASC栅格数据格式输出,并利用ArcGIS 10.6软件的重分类模块把预测栅格数值转换为物种适生区等级,高适生区赋值为0.6~1.0,中适生区为0.4~0.6,低适生区为0.2~0.4,非适生区为0~0.2。同时,生成累积阈值曲线和受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC曲线),用以评价构建模型的精度和准确度。训练遗漏率与理论遗漏率越接近,表明构建的模型精度越高,受试者工作特征曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC)值越接近于1,表明预测准确度越高。
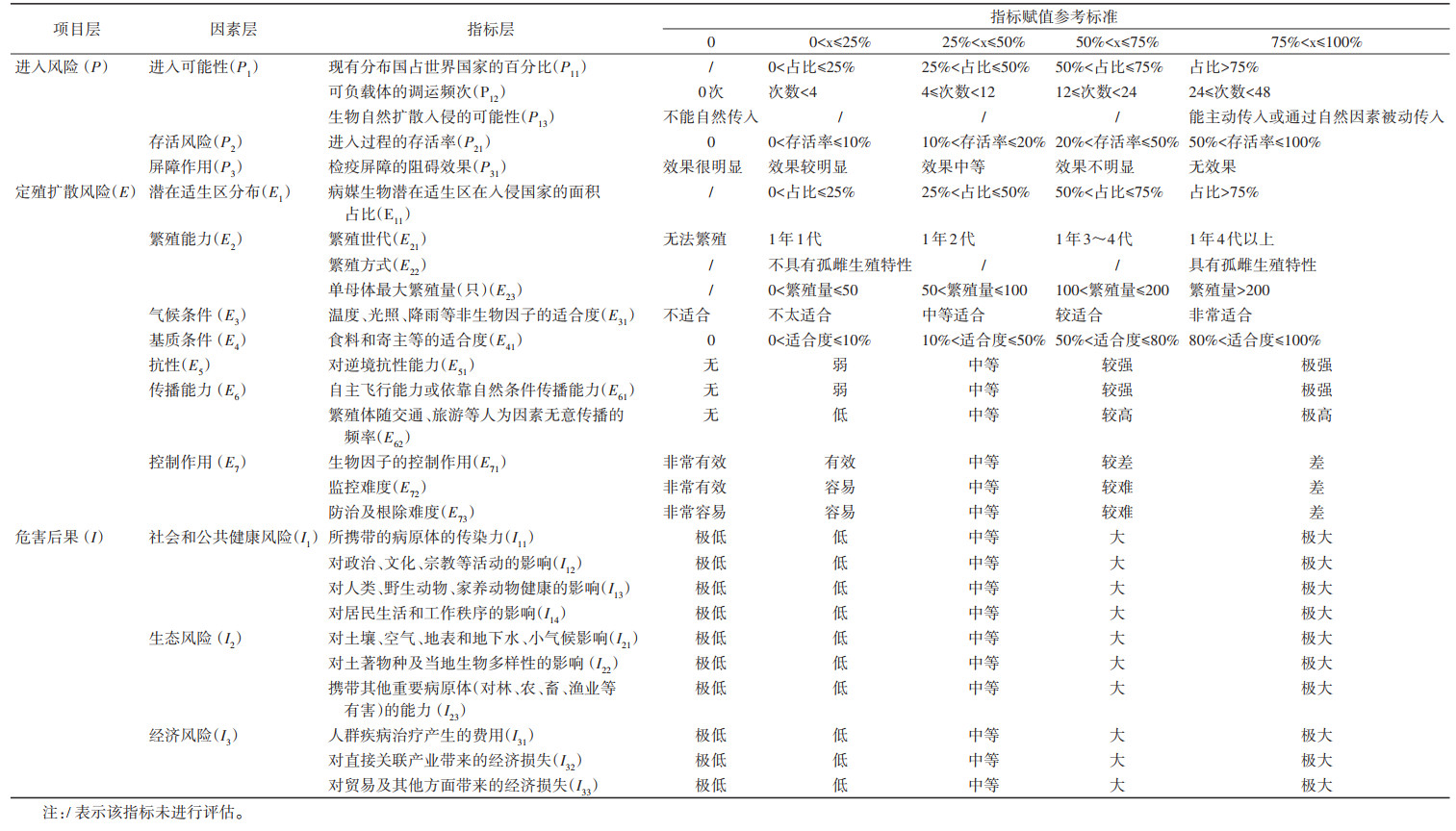
本研究通过综合分析影响外来物种入侵的生物学和生态学特征、入侵地环境和人为影响等因素,参考主要病虫风险评估指标体系[26],以病媒生物能否进入中国大陆地区为起点,综合入侵全过程中促进外来物种入侵风险形成的来源及影响因子,建立病媒生物风险评估指标体系及赋值参考标准(表 2)。邀请生物入侵、病媒生物防治等领域的专家根据已构建的风险评估表,由专家对评估对象的各项指标逐一进行打分,然后筛选出评分记录完整的打分表,统计出各项指标的综合值。最后,根据层次分析法—模糊综合评价模型计算出指标的权重以及最终的风险指数。评估结果为综合风险值(R),用来表示被评估病媒生物传入中国风险评估的最终结果。根据生物入侵的一般过程,将所有影响病媒生物入侵的因素分为3大类,包括进入风险(P)、定殖扩散风险(E)、危害风险(I)。每一类包含因素层,即每类的风险由哪些因素决定。每个因素层对应具体的指标层,即每一个评价因素由哪些具体指标来描述。为便于统一计算,根据模糊数学原理,参考已开展生物入侵风险评估研究案例[27],对于可以定量的指标设定了指标打分可参考的具体数值,不能定量的指标由专家根据经验评估打分。生物的综合风险由进入、定殖扩散和危害的风险共同决定,它们之间的逻辑关系符合乘法原理,计算公式如下:
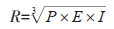
|
|
式中,R为综合风险值,P为进入风险,E为定殖扩散风险,I为危害风险。计算得出的R值应在0~1之间,对风险值的定性等级描述参照《进出境动物和动物产品风险分析程序和技术要求》(SN/T 2486-2010)中对于风险级别使用术语的规定。
进入风险、定殖扩散风险与因素层之间符合乘法原理,计算公式如下:
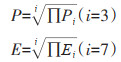
|
危害风险与因素层之间符合替代关系,计算公式如下:
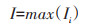
|
进入可能性(P1)和评价指标P11、P12、P13符合乘法原理。因此,计算公式如下:
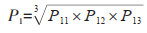
|
E2、E6和E7与对应的指标之间符合加法关系,计算公式如下:
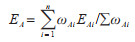
|
式中ωAi为对应指标的权重值,n为对应的指标层数,A=2、6、7。权重系数ωAi通过层次分析法(analytic hierarchy process,AHP)确定。
2 结果 2.1 须喙按蚊分布点及气候因子确定经过筛选和处理,最终得到须喙按蚊的有效分布点为99个(图 1)。根据皮尔森相关性分析和模型初次拟合的结果,将贡献率 > 1.0%的变量纳入模型。最终,有7个气候因子被选为须喙按蚊的预测变量。见表 3。

|
| 图 1 须喙按蚊全球分布点 Figure 1 Global distribution points of Anopheles barbirostris |
| |

|
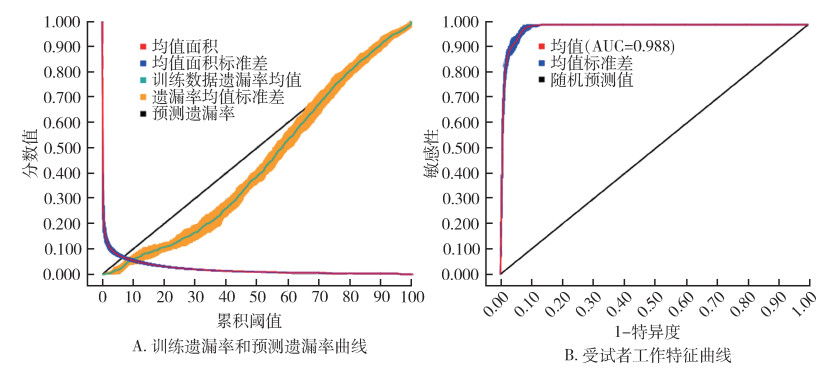
由图 2A可看出,预测遗漏率与训练值遗漏率大体一致;由图 2B可知,近期气候情景条件下模型AUC值为 > 0.9,具有较高的准确性。
|
| 图 2 最大熵模型预测精度曲线 Figure 2 Maximum entropy model prediction accuracy curve |
| |
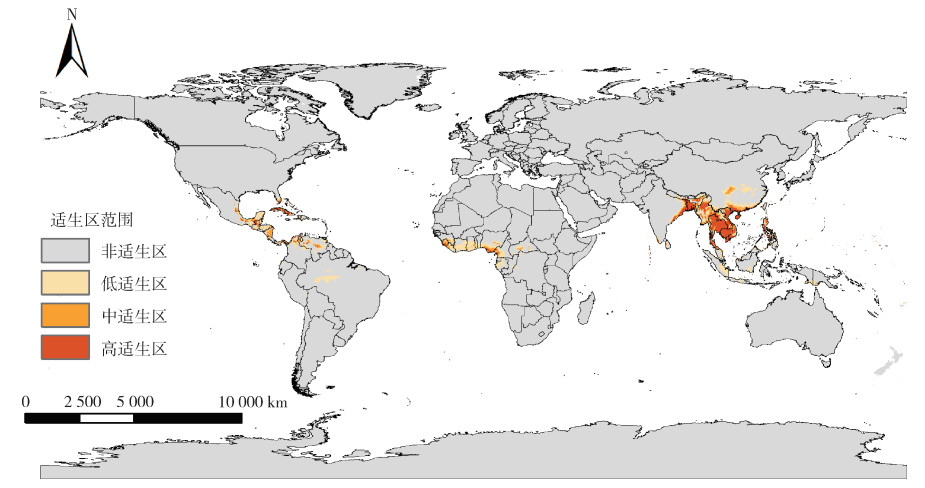
根据MaxEnt模型的输出结果,利用ArcGIS 10.6软件中的重分类制作须喙按蚊在近期气候情景下的全球适生区分布。须喙按蚊的潜在适生区主要集中在亚洲的孟加拉国、缅甸、老挝、泰国、柬埔寨、越南、马来西亚、菲律宾群岛和中国的广东省、广西壮族自治区(广西)、海南省、四川盆地东部等地区;非洲的塞拉利昂、利比里亚、科特迪瓦、尼日利亚、喀麦隆和赤道几内亚等地区;北美洲的巴哈马、古巴、洪都拉斯和墨西哥东南部等地区;南美洲的委内瑞拉和哥伦比亚北部等地区。见图 3。
|
| 图 3 须喙按蚊在近期气候情景下的全球潜在适生区 Figure 3 Global potential suitable areas of Anopheles barbirostris under current climate scenarios |
| |
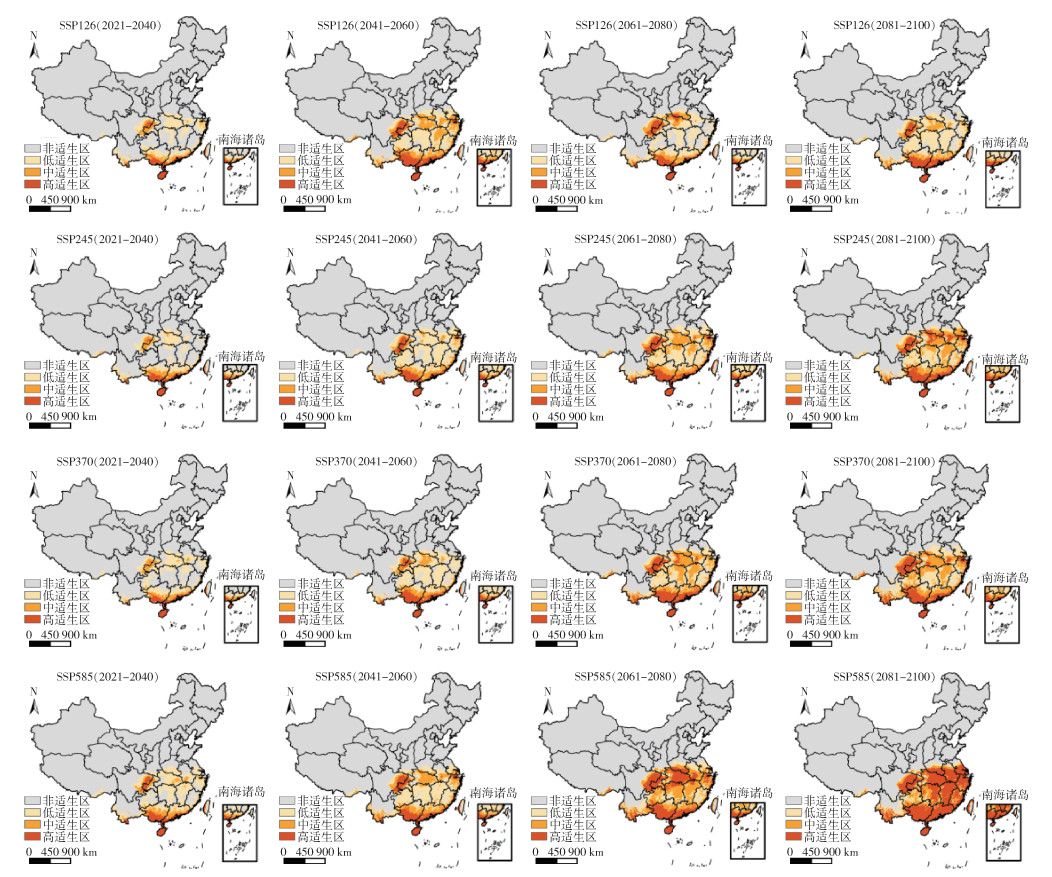
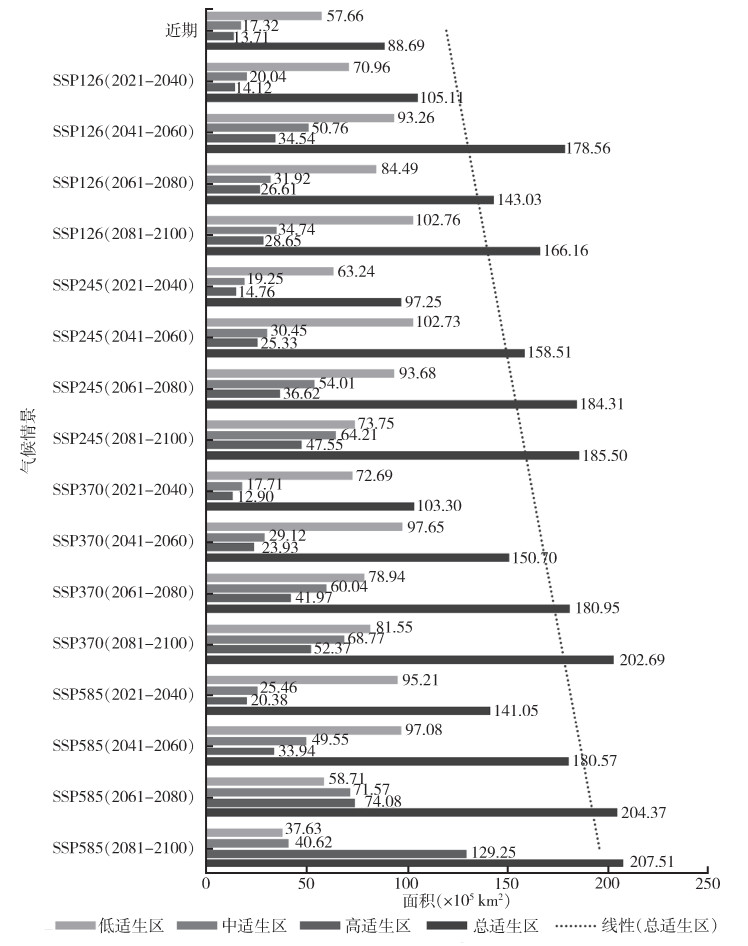
根据未来不同时期和不同气候情景下的预测结果,利用ArcGIS 10.6软件对须喙按蚊在中国的适生区做掩膜提取。须喙按蚊在SSP585气候情景下未来2081-2100年在中国的适生区范围最多(207.51×104 km2),未来各气候情景下潜在适生区面积呈增加趋势。见图 4、5。
|
| 图 4 未来气候情景下须喙按蚊在中国的潜在适生区 Figure 4 Potential suitable areas of Anopheles barbirostris in China under future climate scenarios |
| |
|
| 图 5 不同气候情景下须喙按蚊在中国的潜在适生区变化趋势 Figure 5 Changing trend of potential suitable areas of Anopheles barbirostris in China under different climate scenarios |
| |
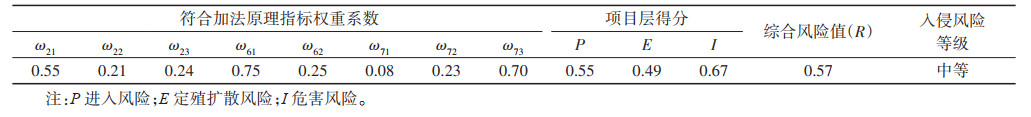
根据构建的风险评估指标体系以及各指标的评分标准,计算得出须喙按蚊入侵中国风险评估的项目层得分和综合风险值。须喙按蚊的综合风险值为0.57,属中等入侵风险等级物种。见表 4。
|
本研究发现,须喙按蚊在中国东南部一带有明显的的适生区,在未来气候情景下,高适生区可能扩散到之前的非适生区和中适生区。作为对人类健康有威胁的病媒生物,须喙按蚊近年来在中国云南和海南省已有监测记录[28-29]。考虑到未来气候变化以及温度和降雨对蚊虫的生存适宜性,中国东南部地区将增加蚊虫扩散及孳生的风险。
本研究表明,对须喙按蚊的潜在分布影响最大的环境变量是9月降雨量(prec9),它在预测该物种生存适宜性中有着独特的贡献;其次对须喙按蚊适生区分布有影响的环境因子按贡献率排列依次是5月降雨量(prec5)、6月最低温(tmin6)、降雨量季节变动系数(bio15)、最湿月降雨量(bio13)、最热季降雨量(bio18)和最冷季降雨量(bio19),可见降雨对须喙按蚊的生存适宜性有着较大影响。得益于印度洋西南季风和喜马拉雅山脉的阻挡,印度东北部成为世界降雨量最多的地区之一。观察须喙按蚊的分布点记录,可以发现物种的分布点大多位于降雨量充足的热带季风气候区。中国台湾南部、广东南部、广西南部、海南岛以及云南西双版纳傣族自治州均位于热带季风气候区,该地区降雨丰沛,年降雨量大部分地区为1 500~2 500 mm。在全球变暖的背景下,多数区域的降雨量可能增加,中国南方地区降雨日数也可能增加。查阅中国1981-2010年9月降雨量的数据,发现长江上游的四川盆地东部有着充沛的降雨,MaxEnt模型预测结果表明,该区域是未来气候情景下须喙按蚊的中适生区和高适生区。总体而言,须喙按蚊未来各气候情景下在中国的潜在适生区呈扩散趋势。受未来全球气候变化的影响,须喙按蚊很有可能扩散到中国内陆地区。
本研究中仅使用气候因子对须喙按蚊在我国近期及未来的潜在适生区进行了系统性预估,气候数据(1970-2000年)在时效上存在局限性,且使用WorldClim提供的全球气候模型中的BCC-CSM2-MR模式下的气候因子,不同模式下的气候因子也存在差异。另外,影响物种分布的环境因素还包括植被覆盖类型及覆盖率、人文社会因素、种间关系等,在今后的研究中将逐步纳入其他变量,探寻更有代表性的气候模式,以进行更准确地预估。
本研究在参考农业害虫危险性评价指标体系的基础上,创新性地构建病媒生物风险评估指标体系,综合评价须喙按蚊的入侵风险值。基于我们的研究结果,须喙按蚊对于中国来说属于中度入侵风险物种,需要提高警惕,完善蚊虫监测体系。虽然中国已经通过了联合国疟疾消除认证,但是境外输入病例形势依然严峻。2022年中国第15个全国疟疾日的口号是“防止疟疾输入再传播,共创无疟世界”,对于防治传疟蚊虫扩散,可以采取以下措施:①控制蚊虫的孳生,在雨季的河床和池塘等地清除蚊的幼虫卵;②完善蚊虫监测预警平台的建设,掌握蚊虫种群动态;③对境外输入病例采取积极地治疗手段,防止疟疾再传播;④气候变化对传疟媒介的影响显得至关重要,有必要进一步结合多模型对疟疾和传疟媒介的扩散进行风险评估。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
Woolway RI, Jennings E, Shatwell T, et al. Lake heatwaves under climate change[J]. Nature, 2021, 589(7842): 402-407. DOI:10.1038/s41586-020-03119-1 |
| [2] |
Willis KJ, Bhagwat SA. Biodiversity and climate change[J]. Science, 2009, 326(5954): 806-807. DOI:10.1126/science.1178838 |
| [3] |
刘起勇. 气候变化对中国媒介生物传染病的影响及应对: 重大研究发现及未来研究建议[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32(1): 1-11. Liu QY. Impact of climate change on vector-borne diseases and related response strategies in China: Major research findings and recommendations for future research[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32(1): 1-11. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2021.01.001 |
| [4] |
刘起勇. 气候变化对媒介生物性传染病的影响[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2013, 19(1): 1-7, 12. Liu QY. The impacts of climate change on vector-borne diseases[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2013, 19(1): 1-7, 12. DOI:10.19821/j.1671-2781.2013.01.001 |
| [5] |
Alam MS, Chakma S, Khan WA, et al. Diversity of anopheline species and their Plasmodium infection status in rural Bandarban, Bangladesh[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2012, 5: 150. DOI:10.1186/1756-3305-5-150 |
| [6] |
Greenwood BM, Bojang K, Whitty CJ, et al. Malaria[J]. Lancet, 2005, 365(9469): 1487-1498. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66420-3 |
| [7] |
Ippolito MM, Denny JE, Langelier C, et al. Malaria and the microbiome: A systematic review[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2018, 67(12): 1831-1839. DOI:10.1093/cid/ciy374 |
| [8] |
Bashar K, Tuno N, Ahmed TU, et al. Blood-feeding patterns of Anopheles mosquitoes in a malaria-endemic area of Bangladesh[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2012, 5: 39. DOI:10.1186/1756-3305-5-39 |
| [9] |
Harbach RE. The classification of genus Anopheles (Diptera: Culicidae): A working hypothesis of phylogenetic relationships[J]. Bull Entomol Res, 2004, 94(6): 537-553. DOI:10.1079/ber2004321 |
| [10] |
Sinka ME, Bangs MJ, Manguin S, et al. The dominant Anopheles vectors of human malaria in the Asia-Pacific region: Occurrence data, distribution maps and bionomic précis[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2011, 4: 89. DOI:10.1186/1756-3305-4-89 |
| [11] |
Elias M. Larval habitat of Anopheles philippinensis: A vector of malaria in Bangladesh[J]. Bull World Health Organ, 1996, 74(4): 447-450. |
| [12] |
Iryani K. Hubungan Anopheles barbirostris dengan malaria[J]. J Mat Sains Teknol, 2013, 12(1): 18-29. |
| [13] |
Paredes-Esquivel C, Donnelly MJ, Harbach RE, et al. A molecular phylogeny of mosquitoes in the Anopheles barbirostris subgroup reveals cryptic species: Implications for identification of disease vectors[J]. Mol Phylogenet Evol, 2009, 50(1): 141-151. DOI:10.1016/j.ympev.2008.10.011 |
| [14] |
Chakravarty SK, Sarkar JK, Chakravarty MS, et al. The first epidemic of Japanese encephalitis studied in India: Virological studies[J]. Indian J Med Res, 1975, 63(1): 77-82. |
| [15] |
Root TL, Price JT, Hall KR, et al. Fingerprints of global warming on wild animals and plants[J]. Nature, 2003, 421(6918): 57-60. DOI:10.1038/nature01333 |
| [16] |
Ricciardi A, Hoopes MF, Marchetti MP, et al. Progress toward understanding the ecological impacts of nonnative species[J]. Ecol Monogr, 2013, 83(3): 263-282. DOI:10.1890/13-0183.1 |
| [17] |
Gao XX, Liu J, Huang ZH. The impact of climate change on the distribution of rare and endangered tree Firmiana kwangsiensis using the MaxEnt modeling[J]. Ecol Evol, 2022, 12(8). DOI:10.1002/ECE3.9165 |
| [18] |
Papeş M, Gaubert P. Modelling ecological niches from low numbers of occurrences: Assessment of the conservation status of poorly known viverrids (Mammalia, Carnivora) across two continents[J]. Divers Distrib, 2007, 13(6): 890-902. DOI:10.1111/j.1472-4642.2007.00392.x |
| [19] |
Moreno R, Zamora R, Molina JR, et al. Predictive modeling of microhabitats for endemic birds in south Chilean temperate forests using maximum entropy (MaxEnt)[J]. Ecol Inform, 2011, 6(6): 364-370. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoinf.2011.07.003 |
| [20] |
马松梅, 张明理, 张宏祥, 等. 利用最大熵模型和规则集遗传算法模型预测孑遗植物裸果木的潜在地理分布及格局[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(11): 1327-1335. Ma SM, Zhang ML, Zhang HX, et al. Predicting potential geographical distributions and patterns of the relic plant Gymnocarpos przewalskii using maximum entropy and genetic algorithm for rule-set prediction[J]. Chin J Plant Ecol, 2010, 34(11): 1327-1335. DOI:10.3773/j.issn.1005-264x.2010.11.010 |
| [21] |
车乐, 曹博, 白成科, 等. 基于MaxEnt和ArcGIS对太白米的潜在分布预测及适宜性评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(6): 1623-1628. Che L, Cao B, Bai CK, et al. Predictive distribution and habitat suitability assessment of Notholirion bulbuliferum based on MaxEnt and ArcGIS[J]. Chin J Ecol, 2014, 33(6): 1623-1628. DOI:10.13292/j.1000-4890.20140327.001 |
| [22] |
徐卫华, 罗翀. MaxEnt模型在秦岭川金丝猴生境评价中的应用[J]. 森林工程, 2010, 26(2): 1-3, 26. Xu WH, Luo C. Application of MaxEnt model in Rhinopithecus roxllanae habitat assessment in Qinling mountain[J]. For Eng, 2010, 26(2): 1-3, 26. DOI:10.16270/j.cnki.slgc.2010.02.020 |
| [23] |
齐国君, 高燕, 黄德超, 等. 基于MaxEnt的稻水象甲在中国的入侵扩散动态及适生性分析[J]. 植物保护学报, 2012, 39(2): 129-136. Qi GJ, Gao Y, Huang DC, et al. Historical invasion, expansion process and the potential geographic distributions for the rice water weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus in China based on MaxEnt[J]. Acta Phytophy Sin, 2012, 39(2): 129-136. DOI:10.13802/j.cnki.zwbhxb.2012.02.006 |
| [24] |
Sarma RR, Munsi M, Ananthram AN, et al. Effect of climate change on invasion risk of giant African snail (Achatina fulica Férussac, 1821: Achatinidae) in India[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0143724. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0143724 |
| [25] |
Galvis-Martinez CA, Moo-Llanes DA, Altamiranda-Saavedra M. Similarity but not equivalence: Ecological niche comparison between sandflies from the Pleistocene and future scenarios in central and South America[J]. Med Vet Entomol, 2023, 37(1): 111-123. DOI:10.1111/mve.12615 |
| [26] |
王瑞, 黄蓬英, 傅建炜, 等. 进境台湾果蔬主要病虫风险评估与早期监测预警[J]. 生物安全学报, 2019, 28(4): 269-279. Wang R, Huang PY, Fu JW, et al. Invasion risk assessment, early warning and monitoring of major invasive pests introduced with fruit and vegetables from Taiwan to mainland China[J]. J Biosaf, 2019, 28(4): 269-279. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1787.2019.04.006 |
| [27] |
鞠瑞亭, 李博. 城市绿地外来物种风险分析体系构建及其在上海世博会管理中的应用[J]. 生物多样性, 2012, 20(1): 12-23. Ju RT, Li B. A risk analysis system for alien species in urban green spaces and application to the 2010 Expo, Shanghai[J]. Biodiv Sci, 2012, 20(1): 12-23. DOI:10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.12139 |
| [28] |
龚正达, 周红宁, 岳仁苹, 等. 云南澜沧江流域居民区蚊类大尺度空间生态位特征[J]. 寄生虫与医学昆虫学报, 2020, 27(2): 86-100. Gong ZD, Zhou HN, Yue RP, et al. Large-scale spatial niche characteristics of mosquitoes in residential areas of Lancang river basin, Yunnan province[J]. Acta Parasitol Med Entomol Sin, 2020, 27(2): 86-100. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-0507.2020.02.005 |
| [29] |
赵宣, 侯乃旭, 陈晨, 等. 海南省传播病毒蚊媒种类及蚊媒病毒流行情况分析[J]. 海南医学, 2017, 28(7): 1174-1179. Zhao X, Hou NX, Chen C, et al. Analysis of mosquito vector species and epidemic situation of mosquito-borne viruses in Hainan province[J]. Hainan Med J, 2017, 28(7): 1174-1179. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2017.07.052 |
 2023, Vol. 34
2023, Vol. 34