扩展功能
文章信息
- 吴群, 孙定炜, 李善干, 曾雪霞, 曾林海, 王绍萍, 吴德雷, 魏家佳, 黎灵刚, 陈成荣, 刘莹, 陈言
- WU Qun, SUN Ding-wei, LI Shan-gan, ZENG Xue-xia, ZENG Lin-hai, WANG Shao-ping, WU De-lei, WEI Jia-jia, LI Ling-gang, CHEN Cheng-rong, LIU Ying, CHEN Yan
- 海南省三亚市中华按蚊抗药性及抗性相关基因突变调查
- Investigation on resistance and resistance-conferring mutations in Anopheles sinensis in Sanya, Hainan province, China
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2022, 33(5): 666-671
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2022, 33(5): 666-671
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2022.05.010
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2022-03-29
2 三亚市疾病预防控制中心,海南 三亚 572000;
3 三亚市天涯区高峰卫生院,海南 三亚 572022
2 Sanya Center for Disease Prevention and Control, Sanya, Hainan 572000, China;
3 Gaofeng Health Center of Tianya District of Sanya City, Sanya, Hainan 572022, China
蚊虫是重要的医学节肢动物,能传播疟疾、流行性乙型脑炎、登革热等多种蚊媒传染病,其中疟疾主要是由媒介按蚊传播,其危害极大,严重影响公众健康。根据世界卫生组织(WHO)《2020年世界疟疾报告》,2019年全世界报告疟疾病例数达到2.29亿例,并造成40.9万人死亡[1]。2021年6月中国被WHO宣布已经消除疟疾,但中国每年还有一定的疟疾输入性病例,仅2020年全国就有1 015例输入性疟疾病例。当输入病例与传播媒介同时存在,主要威胁来自输入性病例经由本地媒介造成的继发性感染[2-4]。海南岛地处热带及亚热带地区,年平均气温24.2 ℃,年均降水量1 684 mm,平均相对湿度85%,自然条件非常适宜蚊虫的孳生繁殖[5]。中华按蚊(Anopheles sinensis)作为亚洲国家主要的传疟媒介[6],同样也广泛分布于海南岛。由于化学防治操作容易,消杀作用快速,当出现疟疾疫情时,目前化学防治仍是传疟媒介快速综合治理的主要方法之一[7]。随着杀虫剂的大量使用,传疟媒介按蚊的敏感性发生改变,例如河南省濮阳市和辽宁省东港市等地均报道了当地中华按蚊对溴氰菊酯产生一定的抗性[8-9]。海南省三亚市曾经于2012-2014连续3年无疟疾病例报告,但间隔3年后,于2015年出现了7例本地疟疾病例[10-12]。作为海南省最后暴发本地疟疾病例的地区,目前关于当地主要传疟媒介中华按蚊的抗药性研究报道主要集中在2014年之前[13-15],而2015年之后相关报道较少。本研究分别于2018和2020年在三亚市天涯区高峰镇现场采集中华按蚊进行抗性水平测定,并对2个常用杀虫剂靶标基因[即编码乙酰胆碱酯酶(Acetyl cholinesterase,AChE)的ace-1基因,编码电压门控钠离子通道(voltage-gated sodium channel,VGSC)的VGSC基因]的抗性等位基因的存在和频率进行检测,揭示三亚市中华按蚊对杀虫剂抗性现状及其产生机制,为三亚市传疟媒介及疟疾防控提供参考。
1 材料与方法 1.1 供试蚊虫参照孙定炜等[13]报道的方法,于2018年9-10月和2020年9月在三亚市天涯区高峰镇(109°24′8″E,18°29′18″N)当地农户牛棚周围,利用牛诱法采集按蚊成蚊,带回实验室饲养至第2天(胃血消化约在谢拉氏Ⅲ~Ⅳ期),经形态学鉴定确认为中华按蚊[16]的成蚊用于后续实验。
1.2 供试杀虫剂0.5%醚菊酯、4%滴滴涕(DDT)、0.05%溴氰菊酯、5.0%马拉硫磷和5.0%溴虫腈5种杀虫剂药膜由中国疾病预防控制中心传染病预防控制所媒介生物控制室提供。DNA提取试剂盒购于生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司;2×Taq PCR预混液购于天根生化科技(北京)有限公司,扩增引物由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成。
1.3 抗药性生物测定按照WHO推荐使用的成蚊接触筒法,按诊断剂量法[17]步骤测定中华按蚊成蚊抗药性。空白对照死亡率 < 5%无需校正;空白对照死亡率在5%~20%之间,用Abbott公式进行校正;对照死亡率 > 20%为无效测定。死亡率(%)=死亡虫数/试虫总数×100;校正死亡率(%)=(实验组死亡率-对照组死亡率)/(1-对照组死亡率)×100。
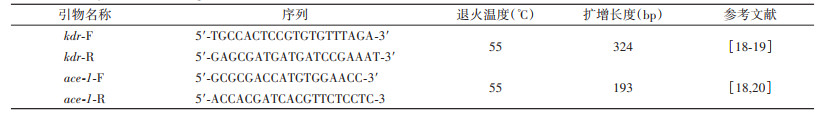
1.4 中华按蚊总DNA提取及VGSC、ace-1基因突变检测随机选取40只生物测定实验后存活的中华按蚊,单只放入1.5 ml的离心管中,利用DNA提取试剂盒,按照操作步骤提取蚊虫总DNA。以提取DNA为模板,表 1中引物分别扩增VGSC基因和ace-1基因片段,总反应体积25 μl,包括2×Taq PCR预混液12.5 μl,10 μmol/L正、反向引物各1 μl,DNA模板4 μl,加蒸馏水至25 μl。PCR反应条件:95 ℃ 3 min;94 ℃ 30 s、55 ℃ 30 s、72 ℃ 45 s,循环35次;72 ℃ 6 min。见表 1。
|
用1.2%琼脂糖凝胶经电泳(120 V,30 min)后,凝胶成像系统检测扩增条带并拍照记录结果。将清晰单一条带PCR产物送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行测序。
1.5 数据处理与分析利用Excel 2021软件计算诊断计量上蚊虫死亡率,根据《蚊虫对杀虫剂抗药性检测方法生物测定法》[17]中成蚊诊断剂量法死亡率判断抗性级别,判别标准:在诊断剂量下蚊虫98%≤死亡率(MR)≤100%为敏感种群(S);80%≤MR < 98%为可能抗性种群(M);MR < 80%为抗性种群(R)。
用DNAStar 7.0软件将VGSC基因1014位点和ace-1基因119位点基因测序结果,分别与GenBank中公布的中华按蚊VGSC基因(GenBank登录号:DQ334052.1)和ace-1基因[参考冈比亚按蚊(Anopheles gambiae)ace-1基因序列(序列号:BN000066)]序列进行峰图比对和分析,统计位点突变频率;利用SPSS 21软件进行χ2检验,分析比值比(OR)及其95%置信区间。
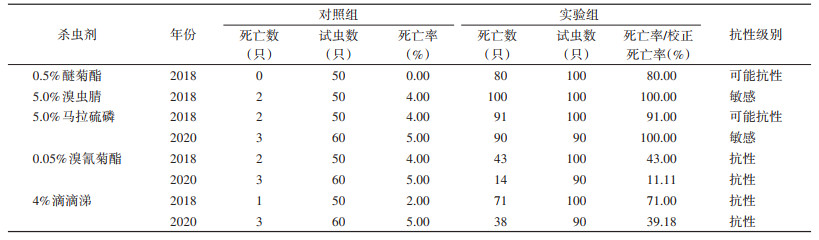
2 结果 2.1 抗药性测定结果2018和2020年中华按蚊抗性测定结果显示,24 h后死亡率为11.11%~100%。由于蚊虫数量不足,2020年未对醚菊酯和溴虫腈进行测定。2018年中华按蚊对0.5%醚菊酯为可能抗性,而对5.0%溴虫腈敏感。此外,2018和2020年的中华按蚊对0.05%溴氰菊酯、4%DDT产生抗性,24 h后死亡率分别为43.00%、11.11%(溴氰菊酯)和71.00%、39.18%(DDT),死亡率呈下降趋势;中华按蚊对5.0%马拉硫磷,2018年死亡率(91.00%)低于2020年(100%),敏感性有所增加。见表 2。
|
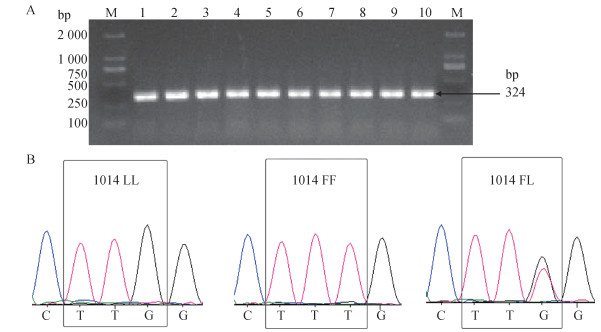
对2018和2020年抗药性测定结束后存活中华按蚊进行VGSC基因1014位点突变检测,如图 1所示,将250~500 bp之间单一条带对应的PCR产物送去测序,共获得75条中华按蚊VGSC基因序列,其中2020年35条,2018年40条。比对结果显示在1014位点共检测到1种突变基因L1014F,即亮氨酸(L)突变为苯丙氨酸(F)(TTG突变为TTT),发现3种基因型(图 1、表 3):1014LL敏感纯合(密码子为TTG)、1014FL敏感与抗性杂合(密码子为TTT/TTG)、1014FF抗性纯合(密码子为TTT)。2018年中华按蚊1014LL(25.00%)和1014FL(52.50%)分别高于2020年(22.86%、40.00%),而2018年的1014FF(22.50%)低于2020年的37.14%,抗性等位基因频率2020年(57.14%)高于2018年(48.75%)。
|
| 注:A M为marker,1~10中华按蚊监测样品;B TTG、TTT和TTG为密码子,L为亮氨酸,F为苯丙氨酸。 图 1 中华按蚊电压门控钠离子通道基因扩增电泳图(A)及其1014位点突变类型(B) Figure 1 Electrophoretogram of voltage-gated sodium channel gene amplification in Anopheles sinensis (A) and mutation types at the 1014 locus (B) |
| |
|
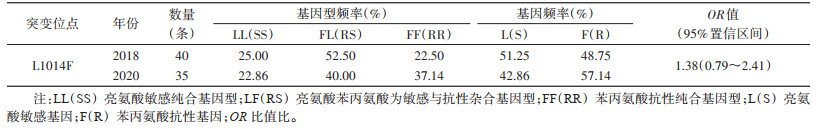
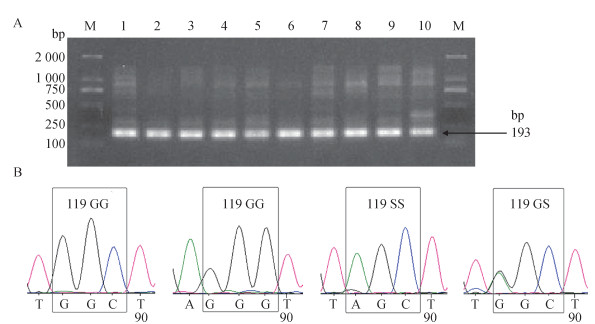
共获得80条中华按蚊ace-1基因序列,2018和2020年各为40条,结果显示在119位点共检测到2种突变基因(图 2),一种为有义突变即G119S:甘氨酸(G)突变为丝氨酸(S)(GGC突变为AGC),另一种为同义突变,即G119G,GGC突变为GGG(氨基酸未发生改变)。发现3种基因型:119GG(密码子为GGC或GGG)、119SS抗性纯合(密码子为AGC)和119GS抗性杂合(密码子为GGC/AGC),其在2018年(表 4)的频率分别为2.50%、7.50%和90.00%,抗性等位基因频率为52.50%,高于2020年的43.75%。
|
| 注:A M为marker,1~10中华按蚊监测样品;B GGC、GGG和AGC为密码子,G为甘氨酸,S为丝氨酸。 图 2 中华按蚊乙酰胆碱酯酶ace-1基因扩增电泳图(A)及其119位点突变类型测序峰图(B) Figure 2 Electrophoretogram of acetylcholinesterase gene 1 amplification in Anopheles sinensis (A) and sequencing chromatograms showing the mutation types at the 119 locus (B) |
| |
|
传疟媒介按蚊的控制除应考虑其种群季节消长等生态学习性外,更应了解其抗药性问题,本研究分别于2018和2020年对海南省三亚市中华按蚊的抗药性及其杀虫剂靶标基因VGSC和ace-1进行检测,了解海南省三亚市中华按蚊对常用杀虫剂及其抗性基因突变情况。生物测定结果显示三亚市中华按蚊对溴氰菊酯(0.05%)和DDT(4.00%)均为抗性水平,与Sun等[14]之前测定结果一致,此外,对5%马拉硫磷由2018年的可能抗性到2020年变为敏感种群,而Sun等[14]于2014年之前测定结果显示三亚市中华按蚊对其为抗性水平,由此可见中华按蚊对有机磷类的抗性水平具有减弱趋势。
DDT和拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂的大量使用,能造成昆虫的钠离子通道基因位点突变,对该类杀虫剂敏感性下降,从而产生击倒抗性。击倒抗性最初在家蝇中被报道[21]。研究发现,蚊虫VGSCⅡS6节段L1014位点是一个较保守的突变位点,在中国地区的中华按蚊主要存在L1014F/L、1014S/L、1014C/L、1014W/N和1013S等5种突变位点[22]。本研究中仅检测到L1014F一种突变类型,其2020年基因突变频率高于2018年,与此同时虽然2018和2020年其对溴氰菊酯均为抗性种群,但其24 h后死亡率2020年(11.11%)低于2018年(43.00%),与之前研究者提出的中华按蚊kdr突变频率与溴氰菊酯抗性显著相关结果类似[23]。由此可见三亚市中华按蚊VGSC基因1014位点突变频率及其对溴氰菊酯类杀虫剂的抗性具有逐年上升的趋势。此外,我们还发现,在三亚市2012年中华按蚊的抗药性研究中,对DDT产生抗性的中华按蚊VGSC基因L1014F突变频率为9.5%[15],低于本研究中的48.75%和57.14%,而DDT已于2010年11月1日起在海南省开始停用,中华按蚊产生对DDT的持续抗性可能与其抗击倒抗性相关基因突变频率上升有关。
此外,AChE是有机磷和氨基甲酸酯类杀虫剂的作用靶标。AChE对杀虫剂的敏感性下降,而根本原因是AChE基因突变,与抗性相关突变位点主要集中在ace-1基因119位点。早在2006年韩国报道了中华按蚊存在G119S突变,其频率达到74.11%[24],后来在我国广西、四川、上海等地中华按蚊均检测到G119S突变[25-27]。本研究中同样检测到G119S突变,且可能因其对有机磷类杀虫剂抗性从可能抗性水平降至敏感水平,其突变频率呈现逐年下降趋势。
在本研究中,我们检测到三亚市中华按蚊VGSC和ace-1均有一定突变频率,特别是VGSC的突变频率呈现逐年上升趋势,如果继续大量使用拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂,中华按蚊可能会通过稀释易感等位基因频率而加剧其抗药性。此外,本研究生物测定结果显示三亚市中华按蚊对溴氰菊酯和DDT均为抗性种群,且24 h后死亡率呈现逐年下降趋势,而对有机磷类和其他新型杀虫剂均较敏感,因此,可以通过管理或轮用杀虫剂来降低目标基因突变的频率。此次仅测定三亚市中华按蚊抗药性随时间变化的情况,下一步亟需对海南省其他地区中华按蚊抗药性及其抗性基因突变多样性进行分子生物学研究,为海南省公共卫生系统开展虫媒传染病防治工作提供技术支持。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
World Health Organization. World malaria report 2020[R]. Geneva: WHO, 2020.
|
| [2] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会疾病预防控制局. 2020年全国法定传染病疫情概况[EB/OL]. (2021-03-12)[2022-04-17]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/jkj/s3578/202103/f1a448b7df7d4760976fea6d55834966.shtml. Bureau of Disease Prevention and Control, Nationl Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Overview of the national epidemic of notifiable infectious diseases in 2020[EB/OL]. (2021-03-12)[2022-04-17]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/jkj/s3578/202103/f1a448b7df7d4760976fea6d55834966.shtml. (in Chinese) |
| [3] |
董昊炜, 南春燕, 周秋明, 等. 基于16S rRNA高通量测序的现场中华按蚊及其孳生地水体菌群结构研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32(5): 533-540. Dong HW, Nan CY, Zhou QM, et al. Composition of microbiota in Anopheles sinensis and water in larvae breeding site: A study based on 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32(5): 533-540. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2021.05.005 |
| [4] |
曹俊, 刘耀宝, 曹园园, 等. 中国消除疟疾的持续挑战: 输入性疟疾[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2018, 36(2): 93-96. Cao J, Liu YB, Cao YY, et al. Sustained challenge to malaria elimination in China: Imported malaria[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2018, 36(2): 93-96. |
| [5] |
赵宣, 侯乃旭, 陈晨, 等. 海南省传播病毒蚊媒种类及蚊媒病毒流行情况分析[J]. 海南医学, 2017, 28(7): 1174-1179. Zhao X, Hou NX, Chen C, et al. Analysis of mosquito vector species and epidemic situation of mosquito-borne viruses in Hainan province[J]. Hainan Med J, 2017, 28(7): 1174-1179. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2017.07.052 |
| [6] |
Ni RY, Liu N, Li M, et al. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of voltage-gated sodium channel haplotypes in the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis using a high-throughput amplicon sequencing approach[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2021, 14(1): 499. DOI:10.1186/s13071-021-05009-5 |
| [7] |
林康明, 杨益超, 黎军. 我国主要传疟媒介抗药性研究进展[J]. 中国热带医学, 2019, 19(6): 584-590. Lin KM, Yang YC, Li J. Progress of insecticide resistance of the main malaria vectors in China[J]. China Trop Med, 2019, 19(6): 584-590. DOI:10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2019.06.21 |
| [8] |
胡亚博, 贺志权, 刘颖, 等. 河南省濮阳市中华按蚊对杀虫剂敏感性调查[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2021, 33(5): 501-504, 509. Hu YB, He ZQ, Liu Y, et al. Susceptibility of Anopheles sinensis to insecticides in Puyang city, Henan province[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2021, 33(5): 501-504, 509. DOI:10.16250/j.32.1374.2020331 |
| [9] |
王纯玉, 李志, 丁俊, 等. 辽宁省东港市蚊虫分布及中华按蚊抗药性调查[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2021, 27(3): 223-225. Wang CY, Li Z, Ding J, et al. Distribution of mosquitoes and insecticide resistance of Anopheles sinensis in Donggang city of Liaoning province[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2021, 27(3): 223-225. DOI:10.19821/j.1671-2781.2021.03.009 |
| [10] |
王善青. 海南疟疾70年: 从肆虐走向消除[J]. 中国热带医学, 2019, 19(8): 707-718. Wang SQ. The seventy years of malaria from hyperendemicity to elimination in Hainan[J]. China Trop Med, 2019, 19(8): 707-718. DOI:10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2019.08.01 |
| [11] |
林常勇, 王善青, 陈朱, 等. 海南省三亚市1名间日疟原虫带虫者的调查与处置[J]. 中国热带医学, 2016, 16(12): 1243-1245. Lin CY, Wang SQ, Chen Z, et al. Investigation and deposition of a Plasmodium vivax carrier in Sanya city, Hainan province[J]. China Trop Med, 2016, 16(12): 1243-1245. DOI:10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2016.26 |
| [12] |
林常勇, 陈朱, 王善青, 等. 海南省三亚市一起罕见的当地三日疟疫情分析及处置[J]. 中国热带医学, 2016, 16(5): 481-484. Lin CY, Chen Z, Wang SQ, et al. Investigation of a rare local epidemic of Plasmodium malariae infection in Sanya city, Hainan province[J]. China Trop Med, 2016, 16(5): 481-484. DOI:10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2016.05.20 |
| [13] |
孙定炜, 王善青, 卓开仁, 等. 海南省中华按蚊对3种杀虫剂的抗药性研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2014, 32(2): 127-129. Sun DW, Wang SQ, Zhuo KR, et al. Resistance of Anopheles sinensis to three common insecticides in Hainan province[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis, 2014, 32(2): 127-129. |
| [14] |
Sun DW, Wang GZ, Zeng LH, et al. Extensive resistance of Anopheles sinensis to insecticides in malaria-endemic areas of Hainan province, China[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2017, 97(1): 295-298. DOI:10.4269/ajtmh.16-0723 |
| [15] |
Qin Q, Li YJ, Zhong DB, et al. Insecticide resistance of Anopheles sinensis and An. vagus in Hainan Island, a malaria-endemic area of China[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2014, 7: 92. DOI:10.1186/1756-3305-7-92 |
| [16] |
陆宝麟. 中国动物志. 昆虫纲. 第九卷. 双翅目: 蚊科(下卷)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 16-17. Lu BL. Fauna Sinica. Insecta, Vol 9. Diptera: Culicidae 2[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 16-17. |
| [17] |
中华人民共和国卫生部. GB/T 26347-2010蚊虫抗药性检测方法生物测定法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011. Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 26347-2010 est methods of mosquito resistance to insecticides-Bioassay methods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2011. (in Chinese) |
| [18] |
梁秋果. 贵州省中华按蚊抗药性靶标kdr、ace-1基因突变检测及种群遗传学研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州医科大学, 2019. Liang QG. Detection of mutations in kdr and ace-1 genes of resistance targets and population genetics of Anopheles sinensis in Guizhou province, China[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Medcial University, 2019. (in Chinese) |
| [19] |
Yang C, Feng XY, Huang ZS, et al. Diversity and frequency of kdr mutations within Anopheles sinensis populations from Guangxi, China[J]. Malar J, 2016, 15(1): 411. DOI:10.1186/s12936-016-1467-3 |
| [20] |
Chang XL, Zhong DB, Fang Q, et al. Multiple resistances and complex mechanisms of Anopheles sinensis mosquito: A major obstacle to mosquito-borne diseases control and elimination in China[J]. PLoS Negl Trop Dis, 2014, 8(5): e2889. DOI:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002889 |
| [21] |
Busvine JR. Mechanism of resistance to insecticide in houseflies[J]. Nature, 1951, 168(4266): 193-195. DOI:10.1038/168193a0 |
| [22] |
Silva APB, Santos JMM, Martins AJ. Mutations in the voltage-gated sodium channel gene of anophelines and their association with resistance to pyrethroids: A review[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2014, 7: 450. DOI:10.1186/1756-3305-7-450 |
| [23] |
Zhong DB, Chang XL, Zhou GF, et al. Relationship between knockdown resistance, metabolic detoxification and organismal resistance to pyrethroids in Anopheles sinensis[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(2): e55475. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0055475 |
| [24] |
Baek JH, Kim HW, Lee WJ, et al. Frequency detection of organophosphate resistance allele in Anopheles sinensis (Diptera: Culicidae) populations by real-time PCR amplification of specific allele (rtPASA)[J]. J Asia-Pac Entomol, 2006, 9(4): 375-380. DOI:10.1016/S1226-8615(08)60317-9 |
| [25] |
Yang C, Feng XY, Liu N, et al. Target-site mutations (AChE-G119S and kdr) in Guangxi Anopheles sinensis populations along the China-Vietnam border[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2019, 12(1): 77. DOI:10.1186/s13071-019-3298-x |
| [26] |
Qian WP, Liu N, Yang Y, et al. A survey of insecticide resistance-conferring mutations in multiple targets in Anopheles sinensis populations across Sichuan, China[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2021, 14(1): 169. DOI:10.1186/s13071-021-04662-0 |
| [27] |
Fang Y, Shi WQ, Wu JT, et al. Resistance to pyrethroid and organophosphate insecticides, and the geographical distribution and polymorphisms of target-site mutations in voltage-gated sodium channel and acetylcholinesterase 1 genes in Anopheles sinensis populations in Shanghai, China[J]. Parasit Vectors, 2019, 12(1): 396. DOI:10.1186/s13071-019-3657-7 |
 2022, Vol. 33
2022, Vol. 33


