扩展功能
文章信息
- 浦恩念, 段兴德, 冯志刚, 刘正祥, 蔡文凤, 王剑, 秦媛, 李豪, 唐永泉, 邵宗体
- PU En-nian, DUAN Xing-de, FENG Zhi-gang, LIU Zheng-xiang, CAI Wen-feng, WANG Jian, QIN Yuan, LI Hao, TANG Yong-quan, SHAO Zong-ti
- 云南省孟连县边境地区小型兽类及其寄生蚤种类组成和分布调查
- Species composition and distribution of small mammals and their parasitic fleas in the border area of Menglian county, Yunnan province, China
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2022, 33(3): 366-370
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2022, 33(3): 366-370
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2022.03.010
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2021-11-10
2 孟连傣族拉祜族佤族自治县疾病预防控制中心, 云南 孟连 665800;
3 普洱市疾病预防控制中心, 云南 普洱 665000
2 Menglian Dai, Lahu and Wa Autonomous County Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Menglian, Yunnan 665800, China;
3 Pu'er City Center of Disease Control and Prevention, Pu'er, Yunnan 665000, China
孟连傣族拉祜族佤族自治县(孟连县)隶属于普洱市,位于云南省西南部,西部和南部与缅甸相连,国境线长133.40 km。孟连县1996年证实存在鼠疫疫源地[1],该疫源地的主要宿主动物是黄胸鼠(Rattus tanezumi),主要传播媒介是印鼠客蚤(Xenopsylla cheopis)。1996-2002年该县共有6年次监测到鼠间鼠疫疫情,2002年之后未监测到鼠疫疫情[2]。孟连县处于中国-缅甸边境地区,鼠疫存在跨境传入的风险。小型兽类(小兽)是多种自然疫源性疾病的宿主,其体表寄生蚤是鼠疫、地方性斑疹伤寒等疾病的传播媒介[3-4],调查小兽及其寄生蚤的种类构成、生境分布情况,能为鼠疫等传染病监测和媒介生物控制提供依据。为此,我们于2020年11月对孟连县边境地区的小兽及其寄生蚤的物种构成、分布等情况进行了系统调查,现将结果分析如下。
1 材料与方法 1.1 调查区域概况孟连县位于云南省西南部,面积为1 893.42 km2,地处东经99°9′~99°46′、北纬22°35′~22°32′,下设2个乡4个镇。年平均气温为19.6 ℃,最高气温达36 ℃,年平均降雨量1 373 mm,属南亚热带气候类型。该地区地处怒山余脉,地貌以山地为主,南北部多高山峻岭;东西部偏低,多河谷盆地。主要植被类型有热带雨林、热带季雨林、常绿阔叶林、暖热性针叶林、落叶阔叶林、暖热性竹林、热性灌木林和人工植被[5]。
1.2 调查方法 1.2.1 小兽调查以孟连县的芒信和勐马2个边境乡镇作为调查样区,对调查样区内4个居民区、3个农耕区和3个林区样点中的小兽进行调查取样。居民区以自然村为调查点,每个调查点选择10~20户,每户布放5~10个鼠笼,每个调查点不少于300笼次。农耕区及林区每个调查点布放鼠夹不少于250夹,以自制油条为诱饵,采用5 m夹线法布放鼠夹,晚放晨收[6],将捕获的小兽以布袋单只分装,带回实验室进行分类鉴定[7]、登记计数。
1.2.2 小兽体表寄生蚤调查带回实验室的小兽置于大整理箱内用乙醚进行体表寄生蚤麻醉后,分别置于白塑料方盘内捡蚤,采集的蚤分装至75%乙醇溶液采样管中编号保存并进行分类鉴定[8]。
1.3 数据分析用Excel2016软件构建小兽及体表寄生蚤数据库,计算小兽密度、物种构成比、鼠体染蚤率和蚤指数。小兽密度用捕获率(R)表示,R=Nr/Ne×100%,式中Nr表示捕获的小兽数,Ne表示有效工具数;鼠染蚤率(%)=(染蚤鼠数/总鼠数)×100,蚤指数=总蚤数/总鼠数;按照小兽不同种类数量占小兽统计总数的百分比(Pi)来确定优势种,将Pi > 10%定为优势种,1%≤Pi≤10%定为常见种,Pi < 1%定为稀有种[9]。采用β多样性指数计算小兽群落相似性系数,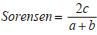
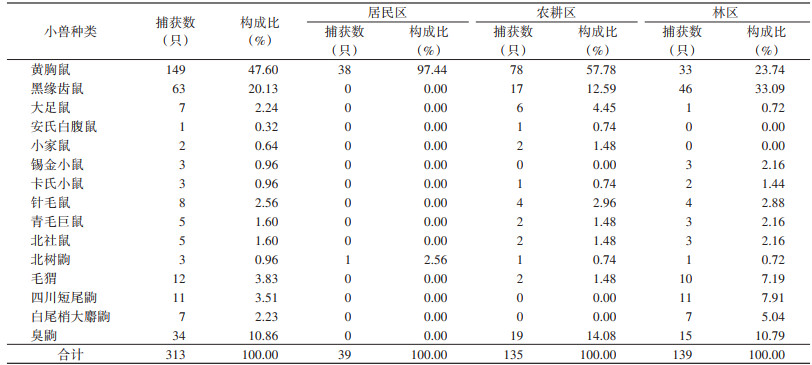
共捕获小兽313只,隶属于3目4科9属15种。居民区捕获39只,黄胸鼠占97.44%,北树鼩(Tupaia belangeri)占2.56%。农耕区捕获135只,黄胸鼠、臭鼩(Suncus murinus)和黑缘齿鼠(R. andamanensis)分别占57.78%、14.08%和12.59%,小家鼠(Mus musculus)、青毛巨鼠(Berylmys bowersii)、北社鼠(Niviventer confucianus)、毛猬(Hylomys suillus)、针毛鼠(N. fulvescens)、大足鼠(R. nitidus)的数量占比在1.48%~4.45%,安氏白腹鼠(N. andersoni)、卡氏小鼠(M. caroli)、北树鼩各占0.74%。林区捕获139只,黑缘齿鼠、黄胸鼠和臭鼩为优势种,分别占33.09%、23.74%和10.79%,卡氏小鼠、锡金小鼠(M. pahari gairdneri)、青毛巨鼠、白尾梢大麝鼩(Crocidura dracula)、北社鼠、针毛鼠、毛猬、四川短尾鼩(Anourosorex squamipes)占比在1.44%~7.91%,大足鼠和北树鼩各占0.72%,为稀有种(表 1)。农耕区和林区小兽的群落相似性系数为0.80,2种生境中的小兽群落相似程度较高,农耕区和林区的捕获率分别为18.42%和19.20%,差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.146,P=0.703)。居民区捕获率较低为3.25%。
|
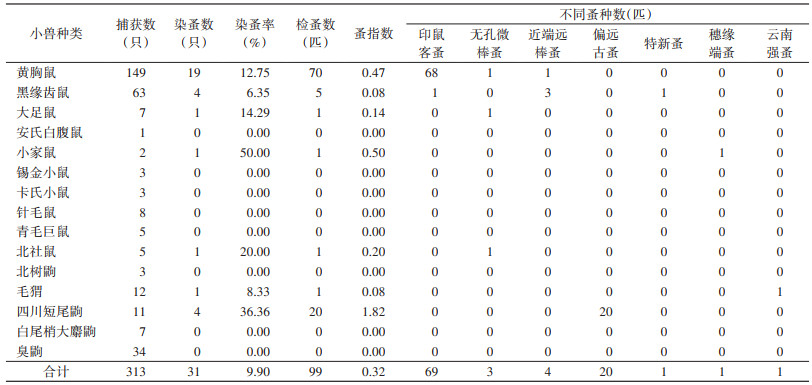
共检测小兽313只,染蚤小兽31只,染蚤率为9.90%,检获99匹蚤,隶属于1目4科7属7种,平均蚤指数为0.32。其中印鼠客蚤69匹,占69.70%,偏远古蚤(Palaeopsylla remota)20匹,占20.20%,近端远棒蚤(Aviostivalius klossi)4匹,占4.04%,无孔微棒蚤(Stivalius aporus)3匹,占3.03%,特新蚤(Neopsylla specialis)、穗缘端蚤(Acropsylla episema)和云南强蚤(Cratynius yunnanus)仅1匹,各占1.01%。见表 2。
|
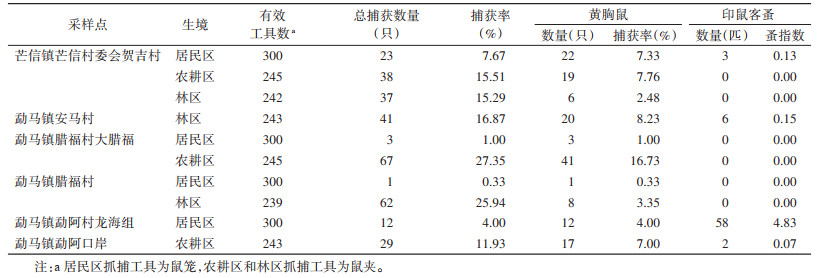
6个采样点共捕获小兽313只,其中黄胸鼠149只,该鼠在居民区、农耕区和林区均有分布。居民区黄胸鼠捕获率在0.33%~7.33%,农耕区黄胸鼠捕获率在7.00%~16.73%,林区黄胸鼠捕获率在2.48%~8.23%(表 3)。共检获印鼠客蚤69匹,蚤指数为0.22。
|
本次调查共捕获小兽3目4科9属15种,小兽优势种由黄胸鼠、黑缘齿鼠和臭鼩组成,与郑宇婷等[11]在孟连县的调查结果不同,可能与调查点选择不同有关。小兽的种类分布与栖息地的环境有关[12],本次在农耕区和林区2种生境中均捕获黄胸鼠、黑缘齿鼠和臭鼩且为优势种,小兽群落相似程度较高,捕获率也无明显差别,可能与调查地点农耕区和林区交错分布界限不明显,林区调查点在农耕区边缘等因素有关。
在小兽染蚤种类的调查中,染蚤率为9.90%,蚤指数为0.32,以印鼠客蚤(69.70%)和偏远古蚤(20.20%)为优势种。不同小兽体外寄生蚤种类不同,携带2种及以上体外寄生蚤的有黄胸鼠、黑缘齿鼠和小家鼠。小兽的染蚤率较以往的调查研究偏低[13],可能与调查季节或地理环境等因素有关。
黄胸鼠、印鼠客蚤是当地鼠疫的主要宿主动物和媒介蚤,本次在孟连县边境区域的居民区、农耕区和林区中均有分布,且均为优势种。按照云南省家鼠鼠疫监测标准,居民区鼠笼密度≥3%,或鼠体印鼠客蚤指数≥1.0时应提出预警,本次调查虽然综合捕获率和蚤指数不高,但芒信镇芒信村委会贺吉村和勐马镇勐阿村龙海组居民区捕获率为7.67%和4.00%,勐马镇勐阿村龙海组的印鼠客蚤指数为4.83,超过了相应的预警值,有可能造成动物间鼠疫流行。云南省自2007年以后近10年一直未监测到家鼠鼠疫疫情,但2016年普洱市毗邻的西双版纳傣族自治州发生人间鼠疫疫情[14]。今后应加强边境地区鼠疫监测,对鼠、蚤密度较高的地区要及时开展预防性灭鼠、灭蚤,同时加强群众健康教育,降低鼠疫流行传播的风险。
志谢 参加本调查研究工作的人员还有程盼、郭牧、陶继宏、别双双、苏娅、黄燕、鱼爱水、王正友、高子厚等,谨此一并感谢利益冲突 无
| [1] |
从显斌, 刘振才, 李群. 中国鼠疫自然疫源地(1950-2014)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2019: 973-974. Cong XB, Liu ZC, Li Q. Natural plague foci in China (1950-2014)[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2019: 973-974. |
| [2] |
赵文红, 郭牧, 苏丽琼, 等. 1992-2014年云南省普洱市鼠疫流行概述及控制现状[J]. 医学动物防制, 2018, 34(4): 325-327, 331. Zhao WH, Guo M, Su LQ, et al. 1992-2014 plague epidemic summary and control situation of Pu'er in Yunnan province[J]. J Med Pest Control, 2018, 34(4): 325-327, 331. DOI:10.7629/yxdwfz201804005 |
| [3] |
琚俊科, 龚正达. 我国小兽与自然疫源性疾病关系研究概况[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2010, 21(4): 293-296, 302. Ju JK, Gong ZD. Relationship between small mammals and natural-focus diseases in China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2010, 21(4): 293-296, 302. |
| [4] |
董文鸽, 郭宪国. 小兽体表寄生虫与疾病关系的研究[J]. 国际医学寄生虫病杂志, 2008, 35(5): 252-257. Dong WG, Guo XG. Research on the relationship between ectoparasites on small mammals and diseases[J]. Int J Med Parasitic Dis, 2008, 35(5): 252-257. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4122.2008.05.006 |
| [5] |
邓桃. 孟连县森林资源现状评价及林业可持续发展建议[J]. 绿色科技, 2017(9): 144-146. Deng T. Current situation evaluation of forest resources and sustainable development suggestion in Menglian county[J]. J Green Sci Technol, 2017(9): 144-146. DOI:10.16663/j.cnki.lskj.2017.09.062 |
| [6] |
浦恩念, 邵宗体, 段兴德, 等. 云南省巧家县小型兽类的组成与分布调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2021, 32(4): 447-450, 480. Pu EN, Shao ZT, Duan XD, et al. Species composition and distribution of small mammals in Qiaojia county, Yunnan province, China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2021, 32(4): 447-450, 480. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2021.04.012 |
| [7] |
黄文几, 陈延熹, 温业新. 中国啮齿类[M]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 1995: 132-162. Huang WJ, Chen YX, Wen YX. Glires in China[M]. Shanghai: Fudan University Press, 1995: 132-162. |
| [8] |
解宝琦, 曾静凡. 云南蚤类志[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 2002: 67-272. Xie BQ, Zeng JF. The Siphonaptera of Yunnan[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2002: 67-272. |
| [9] |
苏超, 李玉琼, 王倩, 等. 云南省剑川县鼠疫自然疫源地宿主媒介情况分析[J]. 兽类学报, 2021, 41(3): 235-244. Su C, Li YQ, Wang Q, et al. Analysis of host and vectors in the plague natural foci of Jianchuan county, Yunnan province[J]. Acta Theriol Sin, 2021, 41(3): 235-244. DOI:10.16829/j.slxb.150519 |
| [10] |
冯威, 赵成章, 岳冉, 等. 张掖国家湿地公园冬春季鸟类群落多样性和相似性分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(8): 2224-2231. Feng W, Zhao CZ, Yue R, et al. Bird community diversity and similarity in Zhangye National Wetland Park of Gansu province in winter and spring[J]. Chin J Ecol, 2017, 36(8): 2224-2231. DOI:10.13292/j.1000-4890.201708.027 |
| [11] |
郑宇婷, 王剑, 曾旭灿, 等. 云南省普洱市南部山区小型兽类组成及其分布特征[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2014, 25(6): 496-501. Zheng YT, Wang J, Zeng XC, et al. Species composition and spatial distribution of small mammals in mountainous region of southern Pu'er, Yunnan province, China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2014, 25(6): 496-501. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.4692.2014.06.003 |
| [12] |
徐兴军, 吕建伟, 谢振丽, 等. 寒温带牧林交错区生境复杂度对啮齿类物种多样性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2009, 29(6): 2945-2952. Xu XJ, Lyu JW, Xie ZL, et al. Effects of habitat complexity on species diversity of small mammals in pastures and forest interlaced regions[J]. Acta Ecol Sin, 2009, 29(6): 2945-2952. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.06.022 |
| [13] |
李奔福, 许翔, 吴方伟, 等. 云南省部分山区小型兽类体内外寄生虫感染状况调查[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30(2): 172-175. Li BF, Xu X, Wu FW, et al. An investigation of ecto-and endoparasites of small mammals in some mountainous areas in Yunnan province, China[J]. China J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30(2): 172-175. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2019.02.013 |
| [14] |
石丽媛, 杨桂荣, 赵春花, 等. 2016年云南省景洪市一起人间鼠疫疫情判定及处置[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2017, 27(10): 1502-1504, 1507. Shi LY, Yang GR, Zhao CH, et al. Determination and disposal of human plague in Jinghong, Yunnan province, in 2016[J]. Chin J Health Lab Technol, 2017, 27(10): 1502-1504, 1507. |
 2022, Vol. 33
2022, Vol. 33


