扩展功能
文章信息
- 赵鑫, 刘建华, 张皓
- ZHAO Xin, LIU Jian-hua, ZHANG Hao
- 三峡库区宜昌段1997-2020年鼠形动物监测报告
- Surveillance report of rodents in Yichang section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, 1997-2020
- 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2022, 33(1): 67-71
- Chin J Vector Biol & Control, 2022, 33(1): 67-71
- 10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2022.01.012
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2021-06-10
鼠形动物是肾综合征出血热(hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome,HFRS)、钩端螺旋体病(leptospirosis,钩体病)等多种自然疫源性疾病的重要储存宿主,其防控在鼠传疾病的预防控制中占有重要的位置[1]。调查和掌握三峡库区宜昌段鼠形动物的物种组成和密度状况,了解库区鼠形动物消长规律,对指导三峡库区卫生防病工作、保护库区居民身体健康和保障三峡工程安全运行具有重要意义[2]。现将1997-2020年三峡库区宜昌段监测结果报告如下。
1 材料与方法 1.1 监测点概况按照《长江三峡工程生态环境监测实施规划》要求,在三峡库区宜昌段开展了媒介生物监测工作,以库区兴山县的峡口镇选择距离长江不足1 km范围为监测点,开展鼠形动物调查,监测点地貌以山区为主,其中包含居民区、农作物地、荒地和林地等生境。
1.2 鼠形动物密度和种群调查密度监测采用夹夜法,分居住区和耕作区2种生境布夹,用中号鼠夹,以生花生米作诱饵,晚放晨收。对捕获的鼠形动物分别进行分类鉴定和计数。
1.3 鼠形动物密度计算
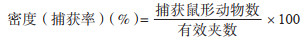
|
采用Excel 16.0和SPSS 20.0软件对监测数据进行整理分析,使用Joinpoint 4.8软件进行时间趋势分析,计算年度变化百分比(annual percentage change,APC),P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
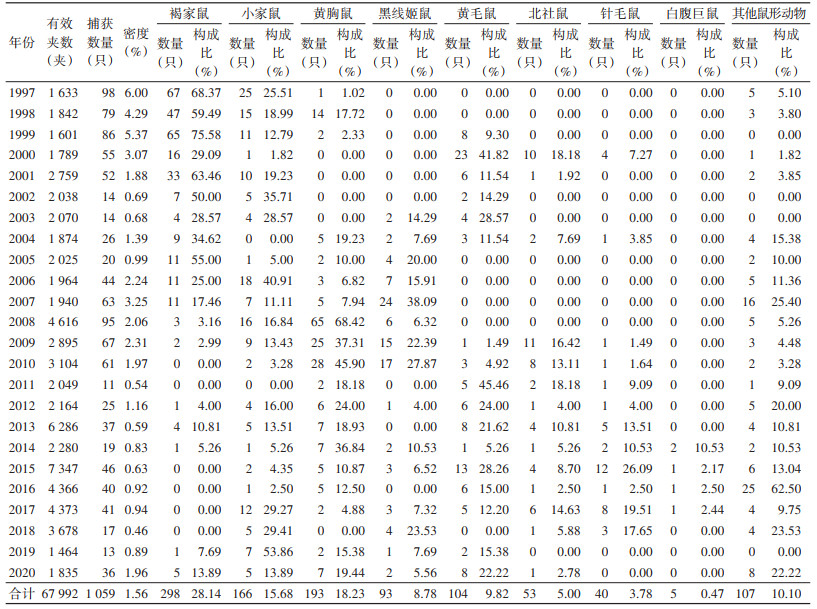
2 结果 2.1 鼠形动物构成三峡库区湖北宜昌段1997-2020年间共布放鼠夹67 992夹次,捕获鼠形动物1 059只,平均鼠密度为1.56%。捕获到的鼠形动物共9种,其中6种在居住区和耕作区均有发现。各鼠形动物的构成比依次为褐家鼠(Rattus norvegicus)占28.14%、黄胸鼠(R. tanezumi)占18.22%、小家鼠(Mus musculus)占15.68%、黄毛鼠(R. losea)占9.82%、黑线姬鼠(Apodemus agrarius)占8.78%、北社鼠(Niviventer confucianus)占5.00%、针毛鼠(N. fulvescens)占3.78%、白腹巨鼠(Leopoldamys edwardsi)占0.47%,其他鼠形动物占10.10%。见表 1。
|
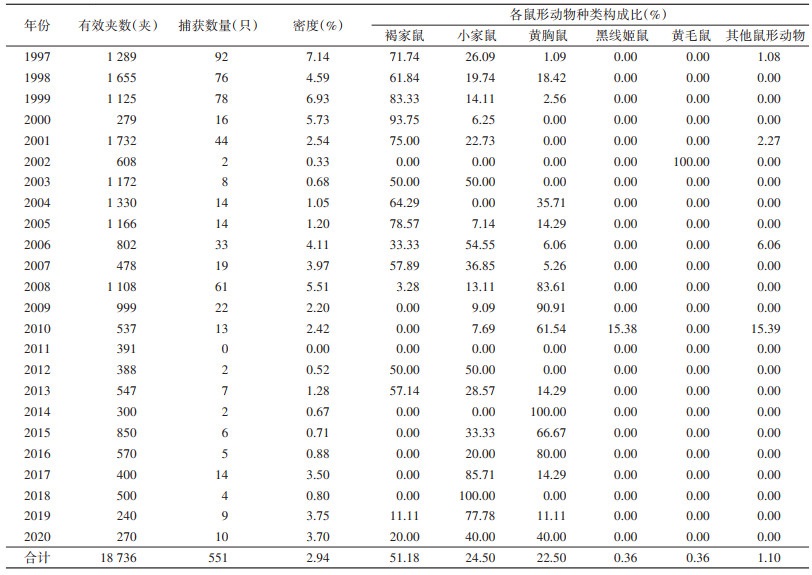
1997-2020年间居住区共布放有效夹18 736夹次,捕获鼠形动物551只,密度为2.94%,1997-2020年居住区鼠形动物密度呈现下降趋势[APC=-3.29%,95%置信区间(CI):-5.20%~-1.34%,P < 0.05](图 1)。鼠形动物种类以褐家鼠(51.18%)、小家鼠(24.50%)和黄胸鼠(22.50%)为主。见表 2。

|
| 注:APC鼠形动物密度年度变化百分比。 图 1 1997-2020年三峡库区宜昌监测点鼠形动物密度变化趋势 Figure 1 Changing trend of the density of small mammals at Yichang surveillance sites in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, 1997-2020 |
| |
|
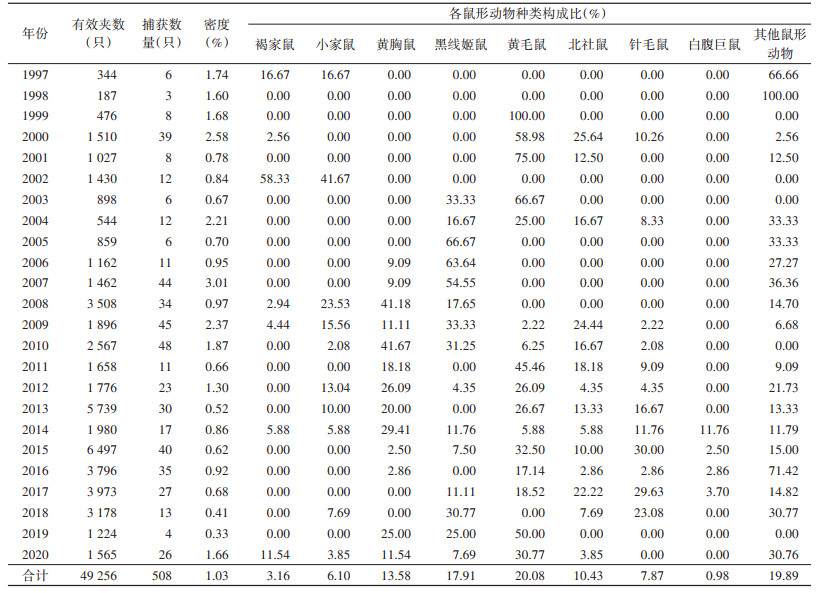
1997-2020年间耕作区共布放有效夹49 256夹次,捕获鼠形动物508只,密度为1.03%。1997-2020年耕作区鼠形动物密度无明显趋势变化(APC=-1.69%,95%CI:-4.71%~1.42%,P > 0.05)(图 1)。鼠形动物以黄毛鼠(20.08%)和黑线姬鼠(17.91%)为主。见表 3。
|
三峡大坝自1994年12月正式动工,1997年实现大江截流,水位从66 m提升到88 m;2003年6月三峡大坝首次蓄水,坝前水位达到135 m;2006年5月三峡大坝建成,9月成功蓄水至156 m水位;2008年正常蓄水达到175 m;2009年长江三峡工程全部竣工并运行至今。三峡库区指由受长江三峡工程淹没的地区和有移民任务的20个县(市)。本研究通过在三峡库区宜昌段开展长期的鼠形动物监测,了解库区宜昌段周边的鼠形动物种群分布及变化情况。根据国内外的既往资料显示,大型水利工程建设蓄水及运行期间引发的环境及生物圈的变化,极易导致传染病的暴发流行[3]。而三峡水库实行“冬储夏排”的运行模式,会造成鼠类自动向上迁移和向库周扩散,极易引起局部的鼠密度增高,从而暴发传染病[4]。但三峡库区宜昌段监测结果显示成库后室内鼠密度呈现下降趋势,室外鼠密度仍保持在较低的水平波动,与三峡库区重庆地区报告的鼠密度水平一致[5]。分析主要原因为我国在三峡工程建设前开展了反复的规划论证与设计,施工后又于1998、2002、2006和2008年4次库底卫生清理期间开展了大规模灭鼠工作,这些早期干预措施迅速降低了库区鼠形动物密度,给工程建设和运行提供了有力保障[6]。监测显示2009年工程运行后库区鼠密度一直持续在较低的水平,考虑主要与宜昌市春秋季开展爱国卫生运动灭鼠活动有关[7]。
据研究报道,黑线姬鼠、褐家鼠、黄胸鼠、北社鼠和小家鼠均为HFRS传播流行中主要保毒宿主,其中黑线姬鼠和褐家鼠是HFRS的主要宿主动物[8],同时黑线姬鼠、黄毛鼠、黄胸鼠和褐家鼠为钩体病主要宿主动物[9]。而本监测结果显示,三峡库区湖北宜昌段居住区鼠形动物种类主要为褐家鼠、小家鼠和黄胸鼠,室外鼠种构成较复杂,以黄毛鼠和黑线姬鼠略占优势。家栖为主的褐家鼠在室内占优势,在室外也占有一定比重,野外为主的黄毛鼠和黑线姬鼠在室内也时有捕获,家鼠和野鼠联系较为密切,增加了库区HFRS、钩体病等自然疫源性疾病传播的风险[10]。近年来监测发现库区宜昌段健康人群HFRS和钩体病免疫水平较低,15种常见的钩体菌群型在宜昌库区人群中均有发现,存在流行和暴发的风险[11-13]。
三峡工程运行后库区沿岸形成了水陆交替的消落区,随着每年水位的升高,消落带生活的鼠类向上迁移[14],将对鼠形动物种群构成及密度带来影响[15]。长期对三峡库区宜昌段鼠形动物开展监测,密切关注其趋势变化,及早发现异常情况,对保障库区人民群众身体健康具有重要意义,监测结果对我国类似区域开展鼠传疾病防制工作具有参考价值。
利益冲突 无
| [1] |
李贵昌, 王玉姣, 鲁亮, 等. 2019年全国鼠类监测报告[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31(4): 389-394. Li GC, Wang YJ, Lu L, et al. National surveillance report on rodents in China, 2019[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2020, 31(4): 389-394. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2020.04.002 |
| [2] |
何亚明, 李洪, 季恒青, 等. 重庆市云阳县2018年潜在鼠疫疫源地调查分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2019, 30(3): 327-330. He YM, Li H, Ji HQ, et al. An investigation of potential plague foci in Yunyang county, Chongqing, China, in 2018[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2019, 30(3): 327-330. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2019.03.023 |
| [3] |
Guo YH, Lai SJ, Zhang J, et al. Mosquito population dynamics during the construction of Three Gorges Dam in Yangtze River, China[J]. Acta Trop, 2018, 182: 251-256. DOI:10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.03.008 |
| [4] |
朱彬彬, 李慧甫, 李枝金, 等. 1959-2009年三峡库区宜昌段鼠形动物变动趋势研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2010, 21(6): 598-600. Zhu BB, Li HF, Li ZJ, et al. Study on the trend of rodents in the Yichang section of the Three Gorges area from 1959 to 2009[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2010, 21(6): 598-600. |
| [5] |
何亚明, 毛德强, 季恒青, 等. 三峡库区重庆段鼠形动物种群分布及密度变化研究[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2020, 31(5): 580-586. He YM, Mao DQ, Ji HQ, et al. A study of the population distribution and density changes of mouse-like rodents in the Chongqing section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2020, 31(5): 580-586. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2020.05.016 |
| [6] |
喻珊, 陈艳, 郭玲, 等. 长江三峡水库四期蓄水重庆市涪陵段库底卫生清理效果分析[J]. 预防医学论坛, 2010, 16(4): 341-343. Yu S, Chen Y, Guo L, et al. Analysis of the cleaning effect on the bottom of reservoir in Fuling area, Chongqing of the Three Gorge Reservoir of Yangtze River[J]. Prev Med Trib, 2010, 16(4): 341-343. DOI:10.16406/j.pmt.issn.1672-9153.2010.04.010 |
| [7] |
汪诚信. 我国鼠害治理的进程和前景[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2016, 22(5): 413-416. Wang CX. A discussion on the progress and prospect of rodent management in China[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2016, 22(5): 413-416. DOI:10.19821/j.1671-2781.2016.05.001 |
| [8] |
张亚萍, 王文英, 李莉莉, 等. 我国肾综合征出血热流行病学特征及预防控制研究现状[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2020, 26(4): 387-393. Zhang YP, Wang WY, Li LL, et al. Research status of epidemiology and prevention and control of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in China[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2020, 26(4): 387-393. DOI:10.19821/j.1671-2781.2020.04.026 |
| [9] |
Murillo A, Goris M, Ahmed A, et al. Leptospirosis in cats: current literature review to guide diagnosis and management[J]. J Feline Med Surg, 2020, 22(3): 216-228. DOI:10.1177/1098612X20903601 |
| [10] |
杨小兵, 徐勇, 赵鑫, 等. 三峡工程蓄水前后湖北宜昌段鼠密度及鼠类种群变化趋势分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2010, 25(10): 813-815, 819. Yang XB, Xu Y, Zhao X, et al. Analysis on changes of rodents density and species in Hubei-Yichang section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area before and after impoundment[J]. Dis Surveill, 2010, 25(10): 813-815, 819. DOI:10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2010.10.015 |
| [11] |
王大军, 龚海燕, 潘会明, 等. 三峡库区兴山县钩端螺旋体宿主动物带菌状况及人群免疫水平分析[J]. 中国热带医学, 2017, 17(4): 367-371. Wang DJ, Gong HY, Pan HM, et al. Status of Leptospira of host animals and serum immunity level of population in Xingshan county, Three Gorges region[J]. China Trop Med, 2017, 17(4): 367-371. DOI:10.13604/j.cnki.46-1064/r.2017.04.11 |
| [12] |
杨瑞, 程均福, 刘力, 等. 2005-2018年湖北省钩端螺旋体病监测分析[J]. 中华卫生杀虫药械, 2020, 26(5): 473-476. Yang R, Cheng JF, Liu L, et al. Analysis on leptospirosis surveillance in Hubei province from 2005 to 2018[J]. Chin J Hyg Insect Equip, 2020, 26(5): 473-476. DOI:10.19821/j.1671-2781.2020.05.021 |
| [13] |
余凤苹, 赵鑫, 张皓, 等. 三峡库区湖北省宜昌段2003-2015年自然疫源性疾病流行病学分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2017, 28(1): 79-81. Yu FP, Zhao X, Zhang H, et al. Epidemiological analysis of natural focus diseases in Yichang of Hubei province in Three Gorges Reservoir during 2003-2015[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2017, 28(1): 79-81. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2017.01.023 |
| [14] |
常昭瑞, 鲁亮, 郭玉红, 等. 三峡库区消落区2010-2014年小兽分布特征分析[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2016, 27(2): 117-120. Chang ZR, Lu L, Guo YH, et al. The population dynamics of small mammals in Three Gorges Reservoir hydro-fluctuation area, 2010-2014[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2016, 27(2): 117-120. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.8280.2016.02.006 |
| [15] |
毛德强, 李洪, 张春华, 等. 三峡库区成库前后鼠疫相关鼠形动物种群及数量变化趋势[J]. 中国媒介生物学及控制杂志, 2016, 27(1): 68-70. Mao DQ, Li H, Zhang CH, et al. Rodent charateristic changes in the Three Gorges Reservoir before and after the water storage[J]. Chin J Vector Biol Control, 2016, 27(1): 68-70. DOI:10.11853/j.issn.1003.4692.2016.01.022 |
 2022, Vol. 33
2022, Vol. 33


