2. 四川省肿瘤医院健康体检中心, 四川 成都 610100;
3. 四川省妇幼保健院妇科, 四川 成都 610031
2. Health Examination Center, Sichuan Cancer Hospital, Chengdu 610100, China;
3. Department of Gynaecology, Sichuan Provincial Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital, Chengdu 610031, China
人乳头瘤病毒(human papillomavirus, HPV)为乳多空病毒科乳头瘤病毒的一种,感染该病毒后可引起皮肤、黏膜增生性疾病,根据其生物特性及致癌潜能可将HPV分为高危型及低危型[1-2]。高危型HPV的持续感染是宫颈癌发病的重要因素,据统计90%以上的宫颈癌患者存在高危型HPV持续感染[3]。因女性阴道的酸性内环境具有较强的自洁功能,大部分女性在感染HPV后可自然清除,仅10%~15%的女性在出现高危型HPV持续感染后可逐渐发展为宫颈癌[4]。准确预测HPV自然清除情况,可有效指导临床正确处理感染,减少不必要的治疗。女性高危型HPV感染后自然清除是多方面因素共同作用的结果,虽然关于女性高危型HPV感染自然清除相关因素已有研究[5],但该研究未将各因素整合成预测模型,不利于患者的个性化预测,临床指导价值有限,且目前研究多在单因素分析基础上进行logistic回归分析,可能存在多重共线性的问题。本研究旨在通过LASSO回归分析降低多重共线性风险,提高筛选因素的代表性,并通过建立列线图模型将各因素整合成可视化预测模型,以期为预测职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除提供参考。
1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料选择2020年3月—2021年3月在某院进行年度职业体检有固定正式职业的职业女性,筛选出高危型HPV感染者,2年后此人群再次体检得到HPV感染清除情况,但在二次体检时询问患者相关信息,排除接受过HPV感染治疗者。纳入标准:①在该院进行年度体检;②经分子快速杂交基因检测证实为高危型HPV感染;③首次检测出高危型HPV;④在该院完成2年体检;⑤患者知情同意。排除标准:①生殖道恶性肿瘤患者;②宫颈上皮内瘤变进行手术治疗者;③首次体检后接受HPV感染治疗者;④妊娠期及哺乳期女性;⑤有子宫切除或宫颈手术史的患者。
1.2 方法(1) 收集可能影响职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除的相关因素。在参考相关文献并结合笔者临床经验的基础上收集以下因素:①一般资料,包括年龄、身体质量指数(BMI)、职业、吸烟史、饮酒史、受教育程度、婚姻状况、宫颈癌家族史;②生殖相关资料,包括初次性生活年龄、避孕方式、阴道分娩次数、性事后外阴清洗情况;③性伴侣相关情况,包括性伴侣数、性伴侣性病史、性伴侣生殖系统恶性肿瘤病史、性伴侣包皮过长;④检查项目,包括初始病毒载荷量、HPV感染类型、初始细胞学结果、生殖道炎症。(2)建立预测模型。2年后入组人群再次体检进行分子快速杂交基因检测,得到HPV感染清除情况,第二次体检时由2名未参与本研究的护理人员询问患者HPV感染治疗情况,接受过HPV感染治疗者被排除。根据随访结果将模型组患者分为自然清除组与持续感染组,比较两组患者一般资料、生殖相关治疗、性伴侣相关情况及检查情况。采用LASSO回归筛选职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除潜在因素后,进行多因素logistic回归,筛选出独立影响因素,根据多因素分析结果以R语言建立列线图模型并进行验证。
1.3 统计学方法应用SPSS 22.0统计学软件进行数据分析,计数资料以例(%)表示,进行χ2检验,计量资料以x±s表示,进行t检验。应用R 4.1.3语言“glmnet”包进行LASSO回归分析以筛选协变量,在此基础上采用多因素logistic回归模型分析职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除的相关因素,以“rms”包构建风险预测的列线图模型,绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价该列线图模型的区分度,采用Bootstrap法重复抽样1 000次进行内部验证,采用H-L拟合优度检验、校准曲线对该列线图模型进行评价和校准,绘制决策曲线评价该列线图模型的临床有效性。以P≤0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 患者分组及基本情况本研究最初纳入423例高危型HPV感染者,排除期间接受HPV感染治疗的78例及2年后未再进行HPV体检的16例,最终纳入329例。以7 ∶3的比例将患者分为模型组230例,验证组99例。模型组23~49岁,平均(37.02±5.88)岁;BMI 19.03~24.29 kg/m2,平均(21.19±3.07) kg/m2;公职人员54例,私企人员176例。验证组21~53岁,平均(38.11±5.97)岁;BMI 18.41~24.27 kg/m2,平均(21.06±3.11) kg/m2;公职人员27例,私企人员72例。两组一般资料比较,差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。
2.2 自然清除组与持续感染组患者各因素比较模型组230例高危型HPV感染患者中,165例(自然清除组)在随访结束后转阴,自然清除率为71.74%;持续感染65例(持续感染组),持续感染率为28.26%,其中16例发展为宫颈上皮内瘤变(cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, CIN),CIN Ⅰ 9例,CIN Ⅱ 5例,CIN Ⅲ 2例。自然清除组与持续感染组患者年龄及吸烟史、宫颈癌家族史、避孕方式、性事后外阴清洗情况、性伴侣数、性伴侣性病史、性伴侣生殖系统恶性肿瘤病史、性伴侣包皮过长、初始病毒载荷量、HPV感染类型及生殖道炎症的比例比较,差异均具有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。见表 1。
| 表 1 自然清除组与持续感染组患者各因素比较 Table 1 Comparison of factors between patients in the natural clearance group and the persistent infection group |
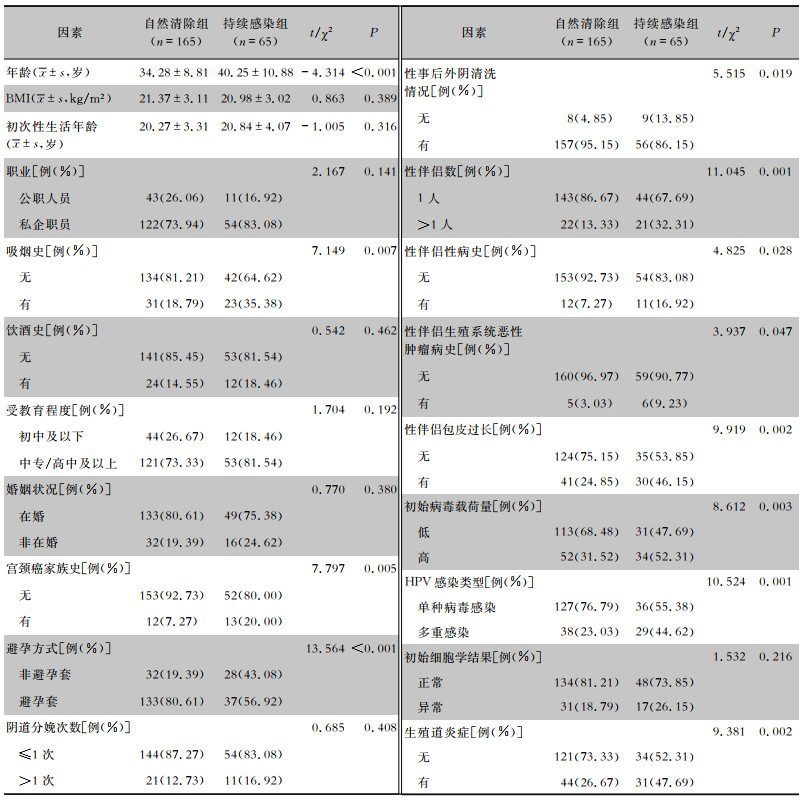
|
以职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除情况作为因变量,将表 1中各因素作为自变量,通过LASSO回归模型的三折交叉验证确定最佳惩罚项系数λ,最终筛选出9个潜在的影响因素,分别为年龄、吸烟史、避孕方式、性伴侣数、性伴侣性病史、性伴侣包皮过长、初始病毒载荷量、HPV感染类型及生殖道炎症,见图 1~2。
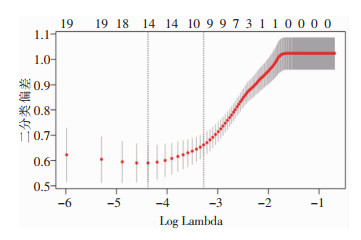 |
| 图 1 LASSO回归的系数路径 Figure 1 Coefficient paths of LASSO regression |
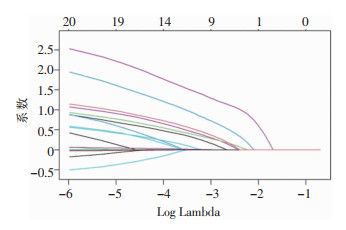 |
| 图 2 LASSO回归交叉验证结果 Figure 2 Cross-validation results of LASSO regression |
以LASSO回归筛选的可能变量作为自变量,职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除情况作为因变量进行多因素logistic回归分析显示:年龄、避孕方式、性伴侣数、性伴侣包皮过长、初始病毒载荷量、HPV感染类型及生殖道炎症为职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除的独立相关因素(均P < 0.05),见表 2。
| 表 2 职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除的相关因素分析 Table 2 Relevant factors for the natural clearance of high-risk HPV infection in professional women |

|
根据表 2结果建立职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除列线图预测模型,见图 3。ROC曲线分析结果显示,模型组职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除的AUC为0.834(95%CI:0.776~0.893),验证组AUC为0.817(95%CI:0.755~0.879),见图 4。H-L拟合优度检验结果显示列线图模型与理想模型差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.307,P=0.858)。采用Bootstrap法重复抽样1 000次,并以验证组进行验证,校准曲线结果显示模型组与验证组预测曲线与标准曲线基本拟合,提示模型预测准确度较高,见图 5~6。
 |
| 图 3 职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除列线图预测模型 Figure 3 Nomogram prediction model for the natural clearance of high-risk HPV infection in professional women |
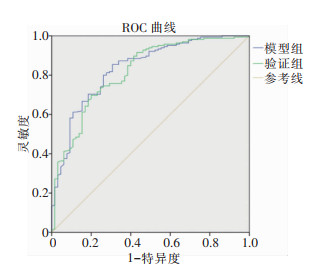 |
| 图 4 职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除列线图预测模型的ROC曲线分析 Figure 4 ROC curve analysis of nomogram prediction model for the natural clearance of high-risk HPV infection in professional women |
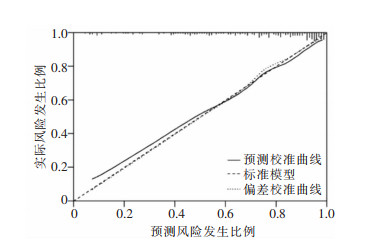 |
| 图 5 职业女性高危型HPV感染模型组校准曲线 Figure 5 Calibration curve for high-risk HPV infection in professional women in the model group |
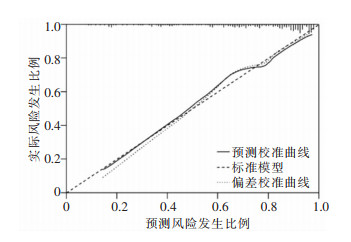 |
| 图 6 职业女性高危型HPV感染验证组校准曲线 Figure 6 Calibration curve for high-risk HPV infection in professional women in the validation group |
模型组决策曲线分析结果显示,该列线图模型预测职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除的概率阈值为0.15~0.95时,患者的净受益率大于0,见图 7。
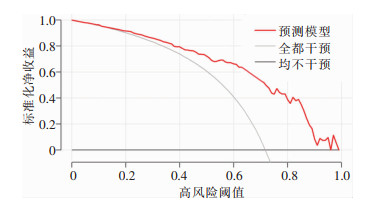 |
| 图 7 职业女性高危型HPV感染列线图模型决策曲线 Figure 7 Decision curve of nomogram prediction model for high-risk HPV infection in professional women |
HPV感染为临床常见的性传播疾病,人类为HPV唯一宿主,目前HPV根据基因型已分离出150多种亚型,其中近40种被发现与生殖系统病变相关[6-7]。高危型HPV感染后可导致宫颈上皮细胞产生E6、E7癌蛋白而引起细胞周期控制失常,出现宫颈癌[8]。高危型HPV持续感染发展至宫颈癌约需25~30年,若能在此过程中采取积极的干预措施,将有助于降低宫颈癌发病率,虽然高危型HPV感染率在性活跃女性中较高,但大部分为一过性感染,普遍在感染数月至2年内可自动清除[9]。大部分高危型HPV感染女性对HPV与宫颈癌的相关知识认识不足,出于对宫颈癌的担心,不合理用药的现象时有发生[10-11]。准确预测高危型HPV感染自然清除率将有助于降低不合理用药风险,并可指导持续感染风险较高人群尽早采取积极干预措施,以降低宫颈癌风险。
高危型HPV感染自然清除受多方面因素的共同影响,虽然刘学伟等[12]曾对职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除相关因素进行研究,但该研究纳入的因素较少且仅在单因素分析基础上进行多因素logistic回归分析,可能存在多重共线性的风险。本研究在LASSO回归筛选变量基础上进行多因素logistic回归, LASSO回归属于惩罚函数模型的一种,该模型可通过压缩回归系数,保留子集收缩而解决复共线性数据有偏估计问题,使变量更具代表性。本研究结果显示,年龄、避孕方式、性伴侣数、性伴侣包皮过长、初始病毒载荷量、HPV感染类型及生殖道炎症为职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除的独立相关因素。年龄方面,本研究中自然清除组年龄较持续感染组更低,与相关研究[13]结果一致,考虑高危型HPV感染的自然清除与患者的免疫力有关,年轻女性体内激素水平更稳定,机体免疫力更强,对高危型HPV的抑制能力也相应更强。避孕套不仅是适应证最广泛的避孕药具,同时还有较强的物理屏障作用,只要性交过程中没有破裂,避孕套可以有效隔绝各种病原体的交叉感染,降低职业女性HPV再感染及性伴侣间相互传播的风险[14-15]。
性伴侣数及性伴侣包皮过长对于高危型HPV感染自然清除也有重要影响,性传播为HPV最主要的传播方式,性伴侣数的增加意味着HPV暴露的风险也相应增加,自然清除率随之相应下降[16]。包皮过长为男性生殖系统常见病,过长的包皮内容易存留包皮垢及分泌物,清除难度较大,加上包皮部位局部温热,潮湿环境容易引起致病菌滋生,不利于HPV的清除,并容易经性行为传播引起性伴侣患病[17]。
除上述因素外,初始病毒载荷量、HPV感染类型及生殖道炎症对职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除也有重要影响。本研究中自然清除组患者初始病毒载荷量更低,病毒载量与高危型HPV自然清除的关系复杂,有报道[18]称高危型HPV低病毒负荷量者相对高病毒负荷量者清除病毒能力更强,当病毒复制至高拷贝时,机体免疫系统对病毒的清除效率将下降,因此,病毒载量越小,高危型HPV自动清除概率越高;反之,则持续感染概率上升。HPV感染类型对自然清除率的影响,不同研究有一定的差异,有研究认为HPV多重感染并不会增加持续感染风险,本研究则发现单种HPV感染者自然清除率更高,这可能与不同HPV基因型间存在交叉保护性抗体,在出现多重感染时可致相互协同促进,导致持续感染风险更高有关。生殖道炎症的发生可使阴道局部环境出现紊乱而致其自清洁功能下降,这可能是有生殖道炎症职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除率较低的一个重要原因[19-20]。
目前关于职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除预测模型的研究较少,多为多因素分析,并未将各因素整合成一个统一的预测模型。本研究建立的列线图模型囊括了一般资料、生殖相关资料、性伴侣相关情况、检查情况,可从不同层面反映患者的机体状况,为职业女性高危型HPV自然清除预测提供更多参考,模型验证结果显示本研究建立的列线图模型对于职业女性高危型HPV自然清除预测具有较高的准确率与区分度。
综上所述,职业女性高危型HPV感染自然清除率为71.74%,其主要受患者年龄、避孕方式、性伴侣数等因素的影响,本研究建立的列线图模型能够较为准确地预测职业女性高危HPV感染的自然清除。
利益冲突:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
| [1] |
李杏婵, 何雅婷, 赵愚. 高危型HPV感染与宫颈癌前病变、宫颈癌的关系分析[J]. 中国医药科学, 2020, 10(16): 71-73. Li XC, He YT, Zhao Y. Analysis of the relationship between high-risk HPV infection and cervical precancerous lesions and cervical cancer[J]. China Medicine and Pharmacy, 2020, 10(16): 71-73. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-0616.2020.16.018 |
| [2] |
Wei FX, Goodman MT, Xia NS, et al. Incidence and clea-rance of anal human papillomavirus infection in 16 164 indivi-duals, according to human immunodeficiency virus status, sex, and male sexuality: an international pooled analysis of 34 longitudinal studies[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2023, 76(3): e692-e701. DOI:10.1093/cid/ciac581 |
| [3] |
Wang WP, Liu YJ, Pu Y, et al. Effectiveness of focused ultrasound for high risk human papillomavirus infection-related cervical lesions[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2021, 38(2): 96-102. DOI:10.1080/02656736.2021.1910736 |
| [4] |
Wang WP, Yao YQ, Liu YJ, et al. Focused ultrasound for high-risk human papillomavirus infection-related low-grade cervical lesions: a prospective cohort study[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2022, 39(1): 1327-1334. DOI:10.1080/02656736.2022.2130443 |
| [5] |
Bettampadi D, Sirak BA, Abrahamsen ME, et al. Factors associated with persistence and clearance of high-risk oral human papillomavirus (HPV) among participants in the HPV infection in men (HIM) study[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2021, 73(9): e3227-e3234. DOI:10.1093/cid/ciaa1701 |
| [6] |
中华医学会妇科肿瘤学分会, 中国优生科学协会阴道镜和宫颈病理学分会. 人乳头瘤病毒疫苗临床应用中国专家共识[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2021, 13(2): 1-12. Gynecological Oncology Society of Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology. Chinese expert consensus on clinical application of human pa-pilloma virus vaccine[J]. Chinese Journal of the Frontiers of Medical Science(Electronic Version), 2021, 13(2): 1-12. |
| [7] |
Nadar HJ, van Bilsen WPH, Marra E, et al. Incidence and clearance of penile high-risk human papillomavirus infection and their determinants among HIV-negative men who have sex with men[J]. Sex Transm Dis, 2021, 48(11): 864-872. DOI:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001455 |
| [8] |
Siegler E, Goldberg Y, Siegler Y, et al. The association between clearance of human papillomavirus after conization for cervical cancer and absence of cancer[J]. J Low Genit Tract Dis, 2021, 25(4): 276-280. DOI:10.1097/LGT.0000000000000622 |
| [9] |
Behnamfar F, Ahmadi Solush F, Allameh T. Age and cervical histology, the most important factors to predict human papi-lloma virus clearance[J]. J Obstet Gynecol Cancer Res, 2023, 8(1): 11-16. |
| [10] |
Bonin-Jacob CM, Almeida-Lugo LZ, Puga MAM, et al. IL-6 and IL-10 in the serum and exfoliated cervical cells of patients infected with high-risk human papillomavirus[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(3): e0248639. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0248639 |
| [11] |
Laurie C, El-Zein M, Tota J, et al. Efficacy of a carrageenan gel in increasing clearance of anal human papillomavirus infections in men: interim analysis of a double-blind, randomized controlled trial[J]. J Infect Dis, 2023, 227(3): 402-406. DOI:10.1093/infdis/jiac019 |
| [12] |
刘学伟, 赵学英, 陈雪. 职业女性生殖道高危型人乳头瘤病毒感染自然清除及其影响因素[J]. 职业与健康, 2016, 32(18): 2533-2536. Liu XW, Zhao XY, Chen X. Natural clearance and influencing factors of high-risk human papillomavirus infection in genital tract of professional women[J]. Occupation and Health, 2016, 32(18): 2533-2536. |
| [13] |
Zhao XL, Liu ZH, Zhao S, et al. Efficacy of point-of-care thermal ablation among high-risk human papillomavirus positive women in China[J]. Int J Cancer, 2021, 148(6): 1419-1427. DOI:10.1002/ijc.33290 |
| [14] |
Yang Y, Zhang L, Zhang YQ, et al. Local hyperthermia at 44℃ is effective in clearing cervical high-risk human papillomaviruses: a proof-of-concept, randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2021, 73(9): 1642-1649. DOI:10.1093/cid/ciab369 |
| [15] |
Backes DM, Bosire C, Hudgens MG, et al. Incidence and clearance of penile human papillomavirus infection among circumcised Kenyan men[J]. Int J STD AIDS, 2020, 31(12): 1202-1211. DOI:10.1177/0956462420948370 |
| [16] |
Wei FX, Guo M, Huang SJ, et al. Sex differences in the incidence and clearance of anogenital human papillomavirus infection in Liuzhou, China: an observational cohort study[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2020, 70(1): 82-89. DOI:10.1093/cid/ciz168 |
| [17] |
Lu XR, Wang TT, Zhang YZ, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of viral load in patients with high-risk human papillomavirus[J]. Virol J, 2021, 18(1): 6. DOI:10.1186/s12985-020-01474-z |
| [18] |
Herzog C, Vavourakis CD, Barrett JE, et al. HPV-induced host epigenetic reprogramming is lost upon progression to high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia[J]. Int J Cancer, 2023, 152(11): 2321-2330. DOI:10.1002/ijc.34477 |
| [19] |
Xiao D, Li WD, Zhang WH, et al. Dietary zinc, copper, and selenium intake and high-risk human papillomavirus infection among American women: data from NHANES 2011-2016[J]. Nutr Cancer, 2022, 74(6): 1958-1967. DOI:10.1080/01635581.2021.1979603 |
| [20] |
Isaguliants M, Nosik M, Karlsen A, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of infection with high risk human papilloma viruses among HIV-positive women with clinical manifestations of tuberculosis in a middle-income country[J]. Biomedicines, 2021, 9(6): 683. DOI:10.3390/biomedicines9060683 |



