电离辐射诱发肿瘤是重要的辐射生物效应之一。多年来,为揭示辐射致癌机制,研究者在细胞及分子水平上进行了大量研究,但至今尚未彻底阐明。本研究在基因组水平上探讨基因多态性与辐射诱发小鼠胸腺淋巴瘤的相关性,为进一步阐明辐射致癌机制提供生物学依据。
1 对象与方法 1.1 对象辐射诱发胸腺淋巴瘤的近交系C57BL/6J、BALB/c小鼠,雌性,各16只。
1.2 基因组DNA提取采用基因组DNA纯化试剂盒(美国Promega公司),提取胸腺淋巴瘤细胞基因组DNA。
1.3 引物rs28185870引物序列为:F:5′-CCACAACGAGATGGCAGAAG-3′,R:5′-TAGCTGTACCCTTCCGCTGT-3′,经PCR扩增出458 bp片段。rs28185923引物序列为:F:5′-ACTTGGATCACCAGGAGTGTCT-3′,R:5′-GGAGGATGGAGAACGATAACTG-3′,经PCR扩增出286 bp片段。rs3695947引物序列为:F:5′-CACCGTGTGCAAAGTACTCC-3′,R:5′-CTTCTCACCTCGCTTGTCAC-3′,经PCR扩增出425 bp片段。
1.4 PCR-RFLP检测单核苷酸多态性 1.4.1 PCR扩增PCR反应体系见参考文献〔1〕。PCR循环条件rs28185870为95 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 40 s,61 ℃ 45 s,72 ℃ 45 s,10个循环;94 ℃ 40 s,59 ℃ 45 s,72 ℃ 45 s,10个循环;94 ℃ 40 s,57 ℃ 45 s,72 ℃ 45 s,20个循环;72 ℃ 10 min。rs28185923退火温度为62,60及58 ℃。rs3695947退火温度为59,57及55 ℃。
1.4.2 限制性酶切酶切方法见参考文献〔2〕。酶切产物用2.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳分离,以DL2000 DNA marker〔北京天根生化科技(北京)有限公司〕为分子量标准品。应用Jel Doc2001型凝胶成像系统(美国Bio-Rad公司)拍照。根据酶切图谱判断基因型。rs28185870位点为C等位基因时,HaeIII(大连宝生物工程公司)酶切后产生109 bp及349 bp 2个片段,在近交系小鼠中有C/C或T/T 2种不同基因型。rs28185923位点为C等位基因时,MspI(大连宝生物工程公司)酶切后产生116 bp及170 bp 2个片段,在近交系小鼠中有C/C或T/T 2种不同基因型。rs3695947位点为G等位基因时,BamHI(大连宝生物工程公司)酶切后产生335 bp及90 bp 2个片段,在近交系小鼠中有G/G或A/A 2种不同基因型。每种近交系小鼠在每个SNP位点只有1种基因型。
2 结果 2.1 C57BL/6J及BALB/c小鼠Ikaros基因rs28185870位点基因型(图 1)
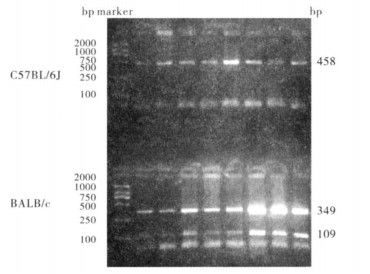
|
图 1 C57BL/6J及BALB/c小鼠Ikaros基因rs28185870位点基因型 |
Ikaros基因rs28185870位点C57BL/6J小鼠基因型为T/T,BALB/c小鼠基因型为C/C。
2.2 C57BL/6J及BALB/c小鼠Ikaros基因rs28185923位点基因型(图 2)
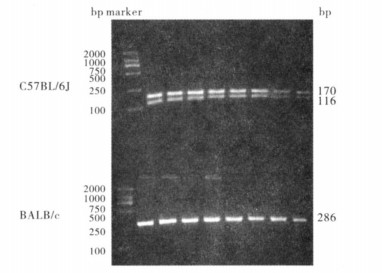
|
图 2 C57BL/6J及BALB/c小鼠Ikaros基因rs28185923位点基因型 |
Ikaros基因rs28185923位点C57BL/6J小鼠基因型为C/C,BALB/c小鼠基因型为T/T。
2.3 C57BL/6J及BALB/c小鼠p16基因rs3695947位点基因型(图 3)
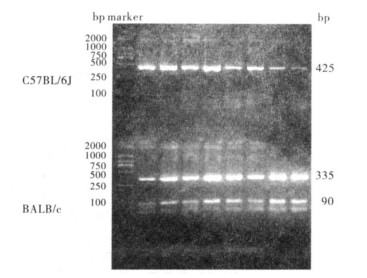
|
图 3 C57BL/6J及BALB/c小鼠p16基因rs3695947位点基因型 |
p16基因rs3695947位点C57BL/6J小鼠基因型为A/A,BALB/c小鼠基因型为G/G。
3 讨论Ikaros及p16基因均为肿瘤抑制基因,有研究显示,它们与辐射诱发胸腺淋巴瘤关系密切〔3, 4〕。Ikaros基因的编码产物在淋巴细胞的发育及分化过程中起重要作用。Ikaros基因敲除的小鼠白血病的发病率为100%〔5, 6〕。有学者报道在辐射诱发的胸腺淋巴瘤中,Ikaros基因异常是关键因素之一〔4, 7〕。p16基因是CDKI基因家族成员,其编码产物p16蛋白可使细胞停滞于G1期,以维持机体细胞的有序增殖,当其功能丧失时,细胞生长失控导致肿瘤形成〔8〕。有报道指出p16蛋白可通过诱导T细胞的凋亡来维持淋巴器官的正常大小,并且在辐射诱发的胸腺淋巴瘤中存在p16基因的失活〔3, 9〕。
本研究探讨Ikaros及p16基因多态性与辐射诱发小鼠胸腺淋巴瘤的相关性。结果显示,在辐射敏感性不同的C57BL/6J及BALB/c小鼠中,Ikaros及p16基因所研究位点的基因型不同,推测二者基因多态性与辐射诱发胸腺淋巴瘤相关。本研究结果为在基因组水平上阐明辐射致癌机制提供了生物学依据。
| [1] | 韩柏慧, 陶然, 史杰萍, 等. 汉族人群PIP3-E基因多态性与精神分裂症关系[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2007, 23(3) : 293–294. |
| [2] | 刘丽波, 鞠桂芝, 史杰萍, 等. 5-HTR4和GABRG2基因多态性与精神分裂症关系[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2007, 23(12) : 1461–1463. |
| [3] | Yoshida MA, Nakata A, Akiyama M, et al. Distinct structural abnormalities of chromosomes 11 and 12 associated with loss of heterozygosity in X-ray-induced mouse thymic lymphomas[J]. Cancer Genet Cytogenet, 2007, 179(1) : 1–10. DOI:10.1016/j.cancergencyto.2007.06.016 |
| [4] | Ohi H, Mishima Y, Kamimura K, et al. Multi-step lymphomagenesis deduced from DNA changes in thymic lymphomas and atrophic thymuses at various times after gamma-irradiation[J]. Oncogene, 2007, 26(36) : 5280–5289. DOI:10.1038/sj.onc.1210325 |
| [5] | Kubota T, Yoshikai Y, Tamura Y, et al. Comparison of properties of spontaneous and radiation-induced mouse thymic lymphomas:role of Trp53 and radiation[J]. Radiat Res, 2005, 163(2) : 159–164. DOI:10.1667/RR3303 |
| [6] | Kathrein KL, Lorenz R, Innes AM, et al. Ikaros induces quiescence and T-cell differentiation in a leukemia cell line[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2005, 25(5) : 1645–1654. DOI:10.1128/MCB.25.5.1645-1654.2005 |
| [7] | Shimada Y, Nishimura M, Kakinuma S, et al. Radiation-associated loss of heterozygosity at the Znfn1a1(Ikaros) locus on chromosome 11 in murine thymic lymphomas[J]. Radiat Res, 2000, 154(3) : 293–300. DOI:10.1667/0033-7587(2000)154[0293:RALOHA]2.0.CO;2 |
| [8] | Viallard JF, Lacombe F, Belloc F, et al. Molecular mechanisms controlling the cell cycle:fundamental aspects and implications for oncology[J]. Cancer Radiother, 2001, 5(2) : 109–129. DOI:10.1016/S1278-3218(01)00087-7 |
| [9] | Bianchi T, Rufer N, MacDonald HR, et al. The tumor suppressor p16Ink4a regulates T lymphocyte survival[J]. Oncogene, 2006, 25(29) : 4110–4115. DOI:10.1038/sj.onc.1209437 |
 2009, Vol. 25
2009, Vol. 25

