2. 青岛即墨区鳌山卫卫生院,山东 青岛 266237
2. Qingdao Jimo Aoshanwei Health Center, Qingdao 266237 China
全脑放疗(whole brain radiotherapy, WBRT)是目前各种脑转移瘤患者的有效治疗模式之一[1]。其中全脑预防性照射(prophylactic carnial irradiation, PCI)可显著控制脑转移的发生概率,提高患者总生存率[2-3]。但WBRT照射会引起患者海马功能区损伤,产生认知障碍[4-5]。随着目前治疗技术的规范和提高,患者生存期延长,对于患者放疗后的生活质量越来越引起重视。研究表明,海马保护性全脑放疗(hippocampal avoidance whole brain radiotherapy, HA-WBRT)可对全脑放疗结束后患者引起的认知功能障碍得到明显改善[6]。有研究证明,VMAT在全脑放疗中相对于IMRT具有较好的剂量学优势[7],Yuen A等[8]设计采用分段弧VMAT模式对比传统双弧VAMT在海马体的保护中,分段弧VMAT更加具有剂量学优势。近年来使用无均整器(flatting filter free, FFF)射束的VMAT模式相比均整器射束(flatting filter, FF),具有较高剂量率、较低射野外剂量和较短的照射时间特点,越来越受到青睐[9]。本研究将无均整器的FFF模式应用于海马保护性全脑放疗,使用分段式VMAT技术,采用多个剂量学参数评估FF和FFF 2种照射模式,在满足临床处方剂量要求的前提下,分析2种计划对患者靶区和危机器官的剂量学差异,为临床技术选择提供参考。
1 材料与方法 1.1 病例资料选取青岛市市立医院2020年12月—2021 年 9 月收治的15例接受海马保护性全脑放疗的患者。女性8例,男性7例;病例年龄范围35~56 岁,年龄中位数为43岁。
1.2 仪器设备采用瓦里安Trilogy加速器(60对多叶光栅,叶片等中心投影宽度0.5 cm)使用飞利浦Brilliance大孔径CT定位机,扫描层厚3 mm,进行CT定位,使用Manteia公司的AccuContour软件将CT定位图像与MR图像进行融合后传输到瓦里安Eclipse 13.5版治疗计划系统,进行靶区和危机器官的勾画及放疗计划设计。
1.3 靶区和危及器官勾画眼睛、晶状体、视神经、视交叉和海马体被定义为危及器官,由放疗医生严格按照RTOG0933图谱定义手工描绘。海马体保护区(PRV)由海马体均匀外扩5 mm生成[10],CTV由放疗医生按照全脑组织进行勾画,在此基础上,CTV 外扩3 mm 并减去PRV生成靶区(PTV)。
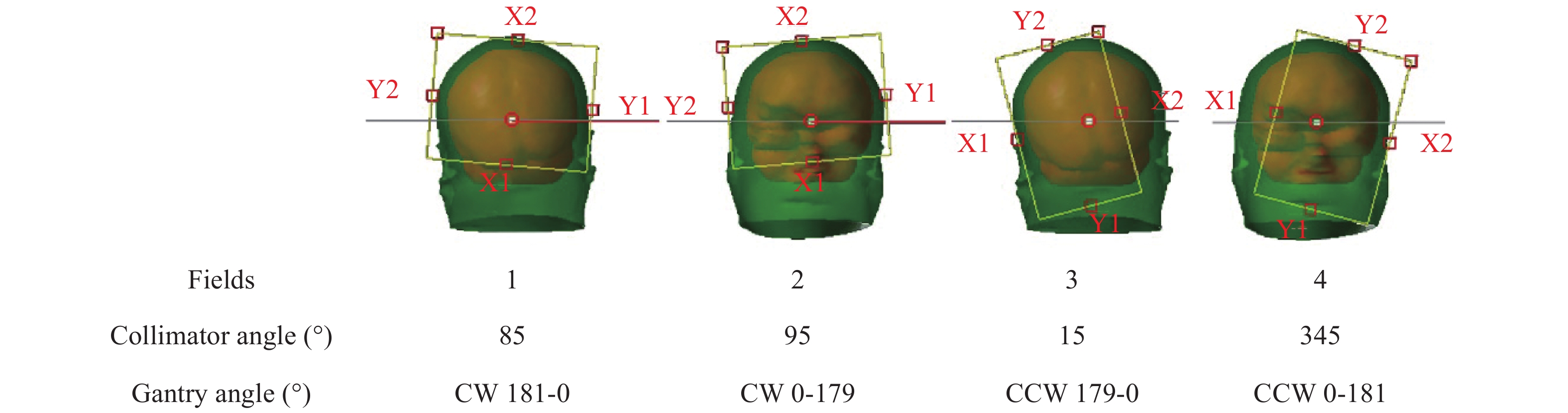
1.4 计划设计为15例患者分别设计FF和FFF 2种VMAT 计划,选用6 MV能量X射线,射野为4个半弧,如图1,4个照射野分别选择了85°、95°、15°和345°的准直器角度。通过减少每个弧的射野大小,以便MLC能够在不牺牲整个大脑PTV覆盖的情况下保护位于中央的海马体。FF和 FFF 计划的最大剂量率分别为 600 MU/min和1400 MU/min。治疗处方剂量设定为30 Gy/10 f。为了避免引入偏差,优化参数在2种计划之间不做调整。剂量计算时使用AcurosXB分析算法,剂量计算网格1.25 mm。按照RTOG0933方案,全脑PTV和危及器官计划剂量的可接受范围符合标准列于表1。
|
图 1 射野参数设置 Figure 1 Field parameter setting 注:CCW为逆时针,CW是顺时针 |
|
|
表 1 RTOG 0933方案的剂量标准 Table 1 Dose criteria of RTOG 0933 protocol |
为评估靶区,提取了PTV的D2%、D98%和V30 Gy,分别是PTV体积的2%、98%所受剂量大小和处方剂量30 Gy所占PTV的体积。其次采用其他指标进一步评价靶区,包括适形度指数(Conformity Index, CI)CI = (TVPV)2/(TV×PV),TV是处方剂量线的全部体积,TVPV是处方剂量线与靶区相交的体积,PV是靶区体积。均匀性指数(Homogeneity Index, HI)HI = (D2%−D98%)/D50%,D50%是PTV体积的50%所受剂量大小;梯度跌落指数(Gradient Index, GI)GI = V50%/V100%,V50%和V100%分别是处方剂量的50%和100%剂量线所形成的体积。
为评估危及器官,提取了海马体的最小剂量Dmin、最大剂量Dmax和平均剂量Dmean,眼睛的最大剂量和平均剂量,视神经、视交叉和晶体提取最大剂量。为进行照射效率的比较,统计出束总跳数(MU)和出束时间(DT)。
1.6 统计学分析采用统计学软件SPSS 21.0进行统计学分析,结果以均数±标准差(
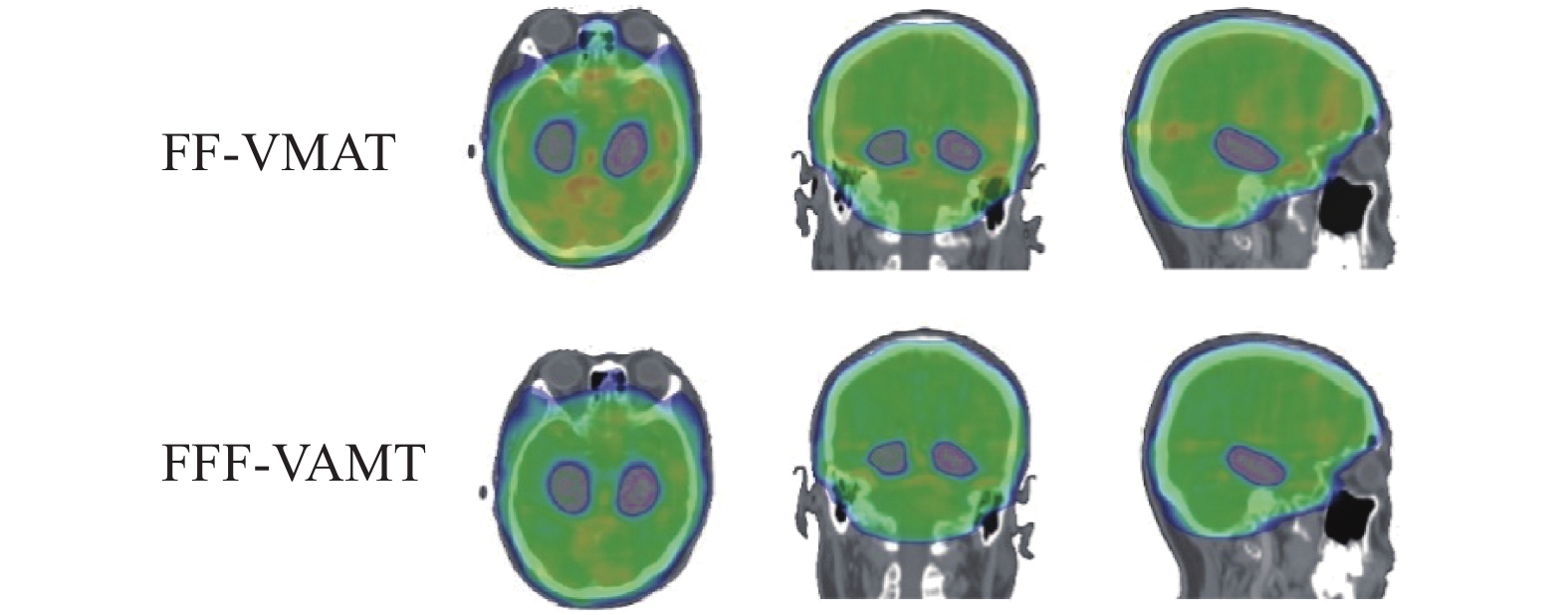
比较15例患者所有治疗计划的靶区剂量分布都能达到RTOG0933方案要求,产生了足够的目标覆盖率,且最大剂量均小于37.5 Gy,图2显示了2种计划的剂量分布20 Gy到37.5 Gy 的色阶。2种治疗技术在全脑PTV的D2%、D98%、HI、CI、GI和V30 Gy比较中差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),2种治疗技术在实现目标覆盖率和剂量均匀性方面具有相似的结果,见 表2。
|
图 2 2种计划剂量分布 Figure 2 Dose distributions of FF-VMAT and FFF-VMAT |
|
|
表 2 2种计划靶区剂量参数比较 Table 2 Comparison of doses to target volume between FF-VMAT and FFF-VMAT |
2种计划的海马体组织剂量比较结果见表3。由表3可知,FFF-VMAT海马体的D100%、Dmax、Dmean均明显小于FF-VMAT,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。
|
|
表 3 2种计划方案海马剂量参数比较 Table 3 Comparison of doses to hippocampus between FF-VMAT and FFF-VMAT |
危及器官剂量及MU值、出束时间比较视交叉、视神经、眼睛和晶状体的剂量参数见表4。对于FF-VMAT和FFF-VMAT,2种技术在视交叉和视神经方面的差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。在眼球中,FFF-VMAT与FF-VMAT相比,Dmax差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),Dmean明显减少(P < 0.05)。FF-VMAT和FFF-VMAT的晶状体 Dmax明显减少(P < 0.05)。其他方面FFF-VMAT明显高于FF-VMAT的出束总跳数,但FFF-VMAT的出束时间明显低于FF-VAMT,差异均有统计学意义( P < 0.01)。
|
|
表 4 其他危及器官剂量及MU值、出束时间比较 Table 4 Comparison of doses to other organsatrisk, monitor units, and beam-on time between FF-VMAT and FFF-VMAT |
全脑放射治疗(WBRT)具有姑息和预防作用,能降低局部复发概率并提高总体生存率,但海马体中的神经干细胞对辐射非常敏感,高剂量照射会造成海马体功能损伤[11]。Gondl等[12]研究表明,在10次30 Gy的WBRT治疗过程中,海马体的最大剂量Dmax或者D100%过高时会造成患者的记忆功能受损。Fiorentino等[13]研究表明,放疗过程中对海马区域及其周围 5到10 mm 范围进行保护,可在一定程度上保护认知功能,同时有助于保护患者的记忆功能,提高生活质量。
有研究表明,加速器机头中的漏射线和散射线主要来自于均整器,而移除均整器后,不仅减少了漏射和散射,同时还提高了剂量率[14]。周鹏等[15]应用蒙特卡洛模拟FFF射线的光子能谱中证明,均整器对光子能谱空间分布产生明显的影响,无均整器对比有均整器状态下分布在射野外的相对光子数明显减少,而且相对于大野,小野的野外相对光子数减少更明显。目前的调强计划基本是由小野叠加而成,所以这种射线特性在降低野外剂量,降低治疗副反应上有重要意义。
本研究对比FF-VMAT计划海马体最大值及左右晶体最大值和左右眼球平均值,FFF-VMAT计划结果相对较低。由于海马体和晶体本身为对放射线敏感的正常组织,其限量要求严格,因此有效地降低受量具有显著临床意义。其它危机器官如视神经视交叉等,由于靶区的处方剂量远未达到这些危机器官的限值,优化过程中并未做过多优化参数限制,所以两计划结果中对比没有显著差异。
本研究的结果显示FF-VMAT 和 FFF-VMAT计划均能满足临床处方剂量要求,但对于靶区的剂量学对比中没有明显差异,REGGIORI 等[16]对肝癌VMAT计划采用FFF模式的研究表明,在 100~300 cm3的靶区体积,FFF模式适形度比 FF模式高,对于小于100 cm3和大于300 cm3的靶区体积,FF 模式适形度更高。本研究没有发现差异的原因可能是局限于样本量的不足,后期需要扩大样本量进一步研究。
本研究发现,FFF-VMAT计划的机器跳数明显高于 FF-VMAT计划,原因是 FFF 模式以薄铜片取代了均整器,射线软化,FFF模式的 6MV-X 射线质更接近于 FF模式的4 MV-X 射线,相比FF,为使深部区域处的靶区得到相同剂量,FFF 模式则需输出更多的机器跳数[17]。FFF虽然总跳数高于FF,但得益于FFF的高剂量率模式,可以快速出束,最后结果FFF相比FF治疗时间显著减少。
近年来使用高端放疗设备质子放疗和TOMO对比常规调强放疗,其在海马保护性全脑放疗方面的优势已被充分证实[18-19],但其治疗费用高昂。在临床放疗计划设计中使用常规加速器进行调强放疗照射全脑并保护海马区一直是难点,近年来的相关研究也在对其进行不断探索。解昕等[20]对使用共面IMRT与共面VMAT进行比较,结果显示VMAT 组 PTV 的均匀性优于 IMRT 组,另外治疗时间更短,提高了治疗效率,但海马体剂量未达到RTOG0933要求。Krayenbuehl等[21]利用非共面 VMAT 实施全脑照射,海马组织的最大剂量降低到14.1 Gy,但靶区覆盖率偏低且非共面计划在治疗过程中治疗效率偏低。Yuen等[8]利用共面技术采用分段弧和部分野照射技术,以降低散射辐射和MLC限制,该技术使得海马和眼睛的剂量显著减少。本研究在总结上述研究基础上,在保证治疗效率的前提下,在海马保护性全脑放疗中将FFF技术应用于分段弧和部分野照射的共面VMAT,取得较为理想的结果。
综上所述,本研究使用无均整器模式与传统均整器模式在海马保护全脑放疗中进行对比研究,结果证明FF -VAMT和FFF -VAMT计划均能满足临床治疗要求,且无均整模式的容积调强放疗计划更利于保护危及器官,减少了治疗时间,为实施海马保护全脑放疗提供了参考。
| [1] |
孟曼, 毕金玲, 黄勇. 脑转移瘤全脑放疗疗效与预后相关因素分析[J]. 中国辐射卫生, 2019, 28(4): 458-461,472. Meng M, Bi JL, Huang Y. Analysis of factors related to the efficacy and prognosis of brain metastases in whole brain radiotherapy[J]. Chin J Radiol Health, 2019, 28(4): 458-461,472. DOI:10.13491/j.issn.1004-714X.2019.04.030 |
| [2] |
李萌, 王祥, 王太芳, 等. 预防性全脑照射治疗非小细胞肺癌的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤研究与临床, 2022, 34(1): 73-76. Li M, Wang X, Wang TF, et al. Progress of prophylactic cranial irradiation in treatment of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Res Clin, 2022, 34(1): 73-76. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115355-20191019-00476 |
| [3] |
Gondi V, Tolakanahalli R, Mehta MP, et al. Hippocampal-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy: a "how-to" technique using helical tomotherapy and linear accelerator–based intensity-modulated radiotherapy[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2010, 78(4): 1244-1252. DOI:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.01.039 |
| [4] |
Redmond KJ, Mahone EM, Terezakis S, et al. Association between radiation dose to neuronal progenitor cell niches and temporal lobes and performance on neuropsychological testing in children: a prospective study[J]. Neuro-Oncology, 2013, 15(3): 360-369. DOI:10.1093/neuonc/nos303 |
| [5] |
Gondi V, Hermann BP, Mehta MP, et al. Hippocampal dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign or low-grade adult brain tumors[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2012, 83(4): e487-e493. DOI:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.10.021 |
| [6] |
陈梦圆, 陈媛媛, 陈明, 等. 海马区保护性全脑放疗研究进展[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2021, 30(7): 735-738. Chen MY, Chen YY, Chen M, et al. Research progress on hippocampal-avoidance whole brain radiotherapy[J]. Chin J Radiat Oncol, 2021, 30(7): 735-738. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn113030-20191011-00414 |
| [7] |
Sood S, Pokhrel D, McClinton C, et al. Volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for whole brain radiotherapy: not only for hippocampal sparing, but also for reduction of dose to organs at risk[J]. Med Dosim, 2017, 42(4): 375-383. DOI:10.1016/j.meddos.2017.07.005 |
| [8] |
Yuen AHL, Wu PM, Li AKL, et al. Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for hippocampal-avoidance whole brain radiation therapy: planning comparison with Dual-arc and Split-arc partial-field techniques[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2020, 15(1): 42. DOI:10.1186/s13014-020-01488-5 |
| [9] |
Hrbacek J, Lang S, Klöck S. Commissioning of photon beams of a flattening filter-free linear accelerator and the accuracy of beam modeling using an anisotropic analytical algorithm[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2011, 80(4): 1228-1237. DOI:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.09.050 |
| [10] |
Gondi V, Pugh SL, Tome WA, et al. Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): a phase II multi-institutional trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2014, 32(34): 3810-3816. DOI:10.1200/JCO.2014.57.2909 |
| [11] |
Ji SJ, Ding X, Ji J, et al. Cranial irradiation inhibits hippocampal neurogenesis via DNMT1 and DNMT3A[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 15(3): 2899-2904. DOI:10.3892/ol.2017.7643 |
| [12] |
Gondi V, Tomé WA, Mehta MP. Why avoid the hippocampus? A comprehensive review[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2010, 97(3): 370-376. DOI:10.1016/j.radonc.2010.09.013 |
| [13] |
Fiorentino A, Tebano U, Sicignano G, et al. Hippocampal dose during Linac-based stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: an observational study[J]. Phys Med, 2018, 49: 135-138. DOI:10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.09.129 |
| [14] |
Ghemiş DM, Marcu LG. Progress and prospects of flattening filter free beam technology in radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiotherapy[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2021, 163: 103396. DOI:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103396 |
| [15] |
周鹏, 胡南, 刘岩海, 等. 医用直线加速器无均整器下6 MV X线能谱特性的蒙特卡罗研究[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2016, 33(8): 761-765. Zhou P, Hu N, Liu YH, et al. Monte Carlo research on 6 MV X-ray spectrum characteristic of linear accelerator without flattening filter[J]. Chin J Med Phys, 2016, 33(8): 761-765. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-202X.2016.08.002 |
| [16] |
Reggiori G, Mancosu P, Castiglioni S, et al. Can volumetric modulated arc therapy with flattening filter free beams play a role in stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver lesions? A volume-based analysis[J]. Med Phys, 2012, 39(2): 1112-1118. DOI:10.1118/1.3679858 |
| [17] |
Fogliata A, Garcia R, Knöös T, et al. Definition of parameters for quality assurance of flattening filter free (FFF) photon beams in radiation therapy[J]. Med Phys, 2012, 39(10): 6455-6464. DOI:10.1118/1.4754799 |
| [18] |
Harrabi SB, Bougatf N, Mohr A, et al. Dosimetric advantages of proton therapy over conventional radiotherapy with photons in young patients and adults with low-grade glioma[J]. Strahlenther Onkol, 2016, 192(11): 759-769. DOI:10.1007/s00066-016-1005-9 |
| [19] |
黄祥, 徐伟, 陈高翔, 等. 螺旋断层和旋转调强技术在小细胞肺癌脑预防放射治疗海马保护的剂量学研究[J]. 中国医学装备, 2018, 15(7): 22-26. Huang X, Xu W, Chen GX, et al. Dosimetric research of TOMO and RapidArc technique on prophylactic cranial irradiation of hippocampal avoidance for small cell lung cancer[J]. China Med Equip, 2018, 15(7): 22-26. DOI:10.3969/J.ISSN.1672-8270.2018.07.005 |
| [20] |
解昕, 李亮, 范雪梅, 等. 基于Varian加速器海马保护全脑放疗剂量学技术比较[J]. 中国辐射卫生, 2021, 30(3): 326-330. Xie X, Li L, Fan XM, et al. Dosimetric study of hippocampal protective whole brain radiotherapy based on Varian accelerator[J]. Chin J Radiol Health, 2021, 30(3): 326-330. DOI:10.13491/j.issn.1004-714X.2021.03.014 |
| [21] |
Krayenbuehl J, Di Martino M, Guckenberger M, et al. Correction to: improved plan quality with automated radiotherapy planning for whole brain with hippocampus sparing: a comparison to the RTOG 0933 trial[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2017, 12(1): 173. DOI:10.1186/s13014-017-0901-1 |




