γ能谱仪因其样品前处理简单、操作方便、能同时测量多种放射性核素等特点,目前被广泛应用于土壤样品的比活度测量[1-2]。但是,在使用γ能谱仪测量土壤样品中放射性核素的比活度之前,通常需要利用土壤标准物质进行效率刻度。在这种相对测量中,如果待测样品与土壤标准物质存在差别,就会给测量结果带来误差。为了保证γ能谱仪测量结果的准确性,一些研究者已对样品的装样密度、体积、高度以及组成成分等因素对测量结果的影响做了大量的研究,这在一定程度上提高了比活度测量的准确性[2-6]。但是有关土壤样品的粒径大小对γ能谱仪测量土壤中放射性核素比活度的影响鲜有报道。此外,γ能谱法测量一些核素如226Ra和228Ra,并不能利用自身发出的γ射线测量其含量,而是通过测量其子体核素发射的γ射线达到测量目的,这种方法的前提是待测核素与子体核素已达到放射性平衡。因此,为保证γ能谱仪测量土壤样品中放射性核含量的准确性,平衡时间也是必须考虑的影响因素之一。基于上述背景,本研究通过比较分析不同过筛粒径的土壤样品在不同平衡时间间隔测量的放射性核素比活度,以定量评价过筛粒径和平衡时间对γ能谱仪测量土壤样品放射性核素含量的影响。
1 材料与方法 1.1 样品采集和处理本研究的测试土壤样品是在2017年9月1日采自辽宁省本溪地区的表层(0~10 cm)棕壤土,采集的新鲜土壤样品放在塑料自封袋中,密封好带回实验室。样品制备前先除去样品中的杂草和碎石等异物,然后用电热恒温鼓风干燥箱在110℃烘干24 h至恒重。将干燥后的土壤样品分成4份,粉碎、研磨后,4份样品分别过2.0 mm、1.0 mm、0.5 mm和0.25 mm筛,然后分别装入Φ75 mm × 70 mm圆柱型塑料样品盒中,擦净,称重,密封,测量。
1.2 样品测量本研究使用的测量设备为美国CANBERRA公司生产的宽能型超低本底高纯锗γ能谱仪(BE5030),相对于3" × 3"NaI(Tl)晶体的探测效率为50.5%,对60Co 1332 keV γ射线的能量分辨率为1.65 keV。探测器置于壁厚16.5 cm、内腔Φ23 cm × 35 cm的复合屏蔽铅室内。
γ能谱仪测量样品中核素比活度时,226Ra的特征峰选取295.21、351.92和609.31 keV,228Ra选取338.32和911.21 keV,210Pb、40K和137Cs的特征峰分别选取46.54、l460.75和661. 66 keV。对4个不同过筛粒径样品分别在装样密封后0、4、8、12、16、21、25和29 d进行测量,每次样品测量时间均为24 h。
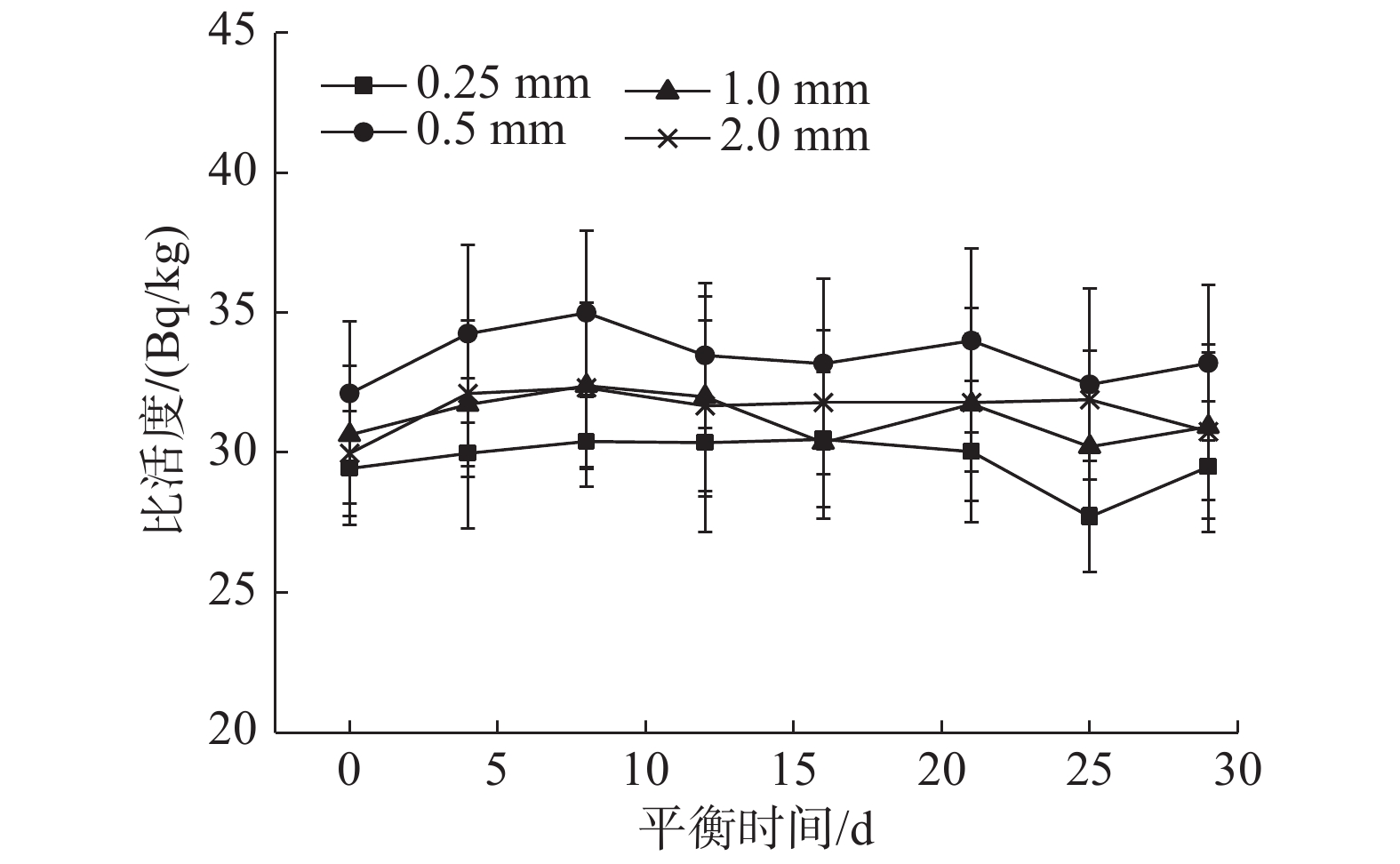
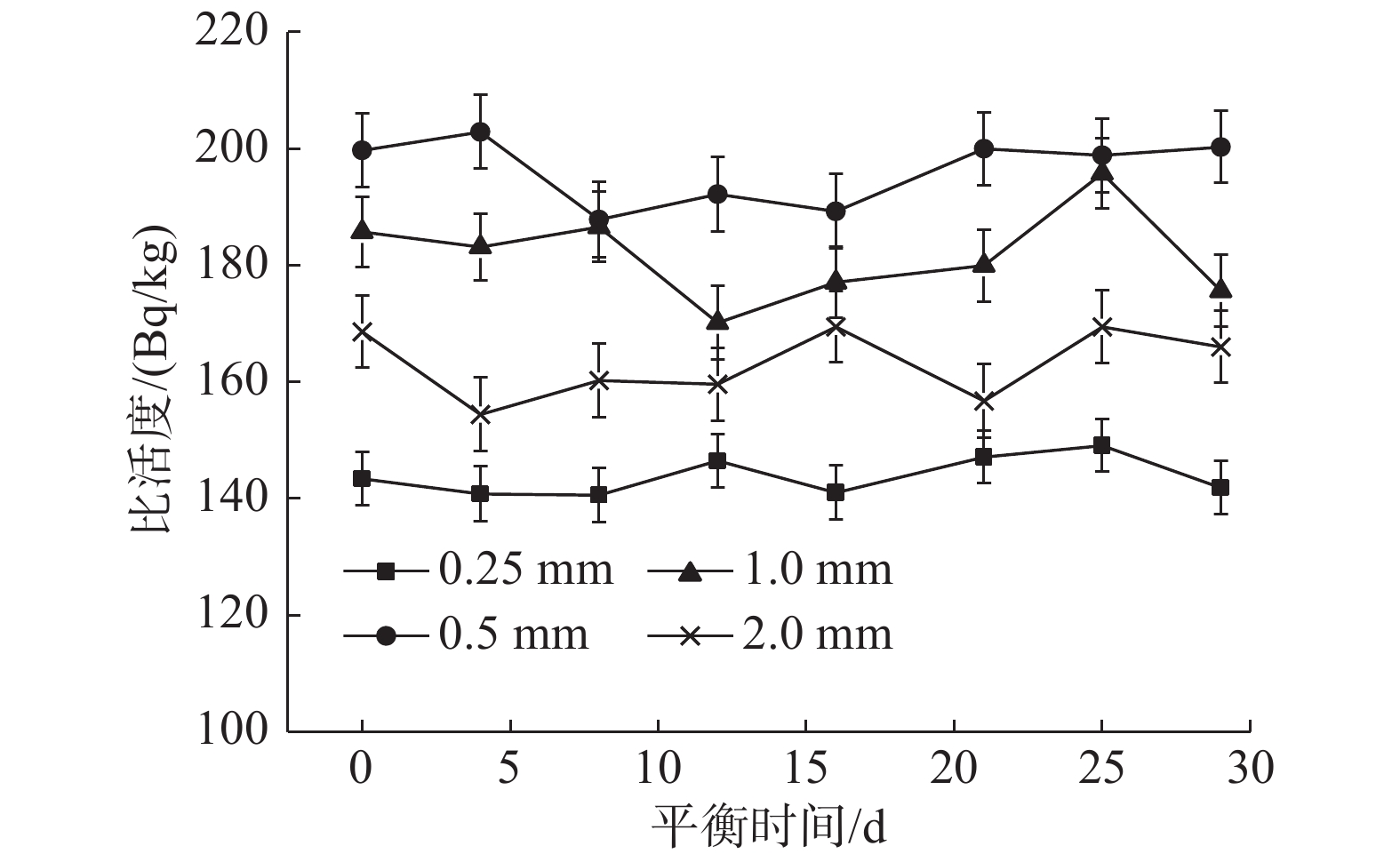
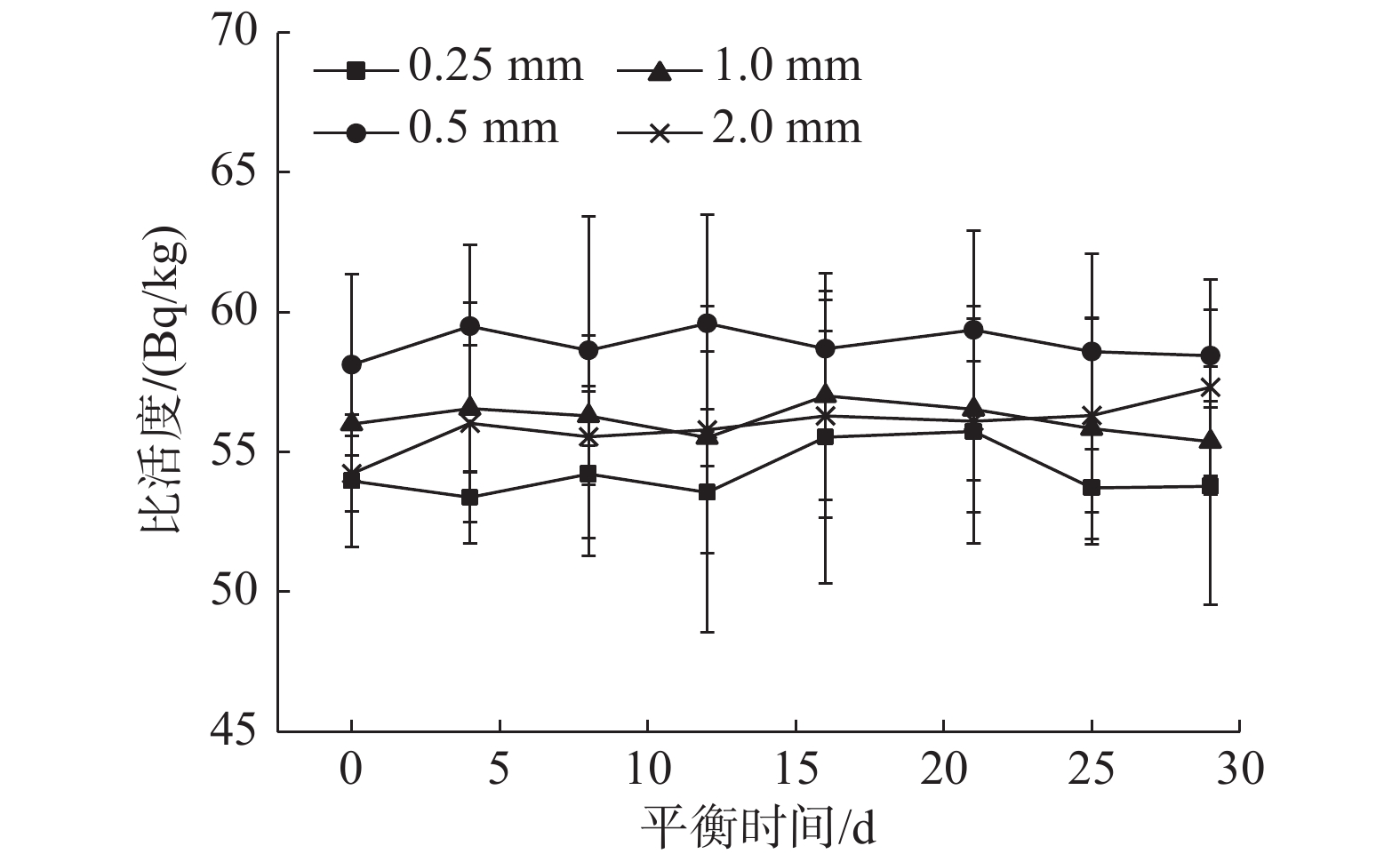
2 结 果 2.1 平衡时间对铀系和钍系核素比活度测量的影响不同过筛粒径土壤样品中226Ra、210Pb和228Ra的比活度与平衡时间的关系分别如图1~3所示,可以看出226Ra、210Pb和228Ra的比活度随样品平衡时间的延长而变化。不同平衡时间土壤样品中226Ra比活度的变异系数分别为3.0%(0.25 mm)、2.8%(0.5 mm)、2.6%(1.0 mm)和2.5%(2.0 mm),210Pb的变异系数为2.3%(0.25 mm)、2.9%(0.5 mm)、4.3%(1.0 mm)和3.7%(2.0 mm),228Ra的变异系数为1.7%(0.25 mm)、0.9%(0.5 mm)、1.0%(1.0 mm)和1.6%(2.0 mm),其变异系数范围为0.9%~4.3%。
|
图 1 不同过筛粒径土壤样品中226Ra的比活度随密封时间的变化 Figure 1 Variations of 226Ra activity concentration with sealing time in soil samples with different sieve sizes |
|
图 2 不同过筛粒径土壤样品中210Pb的比活度随密封时间的变化 Figure 2 Variations of 210Pb activity concentration with sealing time in soil samples with different sieve sizes |
|
图 3 不同过筛粒径土壤样品中228Ra的比活度随密封时间的变化 Figure 3 Variations of 228Ra activity concentration with sealing time in soil samples with different sieve sizes |
表1显示不同过筛粒径土壤样品密封29 d后226Ra、210Pb、228Ra、40K和137Cs的比活度和变异系数。从表中可以看出,4种过筛粒径土壤样品中226Ra、210Pb、228Ra、40K和137Cs的比活度不同,但226Ra、210Pb、228Ra和137Cs呈现出一致的规律,即过筛粒径为0.5 mm的土样所测得的比活度最大,过筛粒径为0.25 mm的土样所测得的比活度最小。对于40K而言,过筛粒径为0.5 mm的土样所测得的比活度最小,过筛粒径为2 mm的土样所测得的比活度最大。4种过筛粒径土壤样品中226Ra、210Pb、228Ra、40K和137Cs比活度的变异系数如表1,按其大小顺序为210Pb(14.1%)>137Cs(13.2%)>40K(8.2%)>226Ra(5.0%)>228Ra(3.7%)。
|
|
表 1 不同过筛粒径土壤样品中226Ra、210Pb、228Ra、40K和137Cs的测量结果 Table 1 Activity concentrations of 26Ra, 210Pb, 228Ra, 40K and 137Cs in soil samples of different sieve sizes |
γ能谱方法测量土壤样品中不平衡铀系和钍系核素前,一般需要将待测样品密封一段时间使其各个子系达到衰变平衡。根据本实验的研究结果,土壤样品中不同平衡时间间隔测量的226Ra、210Pb和228Ra比活度的变异系数均低于5.0%,这很可能与样品经过干燥、粉碎、研磨、过筛机械加工等物理方法处理,样品内固有的放射性平衡关系没有被严重破坏有关[7-8]。因此,在应急情况而不要求高精确度时,土壤样品封装后可以立即测量或缩短放置时间,而不必等待其达到衰变平衡。另外,从图1~图3可以看出,只有226Ra在前5 d有增加的趋势,而210Pb和228Ra并没有呈现明显的规律。这可能是因为220Rn的半衰期只有55 s,测量228Ra仅需要放置1 d就可以达到衰变平衡[9],因此对228Ra的测定基本是没有影响的;而210Pb理论上受222Rn的影响较小,但由于210Pb 发射出的γ射线能量46.5 keV较低,一般会在测量前将制备好的土壤样品放置一段时间,使氡、钍短半衰期子体充分衰变,以减少对γ能谱仪测量210Pb 比活度时的干扰。
目前,实验室使用γ能谱方法测量土壤中放射性核素的比活度时,其样品过筛粒径各异。在国标GB/T 11743—2013 《土壤中放射性核素的γ能谱分析方法》中推荐过筛粒径为40目~60目(0.425 mm~0.25 mm),也有文献报道选用的过筛粒径为2 mm,原因是在此粒径下可以筛分去除土壤中的岩石碎屑[10]。本研究结果显示,过筛粒径对γ能谱法测量土壤样品中226Ra、210Pb、228Ra、40K和137Cs的比活度均有不同程度的影响,尤其是对210Pb和137Cs的影响程度分别达到了14.1%和13.2%。此外,另有研究也表明粒径会影响γ能谱测量土壤和花岗岩样品中放射性核素比活度[10-11]。其原因之一是采集的土壤样品不同粒径中放射性核素的比活度很可能原本就不同,由此导致不同的过筛粒径测量的放射性核素结果出现了一定的差异。已有研究表明,137Cs的比活度与土壤颗粒粒径具有明显的相关性[12]。此外,不同土壤类型的标准物质因其不同化学成分会对土壤中210Pb 测定的准确性有显著影响[13]。土壤作为不同矿物的集合体,不同粒径的土壤其矿物组成组分并不相同,因此也有可能是因为某种粒径的土壤样品与选用的标准物质的化学成分产生了较大差异所致。基于本研究结果,使用γ能谱法测量土壤样品中放射性核素(尤其是210Pb和137Cs)的比活度时,应考虑过筛粒径对测量结果的影响,但是如何对其比活度进行粒度校正,以获取更为精确的结果,还需进一步研究。当前,可将过筛粒径作为B类不确定度的一个因素,在对测量结果进行不确定度评定时加以考虑。
| [1] |
刘兆华. 环境样品放射性活度用HPGeγ谱仪测量的误差来源分析[J]. 中国辐射卫生, 2005, 14(2): 147-148. Liu ZH. Analysis of the source of error of radioactivity intensity in environmental samples measured by HPGe gamma-ray spectrum instrument[J]. Chin J Radiol Health, 2005, 14(2): 147-148. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-714X.2005.02.042 |
| [2] |
陈忠, 徐家云, 周钢, 等. 土壤样品中的含水量对HPGe γ谱仪探测效率的影响[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2005, 25(3): 318-321. Chen Z, Xu JY, Zhou G, et al. Effect of water content in soil samples on the γ detection efficiency for HPGe γ spectrometer[J]. Nucl Electron Detect Technol, 2005, 25(3): 318-321. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2005.03.024 |
| [3] |
李勇, 耿肖臣. 样品厚度对实验室无源效率刻度技术测定~(137)Cs和~(210)Pb的影响[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2010, 44(1): 80-83. Li Y, Geng XC. Effect of sample thickness on determination of ~(137)Cs and ~(210)Pb using LabSOCS[J]. At Energy Sci Technol, 2010, 44(1): 80-83. |
| [4] |
李斌, 徐家云, 倪伟峰, 等. 环境放射性样品装量与γ射线能量的关系[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2008, 42(4): 358-361. Li B, Xu JY, Ni WF, et al. Relationship of soil sample quantities and γ-ray energies for environmental radioactivity survey[J]. At Energy Sci Technol, 2008, 42(4): 358-361. |
| [5] |
Yang BL, Ha YM, Li A, et al. Optimisation design of cylindrical containers for improving the detection efficiency of a high-purity germanium detector using the LabSOCS[J]. J Radioanal Nucl Chem, 2013, 298(3): 1673-1677. DOI:10.1007/s10967-013-2577-9 |
| [6] |
Yang BL, Ha YM, Li A. Effect of the chemical composition of the standard calibration source for measuring radionuclides in biological samples by gamma spectrometry[J]. J Radioanal Nucl Chem, 2014, 299(1): 433-438. DOI:10.1007/s10967-013-2802-6 |
| [7] |
韩寿岭, 李秀珍, 张谦. 226Ra测量中样品密封时间影响研究
[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 1991, 11(2): 123-127. Han SL, Li XZ, Zhang Q. Problems of sealing period of samples in measurement of 226Ra[J]. Nucl Electron Detect Technol, 1991, 11(2): 123-127. |
| [8] |
韩寿岭. 对土壤226Ra含量测定中样品密封时间探讨
[J]. 中华放射医学与防护杂志, 1995(5): 329-329. Han SL. Discussion on the sealing time of samples in the determination of 226Ra in Soil [J]. Chin J Rodiation Mediat Prot, 1995(5): 329-329. |
| [9] |
刘广山, 黄奕普, 李静, 等. 不平衡铀系和钍系核素的γ谱测定[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 2003, 25(5): 65-75. Liu GS, Huang YP, Li J, et al. Measurement of nuclides of uranium and thorium series of disequilibrium using γ-spectroscopy[J]. Acta Oceanol Sin, 2003, 25(5): 65-75. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2003.05.008 |
| [10] |
刘叶涵, 李勇, 于寒青, 等. 过筛粒径大小对HPGeγ谱仪测定137Cs和210Pb的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2012, 26(8): 1172-1177. Liu YH, Li Y, Yu HQ, et al. Determination of 137Cs and 210Pb using HPGe γ spectrometry as influenced by different sieve diameters[J]. Acta Agric Nucleatae Sin, 2012, 26(8): 1172-1177. |
| [11] |
莫晓树. 粒度和测量时间对低本底多道γ能谱仪测量花岗岩放射性比活度和内、外照射指数的影响[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2003, 20(4): 543-545. Mo XS. Effects of particle size and measurement time on radioactivity specific activity and internal and external exposure index of granite measured by low background multichannel gamma-ray spectrometer[J]. J Guangxi Med Univ, 2003, 20(4): 543-545. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-930X.2003.04.037 |
| [12] |
严平, 高尚玉, 董光荣. 土壤颗粒组成影响137Cs含量的初步实验结果[J]. 中国沙漠, 2002, 22(2): 150-153. Yan P, Gao SY, Dong GR. Experimental results of the soil 137Cs activity as influenced by particle size[J]. J Desert Res, 2002, 22(2): 150-153. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2002.02.009 |
| [13] |
李勇, 耿肖臣, 于寒青, 等. 标准物质对HPGeγ谱仪测定环境放射性核素210Pb和137Cs的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2010, 24(6): 1249-1254. Li Y, Geng XC, Yu HQ, et al. Determination of envitonmental radionuclides 210Pb and 137Cs using HPGe γ spectrometry as influenced by different standard reference materials[J]. Acta Agric Nucleatae Sin, 2010, 24(6): 1249-1254. DOI:10.11869/hnxb.2010.06.1249 |




