信号传导与转录激活因子3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, STAT3) 是一种胞质转录因子, 参与了细胞中大量生长因子或细胞因子的应答, 是细胞生长、分化及凋亡等生理过程的重要调节因子[1]。STAT3的过度激活与多种人类恶性肿瘤的发生发展存在密切关系, 其在头颈部鳞癌、食管癌、乳腺癌、前列腺癌、肝癌、肺癌及急性髓系白血病等恶性癌症中呈现高激活状态[2]。在多种癌症中, STAT3活化水平与疾病进展和不良预后相关[3]。
随着研究的深入, STAT3在肿瘤发生发展中的重要地位也逐渐被熟知, 靶向两面神激酶(Janus kinase, JAK)/STAT3信号通路成为抗肿瘤药物研发的焦点之一。目前除美国波士顿生物医学公司研发的BBI608 (Napabucasin) 于2016年获得美国食品药品监督管理局(Food and Drug Administration, FDA) 批准上市应用于胰腺癌治疗外, 相关小分子抑制剂及天然产物来源抑制剂均处于临床前及临床研究阶段[4]。本研究从一系列苯并二咪唑结构化合物中筛选得到了一个全新的化合物LZJ541, 这类具有三环或多环的平面芳香族化合物通常带有荧光, 被认为是分子探针的有效材料[5], 其药理活性往往被忽视。本研究发现LZJ541具有明确的JAK/STAT3信号通路抑制活性, 可显著抑制肝癌HepG2细胞增殖, IC50远小于STAT3表达水平较低的PC-3细胞, 并且能通过抑制HepG2细胞内STAT3的磷酸化, 促进其凋亡和周期阻滞, 有望成为新型STAT3靶向抗肿瘤抑制剂。
材料与方法细胞与试剂 人肝细胞癌细胞HepG2、人前列腺癌细胞PC-3 (中国医学科学院基础医学研究所细胞中心, 由本实验室传代并保种); HEK-BLUETM-IL6细胞(法国InvivoGen公司); 隐丹参酮(cryptotanshinone, CTS, 1149-99-1, 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司); 高效RIPA裂解液(北京索莱宝科技有限公司); MTT (美国Sigma-Aldrich公司); 抗JAK2、p-JAK2、STAT1、p-STAT1 Y701、STAT3、p-STAT3 Y705、STAT5、p-STAT5 Y694抗体(美国Cell Signaling Technology公司); β-actin抗体、辣根酶标记山羊抗兔IgG、辣根酶标记山羊抗鼠IgG (北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司); 细胞凋亡/周期试剂盒(杭州联科生物技术股份有限公司); LZJ541 (本所李莉课题组提供, HPLC测定纯度≥ 98%)。
细胞培养 PC-3细胞培养于含10%胎牛血清(FBS) 及100 u·mL-1青霉素、100 μg·mL-1链霉素的1640培养基, HepG2、HEK-BLUETM-IL6细胞培养于含10% FBS及100 u·mL-1青霉素、100 μg·mL-1链霉素的DMEM培养基。
仪器 Biotek Synergy HIM全波长酶标仪(美国伯腾仪器有限公司); BD FACS Verse流式细胞仪(美国BD医疗器械有限公司); Caliper LabChip 2000 Drug Discovery System (美国Caliper公司)。
STAT3抑制剂筛选 利用本实验室建立的JAK/STAT3通路抑制剂筛选方法进行检测[6]。将HEK-BLUETM-IL6细胞接种于无菌96孔板(每孔细胞数5×104个), 每孔加入终浓度为1 ng·mL-1的白细胞介素6 (interleukin 6, IL6) 及不同浓度的阳性对照药CTS或LZJ541, 终体积为200 μL。在37 ℃、5% CO2饱和湿度条件下继续培养20 h, 然后从每个待测孔中吸取20 μL上清至另一96孔板, 每孔加入QUANTI-Blue显色液180 μL, 37 ℃孵育1 h, 于655 nm波长下检测吸光度(A) 值, 计算IC50。
激酶抑制活性检测[7] 通过microfluidic mobility shift assay采用Caliper LabChip 2000 Drug Discovery System检测LZJ541对JAK1、JAK2、JAK3、表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR)、肉瘤基因(sarcoma gene, SRC) 激酶的抑制活性, 该实验委托上海睿智生物有限公司完成。将终浓度10 μmol·L-1的LZJ541与激酶加入384孔板, 孵育10 min后加入FAM标记的多肽溶液, 孵育后加入终止缓冲液, 计算抑制率。
MTT检测 将对数生长期的PC-3及HepG2细胞消化后, 接种于96孔板, 每孔细胞数为3 000个, 待细胞贴壁后, 加入不同浓度的LZJ541 (0、1.562 5、3.125、6.25、12.5、25、50、100和200 μmol·L-1) 及相应溶剂(DMSO终浓度 < 0.2%) 对照的新鲜培养基, 使每孔溶液体积为200 μL, 每组设3个平行孔, 37 ℃条件下继续培养72 h, 每孔加入20 μL新鲜配制的含5 mg·mL-1 MTT的无血清培养基, 37 ℃条件下孵育3 h, 待蓝紫色沉淀出现后小心弃去上清, 每孔加入150 μL DMSO, 充分震荡后检测A值, 计算IC50。
蛋白质免疫印迹(Western blot) 检测 将HepG2细胞用不同浓度(0、5、10、20 μmol·L-1) LZJ541处理16 h, 用RIPA裂解细胞, 蛋白定量后进行电泳, 然后将蛋白电转至PVDF膜, 相应一抗4 ℃孵育过夜, 对应种属二抗孵育后进行ECL (efficient chemiluminescence) 化学发光检测。
流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡[8] 不同浓度LZJ541 (0、5、10、20、40 μmol·L-1) 处理细胞48 h后, 消化细胞, 加入PI (propidium iodide) 和Annexin-V进行染色, 流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡比例。
流式细胞术检测细胞周期[9] 收集不同浓度LZJ541 (0、5、10、20、40 μmol·L-1) 处理24 h后的细胞, 75%乙醇固定, -20 ℃过夜。将固定的细胞水化后, 加入DNA Staining Solution避光孵育30 min, 流式上机检测。
数据处理 实验重复3次, 数据以平均值±标准差(
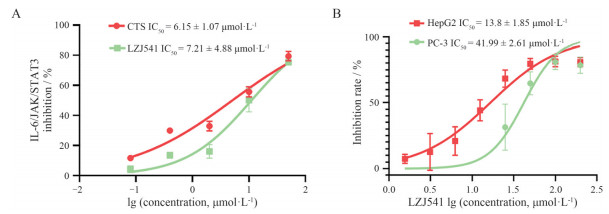
LZJ541是具有新型结构的苯并二咪唑类小分子化合物, 分子式为C26H26N4, 结构如图 1所示。将终浓度为0、0.08、0.4、2、10和50 μmol·L-1的LZJ541或CTS加入HEK-BLUETM-IL6细胞, CTS为已知的STAT3抑制剂[10], 作为阳性对照, 检测LZJ541对IL6/JAK/STAT3通路的抑制情况。结果显示(图 2A), LZJ541与CTS均能明显抑制IL6/JAK/STAT3信号通路激活, 其中LZJ541的IC50为7.21 ± 4.88 μmol·L-1, CTS为6.15 ± 1.07 μmol·L-1。
|
Figure 1 Chemical structure of LZJ541. Chemical formula: C26H26N4, molecular weight: 394.522 0 |
|
Figure 2 LZJ541 significantly inhibited the activity of Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway and inhibited the proliferation of HepG2 and PC-3 cells. A: Interleukin 6 (IL6)/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway inhibitory activities of cryptotanshinone (CTS) and LZJ541; B: The inhibitory activity of LZJ541 in HepG2 and PC-3 cells |
本实验室前期研究表明, PC-3细胞中STAT3蛋白表达远低于HepG2细胞[11], LZJ541作用72 h后, 能剂量依赖地抑制HepG2细胞增殖, 其IC50为13.8 ± 1.85 μmol·L-1 (图 2B), 远低于PC-3细胞的IC50 (41.99 ± 2.61 μmol·L-1), 进一步说明LZJ541能通过抑制STAT3信号通路抑制细胞增殖, 其抑制作用与STAT3的表达水平相关。
3 LZJ541对STAT3信号通路相关激酶的影响JAK1、JAK2、JAK3、EGFR、SRC是STAT3上游激酶, 均可催化STAT3的磷酸化激活。为了探究LZJ541对IL6/JAK/STAT3信号通路抑制的机制, 进一步检测了LZJ541对JAK1、JAK2、JAK3、EGFR、SRC激酶的抑制情况, 结果如表 1所示。LZJ541对这些激酶没有明显抑制, IC50均大于10 μmol·L-1, 推测LZJ541的JAK/STAT3通路抑制活性是由于靶向STAT3而导致。
| Table 1 Kinase inhibitory activity of LZJ541 (10 μmol·L-1). EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; SRC: Sarcoma gene |
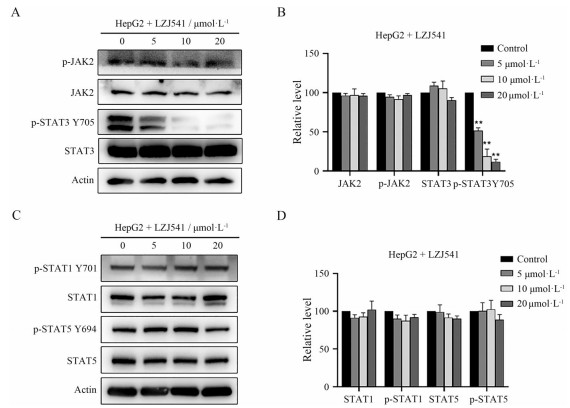
STAT3蛋白酪氨酸705位磷酸化(Y705) 是其活化形式, STAT3磷酸化后形成二聚体并进入细胞核, 进一步激活下游靶基因, 从而驱动肿瘤细胞增殖与凋亡抵抗[12]。为了验证LZJ541的JAK/STAT3通路抑制活性是否由于靶向STAT3激活所导致, 通过Western blot实验检测了不同浓度(0、5、10、20 μmol·L-1) LZJ541处理后HepG2细胞中STAT3、p-STAT3 Y705及上游激酶JAK2、p-JAK2蛋白的表达。结果如图 3A、B所示, LZJ541能剂量依赖地抑制p-STAT3 Y705蛋白的表达, 而对STAT3总蛋白表达无明显影响, 对上游JAK2激酶及其磷酸化也未见明显抑制。STAT1与STAT5具有与STAT3类似的SH2结构域, 同样是通过磷酸化形成二聚体的方式诱导下游靶基因的表达, 本研究通过Western blot实验检测了LZJ541对HepG2细胞STAT1与STAT5磷酸化的影响, 结果如图 3C、D所示, LZJ541对STAT1及STAT5的磷酸化影响不明显, 同时也不会影响STAT1与STAT5的表达。以上结果提示, LZJ541可能通过抑制STAT3 Y705位磷酸化而阻断JAK/STAT3通路的活化, 并对STAT1与STAT5没有明显影响。
|
Figure 3 LZJ541 significantly inhibited the expression of p-STAT3 Y705 in HepG2 cells. A: The levels of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway related proteins were detected via Western blot in HepG2 cells exposure to various concentrations of LZJ541 for 24 h; B: Histogram of the relative expression level of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3 and p-STAT3 Y705; C: The levels of STAT1, p-STAT1 Y701, STAT5, p-STAT5 Y694 were detected by Western blot in HepG2 cells exposure to LZJ541; D: Histogram of the relative expression level of STAT1, p-STAT1 Y701, STAT5, p-STAT5 Y694. **P < 0.01 vs control group |
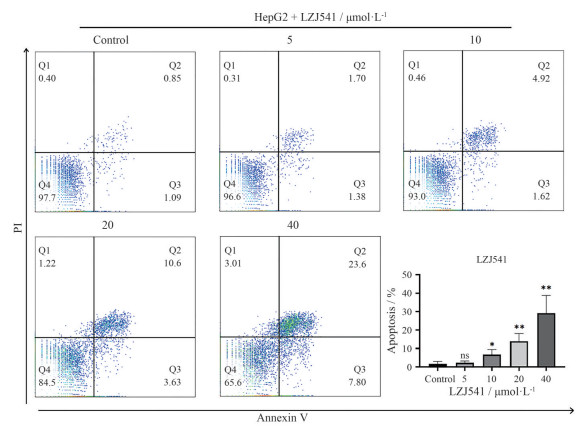
为了进一步探究LZJ541的体外抗HepG2机制, 通过流式细胞仪检测LZJ541对HepG2细胞凋亡水平的影响。结果如图 4所示, 以不同浓度LZJ541 (0、5、10、20、40 μmol·L-1) 处理HepG2细胞48 h后, LZJ541能浓度依赖地促进HepG2细胞凋亡, 凋亡率分别为(1.68 ± 1.34) %、(2.17 ± 1.03) % (P = 0.64)、(6.63 ± 2.76) % (P = 0.04)、(13.90 ± 4.25) % (P = 0.009)、(29.13 ± 9.67) % (P = 0.008), 差异具有统计学意义。
|
Figure 4 Flow cytometric analysis of the apoptotic effect of LZJ541 in HepG2 cells through Annexin-V-FITC/PI staining assay. LZJ541 promoted apoptosis of HepG2 cells in a concentration-dependent manner and the histograms for apoptosis rate. |
在不同浓度LZJ541 (0、5、10、20、40 μmol·L-1) 处理HepG2细胞24 h后, 进一步通过流式细胞仪检测LZJ541对HepG2细胞周期分布的影响。结果如图 5所示, LZJ541处理24 h后, HepG2细胞G1期分布百分比分别增加到(67.1 ± 1.15) %、(71.0 ± 1.2) %、(73.7 ± 1.6) %、(76.24 ± 1.6) %, 说明LZJ541可诱导HepG2细胞G1期阻滞。
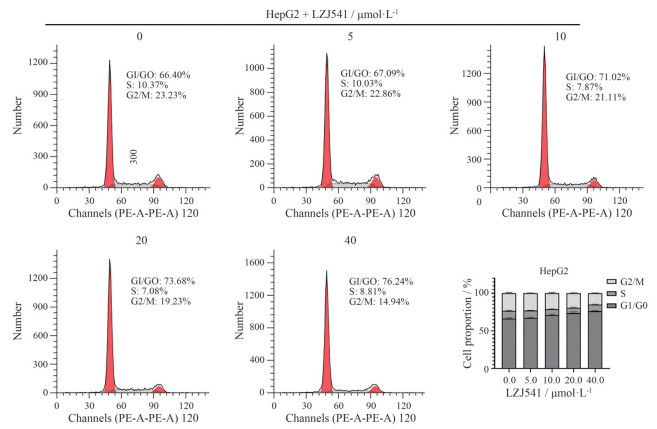
|
Figure 5 Cell cycle analysis of LZJ541 by flow cytometry. HepG2 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of LZJ541 for 24 h. LZJ541 induced G1 phase arrest of HepG2 in a dose-dependent manner. |
综上, LZJ541能通过抑制HepG2细胞STAT3磷酸化激活, 诱导细胞凋亡和G1期阻滞, 从而抑制HepG2细胞的体外增殖。
讨论2020年我国新增肝癌病例超过41万例, 死亡人数超过39万[13], 肝癌以因其高发病率与极差的预后成为国人健康面临的一大威胁。近年来肝癌靶向治疗取得了一定进展, 索拉菲尼和乐伐替尼是目前非手术治疗的一线用药[14], 然而靶向药物对晚期肝癌患者总生存期的延长十分有限[15], 因此进一步研究肝癌发病机制, 发现新的抗肝癌药物具有重要意义。
STAT3在多种恶性肿瘤中异常激活, 促进肿瘤细胞增殖, 抑制凋亡[3], 针对STAT3抑制剂的开发已历时20余年, 目前有多种STAT3抑制剂正处于临床研究阶段, 其中美国波士顿生物医学公司研发的BBI608是目前唯一一个被FDA批准应用于临床的STAT3抑制剂[4], 而其他抑制剂如日本大冢制药公司STAT3抑制剂OPB-31121则由于其活性与外周神经系统毒性等原因终止于临床I期试验[16], 可见提高STAT3抑制剂的靶向性与活性, 降低不良反应, 仍是现阶段STAT3抑制剂研发面临的重要挑战。现有研究证实, JAK/STAT3信号通路与肝癌的发生发展密切相关[17, 18], 然而目前还未有STAT3靶向药物应用于肝癌的治疗。在本研究中, 小分子化合物LZJ541具有明确的STAT3靶点活性, 能通过抑制肝癌HepG2细胞中STAT3蛋白的磷酸化, 诱导细胞凋亡和G1期阻滞, 从而显著抑制HepG2细胞增殖(IC50: 13.8 ± 1.85 μmol·L-1), 具有明确的体外抗肝癌活性。
LZJ541具有苯并二咪唑结构, 这类结构在既往研究中被认为是分子探针的优势前体, 本研究率先发现了其STAT3抑制活性, 提示在新型药物的开发中也应关注某些功能结构, 其药理活性不应被忽视。在后续研究中, 会对LZJ541进行进一步结构优化与筛选, 提升其靶点活性及抗肿瘤活性, 并通过建立异位移植瘤模型对其及其衍生物的体内抗肿瘤活性加以探索, 进一步探究其抗肝癌机制。
综上, 本研究发现苯并二咪唑结构化合物LZJ541具有抑制IL6/JAK/STAT3信号通路的作用, 并首次验证了其抗肝癌细胞体外增殖活性, 为开发新型STAT3小分子抑制剂及通过抑制STAT3信号通路治疗肝癌提供实验基础。
作者贡献: 刘羿晨负责主要实验操作、部分实验设计和部分论文撰写; 季鸣和杜婷婷参与实验操作和论文修改; 刘文强和李莉负责化合物合成及结构改造; 陈晓光负责实验设计、论文撰写及修改。
利益冲突: 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
| [1] |
Banerjee K, Resat H. Constitutive activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: a review[J]. Int J Cancer, 2016, 138: 2570-2578. DOI:10.1002/ijc.29923 |
| [2] |
Ji Y, Liu Y, Xue N, et al. Cryptotanshinone inhibits esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo through the suppression of STAT3 activation[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 883-896. DOI:10.2147/OTT.S187777 |
| [3] |
Lee H, Jeong AJ, Ye SK. Highlighted STAT3 as a potential drug target for cancer therapy[J]. BMB Rep, 2019, 52: 415-423. DOI:10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.7.152 |
| [4] |
Yee NS. Update in systemic and targeted therapies in gastrointestinal oncology[J]. Biomedicines, 2018, 6: 34. DOI:10.3390/biomedicines6010034 |
| [5] |
Boydston AJ, Vu PD, Dykhno OL, et al. Modular fluorescent benzobis(imidazolium) salts: syntheses, photophysical analyses, and applications[J]. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130: 3143-3156. DOI:10.1021/ja7102247 |
| [6] |
Ji M, Xue N, Huang R, et al. Validation and application a cell-based screening model for IL-6/JAK/STAT3 inhibitor[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2018, 53: 749-753. |
| [7] |
Xu L, Lao Y, Zhao Y, et al. Screening active compounds from garcinia species native to China reveals novel compounds targeting the STAT/JAK signaling pathway[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 2015: 910453. |
| [8] |
Jin Y, Chen X, Gao Z, et al. Bisdemethoxycurcumin alleviates vandetanib-induced cutaneous toxicity in vivo and in vitro through autophagy activation[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 144: 112297. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112297 |
| [9] |
Zheng X, Xu K, Zhu L, et al. MiR-486-5p act as a biomarker in endometrial carcinoma: promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion by targeting MARK1[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2020, 13: 4843-4853. DOI:10.2147/OTT.S246841 |
| [10] |
Zhang Y, Lu W, Zhang X, et al. Cryptotanshinone protects against pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting Smad and STAT3 signaling pathways[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2019, 147: 104307. DOI:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104307 |
| [11] |
Chen Y, Ji M, Zhang S, et al. Bt354 as a new STAT3 signaling pathway inhibitor against triple negative breast cancer[J]. J Drug Target, 2018, 26: 920-930. DOI:10.1080/1061186X.2018.1452244 |
| [12] |
Kao JT, Feng CL, Yu CJ, et al. IL-6, through p-STAT3 rather than p-STAT1, activates hepatocarcinogenesis and affects survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a cohort study[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2015, 15: 50. DOI:10.1186/s12876-015-0283-5 |
| [13] |
Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, et al. Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: a secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2021, 134: 783-791. DOI:10.1097/CM9.0000000000001474 |
| [14] |
Ko KL, Mak LY, Cheung KS, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent advances and emerging medical therapies[J]. F1000Res, 2020, 9: F1000Faculty Rev-620. |
| [15] |
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391: 1163-1173. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30207-1 |
| [16] |
Okusaka T, Ueno H, Ikeda M, et al. Phase 1 and pharmacological trial of OPB-31121, a signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 inhibitor, in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatol Res, 2015, 45: 1283-1291. DOI:10.1111/hepr.12504 |
| [17] |
Wan S, Zhao E, Kryczek I, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages produce interleukin 6 and signal via STAT3 to promote expansion of human hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 147: 1393-1404. DOI:10.1053/j.gastro.2014.08.039 |
| [18] |
Liu Y, Luo YH, Li SM, et al. 2-(Naphthalene-2-thio)-5, 8-dimethoxy-1, 4-naphthoquinone induces apoptosis via ROS-mediated MAPK, AKT, and STAT3 signaling pathways in HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Drug Chem Toxicol, 2022, 45: 33-43. DOI:10.1080/01480545.2019.1658767 |
 2022, Vol. 57
2022, Vol. 57


