2. 河南大学药学院, 河南 开封 475004;
3. 河南大学天然药物与免疫工程重点实验室, 河南 开封 475004
2. School of Pharmacy, Henan University, Kaifeng 475004, China;
3. The Key Laboratory of Natural Medicine and Immuno-Engineering, Henan University, Kaifeng 475004, China
食管癌(esophageal cancer, EC)是临床常见的一种起源于食管黏膜上皮的恶性肿瘤。在全世界范围内, 食管癌的发病率在各种恶性肿瘤中位居第8位, 其死亡率位居第6位[1]。食管癌主要包括两种组织学类型, 即腺癌和食管鳞状细胞癌(esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, ESCC)。我国是世界上食管癌发病率和死亡率最高的国家, 约占全世界70%的食管癌病例, 其中近95%的患者为食管鳞癌[2]。目前, 虽然在包括手术、放射治疗、化学治疗以及综合上述治疗手段等方面取得了显著的成就, 但食管鳞癌的治疗效果并不能令人满意, 其术后总体5年生存率不足20%[3]。肿瘤侵袭和转移是导致食管鳞癌患者死亡的一个重要原因[3], 因此, 当前迫切需要寻找毒性较低, 而且能够有效控制食管鳞癌侵袭和转移的药物。
黄芩素(baicalein)又被称作黄芩苷元, 是从中药材黄芩的根部分离得到的一种天然黄酮类化合物。研究表明, 黄芩素具有抗炎、抗病毒、抗氧化和抑制黄嘌呤氧化酶等多种生物学活性。近年来研究发现黄芩素对鼻咽癌[4]、非小细胞肺癌[5]、胶质瘤[6]和甲状腺癌[7]等多种肿瘤细胞具有很强抑制作用, 其作用机制主要包括抑制肿瘤细胞生长[4], 诱导凋亡和自噬[7], 以及增强肿瘤细胞对化疗药物的敏感性[5]。此外, 一些研究表明黄芩素不仅能够显著抑制前列腺癌[8]、结直肠癌[9]、乳腺癌[10]、骨肉瘤[11]和胰腺癌[12]等多种肿瘤细胞在体外的迁移和侵袭, 而且能够明显地降低乳腺癌[10]和胰腺神经内分泌肿瘤[13]细胞在裸鼠体内的转移能力。2013年, Zhang等[14]报道黄芩素能够有效抑制食管鳞癌EC-109细胞生长, 并诱导细胞凋亡。然而, 关于黄芩素对食管鳞癌细胞迁移和侵袭的作用仍不清楚。本实验选用人食管鳞癌细胞EC9706和KYSE30为研究对象, 旨在探究黄芩素对食管鳞癌细胞迁移和侵袭的作用及潜在分子机制, 为黄芩素作为先导化合物用于转移性食管鳞癌的药物设计提供了有力依据。
材料与方法细胞系 人食管鳞癌EC9706和KYSE30细胞株购自中国科学院上海细胞库, 用含10%胎牛血清的DMEM (Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium)培养基(含100 μg·mL-1链霉素和100 u·mL-1青霉素), 置于5%CO2、37℃细胞培养箱中培养。每2~3天对细胞进行传代, 取处于对数生长期的细胞用于以下所有实验。
试剂 胎牛血清(浙江天杭生物科技股份有限公司); DMEM培养基、胰蛋白酶、四甲基偶氮唑蓝(MTT)、U0126和actin抗体(Sigma公司); 黄芩素(批号24282, MCE公司), 用二甲基亚砜配制成浓度为200 mmol·L-1储备液, 于-80℃冻存备用; 基质胶matrigel matrix (BD公司); Transwell小室(Corning公司); 上皮型钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)、神经型钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)、波形蛋白(Vimentin)、果蝇蜗牛同源蛋白(Snail)、细胞外信号调节激酶1/2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, ERK1/2)、p-ERK1/2 (T202/Y204)、含ETS域蛋白1 (ETS-domain containing protein-1, ELK-1)、p-ELK-1 (S383)一抗以及ERK1/2 siRNA (货号6560)(Cell Signaling Technology公司); Lipofectamine® RNAi MAX Reagent(Life Technologies公司)。
实验动物 SPF (specific pathogen free)级BALB/c-nu雄性小鼠, 18~22 g, 购自中国北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司, 合格证号SCXK (京) 2016-0006。饲养条件: (22±1)℃; 相对湿度: (65±10)%; 明暗循环照明: 各12 h。本文中动物福利和实验过程均遵循河南大学实验动物伦理委员会的规定。
MTT法测定ESCC细胞的增殖活性[15] 取处于对数生长期ESCC细胞, 调整细胞密度为每毫升6×104个, 将该细胞悬液接种于96孔板中, 每孔加入50 μL细胞悬液。培养24 h后加入50 μL不同浓度(终浓度分别为0、5、10、20、40、80和160 μmol·L-1)的黄芩素溶液, 放置细胞培养箱继续培养44 h, 每孔加入20 μL浓度为5 mg·mL-1的MTT溶液。孵育4 h后, 弃上清, 每孔加入100 μL DMSO后放置摇床上振摇10 min, 用酶标仪检测570 nm波长处吸光度值。
细胞划痕实验检测ESCC细胞的迁移能力[15] 取对数生长期细胞, 调整细胞密度为每毫升5×105个, 将该细胞悬液加至6孔板中, 每孔加入2 mL, 放置细胞培养箱中培养24 h后使其形成单层细胞。用200 μL的无菌枪头垂直于板底画直线。用无菌PBS (phosphate buffered saline)溶液洗去脱落细胞, 分别加入终浓度为2.5、5和10 μmol·L-1黄芩素溶液, 用倒置显微镜分别在0、24和48 h时拍照, 并计算细胞迁移率。细胞迁移率=(0 h时的划痕宽度-某个时间点的划痕宽度)/0 h时的划痕宽度×100%。
Transwell实验测定ESCC细胞的迁移和侵袭[15] 分别收集经过不同浓度(2.5、5和10 μmol·L-1)黄芩素溶液处理的EC9706和KYSE30细胞, 用不含血清的DMEM培养基重悬并计数。对于Transwell迁移实验, 将含有5×104个细胞的200 μL细胞悬液加至Transwell小室上层, 下室中加入600 μL含10%FBS的培养基。培养24 h后, 去除上下层培养液, 将Transwell小室取出, 用甲醇固定20 min后, 再用0.1%的结晶紫溶液染色10 min, 最后用棉棒去除Transwell上室细胞。待其自然晾干后, 用倒置显微镜拍照, 随机选取6个视野统计穿过小室的平均细胞数目。对于细胞侵袭实验, 预先在Transwell上室加入matrigel, 待其凝固后, 将含有1×105个细胞的200 μL细胞悬液加至Transwell小室上层, 后续操作步骤同上所述。
裸鼠肺转移模型检测黄芩素对ESCC转移的影响 收集对数生长期KYSE30细胞, 用无菌PBS溶液调整细胞密度为每毫升1×107个[16]。通过尾静脉接种于裸鼠体内, 每只小鼠接种100 μL细胞悬液(即1×106个细胞)。培养24 h后, 将小鼠随机分成两组, 每组5只。实验组黄芩素(50 mg·kg-1, 使用玉米油溶解), 空白对照组每天给予相应体积的溶剂(玉米油), 采用灌胃法给药, 每隔1天给药1次, 连续给药3周[17]。继续饲养5周后, 将小鼠麻醉后处死, 取出肺组织, 浸泡于Bouin氏液(苦味酸饱和液∶福尔马林∶冰醋酸=15∶5∶1)中, 24 h后, 统计两组小鼠肺组织表面的肿瘤结节数目。然后将小鼠肺组织进行石蜡包埋和常规苏木素-伊红(hematoxylin-eosin, H & E)染色检测肺组织内部的肿瘤结节数目。
Western blot法检测ESCC细胞中蛋白表达情况[18] 取处于对数生长期的EC9706和KYSE30细胞, 调整细胞密度为每毫升1×105个, 将该细胞悬液加至10 cm细胞培养皿中, 每皿体积10 mL, 24 h后, 分别加入终浓度为2.5、5和10 μmol·L-1黄芩素溶液。培养48 h后收集细胞, 加入含有蛋白酶抑制剂和磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA裂解液, 冰上裂解30 min, 用超声波细胞破碎仪处理后, 在4℃, 12 000 r·min-1离心10 min, 取上清液。用BCA法测定蛋白浓度后, 分别取30 μg蛋白加入一定量5×上样缓冲液, 95℃变性10 min。将该蛋白加至10%SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulphate-poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis)胶中电泳后, 电转移至硝酸纤维素膜上; 5%脱脂牛奶室温封闭1 h; 于4℃冰箱孵育一抗过夜; PBST (phosphate buffered saline with tween 20)洗3次, 每次10 min; 加入与一抗相对应的辣根酶标记的二抗, 室温孵育2 h后, PBST洗3次, 每次10 min。使用ECL (electrochemiluminescence)化学发光试剂盒及免疫印迹成像系统检测目的条带。
统计学方法 所有统计分析均使用Graphpad Prism 6.0软件。每个实验至少重复3次, 所有统计数据采用x±s表示。各组实验的组间差异采用单因素方差分析(analysis of variance, ANOVA)检验。P < 0.05认为差异具有统计学意义。
结果 1 黄芩素对食管鳞癌细胞增殖的影响为了检测黄芩素对食管鳞癌细胞活力的影响, 使用不同浓度(0~160 μmol·L-1)黄芩素(图 1A)分别处理EC9706和KYSE30细胞, 48 h后采用MTT法检测细胞活性。结果显示, 低于20 μmol·L-1的黄芩素对EC9706和KYSE30细胞的生长没有明显的改变(图 1B); 40~160 μmol·L-1的黄芩素能够显著地抑制食管鳞癌细胞的生长, 且具有浓度依赖性(图 1B); 黄芩素对EC9706和KYSE30细胞的半数抑制浓度(half-inhibitory concentration, IC50)分别为(51.49±4.15)和(52.44±3.38) μmol·L-1(图 1B)。
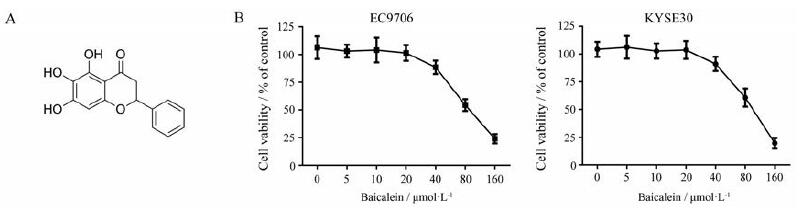
|
Figure 1 The inhibitory effect of baicalein on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell growth.A: The chemical structure of baicalein; B: Baicalein inhibited the proliferation of EC9706 and KYSE30 cells.n=4, x±s |
采用细胞划痕实验检测黄芩素对食管鳞癌细胞的迁移能力的影响。结果显示, 在24 h时, 与对照组相比, 10 μmol·L-1的黄芩素能够明显地降低EC9706和KYSE30细胞的迁移率; 在48 h时, 2.5、5和10 μmol·L-1黄芩素均能显著地抑制EC9706和KYSE30细胞的迁移能力, 且具有浓度依赖性(图 2A)。为了进一步验证这一结果, 采用Transwell迁移实验检测黄芩素对食管鳞癌细胞迁移能力的影响。实验结果显示, 与对照组相比, 不同浓度黄芩素(2.5、5和10 μmol·L-1)均能显著地降低穿过Transwell小室的细胞数目(图 2B)。以上实验结果表明, 黄芩素能够抑制食管鳞癌细胞的迁移。
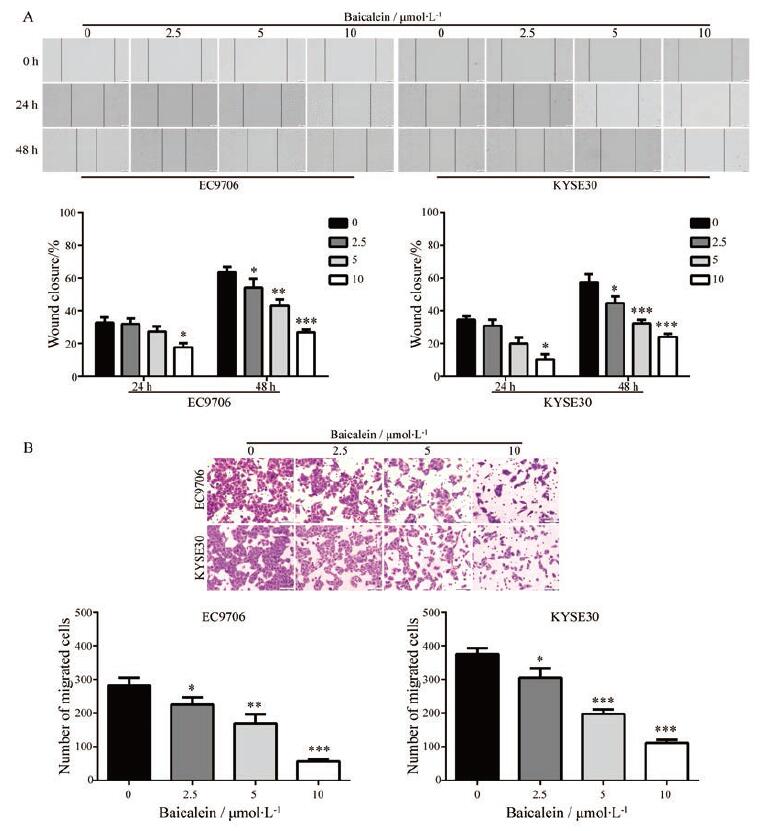
|
Figure 2 Baicalein suppressed the migration of ESCC cells.A: The anti-migrated effect baicalein was detected by wound healing assay after treatment for the indicated time; B: The anti-migrated effect of baicalein was assessed after treatment for 48 h by using Transwell migration assay.Scale bar: 100 μm.n=6, x±s.*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs control group |
为了检测黄芩素是否改变食管鳞癌细胞的侵袭能力, 将经过不同浓度黄芩素(2.5、5和10 μmol·L-1)处理的食管鳞癌细胞接种于预先铺有matrigel的Transwell小室中培养24 h。如图 3所示, 与对照组相比, 黄芩素处理组中穿过Transwell小室的细胞数目均明显地减少, 而且具有剂量依赖性, 表明黄芩素可显著地降低食管鳞癌细胞的侵袭能力。
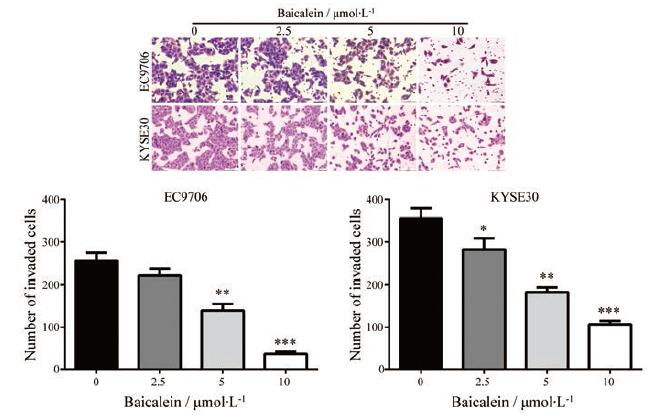
|
Figure 3 Baicalein inhibited the invasion of ESCC cells.EC9706 and KYSE30 cells were treated with the indicated concentration of baicalein for 48 h, and then the cell invasion was measured by using Transwell assay (with matrigel).n=6, x±s.*P < 0.05, **P < 0. 01, ***P < 0. 0 0 1 vs control group |
应用食管鳞癌KYSE30细胞实验构建裸鼠肺转移模型, 检测黄芩素在体内对ESCC转移的影响。结果显示, 黄芩素处理组小鼠肺组织表面的肿瘤转移灶数目明显减少, 与对照组相比具有显著统计学差异(图 4A); 进一步采用苏木素-伊红染色法检测小鼠肺组织内部的肿瘤转移情况, 与对照组相比, 黄芩素处理组小鼠肺组织内部的肿瘤数目也显著降低(图 4B)。以上数据表明黄芩素能够显著抑制食管鳞癌转移。
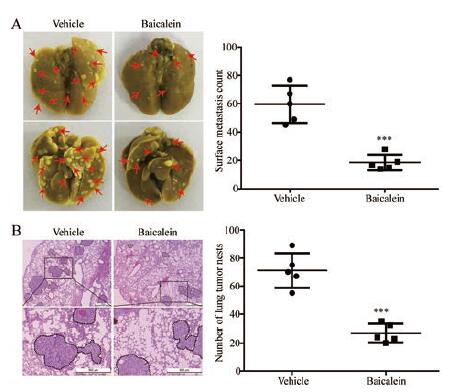
|
Figure 4 Baicalein diminished the lung metastasis of ESCC.A: KYSE30 cells were intravenously injected into nude mice via the tail vein.Left, representative images of excised lungs after 8 weeks injection (arrows indicated the metastatic nodules); right, graph showing the number of surface metastatic foci in the lungs; B: Representative hematoxylin-eosin (H & E) images of harvested lung sections and graph showing the number of metastatic colonization within the lung tissues (right).Scale bar: 500μm.n=5, x±s.***P < 0.001 vs vehicle group |
研究表明ERK1/2信号通路的异常活化在促进ESCC细胞迁移、侵袭和转移中起着非常重要的作用[3], 本研究采用Western blot法检测黄芩素对ERK1/2总蛋白表达及磷酸化的影响。结果显示, 黄芩素呈浓度依赖性抑制ERK1/2 (T202/Y204)的磷酸化, 但对ERK1/2总蛋白的表达没有明显的改变。此外, 黄芩素能够显著地降低参与调控上皮间质转化(epithelial mesenchymal transition, EMT)发生的重要转录因子果蝇蜗牛同源蛋白(Snail)的蛋白表达, 表明黄芩素可能通过ERK信号通路抑制ESCC细胞EMT的发生; 黄芩素以呈剂量依赖性的方式抑制间质细胞标志物神经型钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)和波形蛋白(Vimentin)的蛋白表达, 同时上调上皮细胞标志物上皮型钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)的表达(图 5A), 表明黄芩素可能通过ERK/Snail抑制ESCC细胞EMT的发生。
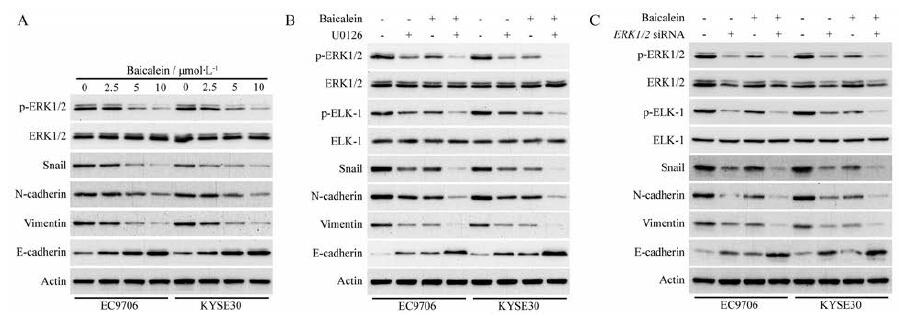
|
Figure 5 Baicalein suppressed ERK/ELK-1/Snail signaling pathway in ESCC cells.A: EC9706 and KYSE30 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of baicalein for 48 h, and then the expression of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin, Snail, ERK1/2, and p-ERK1/2(T202/Y204) was detected using Western blot analysis; B: U0126 enhanced the inhibitory effect of baicalein on ERK/ELK-1/Snail signaling pathway in EC9706 and KYSE30 cells.EC9706 and KYSE30 cells were treated with U0126 (10 μmol·L-1), baicalein (5 μmol·L-1), or both compounds for 48 h; C: ERK1/2 siRNA promoted the action of baicalein on ERK/ELK-1/Snail signaling pathway in ESCC cells.EC9706and KYSE30 cells were treated with ERK1/2 siRNA (100 nmol·L-1), baicalein (5 μmol·L-1), or both compounds for 48 h.ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; ELK-1:ETS-domain containing protein-1 |
有研究表明异常活化的ERK可以通过激活其下游靶点ELK-1在丝氨酸383位点的磷酸化, 进而促进Snail的蛋白表达[19]。Western blot实验检测结果显示, 黄芩素(5 μmol·L-1)能够显著降低EC9706和KYSE30细胞中ELK-1 (Ser383)的磷酸化; ERK1/2抑制剂U0126不仅能够显著下调ELK-1 (Ser383)的磷酸化和转录因子Snail的蛋白表达, 而且能显著增强黄芩素对磷酸化ERK1/2 (T202/Y204)、磷酸化ELK-1 (S383)、Snail以及间质细胞标志物N-cadherin和Vimentin的抑制作用, 增强黄芩素对上皮细胞标志蛋白E-cadherin的上调作用(图 5B)。使用siRNA敲低ERK1/2能够得到与U0126作用类似的结果(图 5C)。以上研究结果表明, 黄芩素可能通过阻断ERK/ELK-1/Snail信号通路, 从而抑制ESCC细胞EMT的发生、迁移、侵袭和转移。
讨论由于食管鳞癌在早期阶段无明显病理特征, 大多数患者在就诊时已处于中晚期, 伴随着肿瘤细胞转移至临近淋巴结, 甚至远端组织或器官[20]。尽管包括手术切除、放疗和化疗等多种治疗手段的应用使食管鳞癌患者的总体生存率得到很大改善, 但是大多数食管鳞癌患者的预后仍不理想[3, 20]。因此, 当前亟需研究新的高效低毒的治疗药物。本研究发现低浓度黄芩素能够显著抑制食管鳞癌细胞的迁移和侵袭能力, 提示该化合物可能成为未来治疗转移性食管鳞癌的药物。
黄芩是一种广泛应用于临床的中草药, 主要用于治疗呼吸道感染、腹泻和肝炎等多种疾病[21]。黄芩素是从黄芩根部提取得到的一种主要成分[21]。一些研究表明黄芩素能够有效抑制肝癌[22, 23]、胰腺癌[24]和鼻咽癌[4]等肿瘤细胞的生长, 并诱导凋亡。此外, Zhang等[14]报道黄芩素能够通过PI3K/Akt信号通路有效抑制食管鳞癌EC-109细胞生长, 并诱导细胞发生凋亡。但是, 到目前为止, 关于黄芩素是否能够抑制食管鳞癌细胞的转移仍未见报道。在本研究中, 作者发现低浓度(2.5~10 μmol·L-1)的黄芩素对食管鳞癌细胞的生长没有明显影响, 但是能够显著抑制细胞的迁移、侵袭及EMT发生; 此外, 黄芩素在体内还能够显著减少食管鳞癌肺转移。与作者研究结果一致的是, 黄芩素已被发现能够有效抑制肝癌[21]、乳腺癌[10]和前列腺癌[8]等多种恶性肿瘤的迁移、侵袭和转移。这些研究表明, 黄芩素对多种转移性癌症均具有很好的治疗价值。
ERK信号通路在包括食管鳞癌在内的多种恶性肿瘤中存在异常活化, 异常活化的ERK通过激活下游靶点(例如ELK-1等), 从而促进肿瘤细胞的生长、侵袭和转移[3, 25, 26]。Wang等[27]采用免疫组化实验检测pERK1/2 (T202/Y204)蛋白在131例食管鳞癌标本中的表达情况, 结果发现50.4%的标本中存在高表达的pERK1/2 (T202/Y204)。使用小分子抑制剂U0126特异性地阻断MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase)/ERK信号通路能够显著地抑制食管鳞癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[3]。在本研究中, 作者发现黄芩素不改变ERK1/2总蛋白的表达, 但能够显著减少ERK1/2 (T202/Y204)和ELK-1 (S383)的磷酸化; 此外, 使用ERK1/2抑制剂U0126不仅能够显著增强黄芩素对p-ERK1/2 (T202/Y204)、p-ELK-1 (S383)、Snail以及间质细胞标志物N-cadherin和Vimentin的抑制作用, 而且可增强黄芩素对上皮细胞标志蛋白E-cadherin的上调, 表明黄芩素通过ERK/ELK-1/Snail信号通路阻断食管鳞癌细胞EMT发生, 进而抑制食管鳞癌细胞迁移、侵袭和转移。然而, 关于黄芩素如何下调ERK信号通路, 以及是否通过其他靶点发挥作用仍有待进一步深入研究。
综上所述, 本研究发现黄芩素能够有效抑制食管鳞癌细胞迁移、侵袭和转移, 其作用机制可能是通过ERK/ELK-1/Snail信号通路阻断食管鳞癌细胞EMT的发生。本研究结果表明黄芩素具有很好的抗食管鳞癌转移的作用, 为黄芩素用于转移性食管鳞癌的临床治疗提供了有力依据。
作者贡献:陈亮负责提出研究思路、设计研究方案及修改文章; 王建涛和曾荟珊为实验的执行者并撰写文章初稿; 韦珍负责数据采集和分析。全体作者都阅读并同意最终的文本。
利益冲突:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
| [1] |
Hu X, Zhai Y, Kong P, et al. FAT1 prevents epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) via MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2017, 397: 83-93. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.033 |
| [2] |
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality world-wide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68: 394-424. DOI:10.3322/caac.21492 |
| [3] |
Chen L, Bi S, Hou J, et al. Targeting p21-activated kinase 1 inhibits growth and metastasis via Raf1/MEK1/ERK signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2019, 17: 31. DOI:10.1186/s12964-019-0343-5 |
| [4] |
Guo J, You H, Li D. Baicalein exerts anticancer effect in naso-pharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo[J]. Oncol Res, 2019, 27: 601-611. DOI:10.3727/096504018X15399945637736 |
| [5] |
Lu L, Zhang M, Wang X, et al. Baicalein enhances the antitumor efficacy of docetaxel on nonsmall cell lung cancer in a betacatenin-dependent manner[J]. Phytother Res, 2020, 34: 104-117. DOI:10.1002/ptr.6501 |
| [6] |
Liu B, Ding L, Zhang L, et al. Baicalein induces autophagy and apoptosis through AMPK pathway in human glioma cells[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2019, 47: 1405-1418. DOI:10.1142/S0192415X19500721 |
| [7] |
Wang M, Qiu S, Qin J. Baicalein induced apoptosis and autophagy of undifferentiated thyroid cancer cells by the ERK/PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2019, 11: 3341-3352. |
| [8] |
Guo Z, Hu X, Xing Z, et al. Baicalein inhibits prostate cancer cell growth and metastasis via the caveolin-1/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2015, 406: 111-119. DOI:10.1007/s11010-015-2429-8 |
| [9] |
Rui X, Yan XI, Zhang K. Baicalein inhibits the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of the AKTsignaling pathway[J]. Oncol Lett, 2016, 11: 685-688. DOI:10.3892/ol.2015.3935 |
| [10] |
Ma X, Yan W, Dai Z, et al. Baicalein suppresses metastasis of breast cancer cells by inhibiting EMT via downregulation of SATB1 and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2016, 10: 1419-1441. |
| [11] |
Zhang J, Yang W, Zhou YB, et al. Baicalein inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion through the miR183/Ezrin pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18: 1104-1112. |
| [12] |
Zhou RT, He M, Yu Z, et al. Baicalein inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and invasion via suppression of NEDD9 expression and its downstream Akt and ERK signaling pathways[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8: 56351-56363. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.16912 |
| [13] |
Tian Y, Zhen L, Bai J, et al. Anticancer effects of baicalein in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in vitro and in vivo[J]. Pancreas, 2017, 46: 1076-1081. DOI:10.1097/MPA.0000000000000895 |
| [14] |
Zhang HB, Lu P, Guo QY, et al. Baicalein induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells through modulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Oncol Lett, 2013, 5: 722-728. DOI:10.3892/ol.2012.1069 |
| [15] |
Bi S, Wei Q, Zhao Z, et al. Wee1 inhibitor AZD1775 effectively inhibits the malignant phenotypes of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 864. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2019.00864 |
| [16] |
Chen L, Wei Q, Bi S, et al. Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase promotes tumor growth and metastasis via stimulating FOXM1 signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 10. DOI:10.3389/fonc.2020.00010 |
| [17] |
Zhao X, Qu J, Liu X, et al. Baicalein suppress EMT of breast cancer by mediating tumor-associated macrophages polarization[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2018, 8: 1528-1540. |
| [18] |
Chen L, Pan J. Dual cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibition by PD-0332991 induces apoptosis and senescence in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2017, 174: 2427-2443. DOI:10.1111/bph.13836 |
| [19] |
Hsu YL, Hou MF, Kuo PL, et al. Breast tumor-associated osteo-blast-derived CXCL5 increases cancer progression by ERK/MSK1/ELK-1/Snail signaling pathway[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32: 4436-4447. DOI:10.1038/onc.2012.444 |
| [20] |
Zhao Y, Lu Q, Li C, et al. PRMT1 regulates the tumour-initiating properties of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through histone H4 arginine methylation coupled with transcriptional activation[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10: 359. DOI:10.1038/s41419-019-1595-0 |
| [21] |
Chen K, Zhang S, Ji Y, et al. Baicalein inhibits the invasion and metastatic capabilities of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via down-regulation of the ERK pathway[J]. PLo S One, 2013, 8: e72927. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0072927 |
| [22] |
He K, Yu X, Wang X, et al. Baicalein and Ly294002 induces liver cancer cells apoptosis via regulating phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway[J]. J Cancer Res Ther, 2018, 14: S519-S525. DOI:10.4103/0973-1482.235356 |
| [23] |
Li J, Duan B, Guo Y, et al. Baicalein sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to 5-FU and Epirubicin by activating apoptosis and ameliorating P-glycoprotein activity[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 98: 806-812. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.002 |
| [24] |
Li Z, Zou X, Zhu H, et al. Inhibitory effect of baicalein combined with gemcitabine in human pancreatic cancer cell lines[J]. Oncol Lett, 2018, 15: 5459-5464. |
| [25] |
Cao J, Wang L, Wang L, et al. Ricolinostat (ACY-1215) suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via miR-30d/PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERKpathways[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9: 817. DOI:10.1038/s41419-018-0788-2 |
| [26] |
Qi SM, Jiang Q, Li Q, et al. Antimetastatic effects of cordycepin and its molecular mechanism inhuman hepatoma MHCC97Hcells in vitro and in vivo[J]. Acta Pharm Sin(药学学报), 2019, 54: 1431-1438. |
| [27] |
Wang H, Zhang Y, Yun H, et al. ERK expression and its correlation with STAT1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8: 45249-45258. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.16902 |
 2021, Vol. 56
2021, Vol. 56


