2. 南方医科大学中医药学院, 广东 广州 510515
2. College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China
慢性肾脏病(chronic renal disease, CKD)作为威胁人类健康的重大疾病, 具有高致死率和致残率, 是公认的全球公共卫生问题[1]。纤维化是各种器质性疾病发展至终末期的标志和共同途径, 因此抑制肾纤维化是减缓CKD发展的重要手段[2]。肾纤维化的发病机制错综复杂, 故难以进行针对性治疗, 目前临床常用抗炎、抗氧化、抗凋亡和降脂等药物进行控制, 但疗效并不显著, 且长期服用甚至出现不良反应[3-6]。
白花蛇舌草(Hedyotis diffusa Willd)是茜草科植物, 始载于《广西中药志》, 于2010年收载于《中国人民共和国药典》 (一部)附录, 为中成药的原料药, 其性微寒, 味甘, 具有清热解毒、利湿消肿和活血定痛功效, 主要用于抗肿瘤、抗氧化、抗炎和调节免疫等治疗[6-8]。本课题组前期已从化学成分和药理活性方面对白花蛇舌草进行大量研究, 在脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide, LPS)诱导的肾损伤小鼠模型中验证了白花蛇舌草水提液的肾脏保护作用, 发现其可降低小鼠血浆和肾脏肿瘤坏死因子α (tumor necrosis factor alpha, TNF-α)、白介素6 (interleukin 6, IL6)和白介素10 (IL10)等炎症因子的表达, 而且发现在LPS诱导的小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞(leukemia cells in mouse macrophage, RAW264.7)的炎症细胞模型中, 鸡屎藤次苷、车叶草苷和车叶草苷酸均可通过抑制NF-κB (nuclear factor-kappa B)和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinase, MAPK)信号通路发挥抗炎作用[9-12]。以上研究结果均表明, 白花蛇舌草的环烯醚萜类成分具有良好的抗炎和抗纤维化作用。由于中药具有多成分、多靶点、多通路协同发挥药效作用的特点, 而肾纤维化的发病机制也复杂多样, 因此本文想要通过运用网络药理学的分析手段对环烯醚萜类化合物中的活性成分、肾纤维化相关靶点及其作用通路进行系统性分析, 以识别潜在的药物靶点和作用机制, 从而为环烯醚萜化合物的临床应用和进一步开发提供科学数据。
材料与方法药品 白花蛇舌草购于南方医院(批号191001-2);车叶草苷、车叶草苷酸、去乙酰车叶草苷酸、鸡屎藤次苷、鸡屎藤次苷甲酯、京尼平和京尼平苷酸对照品(成都普瑞法科技开发有限公司); 甲醇和乙腈(美国Fisher试剂公司); 甲酸(Sigma公司)。
对照品溶液的制备 精密称取各标准品适量于离心管中, 加入10% (v/v)乙腈水配制成500 ng·mL-1的标准品溶液, 涡旋溶解, 微孔滤膜(0.22 μm)过滤, 取滤液即为进样用标准品溶液; 同时取等量各标准品溶液于同一试管中混合, 即得混合对照品溶液。
环烯醚萜的提取方法 定量称取白花蛇舌草原料药, 粉碎, 分别加入10倍体积的75%乙醇, 加热冷凝回流提取2次, 每次1 h, 取合并滤液在60 ℃减压浓缩至相对密度为1.10~1.20;往浓缩液中加入0.5%的活性炭脱色, 高速离心取上清, 60 ℃真空干燥, 即得白花蛇舌草环烯醚萜苷类粗提物; 加30%甲醇溶解粗提物, 以十八烷基硅烷键合硅胶填料开口柱为固定相, 以30%甲醇水溶液进行洗脱, 收集洗脱液, 60 ℃真空干燥, 即得白花蛇舌草环烯醚萜苷类成分。作者在2018年已申请该方法的发明专利[13]。
环烯醚萜类成分分析 ①色谱条件:选用Phenomenex Kinetex (2.1 mm×100 mm, 2.6 μm)色谱柱, 以0.1%甲酸水溶液(A)和含0.1%甲酸的乙腈(B)为流动相进行梯度洗脱。具体梯度如下: 0~15 min, 2%~10% B; 流速: 0.3 mL·min-1; 柱温: 40 ℃。②质谱条件:采用AB SCIEX Triple TOF™ 5 600质谱仪, 离子化模式为电喷雾电离(electrospray ionization, ESI)。参数如下:气体1: 55 psi; 气体2: 55 psi; 气帘气: 30 psi; 离子喷雾电压(ion-spray voltage, IS) 4 500 V、碰撞电压(collision energy, CE) 35 V、去簇电压(declustering potential, DP) 80 V; 气体温度550 ℃。负离子扫描范围m/z: 50~1 000。干燥气体和碰撞气体为氮气。数据处理软件为Peakview 1.2, 相对分子质量误差小于5×10-6为筛选条件。
蛋白靶点筛选 在DisGeNET数据库(https://www.disgenet.org)和MalaCards数据库(https://www.malacards.org)中输入renal fibrosis进行检索, 得到与肾脏纤维化相关靶点, 去除重复数据, 并利用UniProt (https://www.uniprot.org/)数据库将基因名转换为蛋白名, 即得到肾脏纤维化相关靶蛋白。
成分数据库构建 将白花蛇舌草中环烯醚萜类成分与相关蛋白导入SYBYL-X7.3软件进行分子对接, 以对接分值≥6.0作为活性化合物的筛选条件, 得到潜在的高活性化合物。
化合物-靶点网络的构建 将成分数据库构建结果, 即化合物与相关靶蛋白的打分数据导入Cytoscape 3.7.1软件, 构建活性成分-靶点网络图。
蛋白互作(protein-protein interaction, PPI)网络的构建 将上述关键靶点导入String数据库(https://string-db.org/), 物种项选择人, 获取蛋白之间的相互作用关系, 打分值> 0.7则为高置信度数据。将得到的蛋白相互作用数据导入Cytoscape3.7.1软件, 构建PPI网络, 并对PPI网络中的蛋白绘制条形图。
基因本体(gene ontology, GO)功能富集分析 为明确靶蛋白在基因功能中的作用, 通过David v6.8数据库(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/)对PPI网络中的蛋白进行GO功能富集分析。
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)通路富集分析 为了阐明靶蛋白在信号通路中的作用, 采用David v6.8数据库对PPI网络中的蛋白进行KEGG通路富集分析, 并构建靶点-通路网络图。
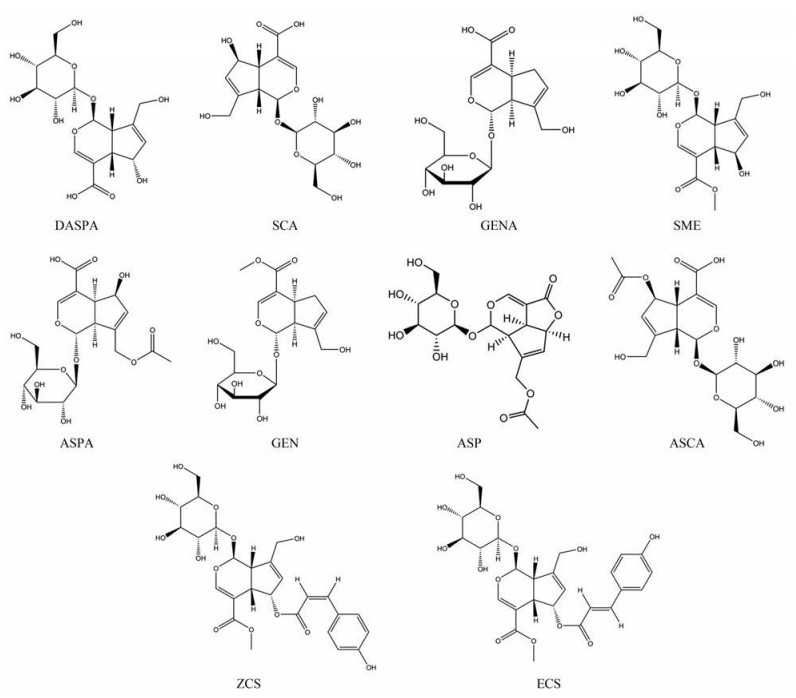
结果 1 白花蛇舌草环烯醚萜提取物成分分析通过SYBYL-X7.3软件将鉴定出的10个环烯醚萜化合物与201个蛋白进行分子对接, 打分值≥6.0作为筛选条件, 最终得到10个化合物和111个相关蛋白。图 1为白花蛇舌草环烯醚萜化合物在负离子模式下的提取离子流图, 表 1为鉴定化合物的基本信息, 图 2为鉴定的10个环烯醚萜化合物的结构图。

|
Figure 1 The extracted ion chromatograms of 10 active cyclic ether terpene compounds of Hedyotis diffusa Willd in negative ion mode. Based on the previous identification and analysis of the composition of Hedyotis diffusa Willd and the mass spectrometry information of the standards, 10 cyclic ether terpene compounds are identified. Each of labeled peaks represented a compound identified, and the corresponding information is shown in Table 1 |
| Table 1 Information for 10 active cyclic ether terpene compounds of Hedyotis diffusa Willd. Rt: Retention time |
|
Figure 2 The structures of 10 active cyclic ether terpene compounds of Hedyotis diffusa Willd |
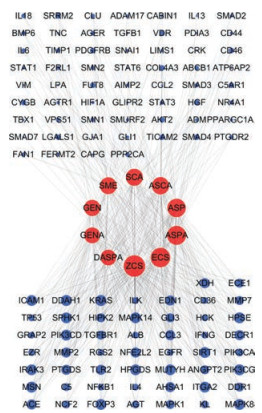
化合物-靶点网络共包括121个节点(10个化合物节点和111个靶蛋白节点)和523条相互作用连线(图 3)。在该网络中, 红色表示化合物, 蓝色表示靶点, 节点大小与节点的度(degree)呈正比关系, degree表示网络中和节点连线的数量, degree较大的节点在整个网络中起枢纽作用, 可能是关键化合物/靶点。作用靶点≥50的化合物有5个, 而另外5个化合物的作用靶点数均 > 35。从化合物的角度来看, degree排名前5位的是ZCS (6-O-Z-p-coumaroyl scandoside methyl ester)、ECS (6-O-E-p-coumaroyl scandoside methyl ester)、ASPA (asperulosidic acid)、ASP (asperuloside)和ASCA (6-O-acetylscandoside); 从靶点角度来看, degree排名前5位的是二甲基精氨酸二甲胺水解酶1 (dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1, DDAH1)、乙酰肝素酶(heparanase, HPSE)、鼠类肉瘤病毒癌基因(kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene, KRAS)、膜突蛋白(moesin, MSN)和PIK3CG (phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit gamma), 均能与所有化合物发生作用。该图中每个化合物对应的平均靶点数为52.3个, 每个靶点平均与4.71个化合物发生作用, 因此该网络中存在1个化合物作用多个靶点, 不同化合物对应同一个靶点的现象, 充分体现了环烯醚萜类化合物与多个靶点共同作用的特点。
|
Figure 3 Compound-target network of cyclic ether terpene compounds. The blue nodes represent related targets of renal fibrosis and the red nodes represent 10 iridoid compounds. The size of a node is proportional to its degree |
PPI网络(图 4)包含99个节点和445条边, 其中节点表示靶蛋白, 每条边则表示蛋白之间的相互作用关系。根据节点的degree绘制出前30个关键蛋白的条形图(图 5)。Degree≥20的节点有8个, 包括信号传导与转录激活因子3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, STAT3)、IL6、肿瘤抑制蛋白53 (tumor protein 53, TP53)、表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR)、MAPK1、MAPK8、原癌基因蛋白PIK3CA和转化生长因子B1 (transforming growth factor beta 1, TGFB1), 其中STAT3、IL6和TP53度值最大, 分别能与38、36和31个蛋白发生相互作用。

|
Figure 4 Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of cyclic ether terpene compound-related targets. The size of a node is proportional to its degree. The larger size of a node represents a stronger association with renal fibrosis |

|
Figure 5 Hub nodes from PPI network. Nodes with a degree value ≥ 12 are graphed and displayed its corresponding degree values |
利用DAVID在线平台对PPI网络中涉及的99个蛋白进行GO功能富集分析。根据错误发生率(false discovery rate, FDR) < 0.05筛选出211个GO条目(表 2根据FDR列出前20个), 其中生物过程相关的条目最多, 有198个, 主要涉及对细胞迁移、坏死和凋亡的调控; 分子功能相关条目有6个, 涉及蛋白二聚体活动和DNA结合等方面; 细胞组成相关条目7个, 主要涉及细胞外间隙和细胞连接等方面。
| Table 2 Gene ontology (GO) entries in PPI network [false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05)]. ID: Identification |
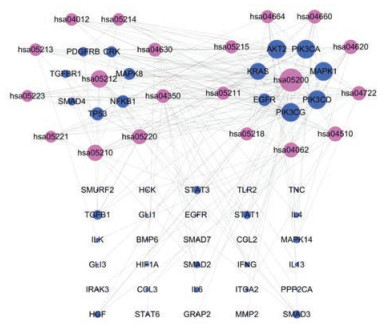
将PPI网络中涉及的99个蛋白导入DAVID平台进行KEGG通路富集分析, 得到49条信号通路(图 6), 蓝色为蛋白靶点, 紫色为信号通路代码(identification, ID), 节点大小与节点度值呈正比例关系。根据FDR < 0.05筛选出20条(表 3), 包括胰腺癌、结直肠癌等癌症通路、Toll样受体信号通路、转化生长因子β (transforming growth factor-beta, TGF-β)信号通路、肾细胞癌和Janus激酶/信号转导与转录激活子(the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of tran-ions, Jak-STAT)信号通路等, 表明环烯醚萜类成分可能通过作用于以上这些信号通路达到治疗疾病的目的。
|
Figure 6 Target-pathway network (FDR < 0.05). Blue nodes represent key targets and purple nodes represent 20 main signal pathways. The detailed information of the signal pathways is shown in Table 3 |
| Table 3 Information of renal fibrosis related target-pathway. TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; Fc epsilon RI: A high-affinity receptor for the Fc region of IgE; ErbB: A family of four structurally related receptor tyrosine kinase; Jak-STAT: The Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of tran-ions |
白花蛇舌草具有清热解毒和利湿消肿等功效, 是近年来新开发的中药, 常用于肝炎、阑尾炎及多种肿瘤的治疗。有文献报道其对急慢性肾炎也有治疗作用, 具有肾脏保护功能[14, 15]。环烯醚萜类化合物为白花蛇舌草的重要活性成分, 其对大鼠肾纤维化有很好的治疗作用。为深入探讨环烯醚萜这一类化合物对肾纤维化的保护机制, 作者通过对化合物与相关靶点的作用分析, 构建了化合物-靶点网络、PPI网络并对靶蛋白进行GO功能富集分析和KEGG通路富集分析, 为环烯醚萜类化合物治疗肾纤维化提供多靶点和多通路的研究思路。化合物-靶点网络中的主要成分有ZCS、ECS、ASPA、ASP和ASCA, 关键靶点涉及DDAH1、HPSE和KRAS等。DDAH是二甲基精氨酸二甲胺水解酶, 有DDAH1和DDAH2两种亚型, 其中DDAH1主要分布于肝脏和肾脏, 通过水解非对称性二甲基精氨酸(属于一氧化氮合酶抑制剂), 来调控内源性一氧化氮的合成[16], 同时有研究表明DDAH1的缺失可影响AMPK信号通路, 因此DDAH1主要与肾纤维化过程中的炎症反应相关。HPSE是一种葡萄糖醛酸酶, 研究表明HPSE的缺失或其抑制剂的应用可诱导肾小管细胞TGF-β的合成, 从而促进肾纤维化的发展[17]。KRAS基因突变与肿瘤的发生密切相关, 主要在结直肠癌和胰腺癌的突变率较高, 白花蛇舌草活性成分发挥抗肿瘤的药理活性可能与KRAS基因有关[18]。因此白花蛇舌草环烯醚萜类化合物可能通过调控多个靶点发挥多种疗效。为了进一步探究这些关键靶点在基因功能和信号通路中的作用, 作者对PPI网络中涉及的蛋白进行GO功能富集分析和KEGG通路富集分析。GO功能富集分析发现, 环烯醚萜类成分的药效作用对应的基因功能主要体现在对细胞增殖分化、细胞组分和受体活性等方面。在靶蛋白的KEGG通路富集中, 筛选得到20条信号通路, 由此推测10种环烯醚萜类成分是通过这些信号通路来发挥疾病调控作用。其中有一半基因富集到了与癌症有直接关系的通路上, 由此推测白花蛇舌草可用于多种肿瘤的治疗, 且环烯醚萜类化合物是主要的药效成分。目前也有多篇文章报道白花蛇舌草的抗肿瘤作用[19-21]。癌症在中医理论中为癌毒阻滞、气淤血淤和气阴两伤, 因此治疗癌症需活血化瘀和益气养阴[22]。而中医古籍中并无肾纤维化、慢性肾脏病的记载, 其临床症状属于中医学中“水肿”、“虚劳”等病症范畴, 益气活血是防治肾纤维化的基本疗法[23]。由此可见, 癌症和肾纤维化的治疗是有所相通的, 因此推测白花蛇舌草的活性成分除抗肿瘤外, 也有一定抗纤维化的作用。此外, 炎症反应相关的通路Toll-样受体信号通路和Jak-STAT信号通路分别富集了12和11个基因。Toll样受体是一类重要的天然免疫识别受体, 可识别外源性物质并激活免疫细胞, 诱导炎症细胞因子的分泌, 参与炎症反应。Jak-STAT信号通路是近年来发现的一条由细胞因子刺激的信号转导通路, 参与细胞增殖、分化、凋亡及免疫调节等生物学过程, 与各种癌症和炎症的发生密切相关。TGF-β信号通路富集了11个基因, TGF-β是肾纤维化的重要介质, 激活的TGF-β/Smad信号通路可诱导肾小球肥大和肾小管上皮细胞-肌成纤维细胞转分化等, 促进细胞外基质的大量合成以及降解减少, 从而造成肾组织纤维化的发生[24]。作者前期研究发现在单侧输尿管结扎构建的肾纤维化大鼠模型中, 给予车叶草苷酸治疗有良好的抗炎和抗纤维化作用。车叶草苷酸可通过抑制TGF-β1/smad2/smad3和NF-κB信号通路从而减缓纤维化进展, 目前已对车叶草苷酸在制备治疗肾纤维化药物中的应用申请了专利[25, 26]。因此, 白花蛇舌草环烯醚萜类化合物可能是通过激活或抑制这些信号通路而发挥治疗疾病的作用。
综上所述, 本研究基于网络药理学技术, 初步阐明了白花蛇舌草中10种环烯醚萜类化合物与多靶点、多通路的复杂关系, 揭示其治疗肾纤维化的作用机制, 为后续的实验研究及临床应用提供科学依据。
作者贡献:论文中所有作者对论文均有实质性贡献。董雅倩主要负责样品提取、化合物分析、化合物数据库建立及论文撰写; 张佳幸和龚琳娜主要负责网络药理学内容分析; 石碧锐负责化合物的分析鉴定; 周凤华和肖炜参与实验方案设计和论文修改; 刘孟华主要负责指导整个实验的完成和投稿。
利益冲突:所有作者均声明无利益冲突。
| [1] |
Romagnani P, Remuzzi G, Glassock R, et al. Chronic kidney disease[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2017, 3: 17088. DOI:10.1038/nrdp.2017.88 |
| [2] |
Yin JQ, Wei MG, Huang XX, et al. Effect of Qigui Yishen Decoction on miR-141 regulation in UUO mice with renal fibrosis[J]. Chin Tradit Pat Med (中成药), 2018, 40: 765-770. |
| [3] |
Sun Y, Zhao YH, Lu YX, et al. The pathogenesis and treatment progress of renal fibrosis[J]. J Clin Med Pract (实用临床医药杂志), 2015, 19: 173-176. |
| [4] |
Zhu PJ. Study on renal fibrosis and anti-fibrosis therapy[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephr (中国中西医结合肾病杂志), 2004, 5: 114-117. |
| [5] |
Liu F, Zhuang S. New therapies for the treatment of renal fibrosis[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019, 1165: 625-659. |
| [6] |
Che JC, Xin N, Feng J. Research progress of pharmacological function of Oldenlandia diffusa[J]. J Anhui Agric Sci (安徽农业科学), 2007, 35: 6162-6167. |
| [7] |
Wang X, Fan HF, Li DH, et al. Progress in research on the anticancer effect of Hedyotis diffusa Willd[J]. J China Pharm (中国药房), 2019, 30: 1428-1431. |
| [8] |
Zeng Z, He CS, Sun JF, et al. Effect of Hedyotis diffusa on proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle of A549 lung cancer stem cell[J]. Chongqing Med (重庆医学), 2019, 48: 2202-2205. |
| [9] |
He J, Lu X, Wei T, et al. Asperuloside and asperulosidic acid exert an anti-inflammatory effect via suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19: 2027. DOI:10.3390/ijms19072027 |
| [10] |
He J, Li J, Liu H, et al. Scandoside exerts anti-inflammatory effect via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19: 457. DOI:10.3390/ijms19020457 |
| [11] |
Chen R, He J, Tong X, et al. The Hedyotis diffusa Willd. (Rubiaceae):a review on phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and pharmacokinetics[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21: 710. DOI:10.3390/molecules21060710 |
| [12] |
Ye JH, Liu MH, Zhang XL, et al. Chemical profiles and protective effect of Hedyotis diffusa Willd in lipopolysaccharide-induced renal inflammation mice[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2015, 16: 27252-27269. DOI:10.3390/ijms161126021 |
| [13] |
Liu MH, Tang L, Liu SW, et al. Application of iridoids of Hedyotis diffusa in the preparation of drugs for the treatment of renal fibrosis: China, CN201710006702.4[P]. 2018-07-13.
|
| [14] |
Deng B. Hedyotis diffusa is good at treating acute nephritis[J]. J Tradit Chin Med (中医杂志), 2008, 49: 532. |
| [15] |
Wei MG, Sun W. Application of Oldenlandia in the treatment of urinary system disease[J]. China J Chin Med (中医学报), 2013, 28: 1741-1742. |
| [16] |
Reddy K, Dasari C, Duscharla D, et al. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1(DDAH1) is frequently upregulated in prostate cancer, and its overexpression conveys tumor growth and angiogenesis by metabolizing asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA)[J]. Angiogenesis, 2018, 21: 79-94. DOI:10.1007/s10456-017-9587-0 |
| [17] |
Masola V, Zaza G, Secchi MF, et al. Heparanase is a key player in renal fibrosis by regulating TGF-beta expression and activity[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014, 1843: 2122-2128. DOI:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.06.005 |
| [18] |
Wang P, Zhang H, Yang J, et al. Mu-KRAS attenuates Hippo signaling pathway through PKCiota to sustain the growth of pancreatic cancer[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235: 408-420. DOI:10.1002/jcp.28981 |
| [19] |
Lu PH. Study on the Inhibition of Colon Cancer by Hedyotis Diffusa in the Xiao Ai Jie Du Prescription and Its Mechanism (消癌解毒方中白花蛇舌草抑制结肠癌的作用及机制研究)[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine (南京中医药大学), 2016.
|
| [20] |
Wang Q. Study on the Anti-Cancer and Anti-Inflammation Effects of Hedyotis Diffusa Willd from Fujian (闵产白花蛇舌草抗肿瘤与抗炎的实验研究)[D]. Fujian: Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (福建中医药大学), 2013.
|
| [21] |
Su X, Li Y, Jiang M, et al. Systems pharmacology uncover the mechanism of anti-non-small cell lung cancer for Hedyotis diffusa Willd[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 109: 969-984. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.162 |
| [22] |
Zhu MW, Chen SQ. Study on the TCM treatment rules for cancer[J]. Jiangsu J Tradit Chin Med (江苏中医药), 2009, 41: 58-59. |
| [23] |
Leng W, Yang NZ, Zhao DX, et al. Discussion and research on the prevention and treatment of renal fibrosis by Yiqihuoxue[J]. Jiangsu J Tradit Chin Med (江苏中医药), 2009, 41: 59-60. |
| [24] |
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, et al. New insights into TGF-beta/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2018, 292: 76-83. DOI:10.1016/j.cbi.2018.07.008 |
| [25] |
Lu X, Zou W, Dong Y, et al. Anti-renal fibrosis effect of asperulosidic acid via TGF-β1/smad2/smad3 and NF-κB signaling pathways in a rat model of unilateral ureteral obstruction[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 53: 274-285. DOI:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.009 |
| [26] |
Liu MH, Lu XY, Tang L, et al. Application of asperulosidic acid in the preparation of drugs for the treatment of renal fibrosis: China, CN201710477449.0[P]. 2020-05-29. http://g.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=patent&id=CN201710477449.0.
|
 2020, Vol. 55
2020, Vol. 55


