2. 北京中医药大学, 北京 102488;
3. 中药资源教育部工程研究中心, 北京 100193
2. Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102488, China;
3. Engineering Research Center of Chinese Medicine Resource, Ministry of Education, Beijing 100193, China
近年来国家重视中医药的发展, 先后出台多项中医药利好政策, 如2017年实施《中华人民共和国中医药法》[1], 将国家对中医药的扶持力度上升至法律高度; 2019年国务院印发《中共中央国务院关于促进中医药传承创新发展的意见》[2]; 2019年版《国家基本医疗保险、工伤保险和生育保险药品名录》[3]中成药与西药比重首次持平; 在国际贸易方面, 《中医药“一带一路”发展规划(2016-2020)》[4]的发布, 为中药产业提供新机遇。目前, 中医药已传播到183个国家和地区, 我国与40余个外国政府、地区和组织签署专门的中医药合作协议。随着中药产业蓬勃发展, 中药市场竞争加剧, 为提高企业核心竞争力, 有效整合资源, 保证中药质量及用药安全性, 建设全产业链模式成为中药企业发展趋势。中药全产业链主要包括上游中药种植、采收环节, 中游中药材加工、炮制、中药制剂生产环节, 下游中药销售、流通环节以及对全产业链的监督管理。中药安全性问题贯穿中药全产业链, 其中, 药材来源复杂、混乱等是中药安全性问题的源头, 基原鉴定准确是保证中药安全性、有效性的基础。DNA条形码技术基于碱基序列信息将中药基原鉴定至物种水平, 具有准确性高、通用性强的特点, 不具专业分类、鉴定知识背景的人员也能进行操作, 能够有效应用于中药全产业链(图 1)。在产业链上游, 鉴定中药种子种苗、药用植物, 从中药产业链源头保证物种正确; 在产业链中游, 明确中药材、中药饮片、中成药组分的基原物种, 保证企业投料准确, 临床用药安全; 在产业链下游, 参与构建中药溯源体系, 整合中药产业链全过程的信息, 为中药流通、使用环节提供便利。同时, DNA条形码技术也可作为监督管理部门的检查手段, 实现中药生产、储存、流通、使用过程的监控, 促进中药产业现代化。本文就DNA条形码技术在中药全产业链的应用进行综述。

|
Figure 1 Application of DNA barcoding technology in the whole industrial chain of traditional Chinese medicine |
随着野生资源的减少以及对物种多样性和生态环境保护的加强, 我国从20世纪50年代起大力发展中药种植, 目前已建设多个中药材规范化种植基地, 有200余种常用大宗中药材实现人工种植。中药种植企业位于中药全产业链最前端, 种质选择对中药质量有一定影响, 基因组技术在中药种质选择、育种方面发挥作用[5], 其中DNA条形码技术作为鉴定手段, 用于明确中药材种子种苗基原物种, 保证种源正确。部分中药材种子体积微小, 形态特征不易观察, 且会受发育程度及环境因素影响, 因而中药材种子市场上存在掺伪混杂现象。目前对于中药材种子的鉴定方法尚不足, 若待种植后再根据植株形态进行鉴定, 则可能浪费时间、增加成本, 给企业带来损失。DNA条形码技术在中药种植企业应用, 可避免因误选或混淆种子造成的损失, 成为中药种植企业鉴定种子种苗的有力手段。2016年, 张娜娜等[6]率先将DNA条形码技术应用于中药泽泻种子的鉴定, 发现所收集的样本仅35%为《中国药典》规定的基原物种。迄今, DNA条形码技术已实现知母[7]、桔梗[8]、黄芩[9]等多种中药材种子的鉴定(表 1)。赵晴等[17]针对不同类型中药材种子, 制定DNA条形码分子鉴定法操作流程, 以期实现中药材种子鉴定的标准化、自动化。目前, 多数中药材种子种苗缺乏国家标准, 以农作物种子质量标准为参照, 监管力度薄弱, 相关监督管理部门可基于该技术在中药材种子种苗鉴定中的应用, 制定中药材种子种苗质量标准, 促进中药材种子种苗市场规范化。
| Table 1 Application of DNA barcoding technology in the seeds and seedlings of traditional Chinese medicine |
我国87%的药用资源属于药用植物, 主要来源于野生资源和人工种植。野生药用植物资源分布较广, 形态变化大, 对采收人员鉴定能力、经验等要求较高。应用DNA条形码技术鉴定野生药用植物, 可提高鉴定准确性, 如对野外采集的常山疑似品进行鉴定, 可将正品与习用品、混伪品明确区分[18]。该技术现已应用于重楼属[19]、蒿属[20]等多种药用植物的鉴定。2017年7月1日实施的《中华人民共和国中医药法》第二十五条要求对药用野生动植物资源实行动态监测和定期普查[1], DNA条形码技术能在药用植物资源普查中发挥作用, 如辛天怡等[21]采用DNA条形码技术对长白山药用植物资源进行调查并构建长白山药用植物DNA条形码数据库, 补充现有数据库。此外, 该技术还能应用于药用植物亲缘关系研究、新物种发现、新药研发、海关检查等方面[22] (图 2)。
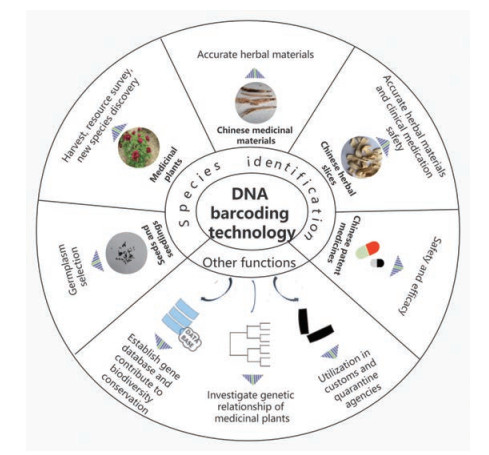
|
Figure 2 The functions of DNA barcoding technology and its specific application fields |
随着中药需求量、使用量增加, 野生药用植物资源逐渐匮乏, 加之野外采收较困难, 人力物力耗费较大, 为满足市场需求、提高生产效率, 我国大部分常用中药均建有种植基地。人工种植的中药, 生长环境、营养成分等与野生资源不同, 表现出的性状会发生改变[23, 24], 采用传统的鉴定方法可能会导致误判, 而DNA条形码技术基于遗传信息进行鉴定, 可明确区分物种[25-27], 防止因基原错误导致采收过程或后续生产出现问题。同时, 为保护药用植物资源, 我国建立各种自然保护区、药用植物园, DNA条形码技术可应用于基因数据库的建立, 从基因层面上保护资源和物种多样性[28]。对于中药企业而言, 野生中药资源品质差别大, 资源供应量不稳定, 为保证原料准确、质量稳定、供应充足, 产业链向产地延伸, 建设种植基地, 规范化种植、采收是企业提高自身竞争力、谋求长远发展的趋势。
2 DNA条形码技术在中药全产业链中游的应用 2.1 准确鉴定中药材与饮片基原由于文化、语言等原因, 中药材同名异物、异物同名现象普遍, 加之中药材市场大多未标明药材基原, 存在大量混伪品、习用品, 影响中药用药安全, 如“关木通事件”、“广防己事件”等, 近年来国内中药材检出问题的不合格原因常与中药基原问题有关。因而采用DNA条形码技术对中药材进行鉴定, 明确其基原物种, 有利于中药材市场监管, 保证临床用药安全。DNA条形码技术现已广泛应用于中药材物种鉴定, 如动物类[29]、种子类[30]中药等。2015版《中国药典》收载其指导原则, 构建中药材DNA条形码数据库并不断丰富物种信息, 已有文献综述2015年以前该技术在中药材物种鉴定方面的应用实例[31], 本文就2015年及以后的应用实例进行总结, 见表 2。
| Table 2 Application of DNA barcoding technology in Chinese medicinal materials |
中药材经加工炮制成为饮片, 直接应用于临床或作为中成药生产原料。经过简单炮制(即仅经过净制、切制处理)的饮片与中药材几乎无异, 仍可按照“中药材DNA条形码分子鉴定法指导原则”步骤操作, 并能准确鉴定[32], 而经过炒、蒸、或加辅料炮制等处理的饮片DNA发生降解, 提取难度加大, 有研究表明通过改良提取方法等处理同样能得到很好的应用[33]。向丽等[34]对不同来源、不同部位中药超微或破壁饮片鉴定研究表明, DNA条形码技术在完全丧失形态特征的中药超微或破壁饮片中仍能发挥良好的鉴定作用, 可推动破壁饮片的发展。中药饮片直接应用于临床或作为中成药生产原料, 其基原准确, 是保证中药临床使用安全、有效以及中药质量评价的前提。我国《药事管理法》明确规定:以非药品冒充药品或者以他种药品冒充此种药品者为假药[35], DNA条形码技术可作为药品监督管理部门日常检验手段, 对中药材及饮片基原物种进行检查, 规范企业行为。
2.2 鉴定中成药组方药物种中成药在中医临床上起着重要作用, 目前已有1.4万余个中成药品种在临床上使用。根据近年来国家药品评价抽验结果, 使用伪品投料是中成药质量不合格的一个重要原因, 如采用藏柴胡代替柴胡投料, 西洋参代替人参投料, 山银花代替金银花投料等[51]。现行版《中国药典》在中成药检查项下多通过显微或理化手段进行检查, 对于含有相似化学成分或具有相同显微特征的中药则区分困难, 难以解决伪品投料问题。下一代测序技术的发展实现了DNA条形码技术在多组分中药混合体系中应用[52], 如张鹏等[53]对生脉散进行鉴定, 组方两种药材均能检出, 辛天怡等[54]对龙胆泻肝丸进行鉴定, 自制样本处方十味药均能检出, 同时可用于市场销售中成药样本的检测。相关应用表明DNA条形码技术对于检测中成药原料药基原物种具有良好效果(表 3), 一方面可应用于中成药企业, 对生产原料进行检查, 保证投料准确; 另一方面可应用于药品监督管理部门, 对生产或流通过程中的中药进行检查, 对于保证临床用药安全, 推动中药产业现代化具有意义。
| Table 3 Application of DNA barcoding technology in Chinese patent medicines |
中药产业链下游主要包括医药流通企业、医院、药店和消费者等, 主要涉及中药运输、储存、销售及使用等环节, DNA条形码技术可参与构建中药溯源体系, 在产业链下游信息流通过程中发挥作用。中药溯源体系是借助现代互联网技术、信息技术, 对中药信息进行记录、查询和溯源, 实现对中药种植、加工、流通和使用全过程追踪和监管[60]。DNA条形码技术在中药种植、加工及生产过程中均有应用, 包含大量信息, 可将该技术与二维码技术相结合, 参与构建中药溯源体系[61]。中药种植基地可记录中药材种子种苗的基原物种、采购地, 中药采收时记录准确的物种, 对应原植物图片, 中药材、中药饮片以及中成药加工生产企业则可以详细记录原料、加工处理过程等, 实现中药生产全过程的监控。DNA条形码技术参与构建中药溯源体系, 可满足不同用户需求, 如中药流通环节相关人员, 可利用该体系了解中药从种子种苗到加工产品每一阶段的信息, 保证产品真实、有效; 监督管理部门可通过该体系追溯药品抽检不合格原因, 追踪所有问题产品去向, 实现“来源可查, 去向可追”; 中医临床应用出现问题, 也可通过该体系探寻是药品质量问题还是不合理使用问题, 为中药临床使用及安全性评价提供数据。
4 展望2019年, 第七十二届世界卫生大会审议通过《国际疾病分类第十一次修订本(ICD-11)》, 首次纳入起源于中医药的传统医学章节, 标志着世界卫生组织对中医药传统医疗价值的认可。此前, 因缺少国际标准化的统计口径等原因, 传统医学一直未被列入国际疾病分类体系框架内, 阻碍传统医学在国际上的发展。同样, 中药在世界上的发展也面临相同问题, 一直以来, 中药药理和化学两个领域是中药研究的热点, 而从基因水平上对中药进行研究则相对较少, 导致前沿生物科学技术难以进入到中药研究领域, 阻碍其在国际上的发展[62]。随着本草基因组学[63]兴起, 前沿生物科学技术逐渐应用到中药研究领域。
DNA条形码技术作为本草基因组学的应用之一, 在中药基原物种鉴定方面发挥重要作用, 推动中药鉴定学的“文艺复兴”[64]。现阶段DNA条形码技术应用已较为成熟, 但仍有局限性与不足: ①无法实现矿物药的鉴别; ②对于中药提取物、口服液鉴别较困难; ③区分亲缘关系很近的物种较困难[65]; ④需经过DNA提取、PCR扩增、测序、生物信息学分析等步骤, 无法实现市场抽检实时检测; ⑤反映信息有限, 无法检测有效成分含量等信息。目前, 已有学者通过联用其他技术, 同时解决中药基原鉴定和质量评价问题[66, 67], 或开发便携式仪器, 扩大其使用范围。贠凯祎等[68]将该技术结合TaqMan探针、实时荧光定量PCR技术实现冬虫夏草及其混伪品鉴别。Shi等[69]基于高曲率纳米结构阵列开发传感器, 结合ITS2序列实现西红花快速鉴别。DNA条形码技术与HRM联用, 可省去测序等步骤, 节省时间, 提高效率[70-73]。另外, 叶绿体基因组超级条形码的应用正在解决一些近缘物种鉴定困难的问题[74-76]。预计将DNA条形码技术与更多技术联用, 可改善现有局限性与不足, 使其成为更加便捷、高效、强大的技术, 促进中药产业规范化和现代化。
作者贡献: 娄千是本文的第一作者, 负责查阅文献, 撰写文章; 辛天怡负责文章的修改, 对文章图、表等提出修改意见; 宋经元是本文的通讯作者, 负责文章的整体设计与把关, 稿件修改等工作。
利益冲突: 本文作者声明无任何利益冲突。
| [1] |
National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Law of the People's Republic of China on Traditional Chinese Medicine (《中华人民共和国中医药法》)[EB/OL]. 2016-12-26[2020-03-11]. http://fjs.satcm.gov.cn/zhengcewenjian/2018-03-24/2249.html.
|
| [2] |
The State Council the People's Republic of China. Opinions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on promoting the inheritance, innovation and development of traditional Chinese Medicine (《中共中央国务院关于促进中医药传承创新发展的意见》)[EB/OL]. 2019-10-26[2020-03-11]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2019-10/26/content_5445336.htm.
|
| [3] |
National Healthcare Security Administration. List of national basic medical insurance, work injury insurance and maternity insurance drugs (《国家基本医疗保险、工伤保险和生育保险药品名录》)[EB/OL]. 2019-08-20[2020-03-11]. http://www.nhsa.gov.cn/art/2019/8/20/art_37_1666.html.
|
| [4] |
State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Development plan of "one belt, one road" in Chinese medicine (2016-2020) (《中医药"一带一路"发展规划(2016-2020)》)[EB/OL]. 2017-02-02[2020-03-11]. http://www.satcm.gov.cn/guohesi/zhengcewenjian/2018-03-24/3942.html.
|
| [5] |
Wei GF, Dong LL, Chen SL, et al. Application of Herbgenomics in breeding of new varieties of Chinese herbal medicines[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (中国实验方剂学杂志), 2018, 24: 18-28. |
| [6] |
Zhang NN, Xin TY, Jin Y, et al. Identification of Alisma plantago-aquatica seeds based on traditional Chinese medicine DNA barcoding system[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2016, 18: 18-23. |
| [7] |
Shi LC, Jin Y, Zhao CY, et al. Species identification of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma seeds by DNA barcoding technique[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (中国实验方剂学杂志), 2018, 24: 21-27. |
| [8] |
Liu JX, Pan M, Zhang GX, et al. Identification of Platycodonis Radix seeds by using ITS2 DNA barcode[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2016, 18: 174-178. |
| [9] |
Liu JX, Wei MJ, Li G, et al. Construction of ITS2 barcode database of Scutellariae Radix and establishment of DNA barcode identification method for its seeds[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (中国实验方剂学杂志), 2018, 24: 37-45. |
| [10] |
Ma SJ, Zhou JG, Jin Y, et al. Identification of the seeds of Vaccaria segetalis (Neck.) Garcke based on ITS2 sequence[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2016, 18: 29-34. |
| [11] |
Zhang GX, Jin Y, Jia J, et al. Identification of the seeds of Glehniae Radix with DNA barcoding method[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2016, 18: 179-183. |
| [12] |
Zhang GX, Jin Y, Jia J, et al. Identification of Notopterygium seeds using DNA barcoding method[J]. China J Chin Mater Med (中国中药杂志), 2016, 41: 390-395. |
| [13] |
Fang HL, Xia CL, Duan BZ, et al. Identification of seeds and seedlings of Chinese medicinal materials using DNA barcoding technology:a case study in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis[J]. J Chin Med Mater (中药材), 2016, 39: 986-990. |
| [14] |
Liu JX, Li G, Chen CX, et al. Identification of DNA barcoding of Atractylodis Rhizoma seedlings by ITS2 sequence[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (中国实验方剂学杂志), 2018, 24: 34-38. |
| [15] |
Lin FY, Cao H, Ren HH, et al. Seeds identification of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolium using ITS2 DNA barcodes[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药), 2019, 50: 2188-2193. |
| [16] |
Zhao Q, Xie HB, Yang L, et al. Molecular identification of Bupleurum chinense seeds based on DNA barcoding technology[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (中国实验方剂学杂志), 2019. DOI: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20200650 http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?doi=10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20200650.
|
| [17] |
Zhao Q, Xie HB, Zhao HL, et al. Advances in identification of traditional Chinese medicinal materials seeds using DNA barcoding technology[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药), 2019, 50: 3471-3476. |
| [18] |
Lei MY, Zhang NN, Zhang J, et al. Identification of Dichroa febrifuga and its adulterants based on DNA barcoding technology[J]. Plant Sci J (植物科学学报), 2017, 35: 379-386. |
| [19] |
Zhu YJ, Chen SL, Yao H, et al. DNA barcoding the medicinal plants of the genus Paris[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2010, 45: 376-382. |
| [20] |
Liu MZ, Song JY, Luo K, et al. Identification of nine common medicinal plants from Artemisia L. by DNA barcoding sequences[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药), 2012, 43: 1393-1397. |
| [21] |
Xin TY. Establishment of DNA Barcoding Database of the Medicinal Plants in Changbai Mountain and Study on the Detection of Biological Components of Two Traditional Chinese Patent Medicines (长白山区药用植物DNA条形码数据库构建及两种中成药生物组分监测研究)[D]. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College, 2019.
|
| [22] |
Chen SL, Song JY, Yao H, et al. Strategy and key technique of identification of Chinese herbal medicine using DNA barcoding[J]. Chin J Nat Med (中国天然药物), 2009, 7: 322-327. |
| [23] |
Yu JB, Feng XF, Wang WQ, et al. Comparative research on pharmacognostic characteristics and microscopic characteristics of Radix Paeoniae Rubra from different areas[J]. China J Chin Mater Med (中国中药杂志), 2010, 35: 2533-2537. |
| [24] |
Feng XF, Fu GF, Ge XG, et al. Difference of shapes and properties and microscopic frame works between wild and cultivated Radix Saposhnikovia[J]. China J Chin Mater Med (中国中药杂志), 2009, 34: 2862-2866. |
| [25] |
Yin XM, Luo K, Liu MZ. Molecular identification of Cnidium monnieri and its closely related species using ITS2 sequences[J]. Mod Chin Med (中国现代中药), 2012, 14: 9-11. |
| [26] |
Shi LC, Song JY, Chen SL, et al. Identification of Amomum (Zingiberaceae) through DNA barcodes[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2010, 12: 473-479. |
| [27] |
Yu H, Wu KY, Song JY, et al. Expedient identification of Magoliaceae species by DNA barcoding[J]. Plant Omics, 2014, 7: 47-53. |
| [28] |
Zhao XH, Liu X, Chen SL, et al. Protection and application of genetic resources of medicinal plants[J]. Mod Chin Med (中国现代中药), 2019, 21: 1456-1463. |
| [29] |
Yao H, Zhang H, Chen SL. Strategies and methods of DNA barcoding medicinal animals in Chinese pharmacopoeia[J]. Mod Chin Med (中国现代中药), 2019, 21: 1137-1146. |
| [30] |
Xiong C, Sun W, Li JJ, et al. Identifying the species of seeds in traditional Chinese medicine using DNA barcoding[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 701. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2018.00701 |
| [31] |
Xin TY, Lei MY, Song JY, et al. DNA barcoding of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Mod Chin Med (中国现代中药), 2015, 17: 170-176, 184. |
| [32] |
Xin T, Li X, Yao H, et al. Survey of commercial Rhodiola products revealed species diversity and potential safety issues[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 8337. DOI:10.1038/srep08337 |
| [33] |
Cheng SQ, Yuan Y, Liu FY, et al. Specific PCR method for identification of Trionycis Carapax and its preparation[J]. China J Chin Mater Med (中国中药杂志), 2018, 43: 4569-4574. |
| [34] |
Xiang L, Tang H, Cheng JL, et al. The species traceability of the ultrafine powder and the cell wall-broken powder of herbal medicine based on DNA barcoding[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2015, 50: 1660-1667. |
| [35] |
The State Council The People's Republic of China. Law of the PRC Governing the Management of Pharmaceutical Products (《中华人民共和国药品管理法》)[EB/OL].[2020-03-11]. http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2019-08/26/content_5424780.htm.
|
| [36] |
Huang Y, Zhang YY, Zhao CJ, et al. DNA barcoding and its utility in commonly-used medicinal snakes[J]. China J Chin Mater Med (中国中药杂志), 2015, 40: 868-874. |
| [37] |
Fan JJ, Song M, Song C, et al. Identification of the skin of Bufobufo gargarizans and its adulterants based on DNA barcoding[J]. Chin Pharm J (中国药学杂志), 2015, 50: 1292-1296. |
| [38] |
Jia J, Shi LC, Xu ZC, et al. Identification of antler powder components based on DNA barcoding technology[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2015, 50: 1356-1361. |
| [39] |
Wang X, Hou FX, Wang YX, et al. Identification of original species of Mantidis Ootheca (Sangpiaoxiao) based on DNA barcoding[J]. China J Chin Mater Med (中国中药杂志), 2015, 40: 3963-3966. |
| [40] |
Jia J, Shi LC, Yao H, et al. Identification of Bombyx Batryticatus based on DNA barcoding technology[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2016, 51: 1784-1790. |
| [41] |
Liu XZ, Zhou LS, Liu JX, et al. Identification of water buffalo horn and its adulterants using COI barcode[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2017, 52: 494-499. |
| [42] |
Chen Y, Zhang JJ, Tang H, et al. DNA barcoding for identification of Picrasma quassioides and its adulterants on the market[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2016, 18: 46-52. |
| [43] |
Ren L, Chen XL, Shi LC, et al. Identification of Ziziphi Spinosae Semen using DNA barcoding technology[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2016, 18: 35-39. |
| [44] |
Tang H, Xiang L, Zhao S, et al. DNA barcode identification of adulterants from commercial Cortex Phellodendri using ITS2 sequence[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2016, 18: 184-190. |
| [45] |
Gao T, Zhu XZ. DNA molecular identification of Radix Actinidiae based on ITS2 sequence[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2016, 18: 214-220. |
| [46] |
Guo MY, Ren L, Chen XL, et al. Identification of Scutellaria barbata and its adulterants using ITS2 barcode[J]. World Chin Med (世界中医药), 2016, 11: 796-800. |
| [47] |
Zhou JG, Ma SJ, Huang YL, et al. Identification of Psoraleae Fructus and its adulterants using ITS2 sequence[J]. World Chin Med (世界中医药), 2016, 11: 786-790. |
| [48] |
Ren L, Xin TY, Guo MY, et al. Identification of Polygoni Orientalis Fructus and its adulterants using ITS2 barcode[J]. World Chin Med (世界中医药), 2016, 11: 781-785. |
| [49] |
Gao T, Xin TY, Song JJ, et al. Identification of Malvae Semen and Abutili Semen using ITS2 DNA barcode[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药), 2017, 48: 2740-2745. |
| [50] |
Yao N, Hu CY, Wei YD, et al. Identification of Uncariae Ramulus Cumuncis and its relatives adulterants by ITS2 sequence[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res (时珍国医国药), 2019, 30: 361-364. |
| [51] |
Liu J, Wang C, Feng L, et al. Quality and safety analysis of Chinese patent medicines based on national drug sampling and inspection work[J]. Mod Chin Med (中国现代中药), 2019, 21: 279-283. |
| [52] |
Lo YT, Shaw PC. Application of next-generation sequencing for the identification of herbal products[J]. Biotechnol Adv, 2019, 37: n107450. DOI:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107450 |
| [53] |
Zhang P, Liu C, Zheng X, et al. Full-length multi-barcoding:DNA barcoding from single ingredient to complex mixtures[J]. Genes, 2019, 10: 343. DOI:10.3390/genes10050343 |
| [54] |
Xin TY, Su C, Wang SH, et al. Precise species detection of traditional Chinese patent medicine by shotgun metagenomic sequencing[J]. Phytomedicine, 2018, 47: 40-47. DOI:10.1016/j.phymed.2018.04.048 |
| [55] |
Jia J, Xu Z, Xin T, et al. Quality control of the traditional patent medicine Yimu Wan based on SMRT sequencing and DNA barcoding[J]. Front Plant Sci, 2017, 31: 926. |
| [56] |
Shi LC, Liu JX, Wei MJ, et al. DNA metabarcoding identification of prescription ingredients in traditional medicine RuyiJinhuang San[J]. Sci Sin Vit (中国科学:生命科学), 2018, 48: 490-497. DOI:10.1360/N052017-00204 |
| [57] |
Xin TY, Xu Z, Jia J, et al. Biomonitoring for traditional herbal medicinal products using DNA metabarcoding and single molecule, real-time sequencing[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2018, 8: 488-497. DOI:10.1016/j.apsb.2017.10.001 |
| [58] |
Wei MJ, Liu JX, Zhao Q, et al. Identification of Pule'an Tablets based on DNA barcoding molecular technology[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2020, 55: 1327-1333. |
| [59] |
Wei MJ, Shi LC, Zhao Q, et al. Molecular identification of Sanqi Tablets using DNA barcoding and its methodological evaluation[J]. Chin Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药), 2020, 51: 1893-1899. |
| [60] |
Shi MY, Zhao ST, Yang C, et al. Development of trace ability system for planting Chinese medicinal plants[J]. World Sci Technol/Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med (世界科学技术-中医药现代化), 2018, 20: 1540-1546. |
| [61] |
Xin TY, Li XW, Yao H, et al. A two-dimensional DNA barcode system for circulation regulation of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Sci Sin Vit (中国科学:生命科学), 2015, 45: 695-702. DOI:10.1360/N052015-00082 |
| [62] |
Chen SL, Song JY. Herbgenomics[J]. China J Chin Mater Med (中国中药杂志), 2016, 41: 3881-3889. |
| [63] |
Xin TY, Zhang Y, Pu XD, et al. Trends in herbgenomics[J]. Sci China:Life Sci, 2019, 62: 288-308. DOI:10.1007/s11427-018-9352-7 |
| [64] |
Chen SL, Pang XH, Song JY, et al. A renaissance in herbal medicine identification:from morphology to DNA[J]. Biotechnol Adv, 2014, 32: 1237-1244. DOI:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2014.07.004 |
| [65] |
Zheng H, Deng KY, Chen AQ, et al. Molecular identification and genetic relationship of Fritillaria cirrhosa and related species based on DNA barcode[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2019, 54: 2326-2334. |
| [66] |
Wu L, Sun W, Wang B, et al. An integrated system for identifying the hidden assassins in traditional medicines containing aristolochic acids[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 11318. DOI:10.1038/srep11318 |
| [67] |
Wei S, Luo Z, Cui S, et al. Molecular identification and targeted quantitative analysis of medicinal materials from Uncaria species by DNA barcoding and LC-MS/MS[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24: 175. DOI:10.3390/molecules24010175 |
| [68] |
Yun KY, Xiang L, Wang XY, et al. Identification of Ophiocordyceps sinensis and its adulterants based on portable and CFX96 real-time fluorescent PCR systems[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2019, 54: 746-752. |
| [69] |
Shi RX, Hu ZG, Lu H, et al. Hierarchical nanostructuring array enhances mid-hybridization for accurate herbal identification via ITS2 DNA barcode[J]. Anal Chem, 2020, 92: 2136-2144. DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04687 |
| [70] |
Mishra P, Shukla AK, Sundaresan V. Candidate DNA barcode tags combined with high resolution melting (Bar-HRM) curve analysis for authentication of Senna alexandrina Mill. with validation in crude drugs[J]. Front Plant Sci, 2018, 9: 283. DOI:10.3389/fpls.2018.00283 |
| [71] |
Sun W, Xiong C, Li JJ, et al. Application of high resolution melting curve to identification of Cimicifugae Rhizoma[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2016, 51: 1638-1642. |
| [72] |
Xiong C, Li JJ, Sun W, et al. Application of HRM combined with DNA barcoding to analysis of the Armeniacae semen amarum mixed in Persicae semen[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2017, 52: 647-652. |
| [73] |
Guo LN, Liu J, Zhao CY, et al. Rapid identification of Cistanches herba based on DNA barcoding and high resolution melting[J]. Chin J Pharm Anal (药物分析杂志), 2018, 38: 665-671. |
| [74] |
Chen X, Zhou J, Cui Y, et al. Identification of Ligularia herbs using the complete chloroplast genome as a super-barcode[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 695. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2018.00695 |
| [75] |
Xia Y, Hu Z, Li X, et al. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Chrysanthemum indicum[J]. Mitochondrial DNA A, 2016, 27: 4668-4669. DOI:10.3109/19401736.2015.1106494 |
| [76] |
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Song M, et al. Species identification of Dracaena using the complete chloroplast genome as a super-barcode[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 29: 1441. |
 2020, Vol. 55
2020, Vol. 55


