2019世界糖尿病联盟公布的最近数据显示, 全球糖尿病患者人数高达4.63亿, 已成为当今世界性公共健康问题[1], 而中国糖尿病患者人数排名第一, 约为1.164亿人, 糖尿病的防治形势尤为严峻。
胰高血糖素样肽-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1, GLP-1)是一种具有葡萄糖浓度依赖性的肠促胰素[2], 通过与GLP-1受体(GLP-1R)结合发挥作用。GLP-1具有促进胰岛素分泌、抑制胰高血糖素水平、增强胰岛素敏感性、保护胰岛β细胞等多重功效[3-5]。因此, GLP-1/GLP-1R成为近年来倍受关注的降血糖药物靶点与研究热点, 相关药物如艾塞那肽、利西拉来、利拉鲁肽等陆续获批上市。
传统中药葛根临床应用广泛, 葛根素是其主要有效成分, 具有多种药理作用, 包括降血糖、改善胰岛素抵抗、降血脂、抗氧化、改善微循环等[6, 7]。前期研究发现, 葛根素通过上调胰岛β细胞GLP-1R的表达, 激活GLP-1R通路, 实现保护胰岛β细胞生存的作用[8]。而GLP-1R拮抗剂毒蜥外泌肽9-39 (exendin 9-39, Ex9-39), 能够抑制葛根素对胰岛β细胞的保护作用[8, 9]。但GLP-1R激动剂是否能够协同促进葛根素的综合降糖作用, 尚未进行探讨。本研究将采用GLP-1R激动剂艾塞那肽(exendin-4, Ex4)及GLP-1R拮抗剂Ex9-39, 综合评价其对葛根素降糖作用的影响, 论证GLP-1R是葛根素降糖功效中的关键性调控分子, 为葛根素的潜在应用奠定实验基础。
材料与方法药品与试剂 Ex4 (货号E7144, 规格为0.1 mg, 纯度 > 97%)、Ex9-39 (E7269, 规格为0.1 mg, 纯度 > 95%)、葡萄糖(货号G7021, 纯度 > 99.5%)和羧甲基纤维素钠(CMC-Na, 货号C5678), 均购自美国Sigma公司; 葛根素(货号P111270, 纯度 > 96%), 中国泽朗医药科技有限公司; 甘油三酯与总胆固醇检测试剂盒, 中国建成生物工程研究所; 胰岛素与胰高血糖素放射免疫试剂盒, 中国北方生物技术研究所; 蛋白酶抑制剂(货号HY-K0010, 能够同时抑制半胱氨酸蛋白酶、丝氨酸蛋白酶、天冬氨酸蛋白酶及氨肽酶)和磷酸酶抑制剂(货号HY-K0021, 能够同时抑制碱性磷酸酶、丝氨酸/苏氨酸磷酸酶及蛋白磷酸酶PP1和PP2A的活性), 美国Med Chem Express公司; RIPA蛋白裂解液, 中国碧云天生物技术有限公司; BCA蛋白定量试剂盒和ECL化学发光显色液, 中国诺唯赞公司; GAPDH抗体(货号2118)、p-Akt抗体(货号9271)、p-FOXO1抗体(货号9461)、Akt抗体(货号9272)、FOXO1抗体(货号2880), 美国Cell Signaling公司; PVDF膜、血糖仪试纸, 德国罗氏公司。
实验仪器 血糖仪, 型号ACCU-CHEK, 德国罗氏公司; Western blotting凝胶电泳转膜系统, Mini-PROTEAN Tetra System, 美国Bio-Rad公司; Milli-Q型纯水机, 美国Millipore公司; 高速冷冻离心机, 型号5430R, 美国Beckman公司; 化学发光凝胶成像系统, 型号5200, 上海Tanon天能公司。
实验动物模型建立与分组给药 动物实验已获得南京中医药大学附属中西医结合医院动物伦理委员会批准(批准号AEWC-025)。4周龄雄性C57BL/6小鼠购自上海斯莱克实验动物有限责任公司, 共50只, 许可证编号为SCXK (沪) 2017-0005。小鼠饲养于本单位SPF级实验动物中心, 室温23~25 ℃, 湿度适宜, 且保持12 h昼夜循环。小鼠适应性饲养一周后, 10只小鼠以普通饲料喂养作为对照组, 40只小鼠以高脂饲料high-fat diet (HFD) (上海斯莱克公司, p1400f)喂养建立小鼠糖尿病模型, 造模过程中, 小鼠自由摄食饮水。持续喂养12周后, 检测小鼠空腹血糖水平, 空腹血糖 > 8 mmol·L-1则认为糖尿病模型造模成功。将高脂造模成功的小鼠随机分为4组, 平均每组8只。分组给药方案如下:对照组(普通饲料喂养, con), 生理盐水灌胃; 高脂组(高脂饲料喂养, HFD), 生理盐水灌胃; 高脂/葛根素给药组(HFD/pue), 采用0.5%的CMC钠溶解制备葛根素混悬液, 300 mg·kg-1·d-1, 灌胃给药; 高脂/葛根素/Ex9-39组(H/pue/Ex9-39), 葛根素300 mg·kg-1·d-1, 灌胃给药, Ex9-39 10 nmol·kg-1·d-1, 腹腔注射给药; 高脂/葛根素/Ex4组(H/pue/Ex4), 葛根素300 mg·kg-1·d-1, 灌胃给药, Ex4 10 nmol·kg-1·d-1, 腹腔注射给药。连续给药10天后, 继续相关检测。
空腹体重和血糖检测 小鼠禁食12 h, 不禁水, 分别测量各组小鼠的空腹体重(fasting body weights), 采用ACCU-CHEK血糖仪测空腹血糖(fasting blood glucose)。
口服葡萄糖耐量实验(oral glucose tolerance test, OGTT) 给药结束后, 小鼠禁食12 h, 灌胃葡萄糖2 g·kg-1进行OGTT实验。分别测量糖负荷前0 min, 糖负荷后30、60、90和120 min的小鼠血糖值, 计算时间血糖值曲线下面积: AUC (h·mmol·L-1) = 0.5×(1/2×BG0+BG30+ BG60+BG90+1/2×BG120)。
血清样品生化分析 小鼠摘眼球取血, 静置分层, 室温离心, 3 000 r·min-1, 15 min, 取上层血清。参照检测试剂盒说明书, 检测小鼠胰岛素与胰高血糖素, 以及甘油三酯和总胆固醇水平。
Western blotting实验 称取小鼠肝脏组织约80 mg, 加入RIPA裂解液(组织/裂解液=1:8), 同时按比例加入蛋白酶抑制剂和磷酸酶抑制剂, 充分匀浆裂解, 冰上静置30 min后12 000 r·min-1, 4 ℃离心30 min, 取上清即得总蛋白, 用BCA法测定蛋白浓度。取蛋白样品30 μg进行SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳及转膜, 用5%脱脂奶粉TBST溶液封闭1.5 h, 加一抗(1:1 000稀释)4 ℃孵育过夜。TBST溶液洗膜3次, 每次6 min, 加辣根过氧化物酶标记二抗(1:2 000稀释), 室温孵育1 h, TBST洗3次, 每次10 min, 最后加ECL发光液, 采用化学发光凝胶成像系统, 进行图像采集并分析。
统计学分析 数据用Mean ± SE表示, 采用SPSS 16.0统计软件进行统计分析, 组间比较采用t检验。
结果 1 Ex4与Ex9-39对葛根素改善HFD小鼠空腹血糖的影响如图 1所示, 高脂喂养显著增加小鼠空腹血糖(图 1B)与体重(图 1A), 而葛根素有效降低HFD小鼠的空腹血糖, 体重无显著性影响。GLP-1R激动剂Ex4有效增强葛根素的降糖作用(图 1B), 并且两者联用能够降低HFD小鼠体重(图 1A)。而GLP-1R拮抗剂Ex9-39对葛根素的降糖作用表现出显著抑制作用(图 1B), 对小鼠体重无影响。以上结果表明, GLP-1R激活能够促进葛根素的降糖效果, 而阻断GLP-1R通路, 葛根素的降糖作用被抑制。

|
Figure 1 The fasting body weights (A) and blood glucose levels (B) of mice after 10 days treatment. n = 6-8, x±s. *P < 0.05 vs Con; #P < 0.05 vs HFD saline; ^P < 0.05 vs HFD/pue. HFD: High fat diet; Ex9-39: Exendin 9-39; Ex4: Exendin-4; pue: Puerarin |
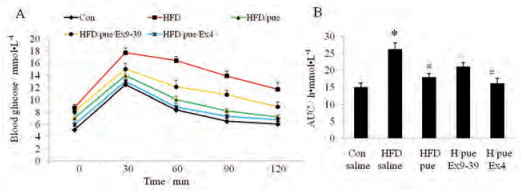
给药结束后, 对各组小鼠进行OGTT (图 2A), 并计算时间血糖值曲线下面积AUC (图 2B)。HFD糖尿病小鼠的糖耐量曲线异常升高, 糖耐量受损, 而葛根素能够有效改善HFD小鼠糖耐量。葛根素与GLP-1R激动剂Ex4联用, 对OGTT改善效果未见显著性差异(图 2B)。而GLP-1R拮抗剂Ex9-39显著抑制葛根素对OGTT的改善作用(图 2B)。
|
Figure 2 The results of oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) (A) and area under curve (AUC) (B) after 10 days treatment. n = 6-8, x±s. *P < 0.05 vs Con; #P < 0.05 vs HFD saline; ^P < 0.05 vs HFD/pue |
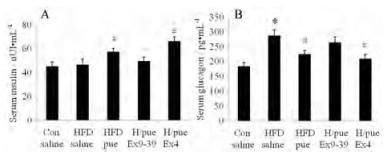
小鼠血清胰岛素(图 3A)与胰高血糖素(图 3B)测试结果表明, 葛根素能够上调胰岛素水平而抑制胰高血糖素。与Ex4的联用, 能有效增强葛根素的促胰岛素作用, 但对胰高血糖素没有显著性影响(图 3A), 而与Ex9-39联用时, 葛根素对胰岛素及胰高血糖素的调节效果均减弱, 提示葛根素可能通过激活GLP-1R通路从而调节胰岛素和胰高血糖素的释放。
|
Figure 3 The impacts of puerarin, Ex9-39 or Ex4 on serum insulin (A) and glucagon (B) levels of mice after 10 days treatment. n = 6-8, x±s. *P < 0.05 vs Con; #P < 0.05 vs HFD saline; ^P < 0.05 vs HFD/pue |
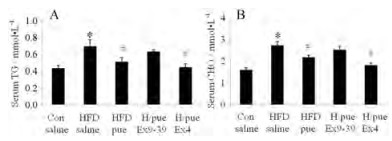
本实验采用高脂喂养诱导肥胖糖尿病小鼠模型, 小鼠体重显著增加, 进而对小鼠常规脂代谢指标血清甘油三酯(serum triglycerol, TG)和总胆固醇(serum cholesterol, CHO)也进行了检测。结果如图 4A、4B所示, HFD组小鼠血清TG和CHO均显著高于对照组, 葛根素能够显著降低血清甘油三酯和总胆固醇水平, 且其降脂作用同样受到GLP-1R激活调控, 被GLP-1R激动剂Ex4所增强, 而与GLP-1R拮抗剂Ex9-39联用, 其降脂作用被减弱。
|
Figure 4 The effects of puerarin, Ex9-39 or Ex4 on the lipid metabolism of HFD mice. (A) Levels of serum triglycerol (TG), and (B) levels of serum cholesterol (CHO) of mice after 10 days treatment. n = 6-8, x±s. *P < 0.05 vs Con; #P < 0.05 vs HFD saline; ^P < 0.05 vs HFD/pue |
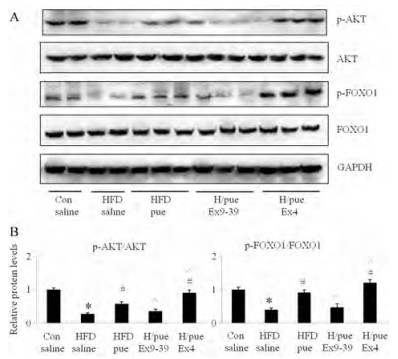
进一步, 通过Western blotting实验检测了葛根素对小鼠肝脏胰岛素信号通路的调节作用。AKT是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶, 又被称为蛋白激酶B (protein kinase B, PKB), 是胰岛素信号通路中的重要分子, AKT磷酸化后被激活, 调控下游多个靶蛋白, 发挥促进糖原合成、抑制糖异生、维持机体血糖平衡等多重效应[10]。而转录因子FOXO1 (Forkhead box protein O1)具有促进糖异生升高血糖的作用, 其活性可受PI3K/Akt信号通路调节, 被AKT磷酸化后失活[11]。
结果如图 5所示, 与对照组相比较, 高脂组p-AKT与p-FOXO1水平均显著降低, 而葛根素能够上调p-AKT与p-FOXO1水平, 证实葛根素对胰岛素敏感性具有改善作用。与之前结果相类似, 也观察到Ex4显著增强葛根素对p-AKT和p-FOXO1的调控作用, 而葛根素的作用被Ex9-39有效阻断, 提示GLP-1R是葛根素胰岛素增敏作用中的关键调控分子。
|
Figure 5 Results of Western blotting assays (A) and comparing changes (B) of p-AKT and p-FOXO1 in liver samples of mice. (A) The representative pictures of Western blotting assays were shown. (B) All bands were quantified by densitometry and were presented as fold change compared with con. n = 3, x±s. *P < 0.05 vs Con; #P < 0.05 vs HFD saline; ^P < 0.05 vs HFD/pue |
胰高血糖素样肽GLP-1是由肠道L细胞分泌的一类肽激素, 通过与GLP-1受体GLP-1R结合激活下游信号通路, 发挥多重生理效应, 维持机体能量稳态, 是近年来2型糖尿病治疗与药物研发的重要靶点[12, 13]。GLP-1R是一种G蛋白偶联受体, 在胰岛、脑和肠中都有表达[14]。GLP-1作用于胃肠道和脑, 延缓胃排空, 抑制食欲[15], 增加饱腹感, 减少食物摄入, 控制体重[16]。GLP-1与胰岛β细胞表面GLP-1R结合, 可激活β细胞中GLP-1R通路, 增加胰岛素释放, 保护β细胞的生存, 抑制β细胞的凋亡, 促进胰岛β细胞再生[17, 18]。天然GLP-1半衰期非常短, 无法作为药物应用, 对GLP-1结构进行修饰与优化, 是降糖新药研发的有效策略[19]。但研究也发现, 在糖尿病模型动物及体外细胞实验中, 高糖能够显著抑制GLP-1R的表达[20, 21]。因此, 糖尿病环境下GLP-1R表达的降低, 可能在一定程度上影响GLP-1R激动剂类药物的疗效。
本课题组前期研究报道了中药葛根活性成分葛根素降糖作用的新机制[8]。发现葛根素能够上调胰岛β细胞GLP-1R的表达, 进而增强GLP-1R通路激活, 实现保护胰岛β细胞, 促进胰岛素分泌, 降低糖尿病小鼠血糖的作用。本研究在其基础上, 进一步通过HFD糖尿病模型小鼠实验, 综合评价了葛根素与GLP-1R激动剂Ex4或GLP-1R拮抗剂Ex9-39的联合给药效果。结果表明, 葛根素有效降低HFD糖尿病小鼠空腹血糖与血脂水平, 改善HFD小鼠的口服葡萄糖耐受, 上调血清胰岛素水平而下调胰高血糖素水平。而葛根素对小鼠糖脂代谢的改善作用, 受到GLP-1R激活的显著性影响, 其作用被Ex4增强, 而被Ex9-39有效阻断。此外, 葛根素能够上调HFD小鼠肝脏组织中p-AKT和p-FOXO1的水平, 增强胰岛素敏感性, 此作用同样受到GLP-1R激动剂与GLP-1R拮抗剂的调控。
综上所述, 本研究提示GLP-1R是葛根素降糖功效中的关键性调控分子, 葛根素能够通过上调GLP-1R的表达, 增强GLP-1R的激活效应。葛根素的这一独特作用机制, 有望改善糖尿病环境下GLP-1R的低表达, 从而协同促进GLP-1R激动剂类药物的治疗效果, 为葛根与GLP-1R激动剂类药物联合应用的可能提供实验支撑。
| [1] |
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045:Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2019, 157: 107843. DOI:10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843 |
| [2] |
Farilla L, Hui H, Bertolotto C, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 promotes islet cell growth and inhibits apoptosis in Zucker diabetic rats[J]. Endocrinology, 2002, 143: 4397-4408. DOI:10.1210/en.2002-220405 |
| [3] |
Drucker DJ, Habener JF, Holst JJ. Discovery, characterization, and clinical development of the glucagon-like peptides[J]. J Clin Invest, 2017, 127: 4217-4227. DOI:10.1172/JCI97233 |
| [4] |
Xiong X, Shao W, Jin T. New insight into the mechanisms underlying the function of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 in pancreatic beta-cells:the involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway effector beta-catenin[J]. Islets, 2012, 4: 359-365. DOI:10.4161/isl.23345 |
| [5] |
Lee WY. New potential targets of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in pancreatic beta-cells and hepatocytes[J]. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul), 2017, 32: 1-5. DOI:10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.1 |
| [6] |
Zhou YX, Zhang H, Peng C. Puerarin:a review of pharmacological effects[J]. Phytother Res, 2014, 28: 961-975. DOI:10.1002/ptr.5083 |
| [7] |
Chen R, Wu P, Cai Z, et al. Puerariae Lobatae Radix with Chuanxiong Rhizoma for treatment of cerebral ischemic stroke by remodeling gut microbiota to regulate the brain-gut barriers of dietary capsaicin against chronic low-grade inflammation[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2019, 65: 101-114. DOI:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.12.004 |
| [8] |
Yang L, Yao D, Yang H, et al. Puerarin protects pancreatic beta-cells in obese diabetic mice via activation of GLP-1R signaling[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 2016, 30: 361-371. DOI:10.1210/me.2015-1213 |
| [9] |
Wang CJ, Ju LJ, Wen XH, et al. Puerarin activates GLP-1R pathway to improve hyperglycemia in HFD mice induced by high fat (English)[J]. J Nanjing Univ Tradit Chin Med (南京中医药大学学报), 2017, 33: 587-590. |
| [10] |
Guo S. Insulin signaling, resistance, and the metabolic syndrome:insights from mouse models into disease mechanisms[J]. J Endocrinol, 2014, 220: T1-T 23. |
| [11] |
Lee S, Dong HH. FoxO integration of insulin signaling with glucose and lipid metabolism[J]. J Endocrinol, 2017, 233: R67-R79. DOI:10.1530/JOE-17-0002 |
| [12] |
Drucker DJ. The biology of incretin hormones[J]. Cell Metab, 2006, 3: 153-165. DOI:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.01.004 |
| [13] |
Tasyurek HM, Altunbas HA, Balci MK, et al. Incretins:their physiology and application in the treatment of diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2014, 30: 354-371. DOI:10.1002/dmrr.2501 |
| [14] |
Campbell JE, Drucker DJ. Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action[J]. Cell Metab, 2013, 17: 819-837. DOI:10.1016/j.cmet.2013.04.008 |
| [15] |
Kalra S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors agonists (GLP1 RA)[J]. J Pak Med Assoc, 2013, 63: 1312-1315. |
| [16] |
Rowlands J, Heng J, Newsholme P, et al. Pleiotropic effects of GLP-1 and analogs on cell signaling, metabolism, and function[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2018, 9: 672. DOI:10.3389/fendo.2018.00672 |
| [17] |
Hao T, Zhang H, Li S, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist ameliorates the insulin resistance function of islet beta cells via the activation of PDX-1/JAK signaling transduction in C57/BL6 mice with high-fat diet-induced diabetes[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2017, 39: 1029-1036. DOI:10.3892/ijmm.2017.2910 |
| [18] |
Sasaki S, Miyatsuka T, Matsuoka TA, et al. Activation of GLP-1 and gastrin signalling induces in vivo reprogramming of pancreatic exocrine cells into beta cells in mice[J]. Diabetologia, 2015, 58: 2582-2591. DOI:10.1007/s00125-015-3728-z |
| [19] |
Guo ZR. Developments of liraglutide and exenatide[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2019, 54: 1706-1710. |
| [20] |
Rajan S, Dickson LM, Mathew E, et al. Chronic hyperglycemia downregulates GLP-1 receptor signaling in pancreatic beta-cells via protein kinase A[J]. Mol Metab, 2015, 4: 265-276. DOI:10.1016/j.molmet.2015.01.010 |
| [21] |
Xu G, Kaneto H, Laybutt DR, et al. Downregulation of GLP-1 and GIP receptor expression by hyperglycemia:possible contribution to impaired incretin effects in diabetes[J]. Diabetes, 2007, 56: 1551-1558. DOI:10.2337/db06-1033 |
 2020, Vol. 55
2020, Vol. 55


